Important Terminology for Basics of Ch 1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
parasagittal plane
Divides body into unequal right and left sides
frontal plane (aka coronal)
Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions
transverse plane (aka horizontal or cross-sectional plane)
divides body into upper and lower portions
superior
above (an example: the head in relation to the neck)
inferior (word association tip: Dante's Inferno)
below (an example: the neck in relation to the head)
Anterior
in front of (an example: the canines in relation to the molars)
Posterior
behind (an example: the molars in relation to the incisors)
medial
Toward the midline of the body (an example: the nose in relation to the eyes; the word means what it sounds like)
Lateral
away from the midline (an example: the eyes in relation to the nose)
proximal (tip: think proximity)
Closer to the main axis of the body (an example: the shoulder in relation to the wrist)
distal (tip: think distance)
away from the point of attachment (an example: the wrist in relation to the shoulder)
intermediate (aka middle)
between two structures
deep
away from the surface/beneath another structure (an example: the ribs in relation to the pectoralis major)
superficial
closer to the surface than another structure (an example: the pectoralis major in relation to the ribs)
Cranial or Cephalad
toward the head
caudal
the tail; directionally, toward the tail
head
cranial or cephalic
neck
cervical
gills
branchial
trunk
thoracic
chest
pectoral
armpit
axillary
arm (shoulder to elbow)
brachial
forearm
elbow to wrist
wrist
carpal
stomach
abdominal
lower back
lumbar
sacral
buttocks
pelvic
hip and pubic area
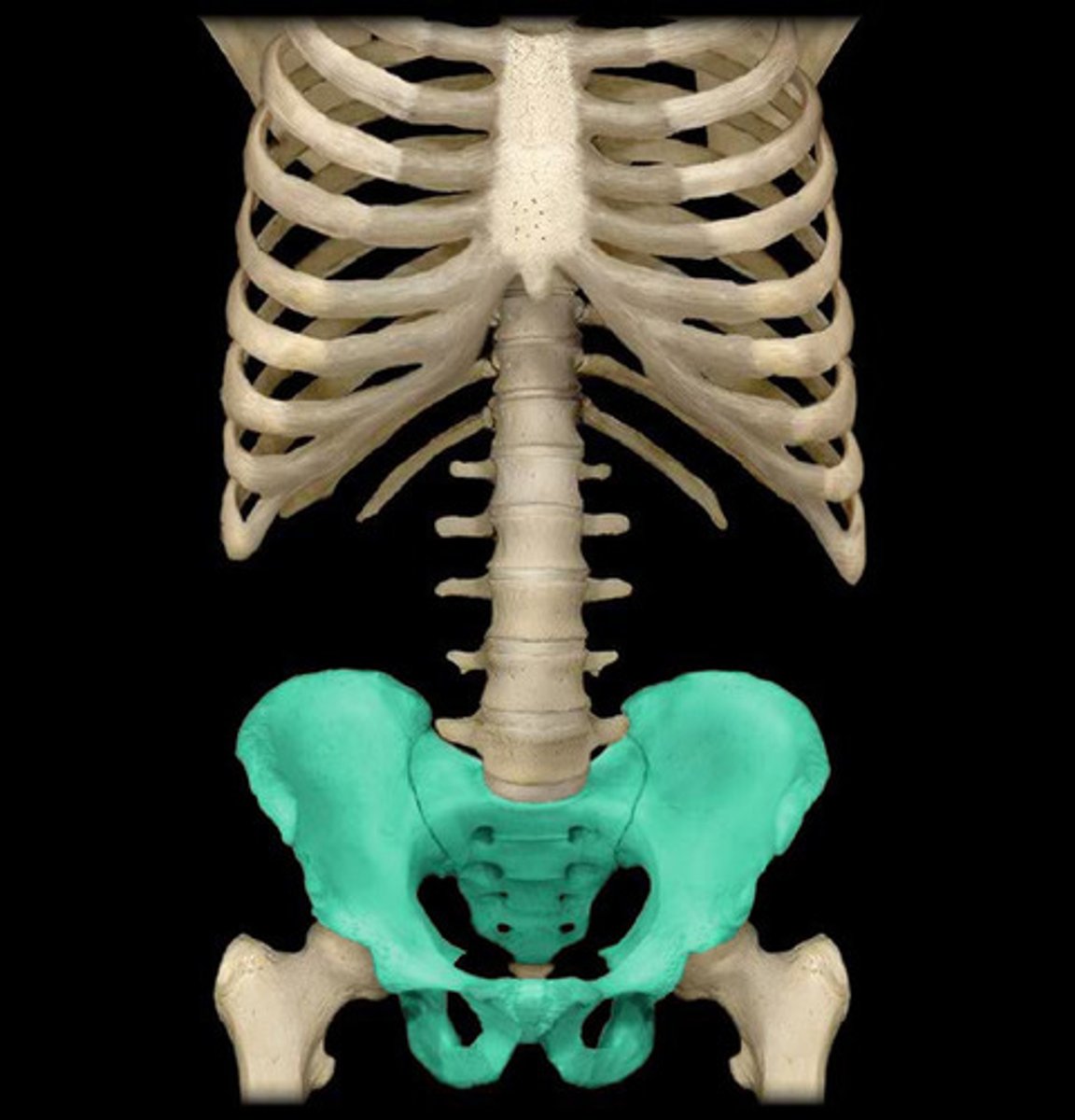
thigh
hip to knee
popliteal
back of knee
leg
knee to ankle
tarsal
ankle
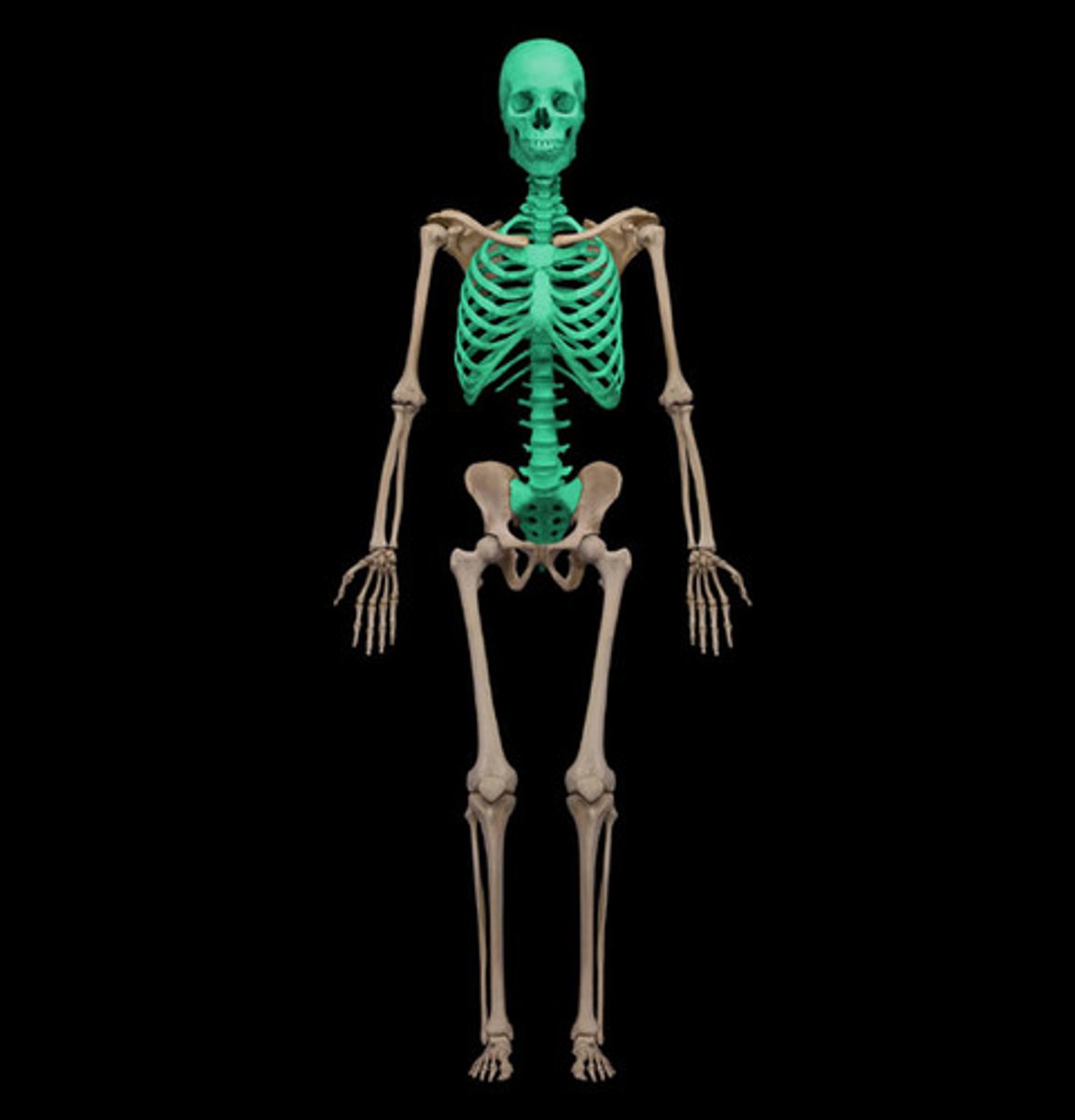
axial skeleton
structures on the main axis of the body; consists of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage
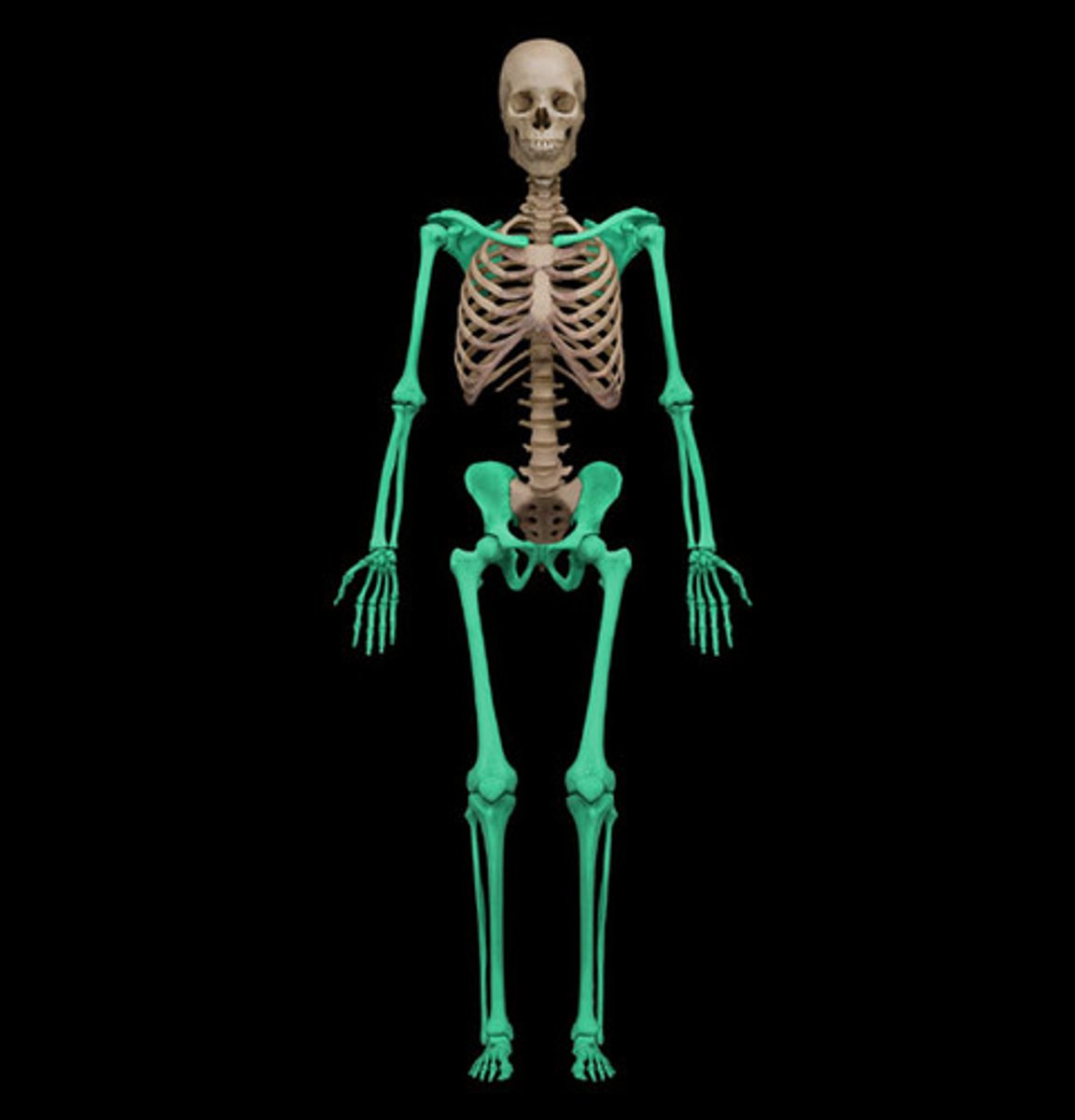
appendicular (think appendages)
structures consisting of the limbs and associate girdles (pelvic/pectoral)
classes of cartilage
hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic, calcified (aka mineralized)
osteology
Study of bones and the skeleton
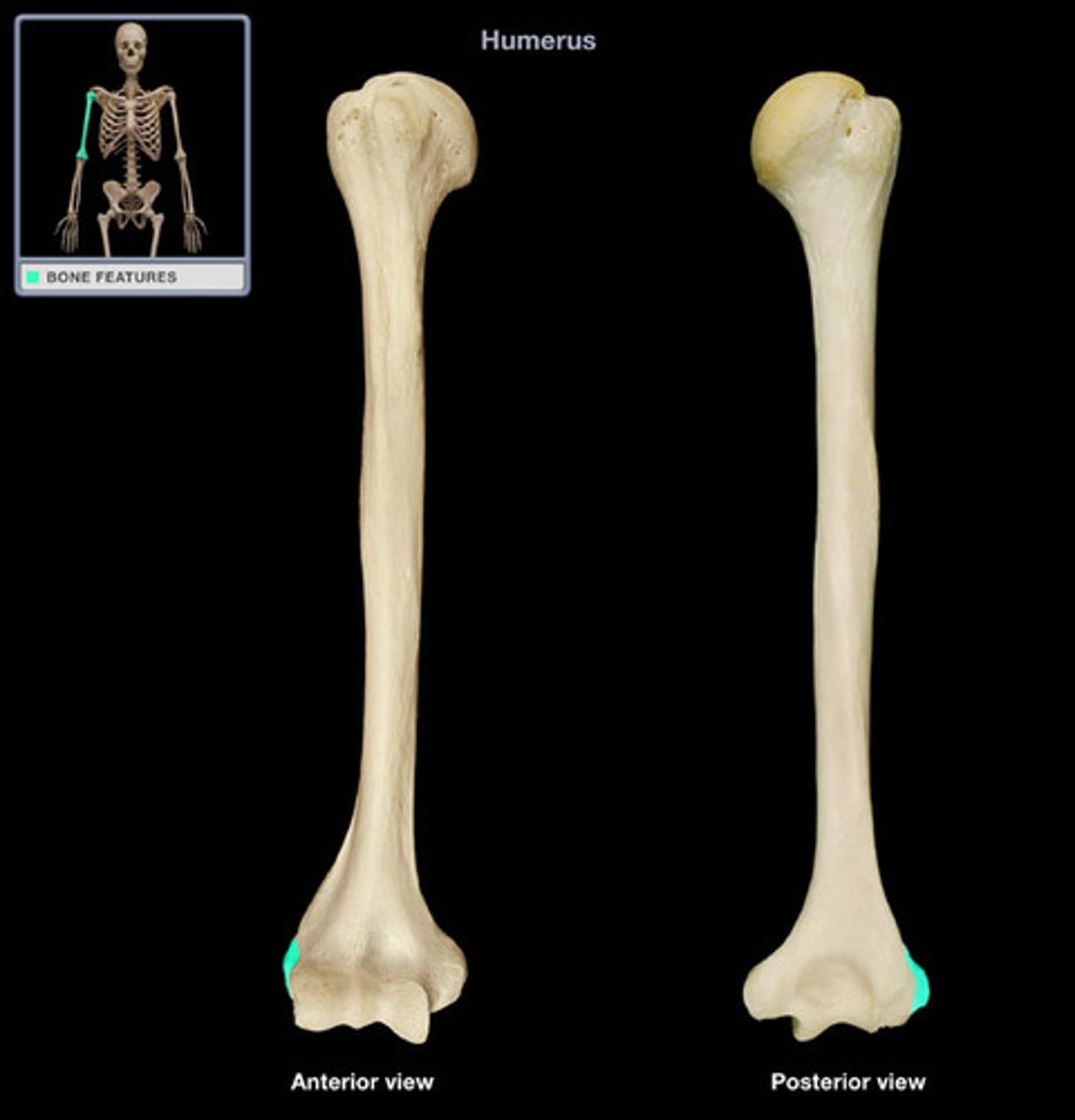
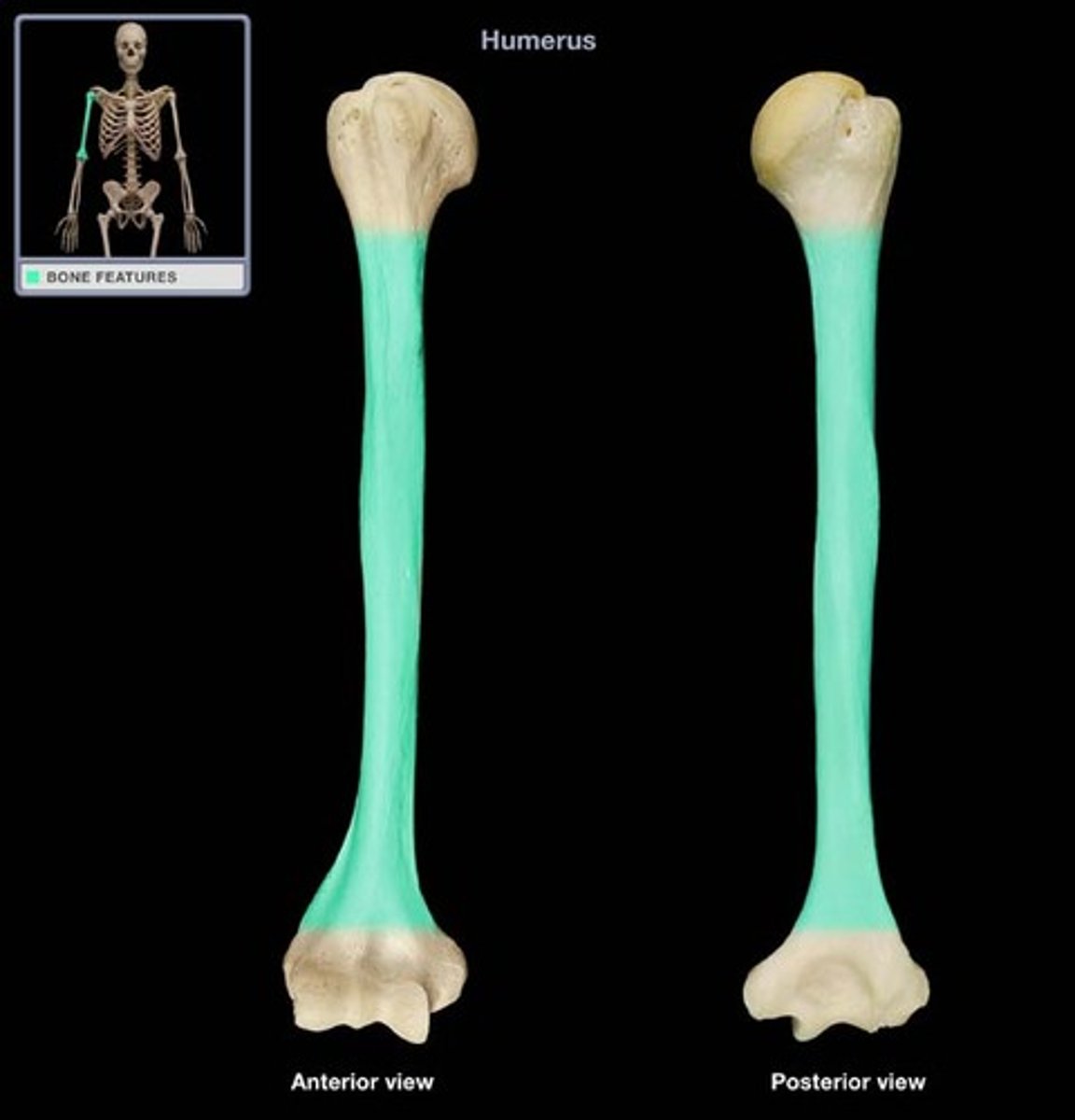
long bones
bones that are longer than they are wide (examples: the femur and the humerus)
short bones
bones of the wrist (carpal) and ankles (tarsal); subclass is sesamoid bones (the patella)
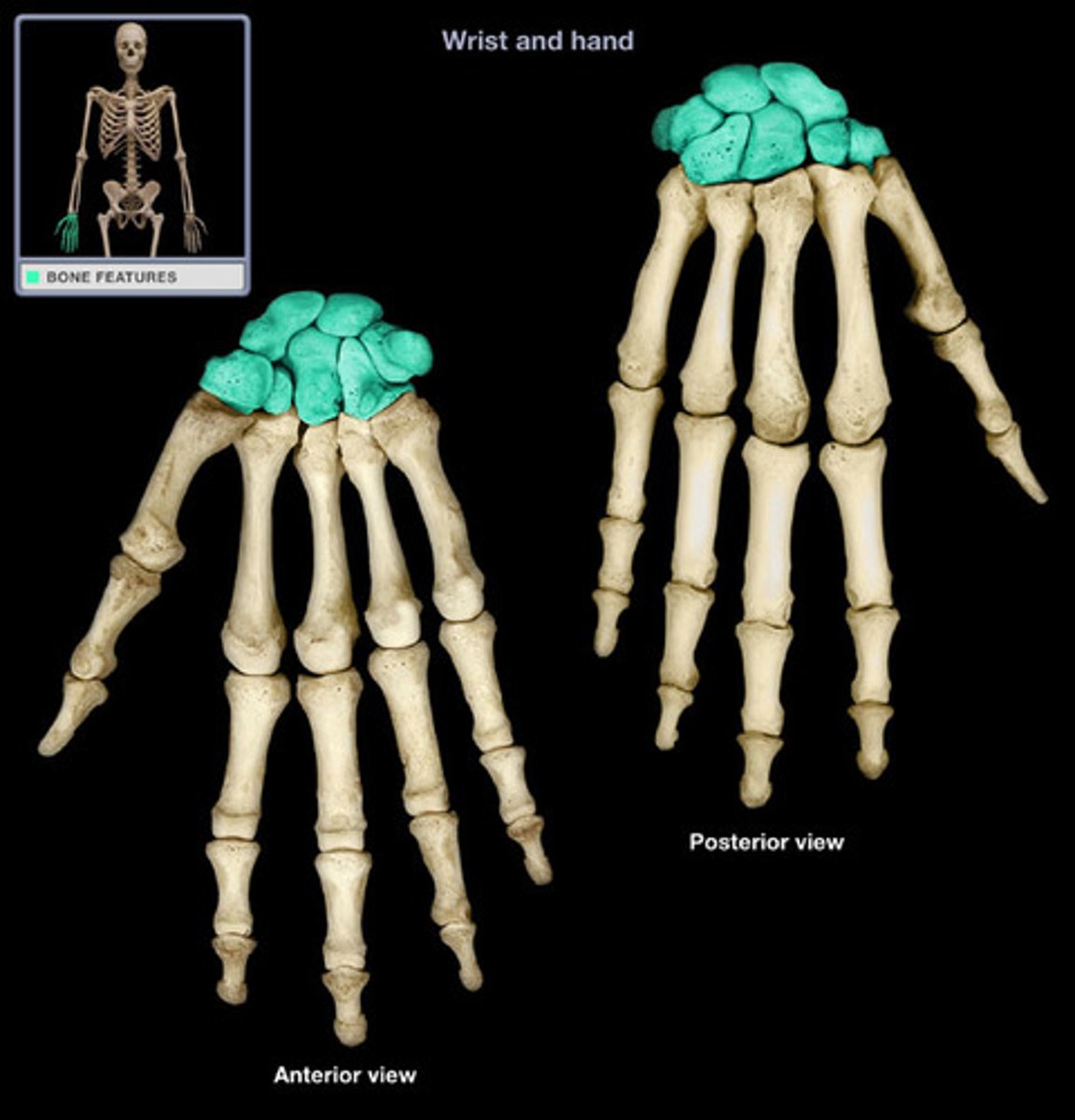
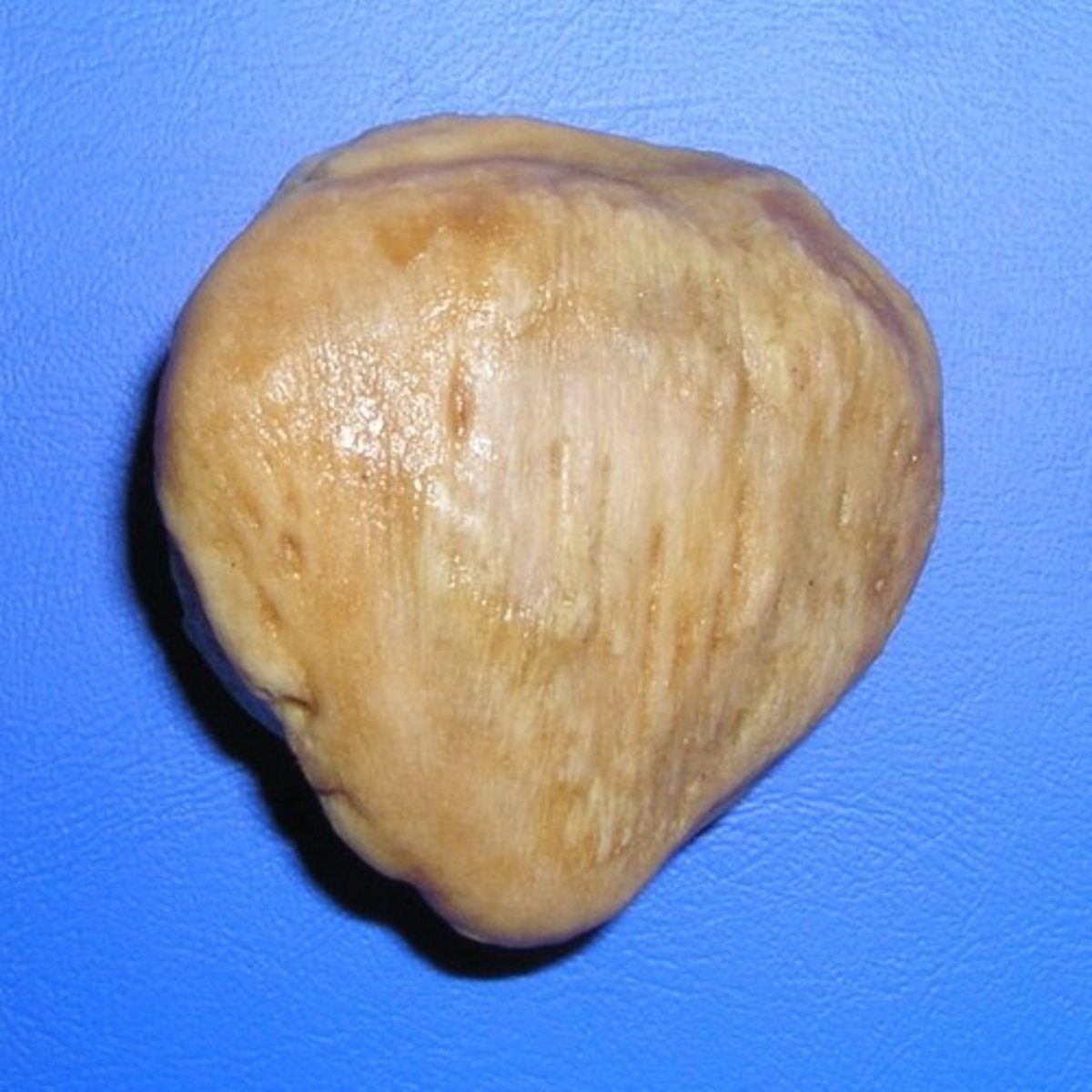
sesamoid bones
subclass of short bones; indirect skeletal attachment; example: patella

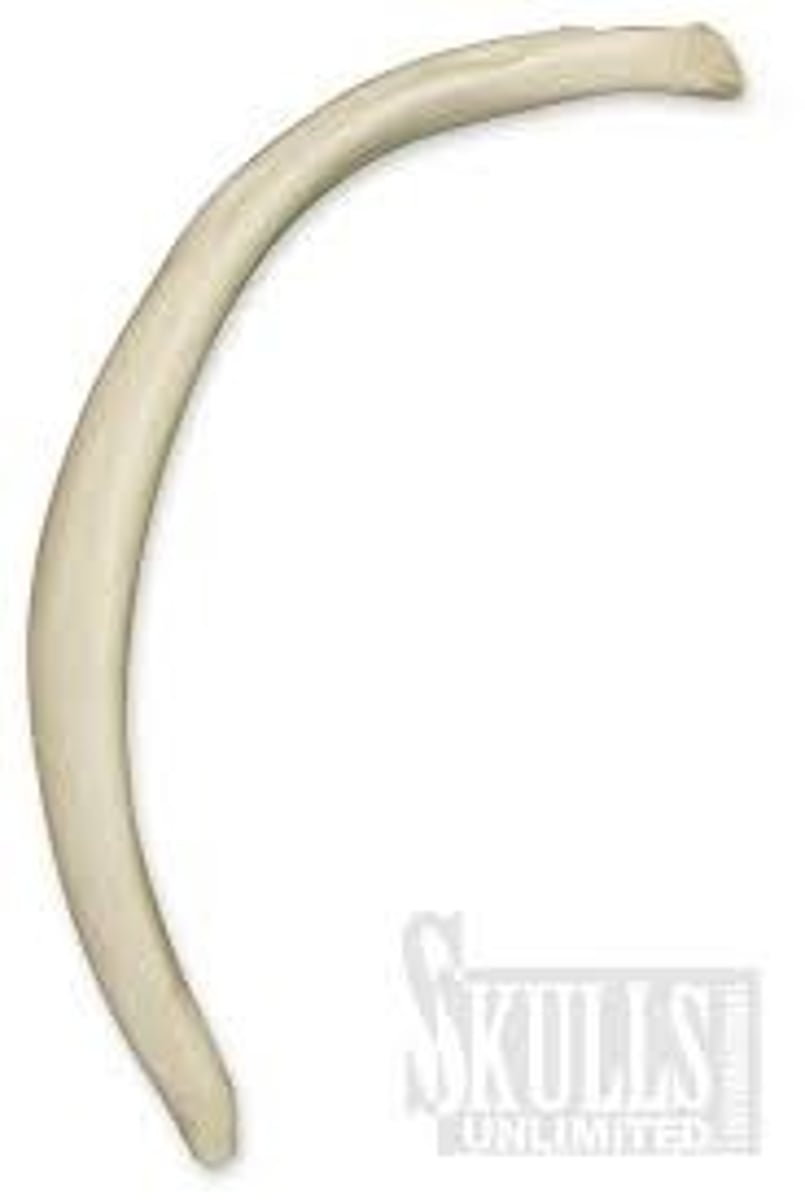
flat bones
thin, flattened, and usually curved; examples are some bones of the skull and the ribs; can be easily confused with long bones

irregular bones
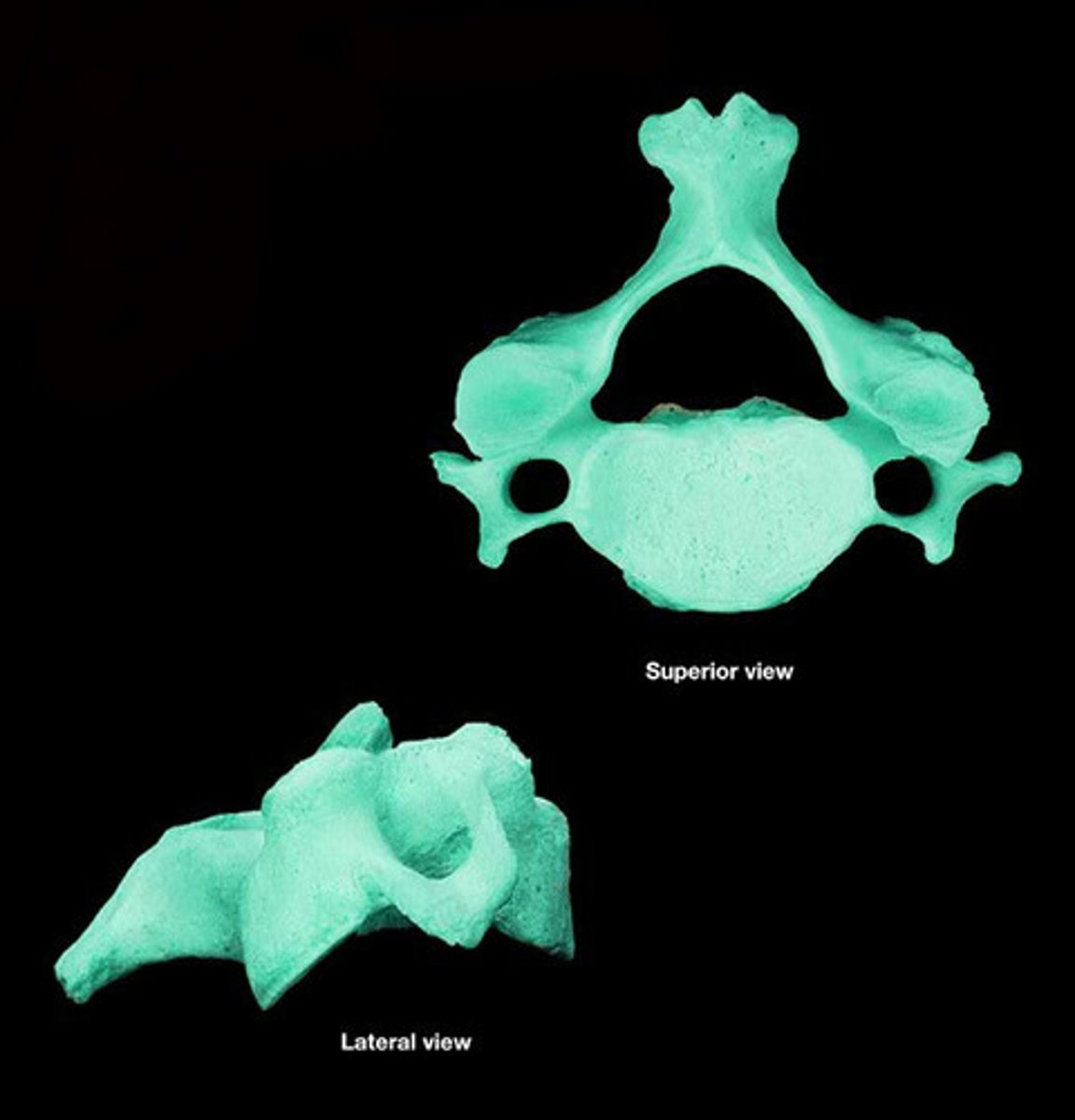
bones of the vertebrae; odd shapes that don't fit in the other categories
epiphyses
"heads" of a long bone
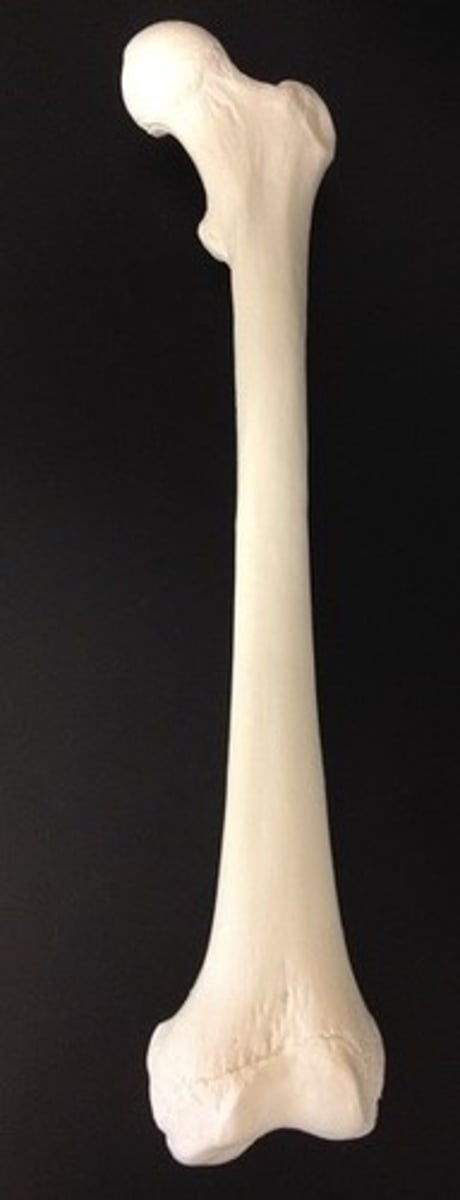

proximal epiphysis
the end of the bone closer to the axial skeleton
distal epiphysis
the end of the bone located further from the axial skeleton
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
epiphyseal plate
where bone growth occurs
epiphyseal line
remnant of the epiphyseal plate, seen in adult bones
medullary cavity
cavity within the shaft of the long bones filled with yellow bone marrow (packed with adipose tissue)
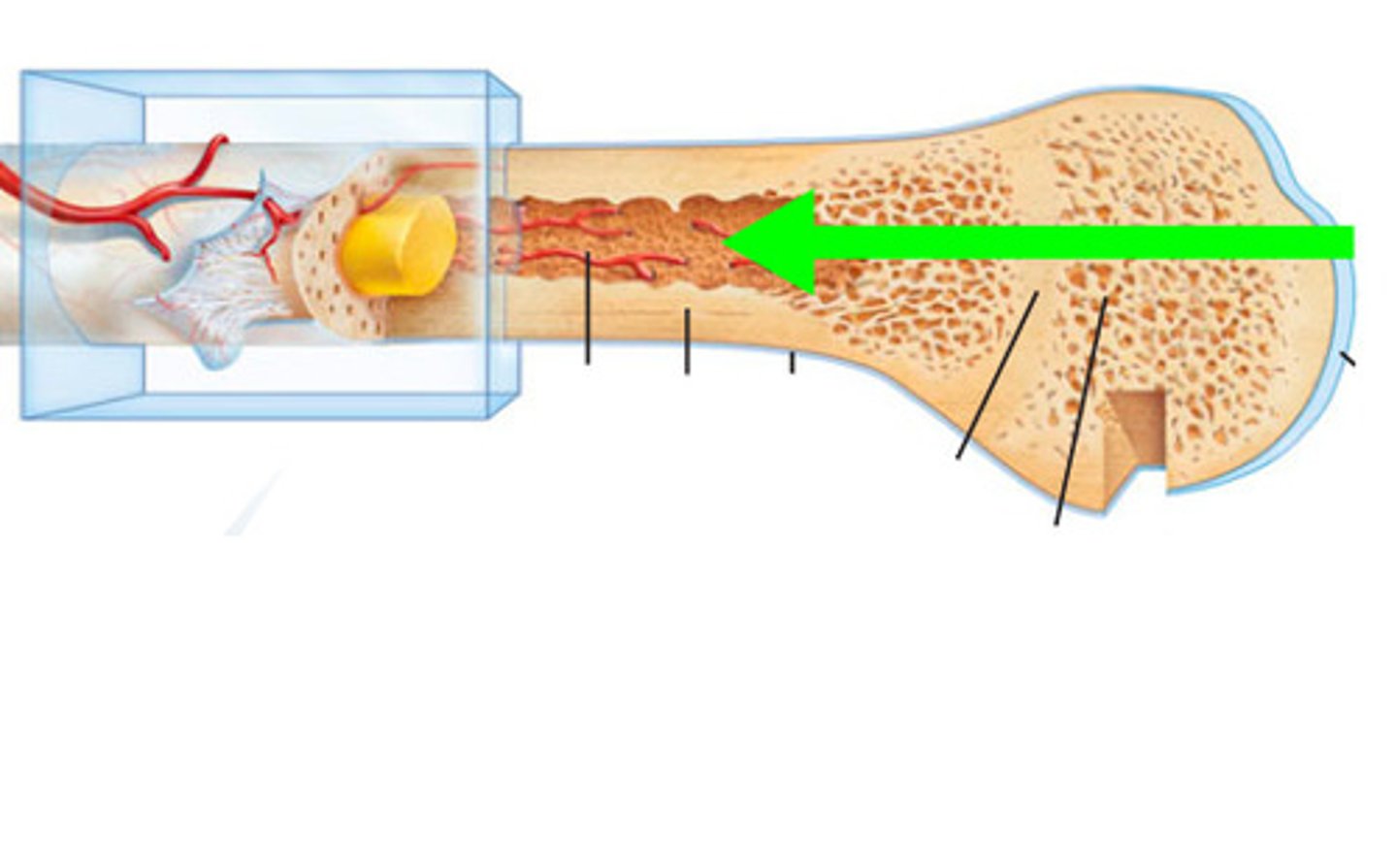
compact bone tissue
the strongest form of bone tissue that makes up the outer layer of cortical bone
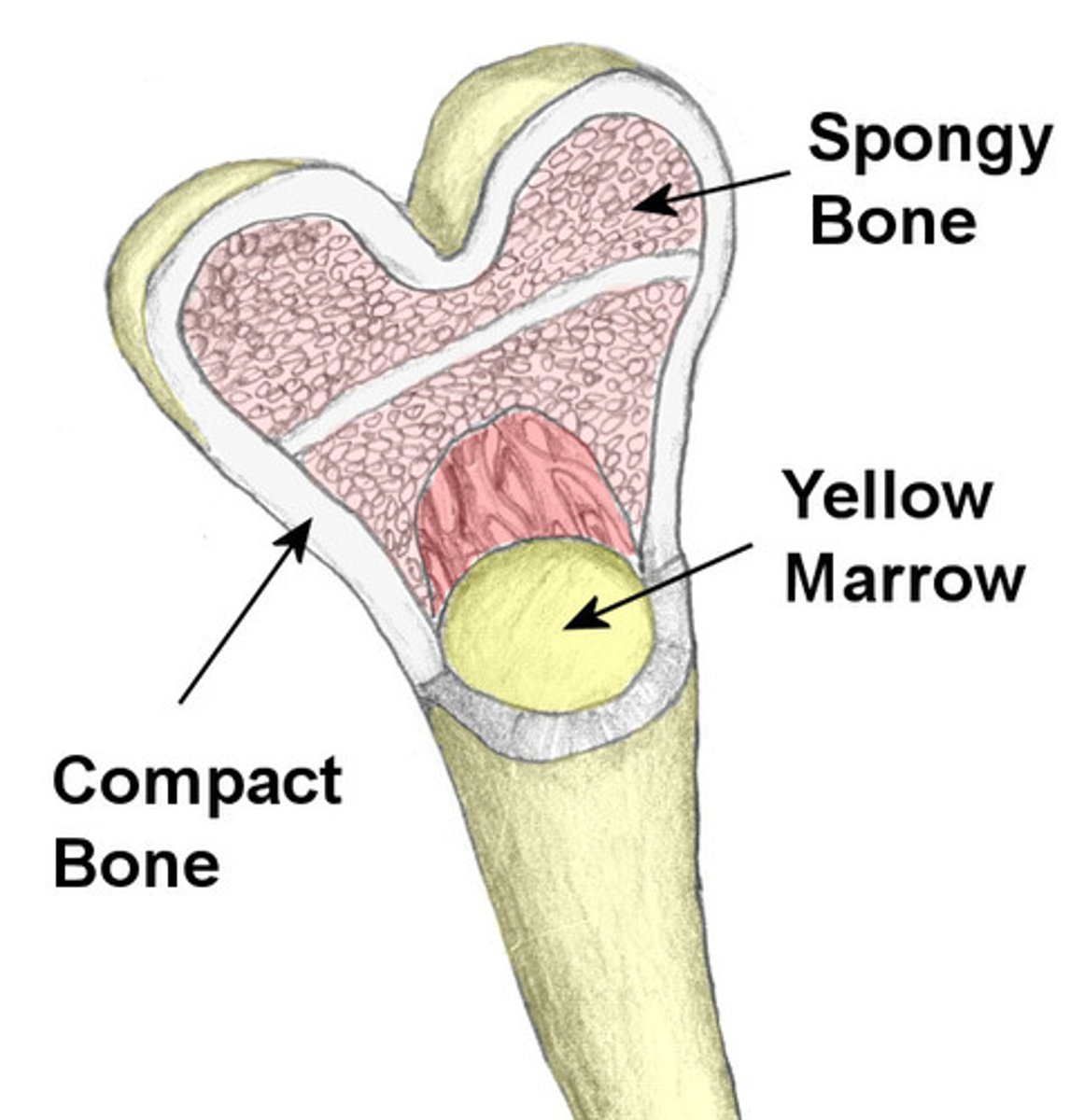
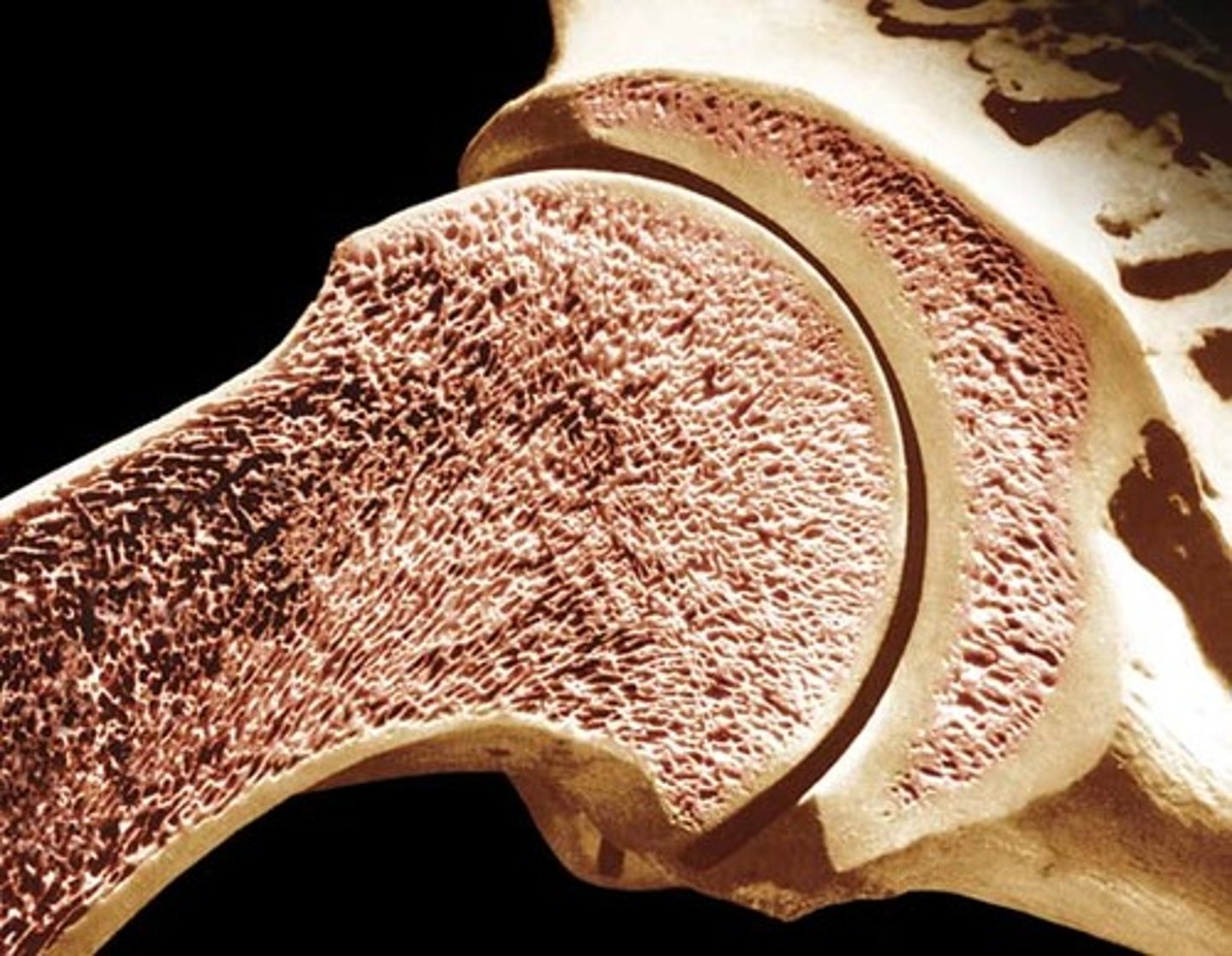
spongy bone tissue
hard, lightweight tissue of bone that has many spaces; where red marrow is found
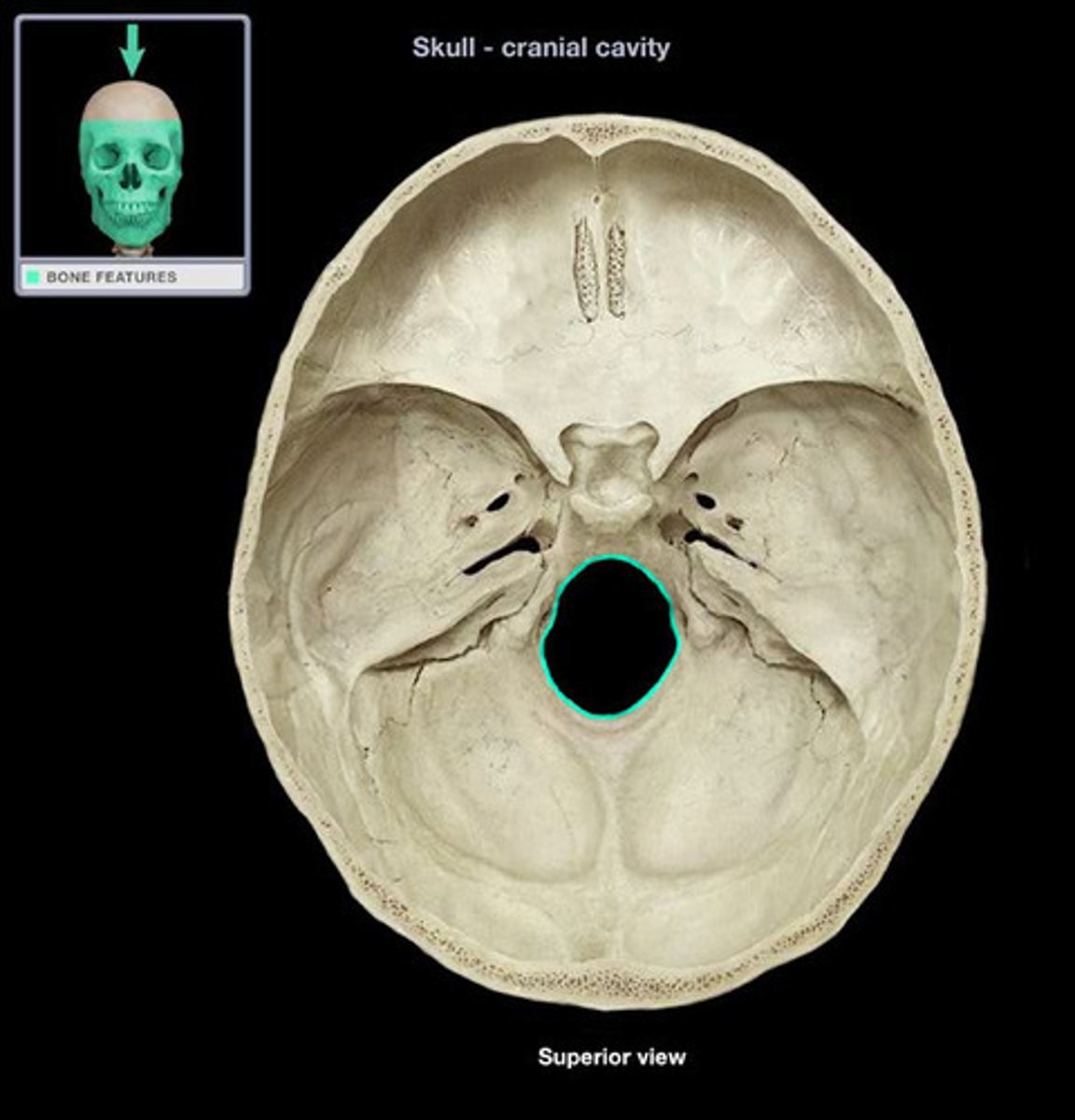
foramen
"hole"
fissure
a long narrow opening
meatus
"canal"
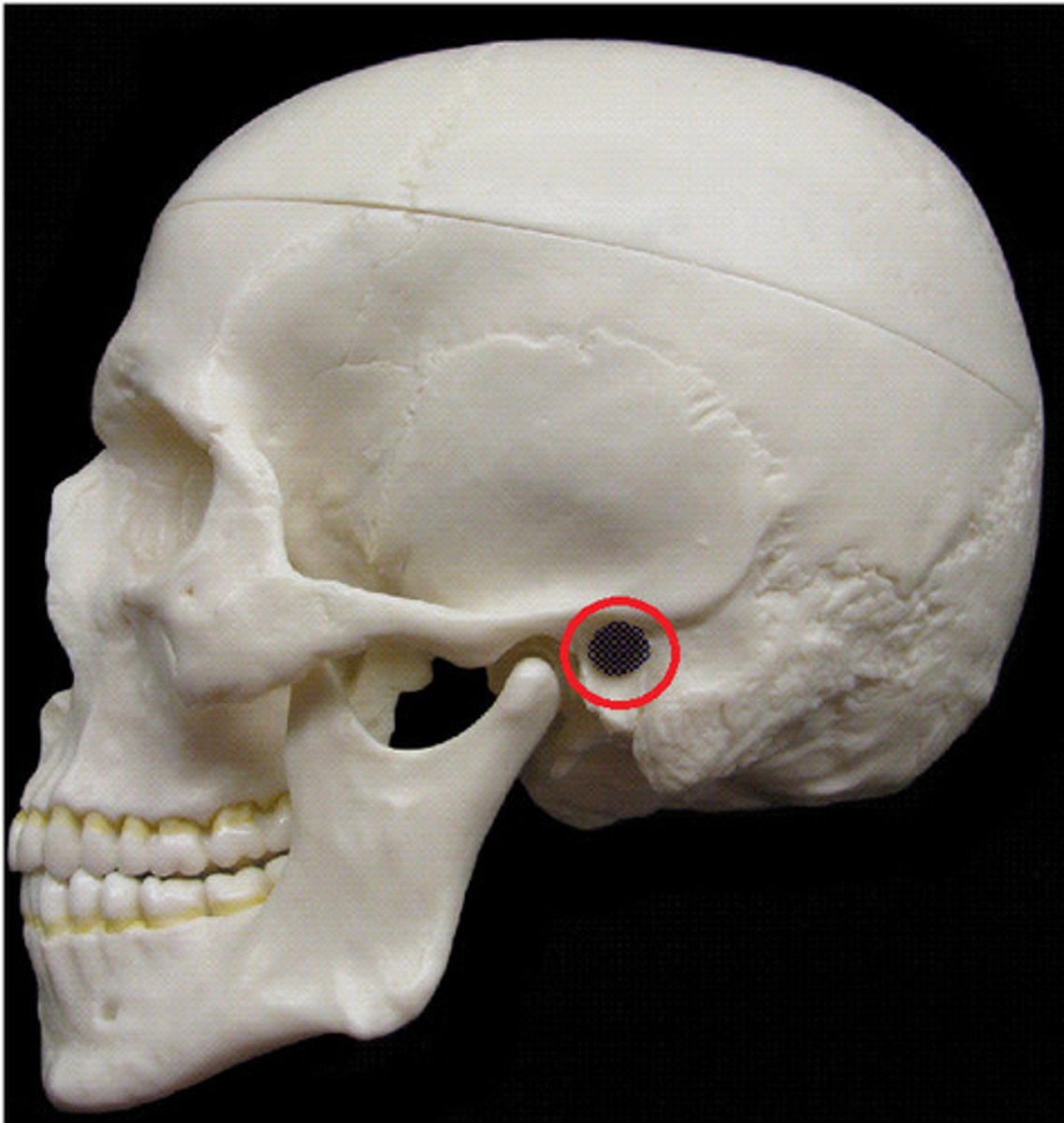
fossa
a depression on a bone surface
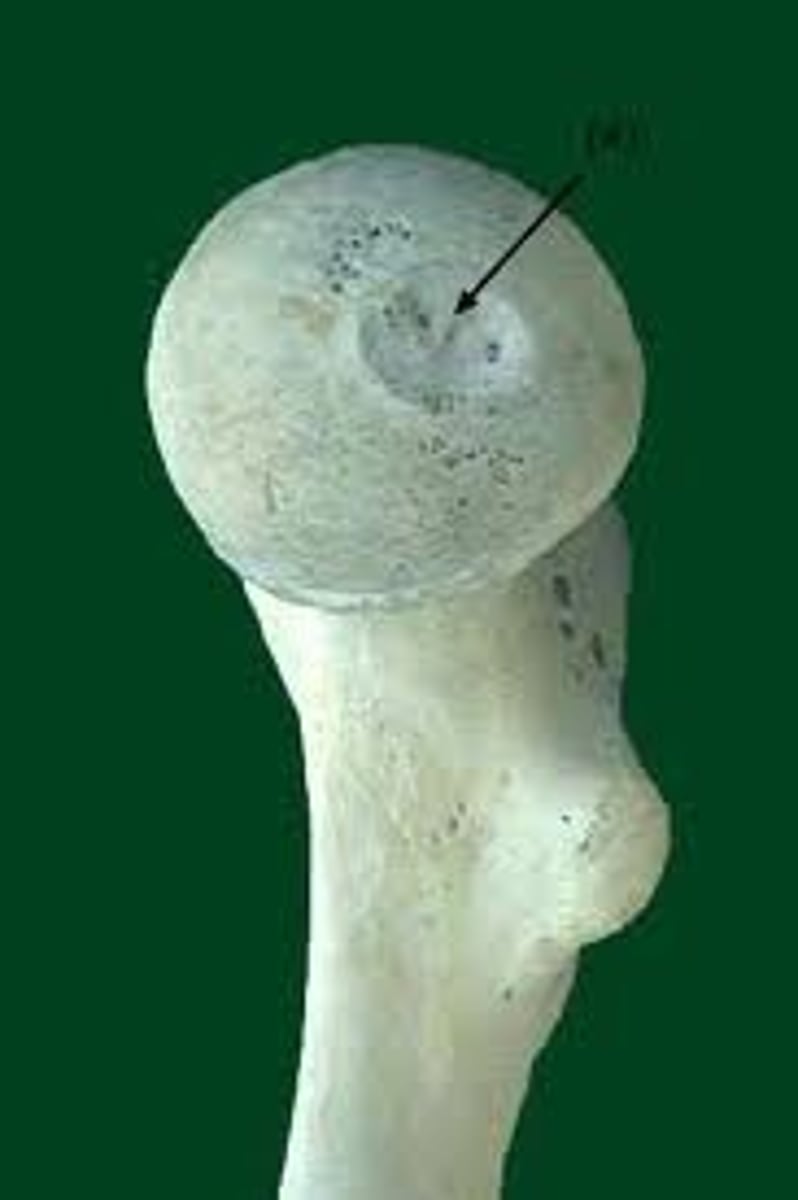
fovea
pit in the surface of a bone
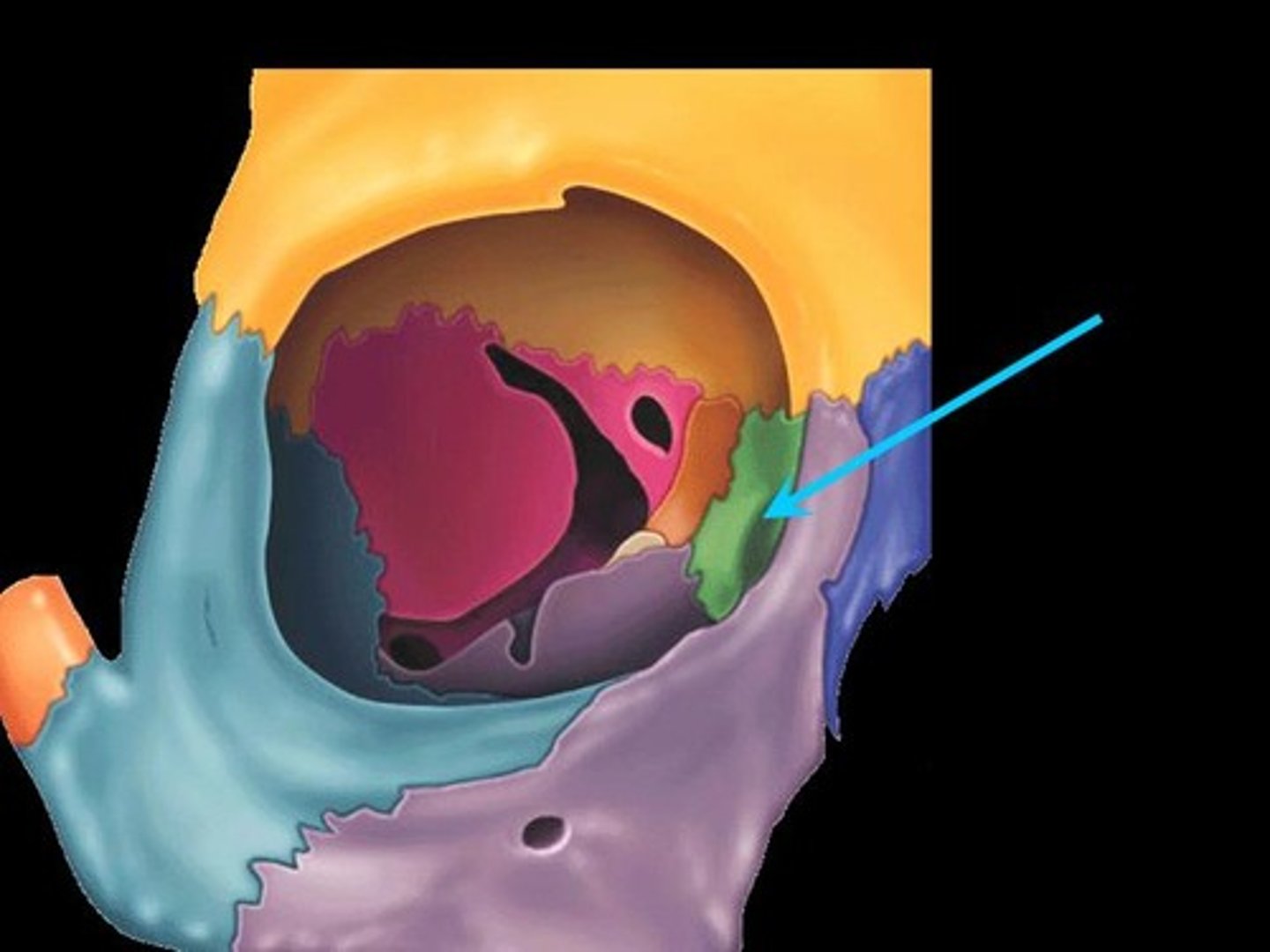
sulcus
groove on the surface of a bone
tubercle
small rounded projection/elevation on a bone
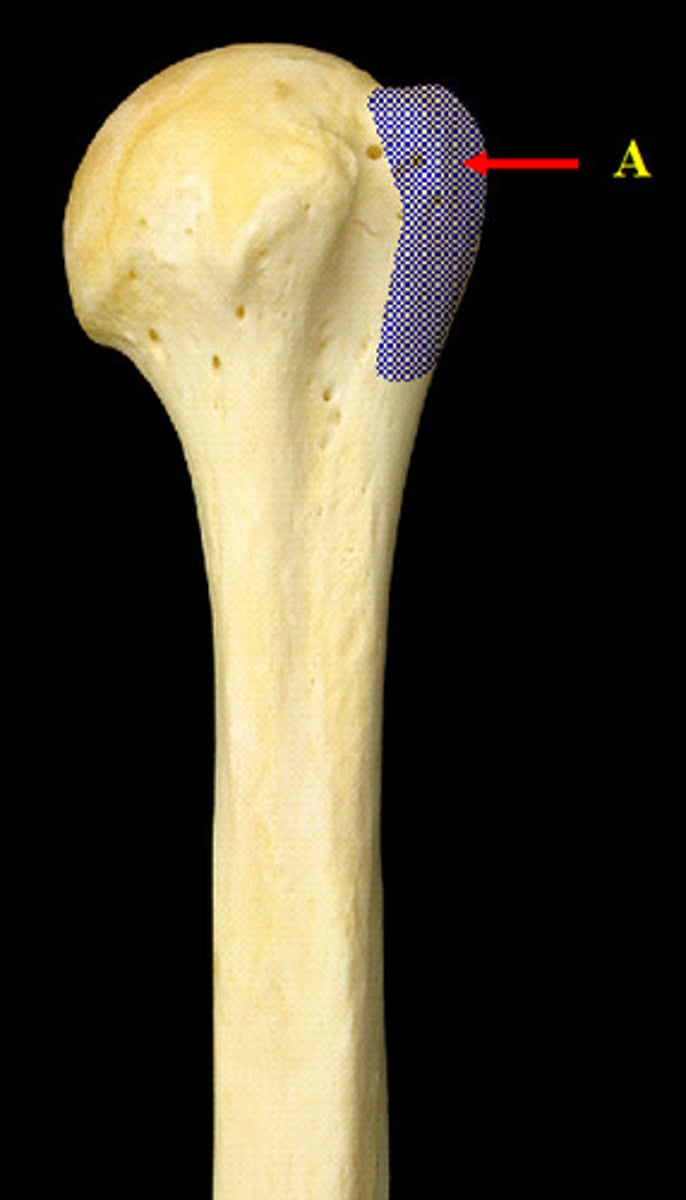
tuberosity
rough elevation on a bone
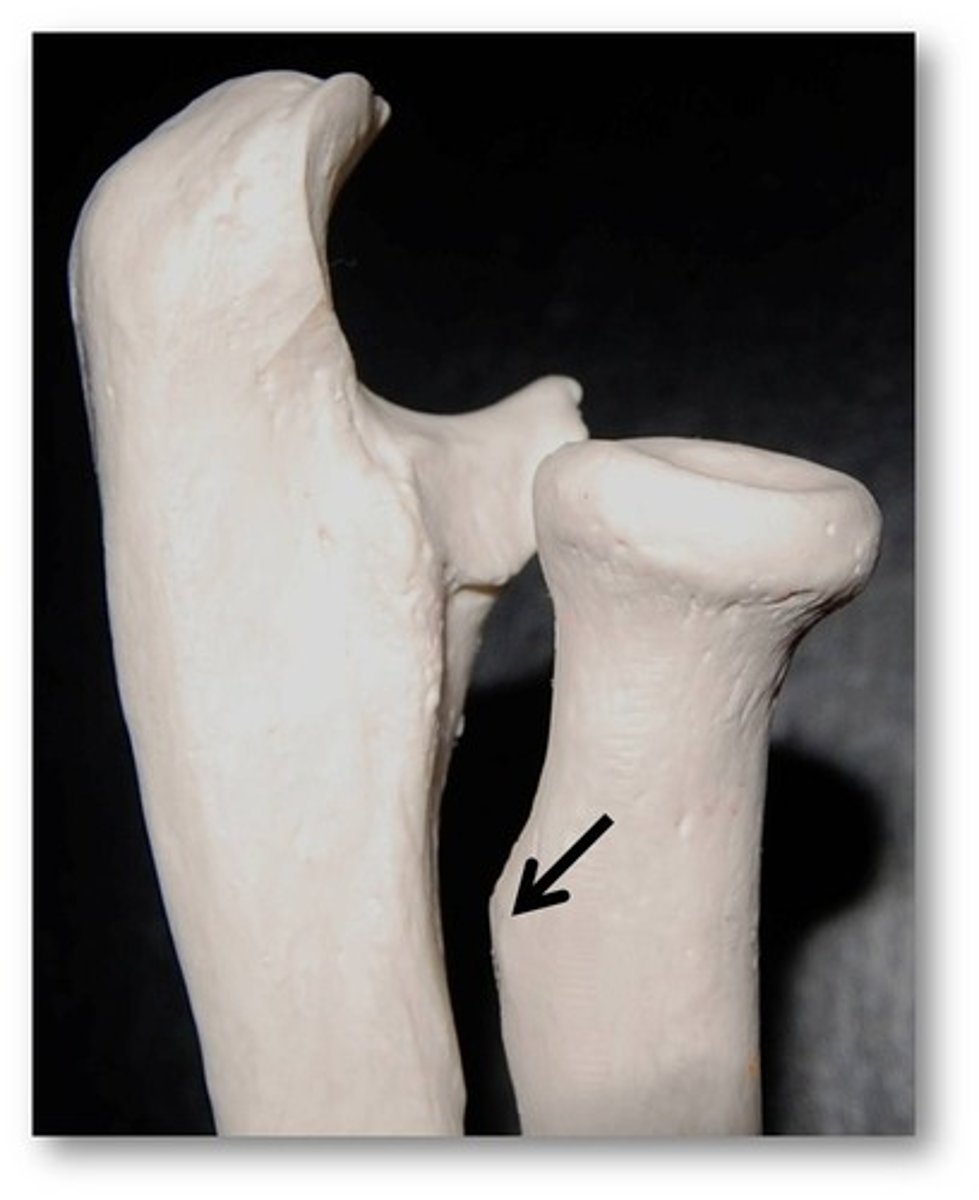
line
shallow linear elevation
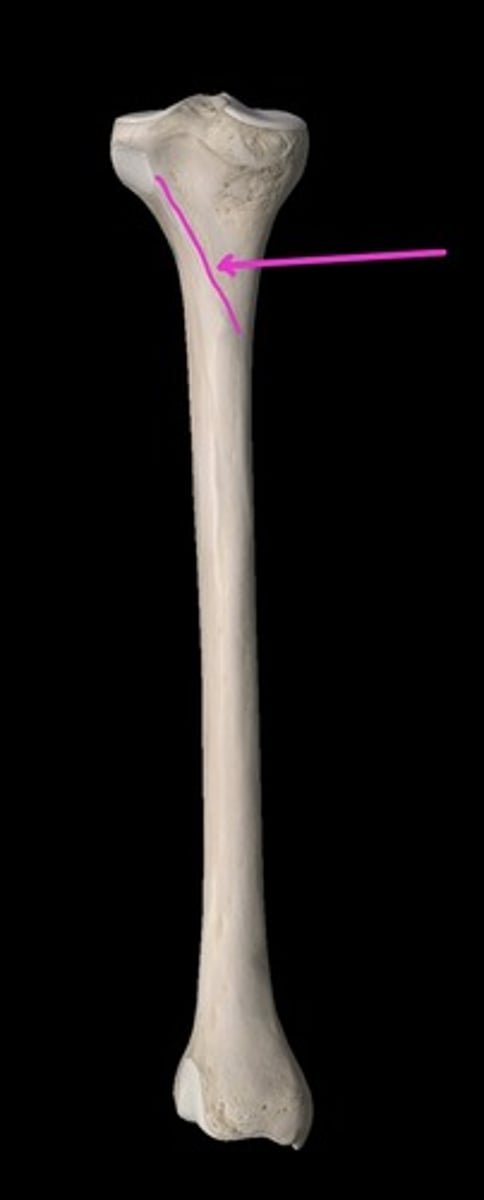

crest
linear elevation; higher/more raised than a line
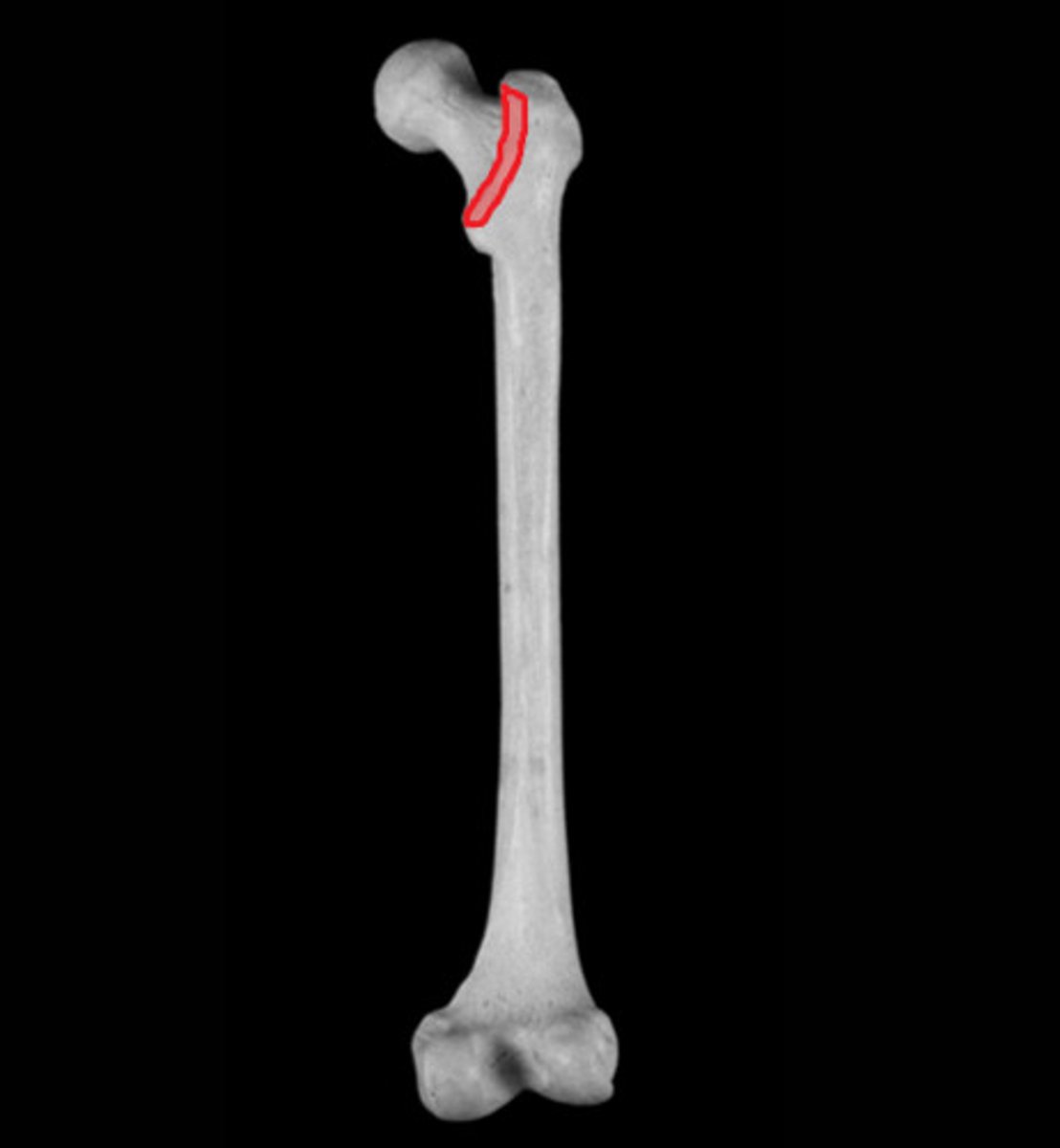
process
an extension/projection of a bone
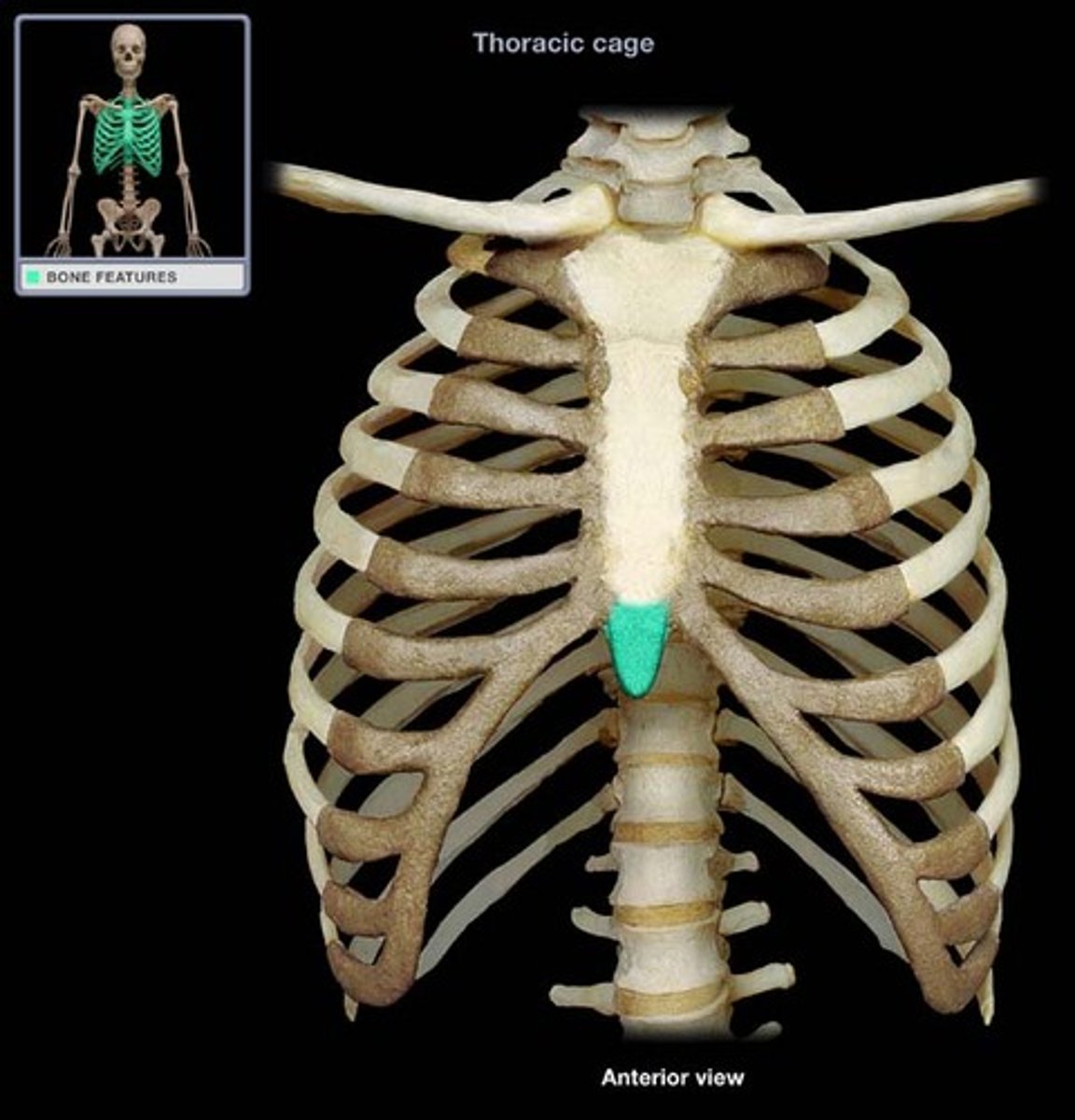
condyle
flared extension of a long bone to allow for better attachment; add to strength/stability of a joint
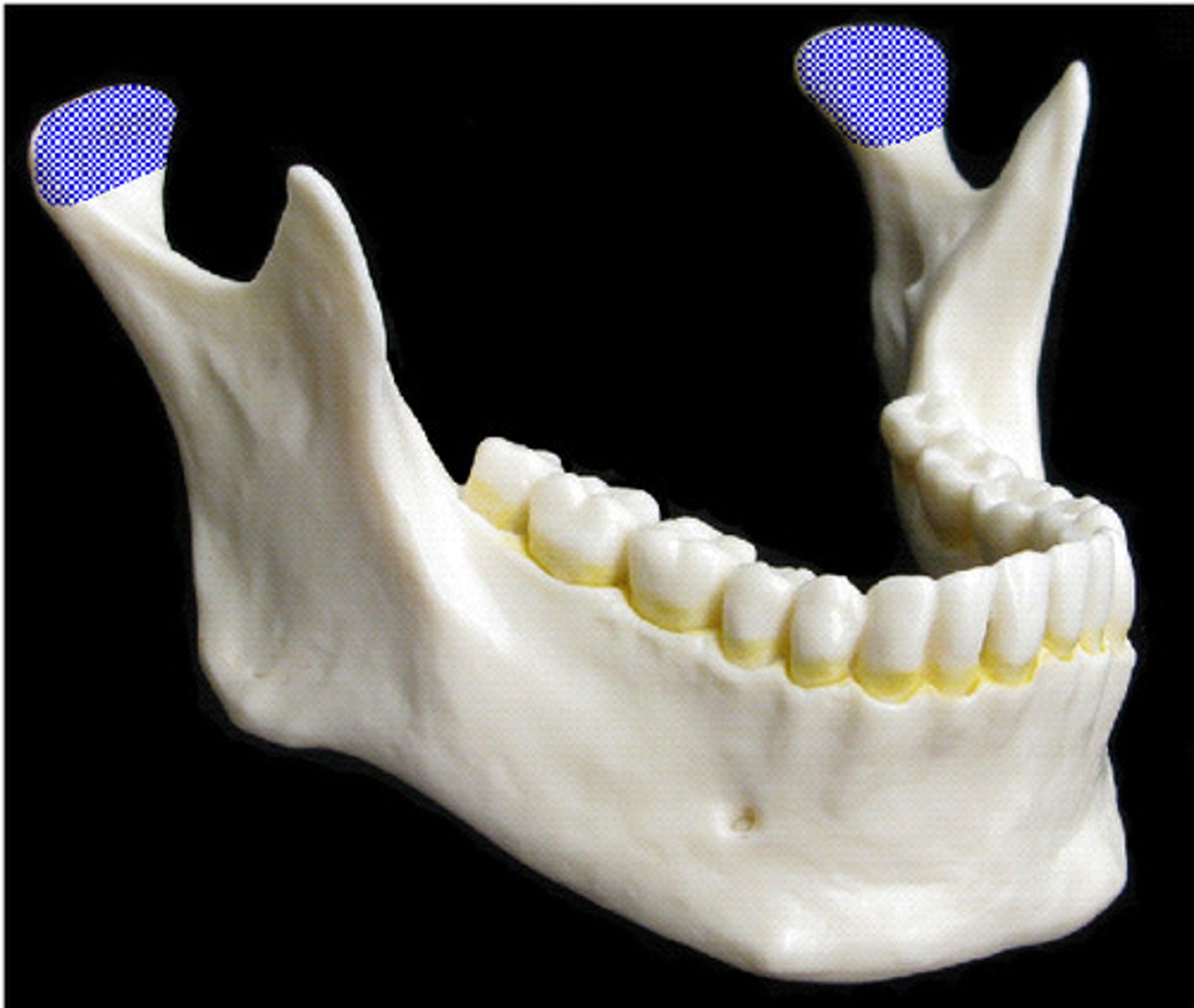
condyloid
a condyle-like structure found on a bone that is not a long bone
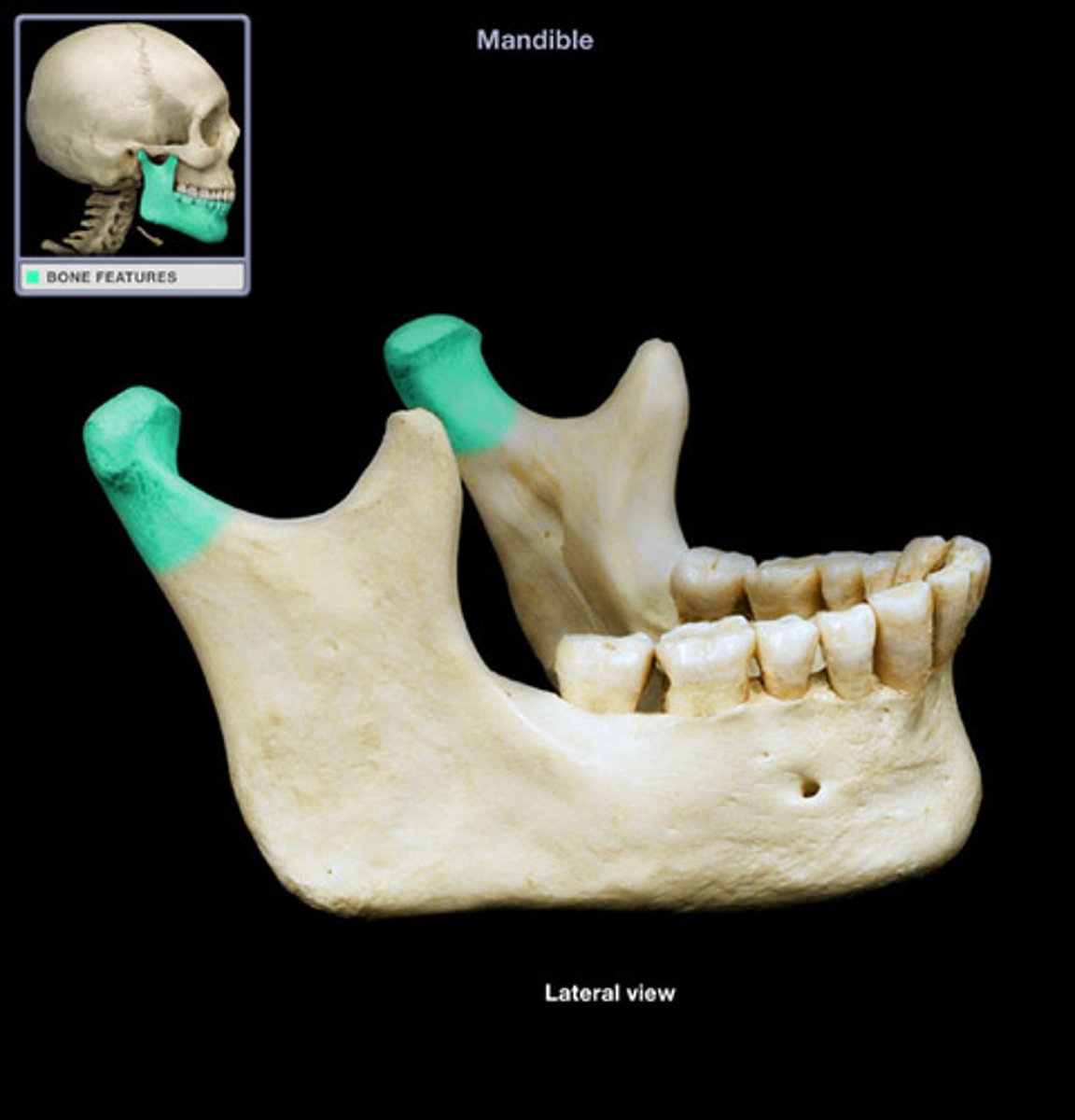
epicondyle
Raised area on or above a condyle; anchoring points for ligaments
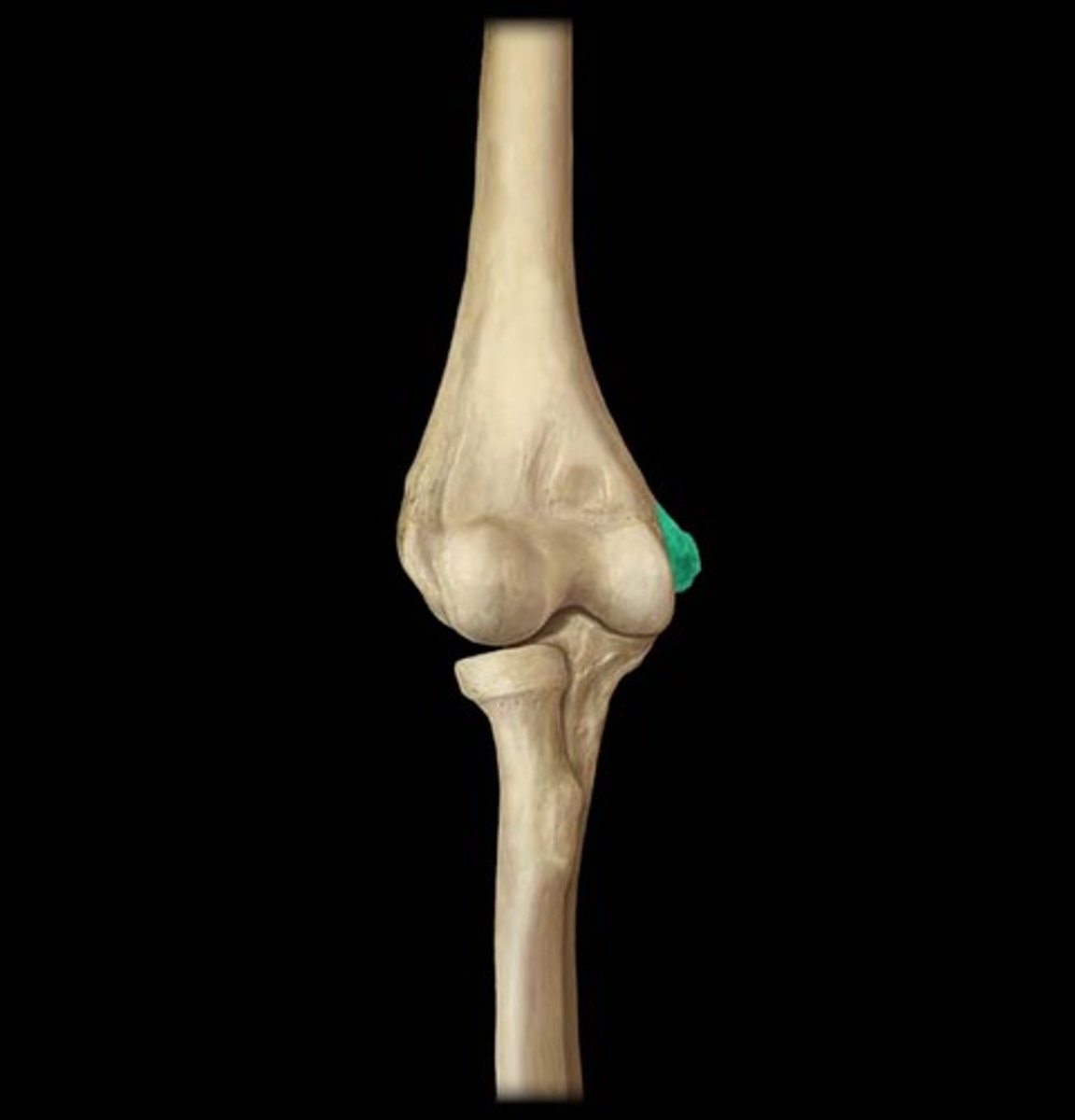
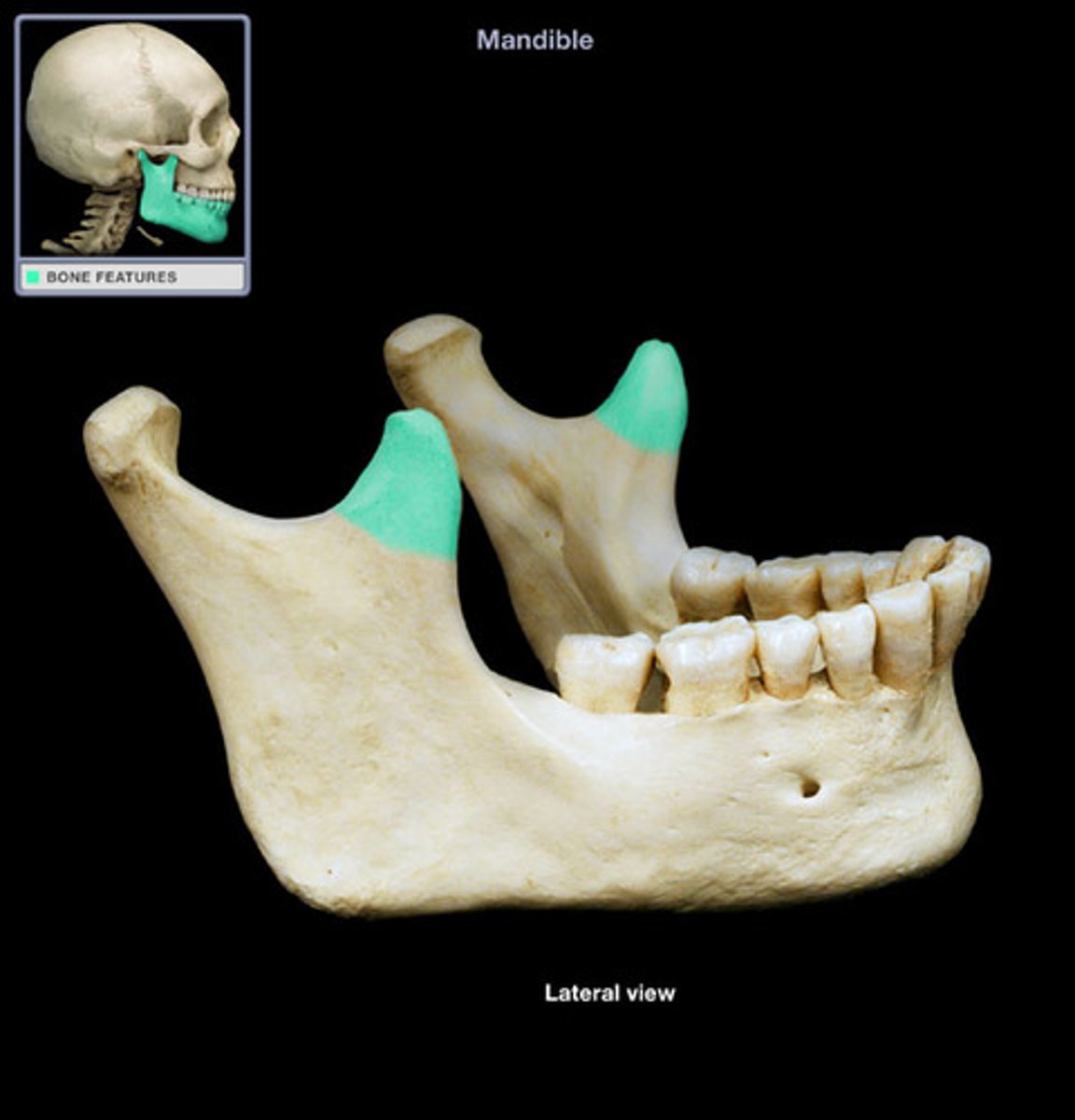
coronoid
a wave-like extension of a bone
malleolus
a flattened projection
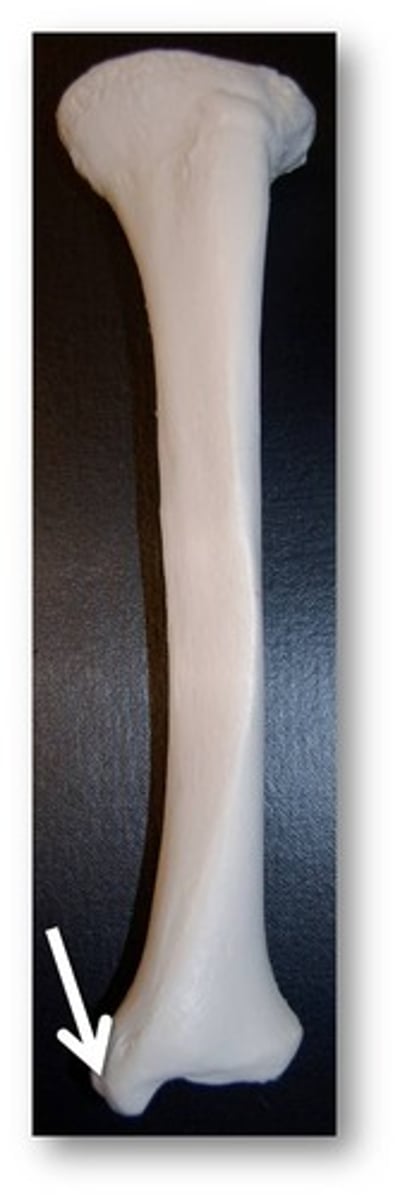

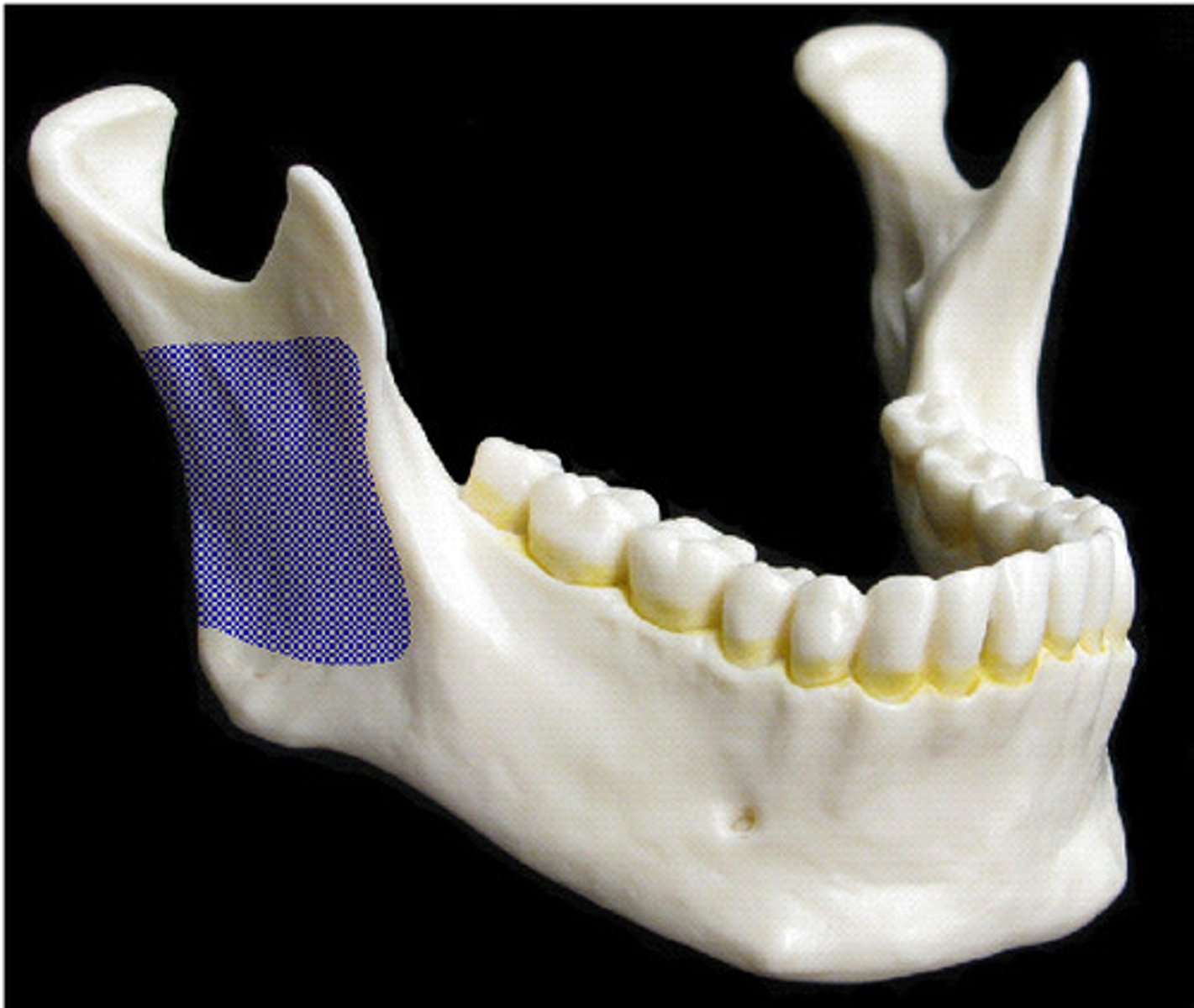
ramus
bridge-like structure
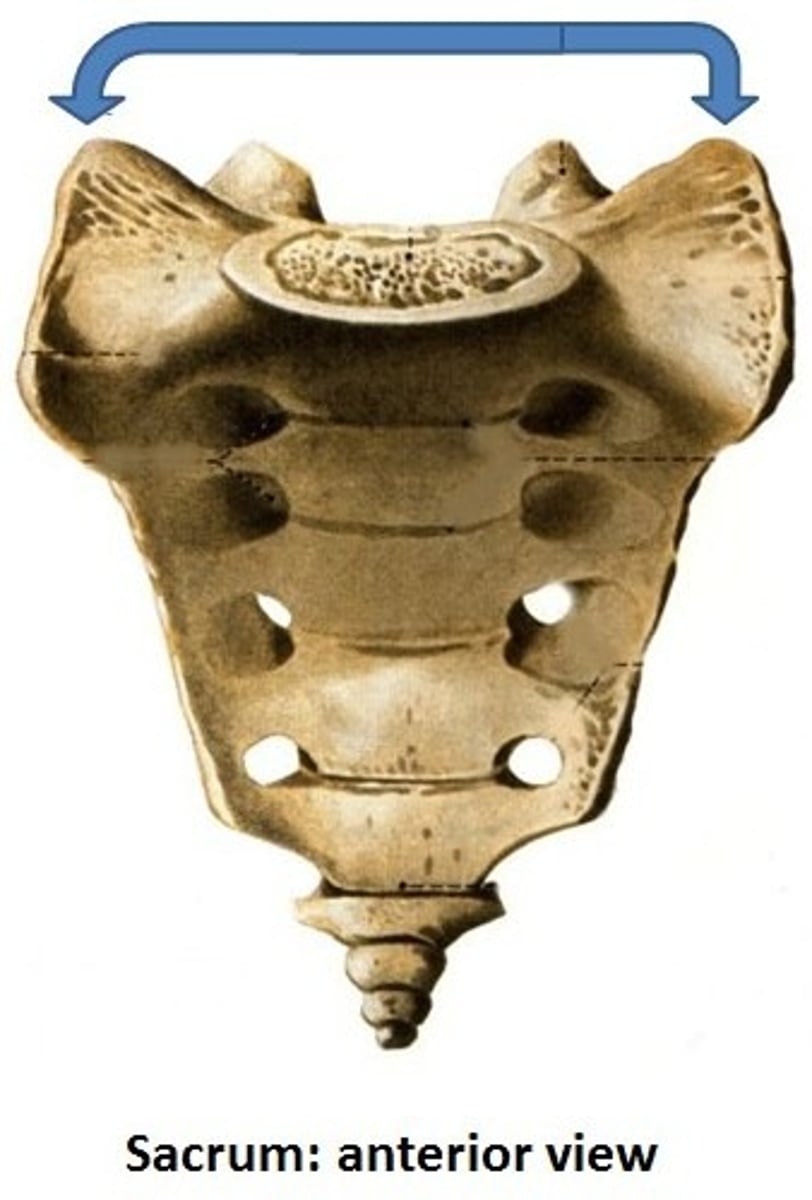
ala
wing-shaped structure
articulating surface
a smooth area for bone to bone attachment
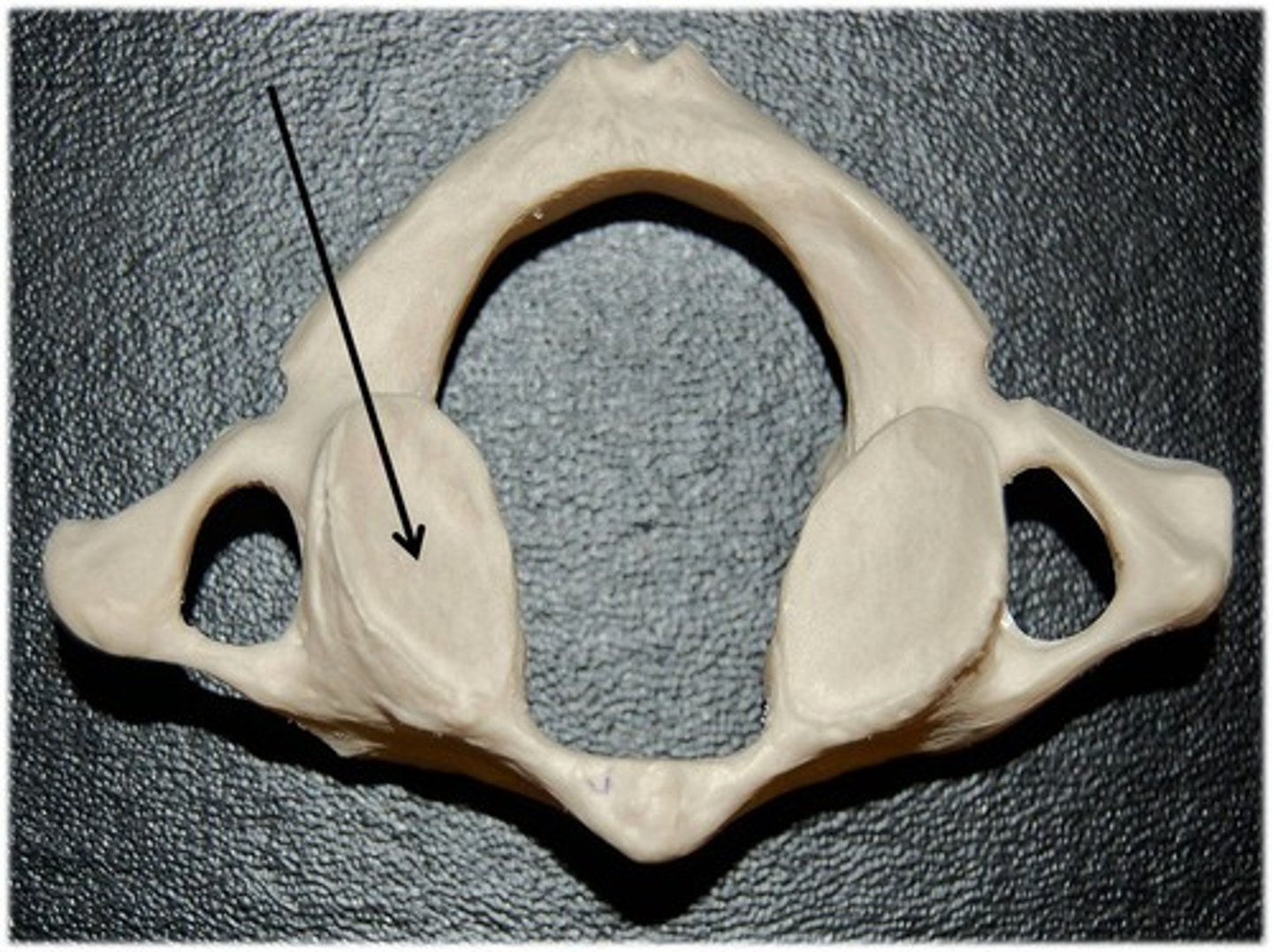
facet
articulating surface (full moon)
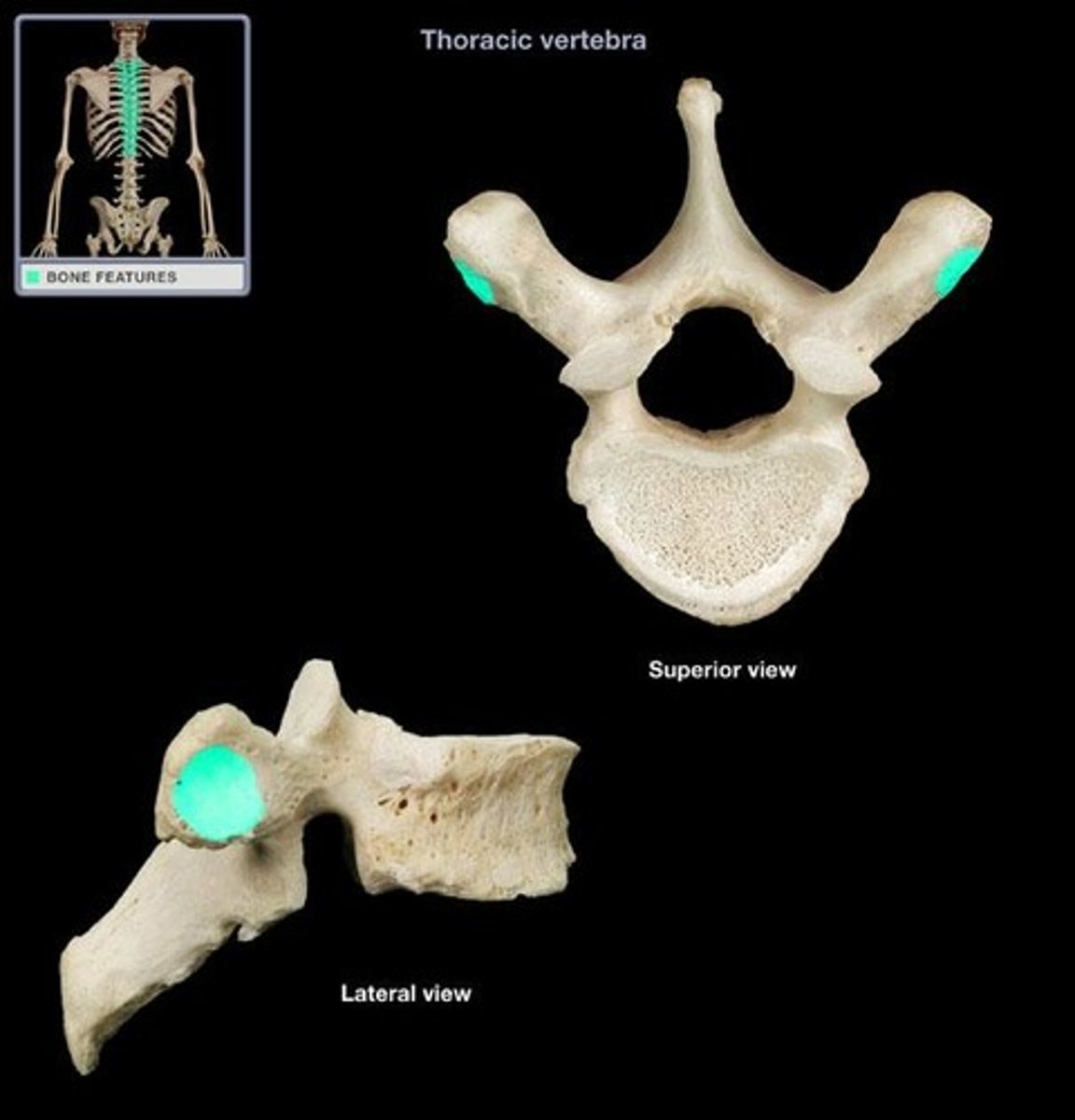
demifacet
half of an articulating surface (half moon)
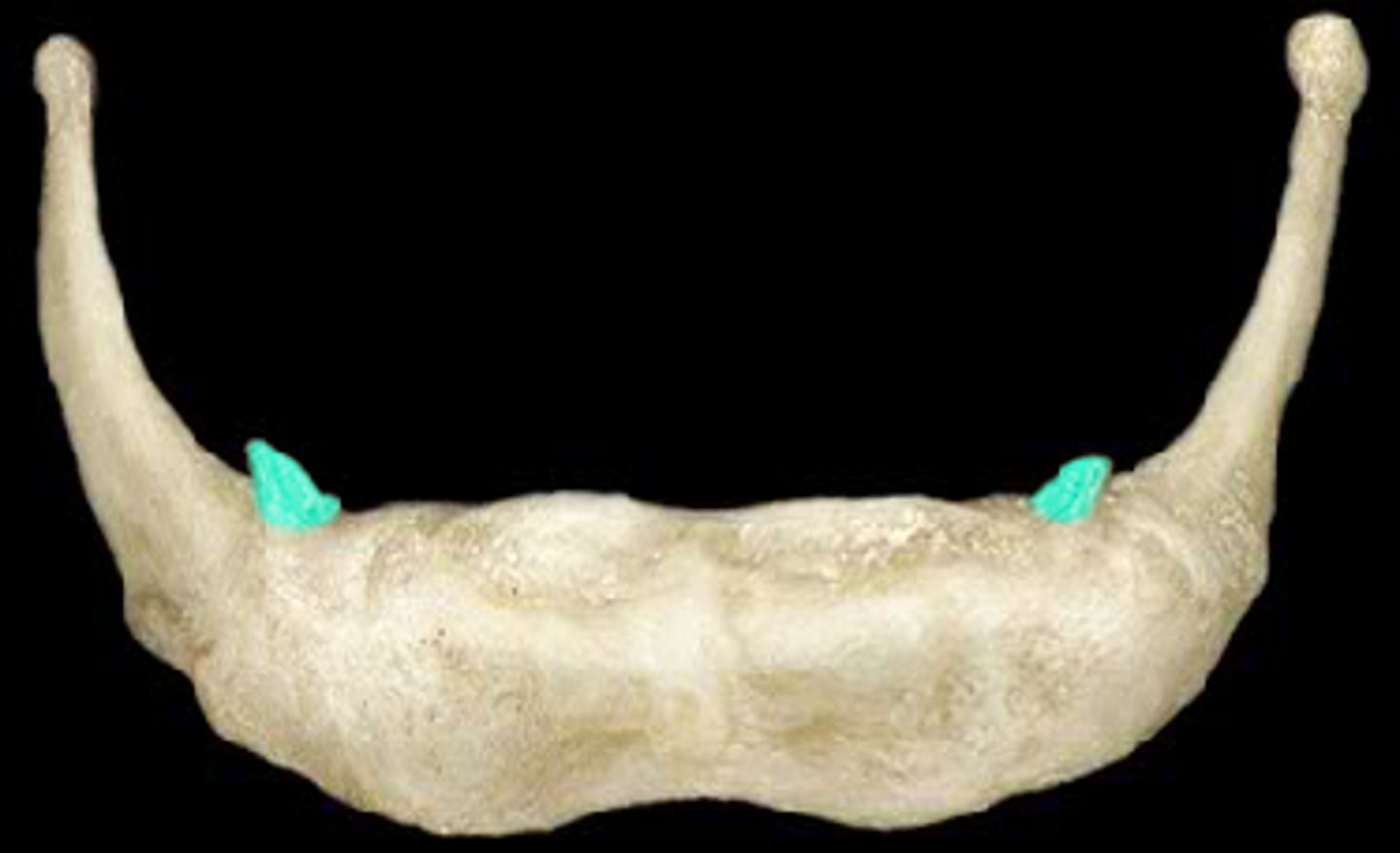
cornu
horn-shaped extension of bone
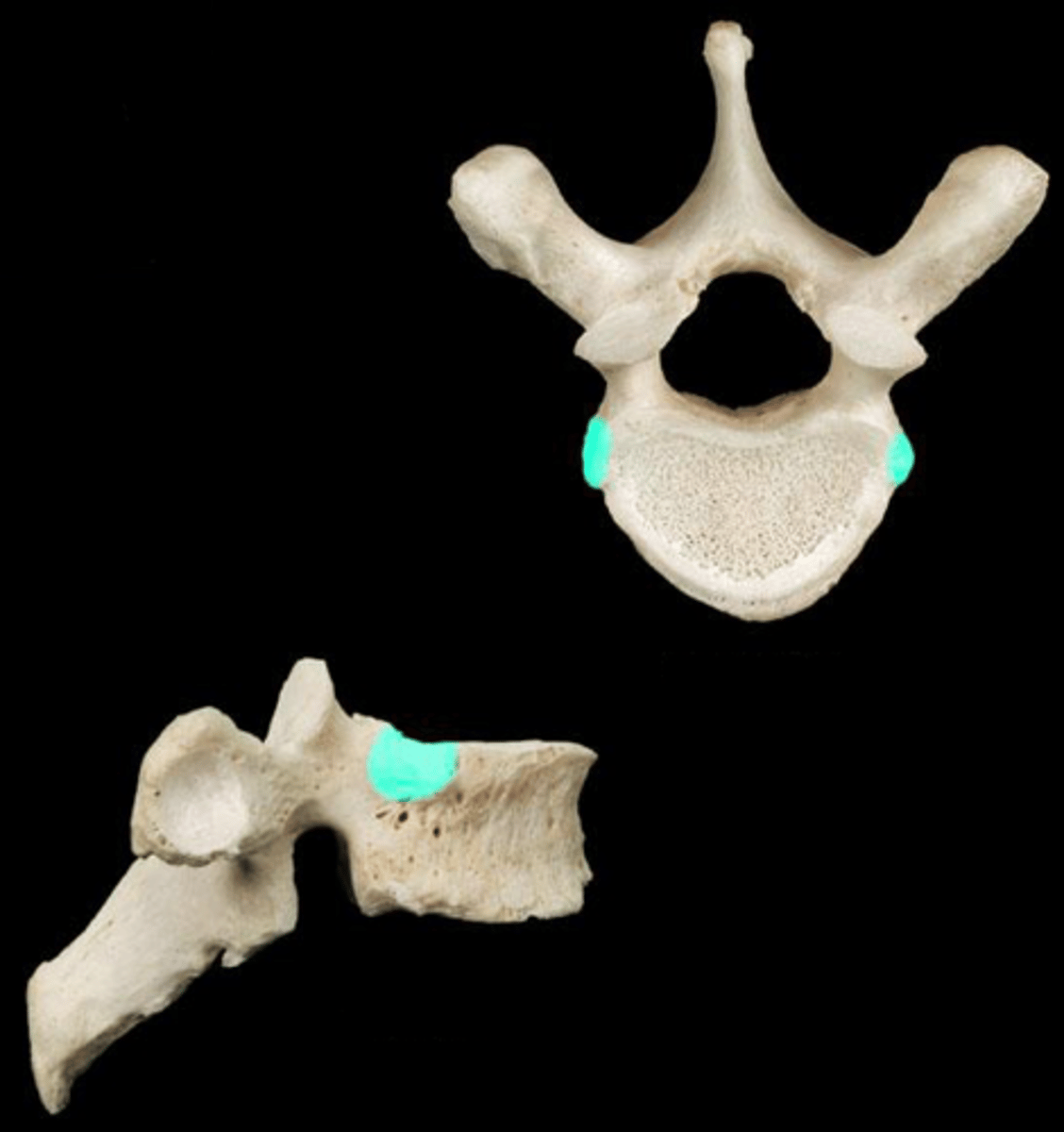
apophyses
Projections on the vertebrae that articulate with ribs
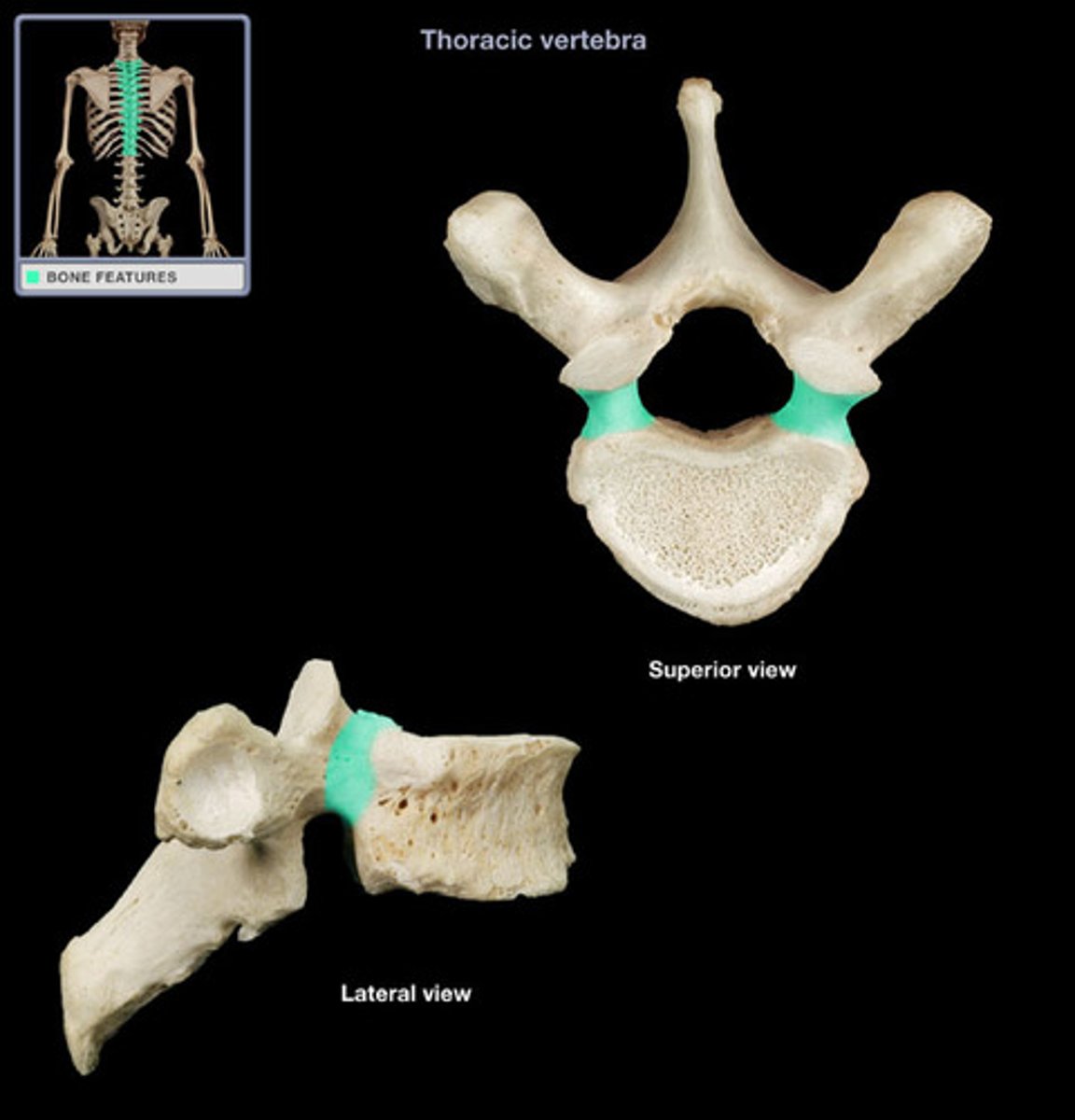
pedicle
base of vertebral arch
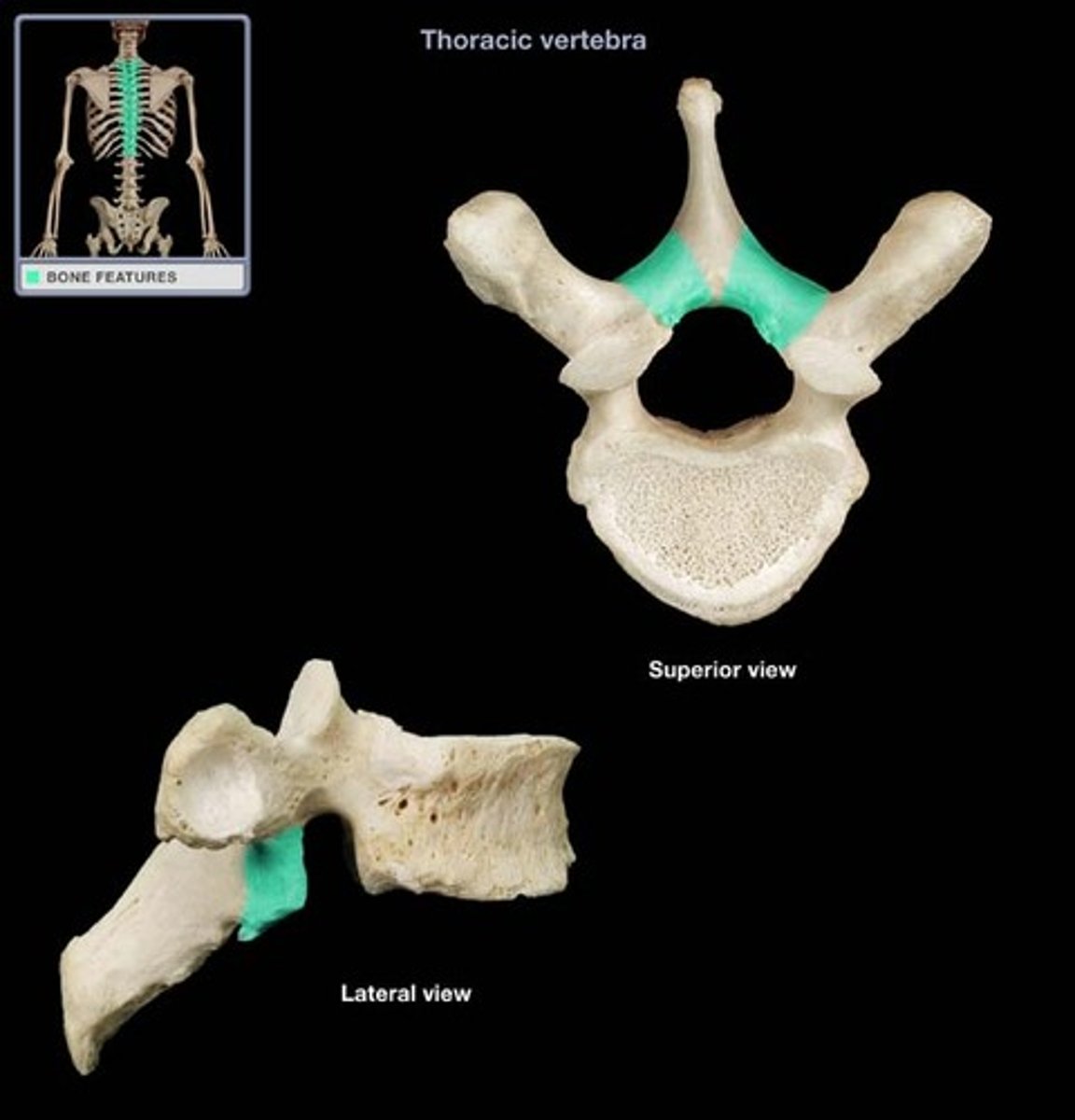
lamina
roof and sides of vertebral arch
hemal arch
present in some vertebrates; located in tail; called chevron bones in amniotes
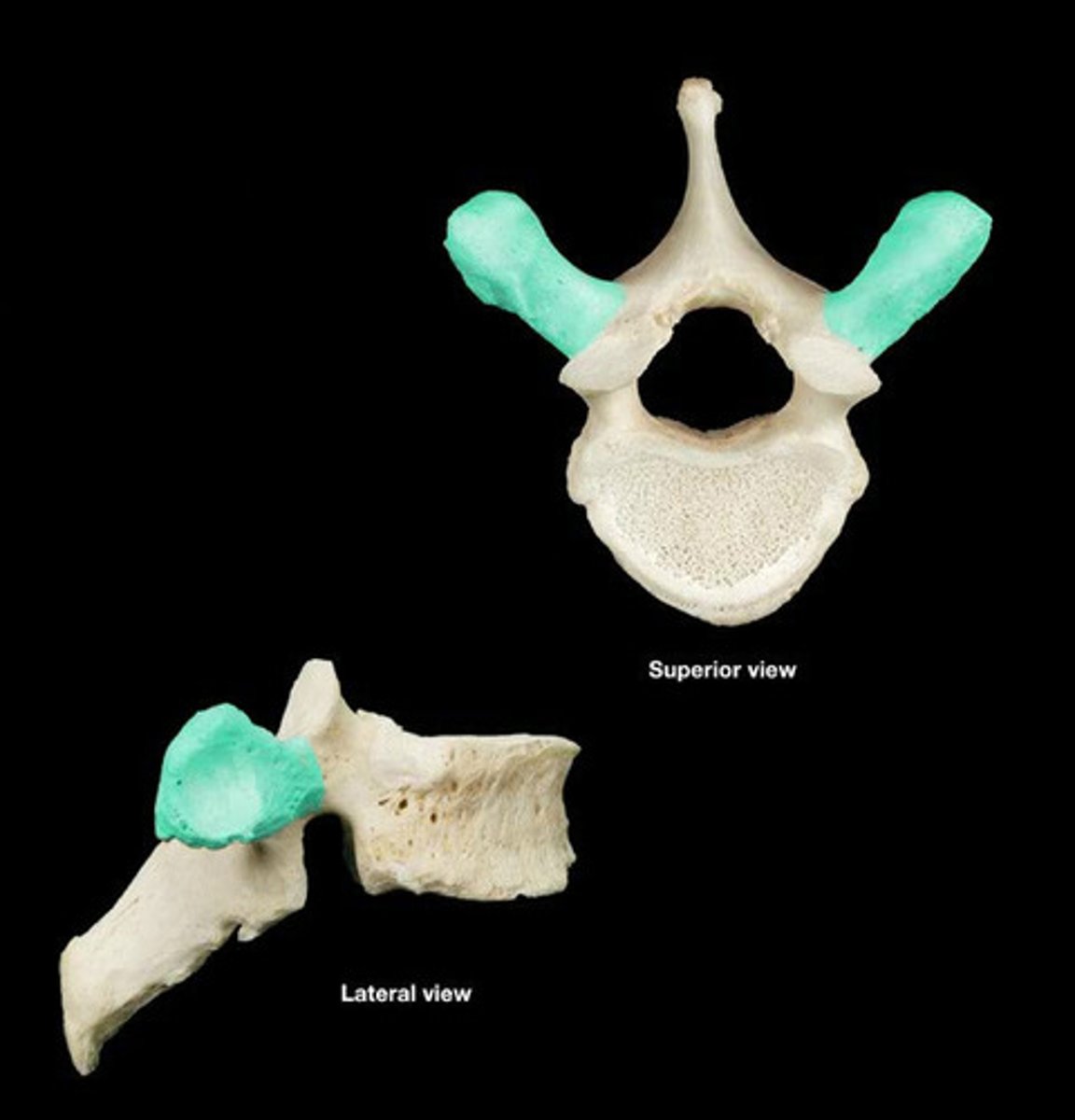
diapophyses (transverse process)
articulate with ribs; attach to tuberculum of rib in vertebrates with biccipital ribs
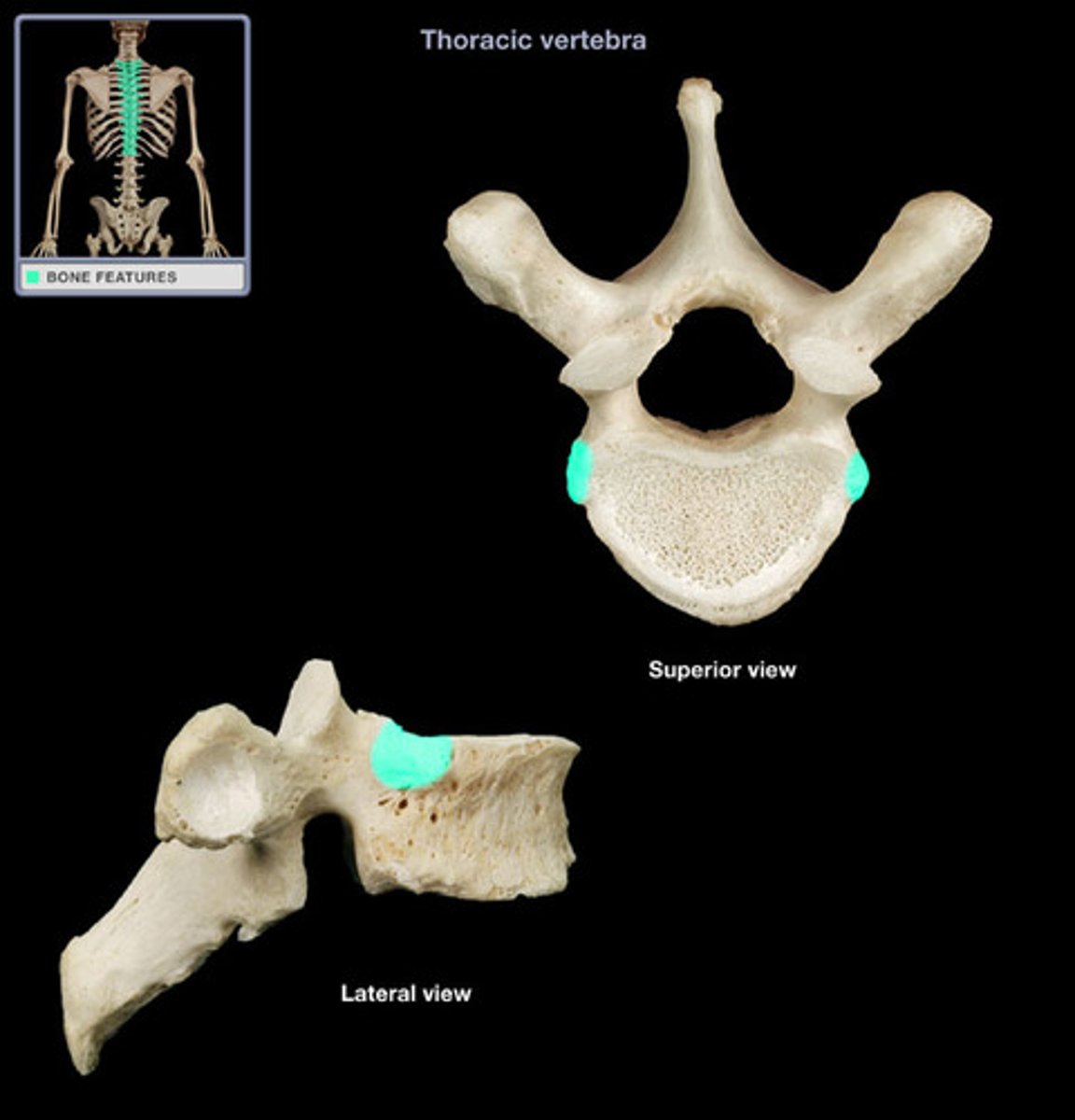
parapophysis
found in vertebrates with biccipital (2 headed) ribs; attaches to capitulum of rib
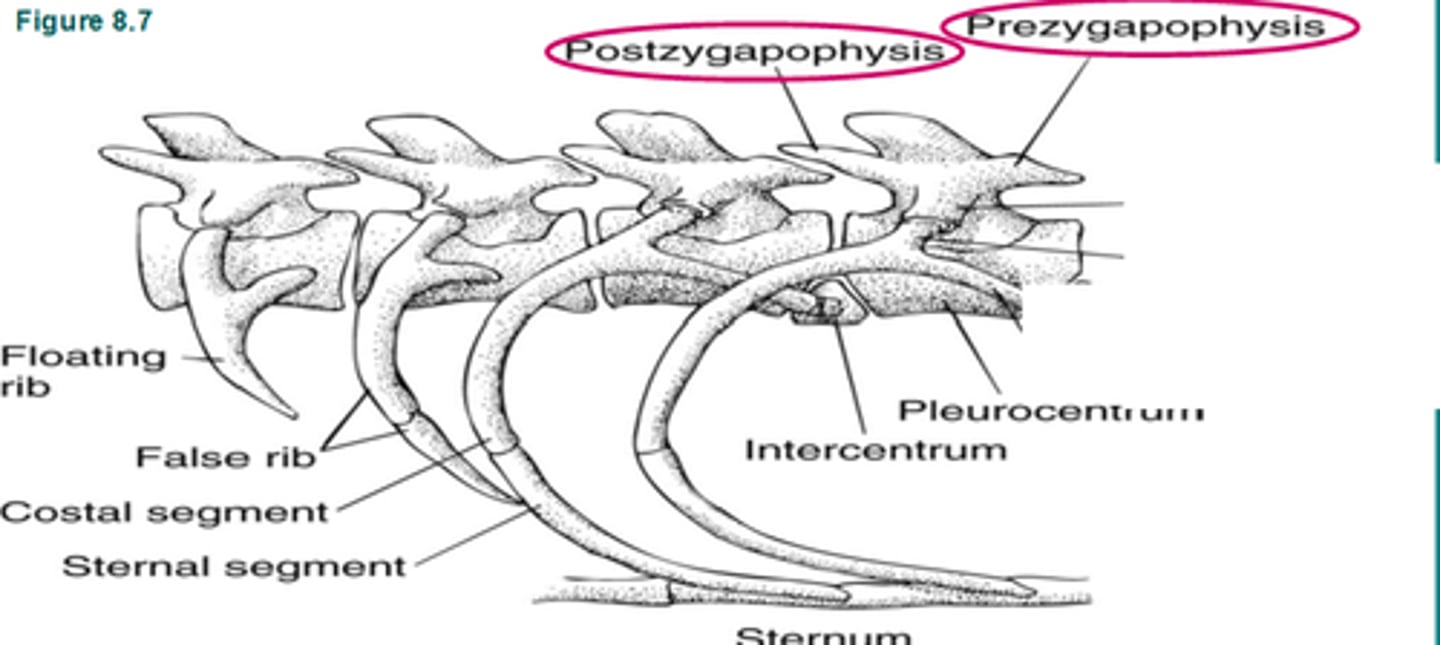
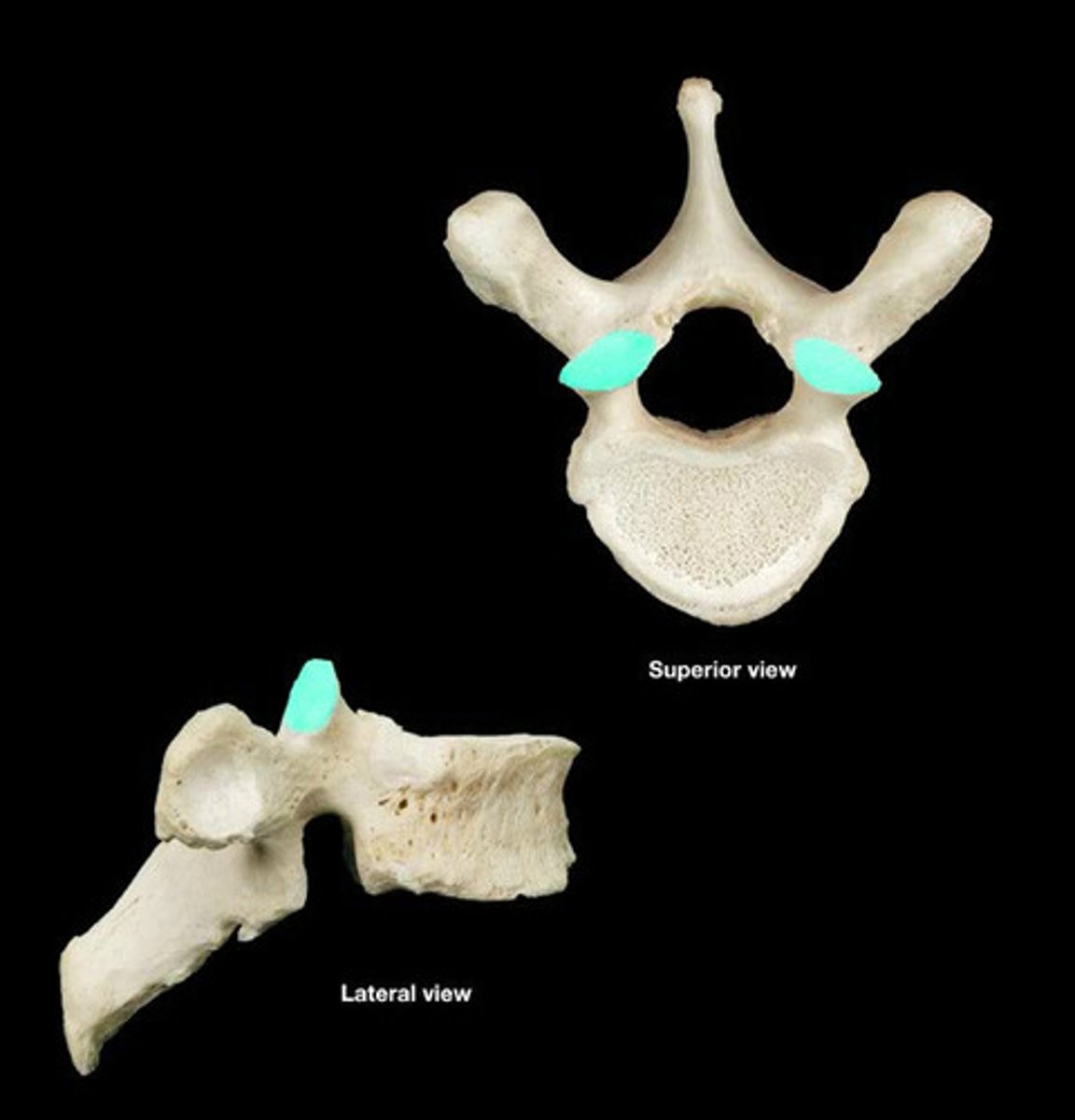
zygapophyses
articulating surfaces; attachment between successive vertebrae
prezygapophyses (cranial/superior articulating process)
allow one vertebra to attach to the vertebra in front of it
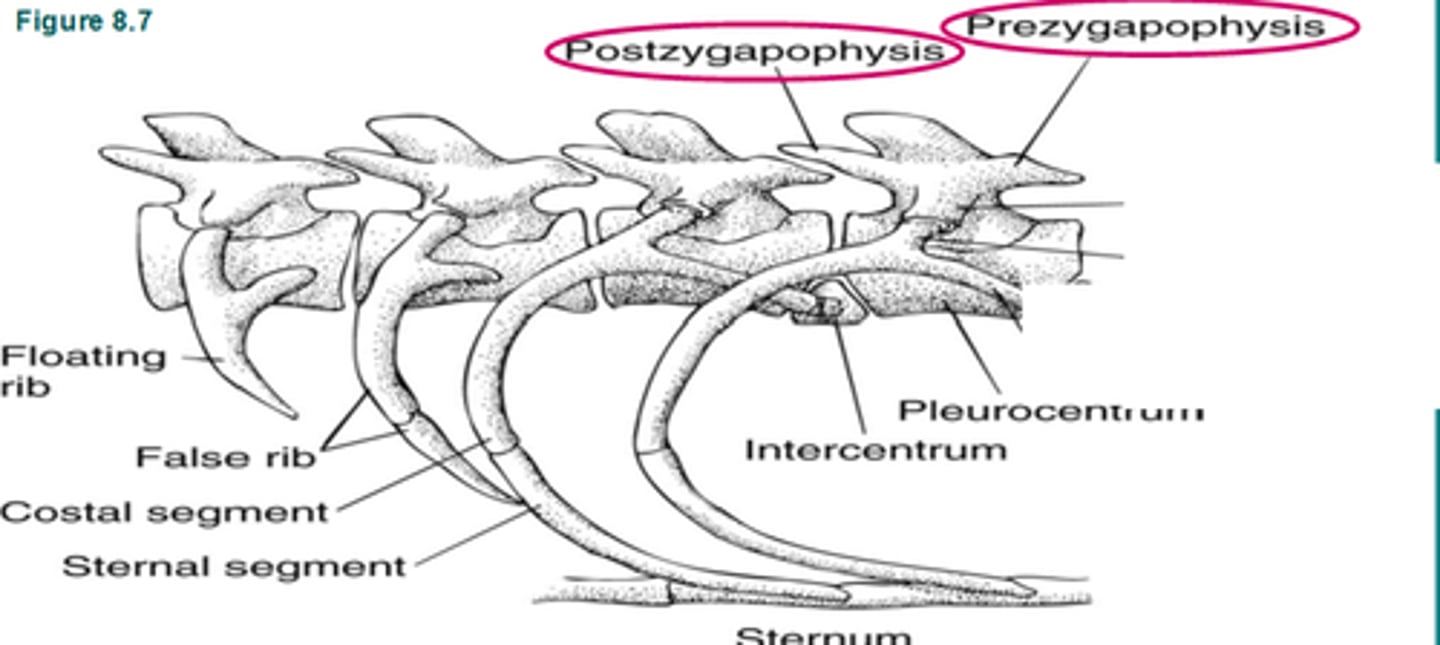
postzygapophyses (caudal/inferior articulating process)
allow one vertebra to attach to the vertebra behind it