lec 8 - aorta to arterioles
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
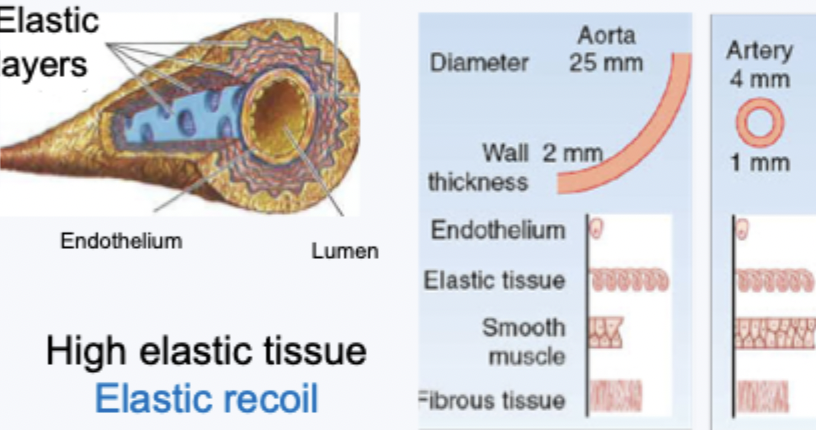
arteries structure
high elastic tissue for elastic recoil
arterioles structure
high smooth muscle - contraction and relaxation
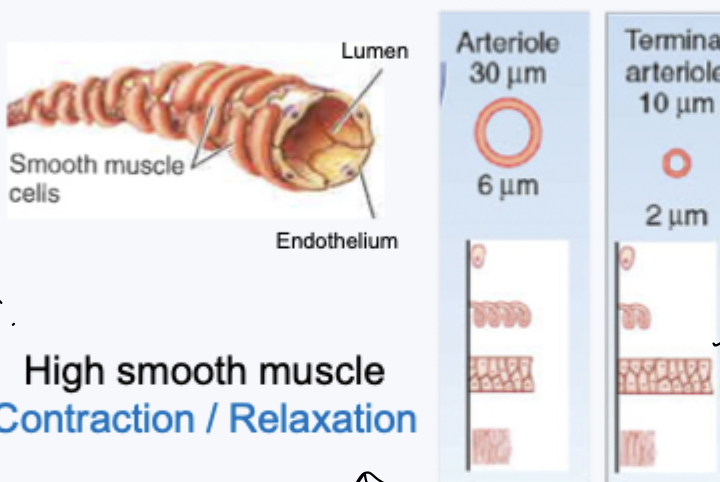
arterioles vs arteries structure
proportion of smooth muscle and elastic tissue is different - structure related to function
function of aorta (and other large elastic arteries)
distribute blood
pressure reservoir - reduce fluctuations in pressure and flow - maintain flow throughout the cardiac cycle
pressure reservoir
systole - stretching stores potential energy
diastole - recoil to release stored energy
recoil during diastole causes blood flow away from the heart as the aortic valve shuts
maintains arterial flow throughout the cardiac cycle
ageing and cardiovascular disease
compliance is inveresley proportional to stiffness
arteries have high compliane
when you age get decreased compliance and increased stiffness = dysregulated blood flow
function of arterioles
smooth muscle cells wrap around the vessel
contraction squeezes the lumen to reduce diameter = vasoconstriction
main determinant of resistance (local and total peripheral resistance)
important in controlling regional blood flow
arterial blood pressure
minimum pressure just before ventricle contraction = diastolic pressure (DP)
maximum arterial pressure during peak ventricular ejection = systolic pressure (SP)
MAP = DP + 1/3 x PP
normal is 120/80
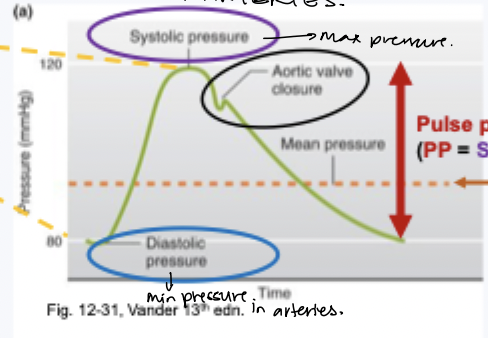
dicrotic notch
aortic valve shuts
transient increase in pressure
determinants of arterial blood pressure
MAP = Q x TPR
Q in this case is CO
TPR is sum of global resistance (from all systemic vascular beds)
arterial pressure depends on both so can be mantained by alterations to either
decreased MAP → vasoconstriction = increased TPR = increased MAP
decreased map → increased HR → increased Q → increased MAP
MAP is a critical homeostatic variable
blood flow distribution
regionally blood flow can be dynamically regulated to match demand
changes in local resistance (through arterioles constricting or dilating)
different reponses in vascular beds - cause MAP to remain stable

blood flow redistribution - how
altered metabolic demands
no change in pressure gradient → differential changes in regional resistance → same total volume is redistributed - regional changes to flow
different responses in vascular beds - MAP remains stable
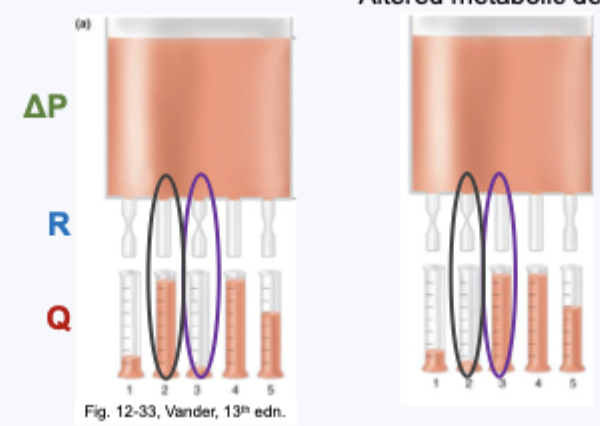
what mechanisms to control vascular diameter
complex control systems
neural, hormonal and local controls
flexibility
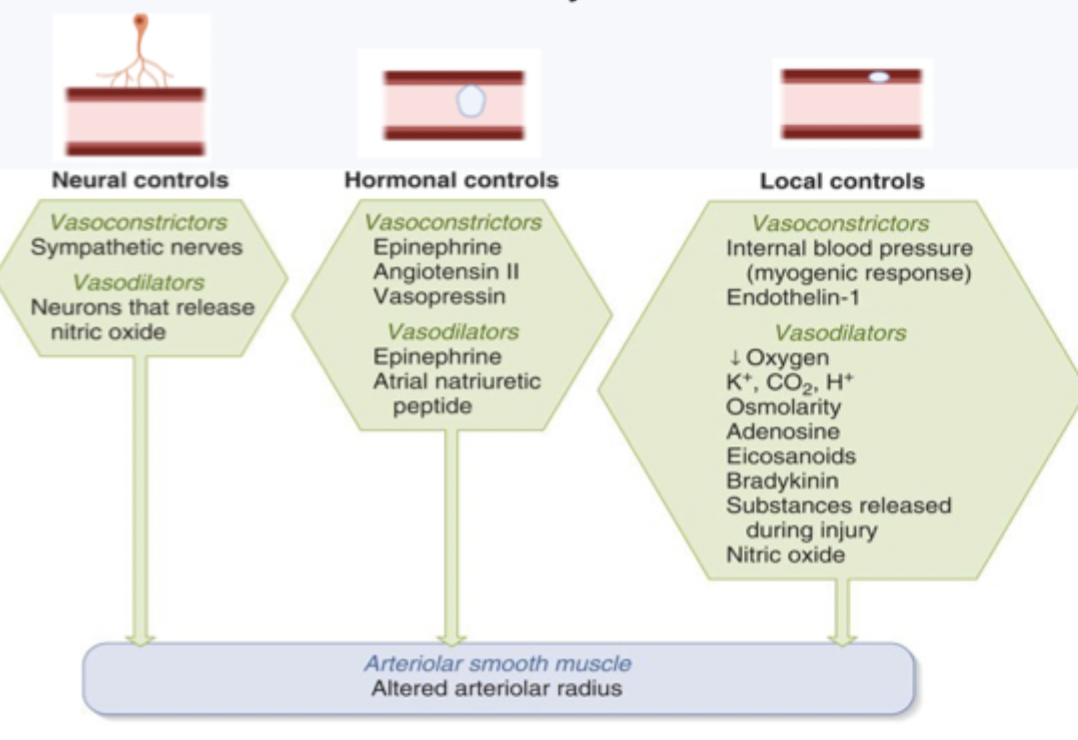
neural control mechanisms - extrinsic control symoathetic
sympathetic nervous system → noradrenaline → binds to alpha1-adrenergic receptors → vasoconstriction
types of receptors in different tissues
in brain: low numbers of alpha1 adrenergic receptors = limited vasoconstriction - important because brain needs constant flow
skin and GI: high numbers of alpha1-adrenergic receptors = vasoconstriction - important because flow needs to be flexible
non cholingeric/non-adrenergic - extrinsic control
postganglionic autonomic nerves → nitric oxide → relaxes smooth muscle cells → vasodilation
specalised innervation system - not widespread
GI system
reproductive (penis)
hormonals and effects dilation vs constriction
ciculating hormones can alter vascular diameter
constriction (aldrenaline, angiotensin II, vasopressin)
dilation (adrenaline, atrial natriuretic peptide)
blood vessles have alpha1 and beta2 adrenergic receptors
a1:b2 ratio
tissue/organ specific which related to function
skin - predominant alpha1 - vasoconstriction
skeletal muscle - predominantly b2 - vasodilation
long term control of CO - hormonal
hormones that play a role in long term regulation of MAP are also vasoactive
increase blood volume:
ADH - increases water reabsorption
angiotensin II - stimulates Na+ (and therefore H2O) reabsorption
= vasoconstriction
decreased blood volume:
atrial natriuretic peptide - decreases water reabsorption = vasodilation
local control mechanisms - intrinsic control
local factors can alter vascular diameter
no nerves or hormones involved
autoregulation
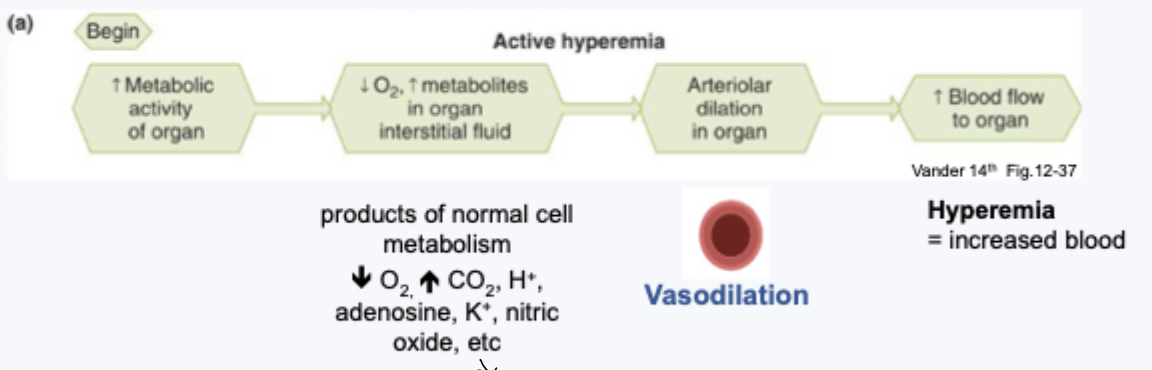
active hyperemia (aka metabolic autoregulation) = dilation
flow autoregulation (aka myogenic autoregulation), reactive hyperemia = constriction/dilation
active hyperemia
blood flow changes to match changes in local metabolism
tissue specific responses
based on metabolism - highly developed in skeletal and cardiac tissue (with high metabolic demands)
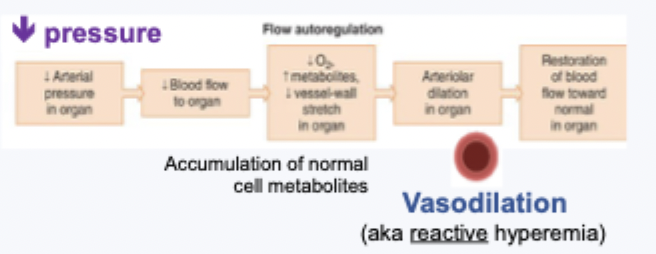
flow autoregulation
control of blood flow to maintain flow with changes in perfusion pressure
no changes in local metabolism
myogenic = from muscles
autoregulation maintains a steady flow - similar over a wide range of pressures
outside autoregulation range - flow not constant as limits of constriction/dilation reached
increased pressure stretxhed smooth muscle cells and causes vasoconstriction
in contrast: