Language Change
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Prescriptive vs Descriptive
P = belief that language should be prevented from change
D = belief that all language change is positive
Blending
Taking parts of two words and mixing (Brexit)
Clipping
Removing part of word (exam/examination)
Conversion
Word changes class (Google, from noun to verb Googling)
Borrowing
New words brought in from different languages (Blitz from German)
Neologisation
New invented word (Mx)
Amelioration
Word gains positive meaning
Bleaching
Word loses meaning or power (crap/wicked)
Derogation
Word gains a negative meaning
*Caxton
Brought printing press to England in 1476, made decisions on spellings and orthography, became fixed as a result
*Wycliffe and *Tyndale
W - translated Bible from Latin to English
T - Translated Bible more successfully
The Great Vowel Shift
Long vowel sounds moved from front of mouth to back and higher up
Sounds became dipthongs
‘moose’ became mouse
‘hoose’ became house
‘beat’ became bite
*Johnson
Published 1755 dictionary
40k words and spellings
Lingua Franca
Language adopted as a common language between native speakers whose language is different
can be explained through colonisation and the British Empire
Aitchison’s metaphors (descriptivist)
Damp spoon - Change is as a result of laziness
Crumbling castle - English was once something grand, now ruined
Infectious disease - Change spreads like a plague.
Hitchings
ALL prescriptive views are proxy arguments for something else
Halliday’s Functional theory
Language changes due to its’ users changing their needs
With tech, as we need new words to describe something, we can invent them
Hockett - Random Fluctuation
Mistakes in language are made and become codified
Fuck to duck through text
Substratum theory
Language changes primarily through contact with other countries
not ALL changes
Lexical gaps theory
New words enter language when we need to express something but there is no word for it
increased with new tech
Bailey and Trudgill - Wave Model
B - Change starts in geographical centre and ripples out, adopting change quicker if in centre
T - Disputed this, smaller villages will miss out on changes as they only spread to large cities
Chen’s S-Curve
Change is new
Change gained traction and few people using
Many people using change
Everyone who is going to adopt it is now using it
Will NEVER be the case as people will always resist change
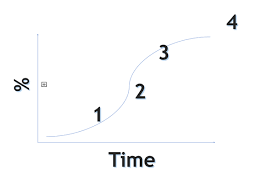
Aitchison’s PIDC Model
Potential - Room for change
Implementation - Change takes place
Diffusion - Change spreads
Codification - Becomes recognised/added to dictionary
‘Brat’ was Collins Dictionary word of the year 2024
Crystal - Tide Metaphor
Language change is like a tide
tide will wash things ashore, these things might stay for a long time and sometimes washed away again
almost cyclical change
Sharon Goodman - Informalisation 1996
Language becoming more and more informal
First names for colleagues
Terms of endearment for children like sweetheart
Sharon Goodman - ‘X’ 1996
X appears infrequently in written words, used for wide range of things
‘supercharged typographic icon’
Texts no longer reliant on words as they are becoming more mutimodal
Guy Deutscher - Three reasons for change (EEA)
Economy - people want to use as little energy as possible
handbag = bag, omnibus = bus
Expressiveness - express themselves as powerful and extend range
slang for good/bad/sexy/disgusting
Analogy - To fit linguistic patterns and find regularity
Housen/house (goes against Aitchsison’s castle view)
Deutscher - Field and traffic jam analogy
Language change is unintentional, where small actions accumulate and create a noticeable pattern
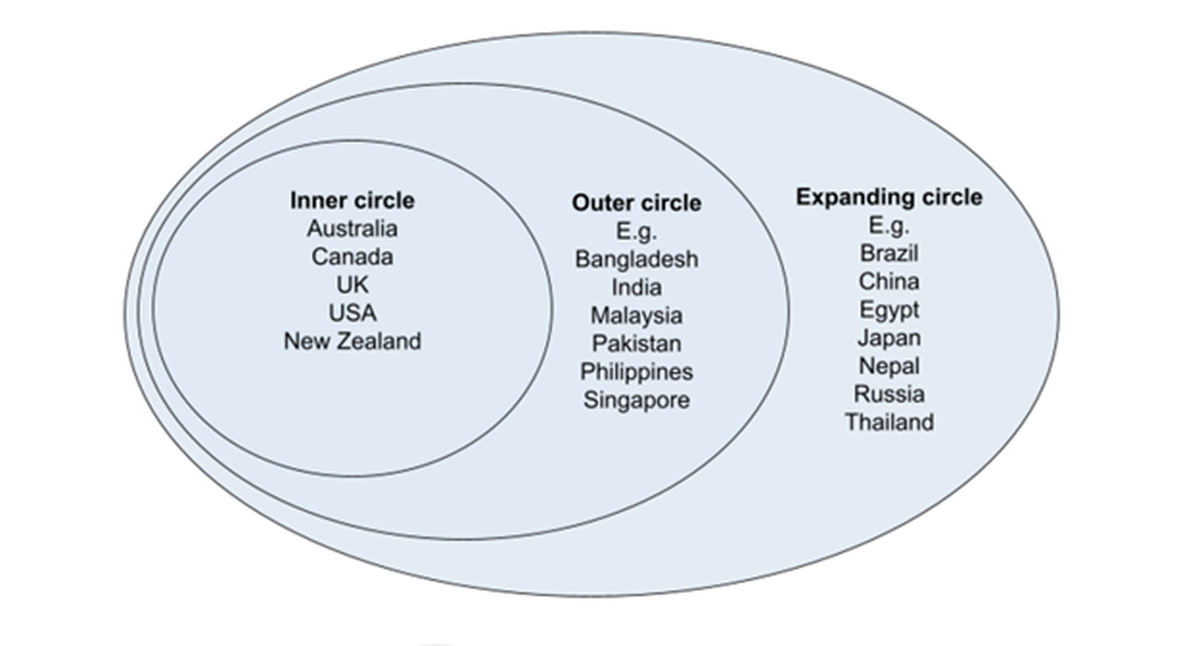
Kachru’s 3 circles of English (1985)
Explains the global spread of English
Inner circle = Native language
Outer circle - Second language
Expanding circle - Lingua Franca / English as a foreign language
Different levels of importance
Synchronic vs Diachronic
Synchronic - study of language at a particular time period
Diachronic - study of language over a long time period
lee (coincidence? lol)
the more intensive a texter, the smaller their vocab
reduced linguistic flexibility
vyvyan evans 2017 - emojis
type of paralanguage
conveying many different non-verbal things
enhances digital clarity