Computer Hardware and Software: Key Concepts for IT Students
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Hardware
The physical equipment used for the input, processing, output, and storage activities of a computer system.
Hardware components include:
1. Central processing unit (CPU)
2. Primary storage
3. Secondary storage
4. Input device
5. Output device
6. Communication device
Supercomputers
-The fastest computers available,
-Used by large organizations to execute computationally demanding tasks involving very large data sets.
-Supports military, scientific, and some business applications
Mainframe computers
-Used for transaction processing and business applications
-Supporting thousands of users at one time.
Midrange computers (minicomputers)
Perform the same functions as mainframe but to a more limited extent.
Microcomputers (micros, personal computers (PCs))
-The smallest and least expensive general-purpose computers.
-Categories: Desktops, thin clients, notebooks and laptops, netbooks, and tablets.
Input technologies
Allow people and other technologies to enter data into a computer.
Output technologies
Transmit output generated by a computer to the user.
-Examples: Monitors, printers, plotters, and voice
Central processing unit (CPU)
-Performs the actual computation inside any computer.
-CPU is a microprocessor (chips) made up of millions of microscopic transistors embedded in a circuit on a silicon wafer or chip
Moore's law
In 1965, Gordon Moore predicted that microprocessor complexity would double approximately every 2 years.
Primary storage
Stores small amounts of data and information that will be used immediately by the CPU.
Secondary Storage
Stores much larger amounts of data and information for extended periods.
Bits
The basic unit of data in computing, represented as 0 or 1.
Bytes
1 Byte = 8 bits.
Kilobyte (KB)
1,000 bytes.
Megabyte (MB)
1 million bytes.
Gigabyte (GB)
1 billion bytes.
Terabyte (TB)
1 trillion bytes.
Petabyte
1,000 terabytes.
Exabyte
1,000 petabytes.
Zettabyte
1,000 exabytes.
Register
Least capacity, storing instructions and data only immediately before and after processing - volatile.
Cache memory
High speed memory for temporarily storing often used data - volatile.
Random access memory (RAM)
Holds a software program and small amounts of data for processing - volatile.
Read-only memory (ROM)
Nonvolatile memory that stores critical instructions for the computer and cannot be changed by the user.
Non-volatile storage
Keeps data when the computer is shut down.
Magnetic disks
Also known as hard drives or fixed disk drives.
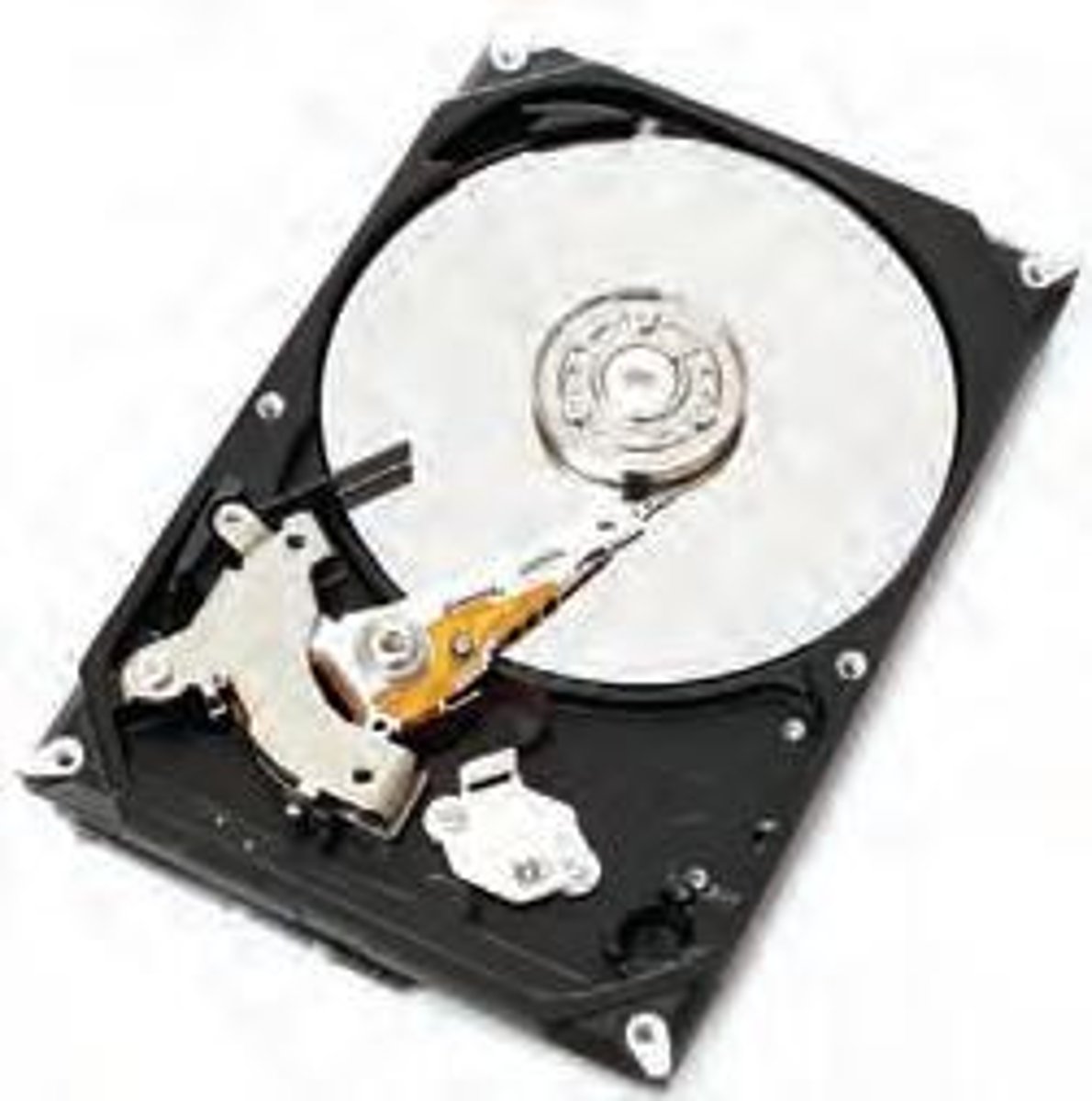

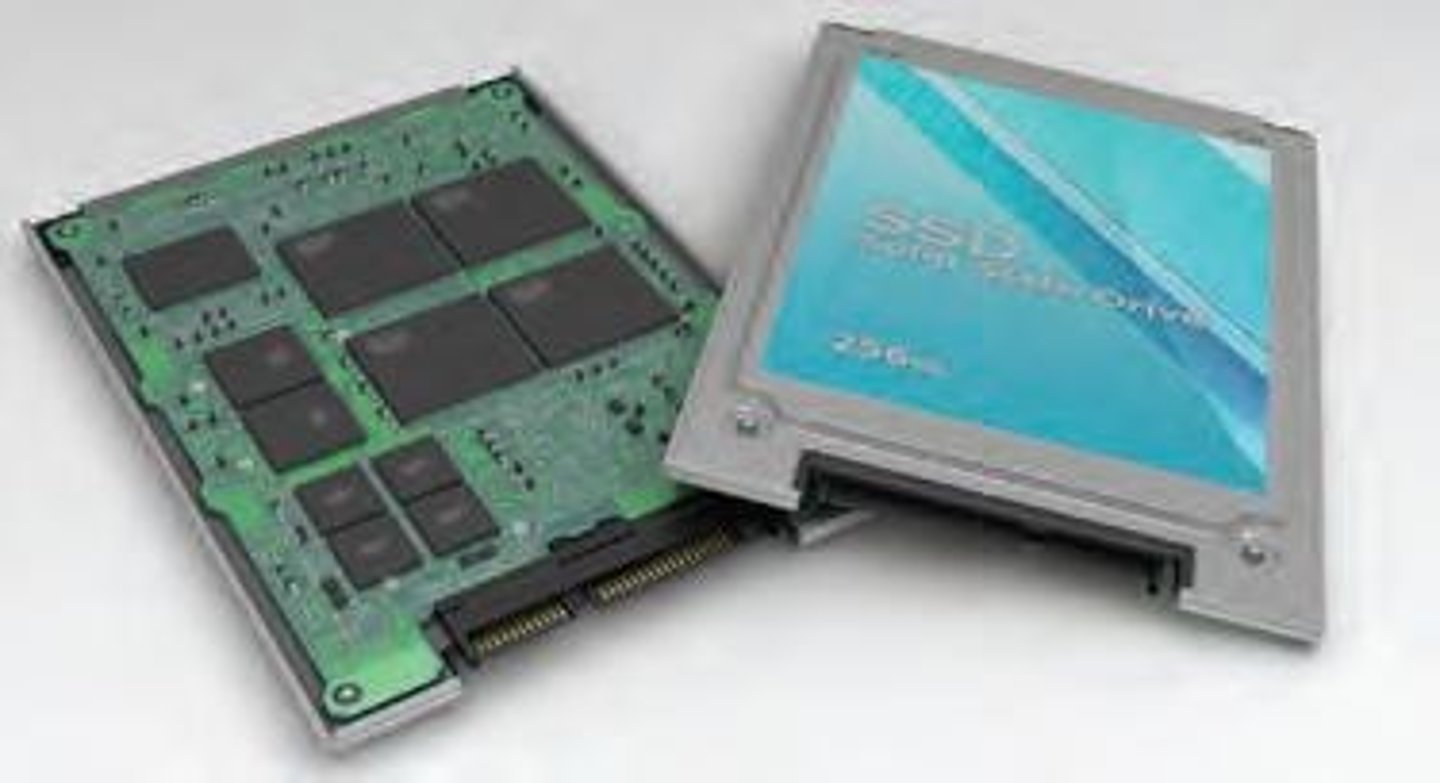
Solid state drives (SSDs)
A type of storage device that uses flash memory.

Open-source software
Source code is available at no cost to developers and users.
Operating system (OS)
Supervises the overall operation of the computer including monitoring the computer's status and managing the input and output processes.
Graphical user interface (GUI)
Replaces complex commands with visible objects (e.g., icons).
Natural user interfaces (NUIs)
Allows interaction through natural human behaviors.
-Haptic interfaces: allows the user to feel a sense of touch by applyingforces, vibrations, and/or motions to the user
-Social interfaces: guides the user through computer applications by using cartoonlike characters, graphics, animation, and voice commands
- Touch-enabled gesture-control interfaces
• Motion control gaming consoles (i.e., Wii, Kinect, Move)
• Microsoft Surface and the Apple iPhone
Software package
A computer program (or group of programs) that has been developed by a vendor and is available for purchase in a prepackaged form.
Human data-entry devices
keyboard, mouse, pointing stick, trackball, joystick, touchscreen, stylus, voice recognition
Source-data automation
-Bar code readers
CPU Works
1.Fetch
2. Decode
3.Execute
4. Store
primary storage (main memory) briefly stores 3 types of information
-Data to be processed by the CPU
-Instructions for the CPU as to how to process the data
-Operating system programs for managing computer's operations
semiconductor (primary storage)
register
cache
RAM
ROM
Secondary Storage Devices
-Magnetic Disks
-Optical
-Magnetic tape
characteristic of secondary storage
Non-volatile - Keeps data when the computer is shut down• Takes more time to retrieve data from it than from RAM
• Cheaper than primary storage• Utilize a variety of media/technology• Magnetic disks (or hard drives or fixed disk drives )
• Solid state drives (SSDs)
• Optical storage devices (CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray discs)
• Flash memory devices (memory cards, thumb drive, memory stick, jump drive, or flash drive)
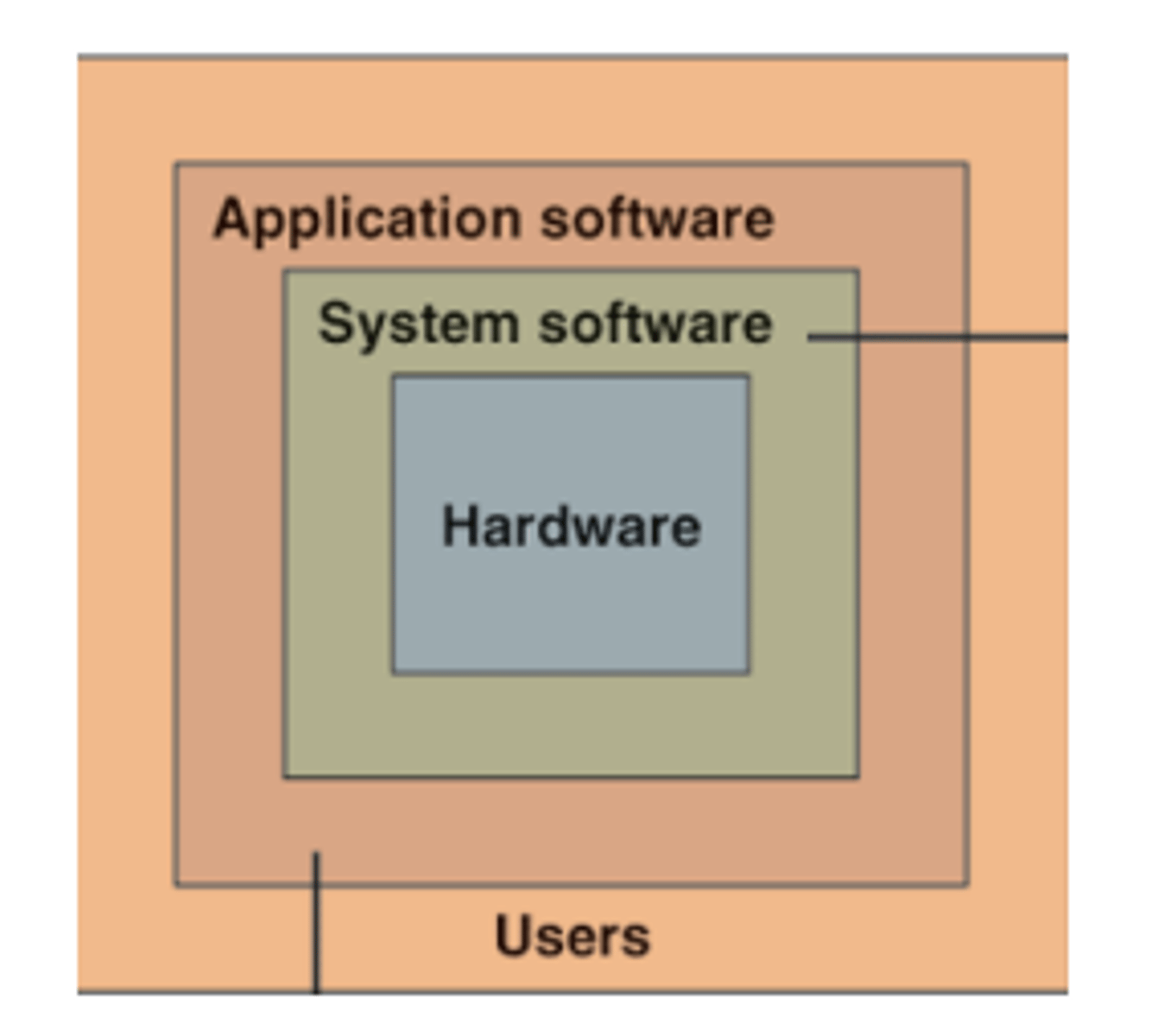
Two major types of software
• Systems software
-Intermediary between computer hardware and application programs
• Application software
-Provide more specific functionality to a use
Software defects (bugs)
•Good software should be usable, reliable, defect free, cost effective, and maintainable
• Professional programmers make between 100 and 150errors in every 1,000 lines of code
Licensing
Making copies of software without the manufacturer's explicit permission is illegal.
Open systems
A model of computing products that work together
software
A program or instructions that give directions to the computer.