Molecules of Life
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
chemical composition of bacterial cell
-mainly composed of water, rest is proteins
-cell may contain 1000 dif types of organic molecules
-can be classified into 4 families
what are the 4 families of biomolecules
-carbohydrates
-proteins
-nucleic acids
-lipids
carb monomer
-monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
protein monomer
amino acid joined by peptide bonds
nucleic acids monomer
nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds
lipids monomer
fatty acids and glycerol joined by ester bonds
carbohydrates functions
-energy source
-structural component
-signallingpro
proteins functions
-structural support
-enzymes
-movement
-hormones
nucleic acids functions
-stored genetic information
-energy source (ATP)
lipids functions
-long term energy source
-membrane component
-hormones
polar
an unequal distribution of charge, creating partial or full positive or negative charges
chemical property of water
-polar
-unequal distribution of charge: creates full/partial -ve & =ve charges
what kind of environment is cell
-aqueous: water based environment
-most proteins and other molecules within cell have to interact w/ water
-cytosol is mainly water
cytosolic proteins
-have side chains that are hydrophilic as they are in cytosol
hydroxyl structural formula and where they are found in
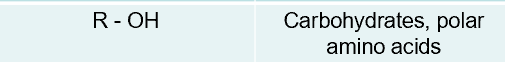
carbonyl structural formula and where they are found in

carboxyl structural formula and where they are found in

amino structural formula and where they are found in

phosphate structural formula and where they are found in

carb molecular formula
-CnH2nOn
carb chemical property
-hydrophilic
-polar due to hydroxyl group
-water soluble
carb func grp
-carbonyl
-hydroxyl
how are monosaccharides classified
-if they contain aldehyde: aldoses (carbonyl group at the end)
-if they contain ketone: ketoses (carbonyl group in middle)
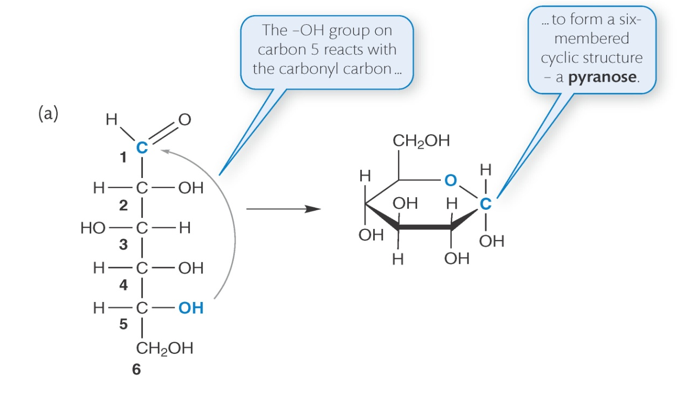
carbohydrate ring formation
-in aqueous solution 5 and 6 carbon sugars spontaneously form ring structures
-only 1:40,000 glucose molecules are linear
how does ring structure form from carbon sugar
-carbonyl group on C1 reacts with hydroxyl group on C5
how does ring structure form from carbon sugar diagram
monosaccharide isomerism
-optical isomers: D or L isomer
-structural isomers
-epimers
what is the difference between enantiomers and general optical isomers?
-enantiomer is an example of an optical isomer
-can rotate a plane of polarised light in equal but oppo directions
which optical isomer is naturally occurring
-most naturally occurring sugars are d isomer
-L isomers cannot be metabolised by the body
-eg: D glucose (dextrose can be metabolised by glucose pathway but L glucose cannot)
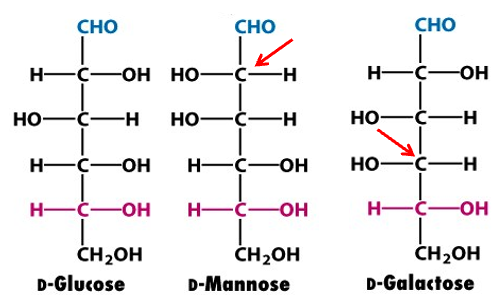
what are epimers and give example
-stereoisomers that duffer in configuration at a single asymmetric carbon
why cant we digest beta glucose
we dont have enzymes that can break beta linkage
how complex carbohydrates formed
-glycosidic bonds formed between monosaccharides
-a or B config locked when bond is formed
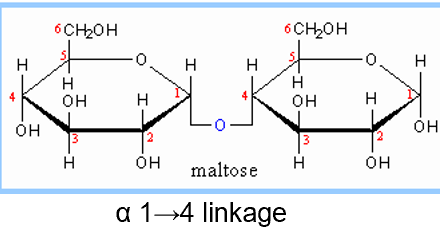
maltose diagram and linkage
cellobiose diagram and linkage
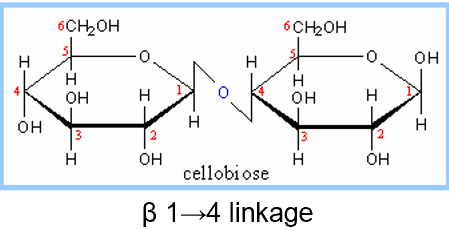
disaccharides
2 monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bond
sucrose diagram and linkage
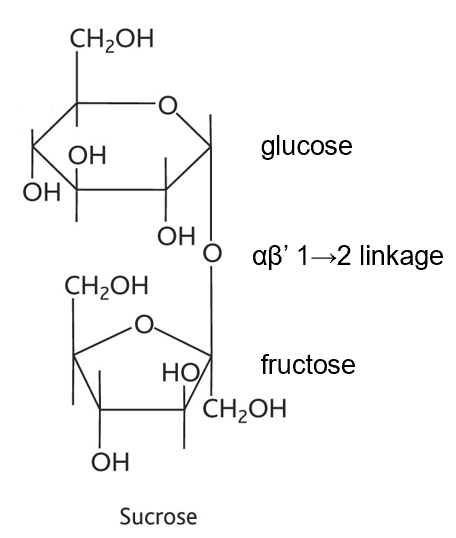
what does sucrose consist of
2 anomeric carbons (straight chain carbons that are turned into cyclic) linked
lactose diagram and linkage
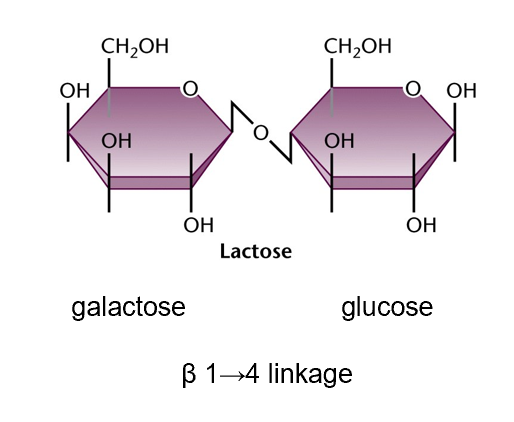
how is galactose digested
-lactase
-galactose enter metabolism through conversion to glucose-1-phosphate
polysaccharides of glucose function
act as energy stores
types of polysaccharides in plants
starch:
-amylose
-amylopectin
types of polysaccharides in animals
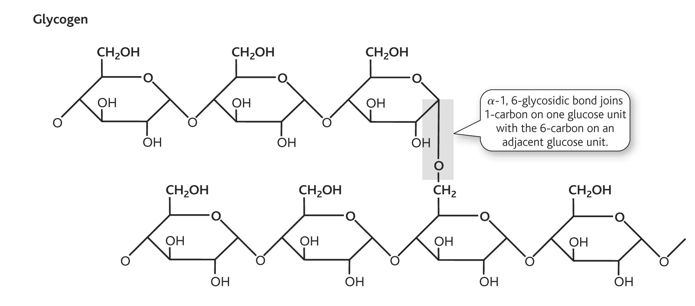
glycogen
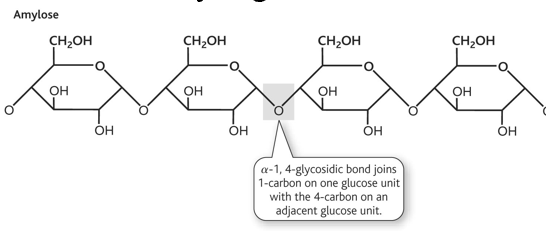
amylose structure
-linear
-not very soluble
-forms hydrated micelles
-at least 1000 glucose units
amylose structure diagram and linkage
glycogen structure diagram and linkage
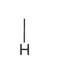
glycine diagram
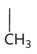
alanine diagram
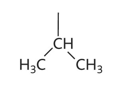
valine diagram
leucine diagram
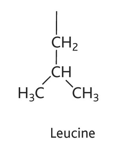
isoleucine diagram
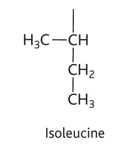
phenylamine diagram
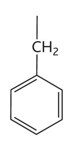
methionine diagram
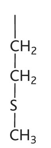
proline diagram
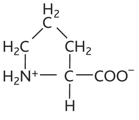
tryptophan diagram
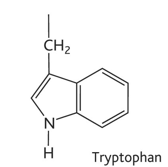
serine diagram
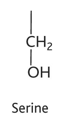
threonine diagram
tyrosine diagram
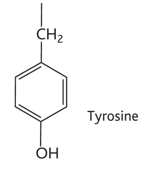
cysteine diagram
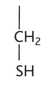
asparagine diagram
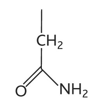
glutamine diagram
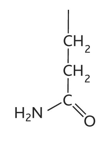
aspartic acid diagram
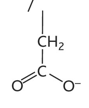
glutamic acid diagram
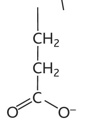
histidine diagram
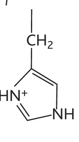
base
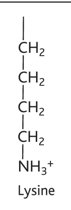
lysine diagram
base
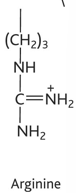
arginine diagram
base
glycine property
-gly or g
-non polar
-not strongly hydrophobic
alanine property
-ala or a
-non polar hydrophobic
phenylalanine property
-phe or F
-hydrophobic
tyrosine property
-tyr or Y
-non polar
-hydrophobic/philic (uncharged polar)
serine property
-ser or s
-hydrophilic
-uncharged polar
cysteine property
-cys or c
-non-polar hydrophobic/hydrophilic (uncharged polar)
aspartic acid/ aspartate property
-asp or d
-hydrophilic
-charged, acidic
glutamic acid/ glutamate property
-glu or E
-hydrophilic
-charged
-acidic
asparagine property
-asn or n
-hydrophilic
-uncharged polar
glutamine property
-gln or q
-hydrophilic
-uncharged polar
lysine property
-lys or k
-hydrophilic
-charged
-basic
arginine property
-arg or r
-hydrophilic
-charged, basic
histidine property
-his or h
-hydrophilic
-charged, basic/uncharged polar
-easily gains or loses a proton at pH 7
proline property
-pro or p
-non polar hydrophobic
valine property
-val or v
-non polar hydrophobic
leucine property
-leu or l
-non polar hydrophobic
isoleucine property
-ile or I
-non polar hydrophobic
tryptophan
-trp or w
-non polar hydrophobic
methionine
-met or m
-non polar hydrophobic
thronine
-thr or t
-hydrophilic
-uncharged polar