Social Determinants of Health Community Module 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What are the six social determinants of health?
economic stability
neighborhood & built environment
access to and quality of education
access to and quality of food
social and community context
access to and quality of healthcare
what do social determinants of health contribute to?
SDOH contribute to health inequities and disparities.
What is a major factor linked to disparities?
socioeconomic status is a major factor linked to disparities
What experiences influence school readiness?
Early childhood experiences influence school readiness
Children with what type of income may lack skills for success?
low income children may lack skills for success
what does poor education look like in a clinical setting?
poor health literacy
mismanagement of chronic conditions
How poverty affect health?
Poorer people have poorer health outcomes.
Where does being poor force a person to live?
poor people tend to live in hazardous living environments
what type of jobs do poor people work? do these jobs usually give them paid leave for illness?
Poor people work high-risk jobs. These jobs do not give paid leave for illness, so poor people usually work while they are sick.
Do poor people have better or worse healthcare access?
Poor people have a lack of healthcare access.
What are poor people exposed to because they live in cheaper housing?
Poor people are exposed to elements in their own home, like lead.
Do poor people usually drink from a contaminated water supply?
Yes, poor people usually drink from a contaminated water supply.
Are the homes of poor people cramped or open?
The homes of poor people are cramped, and there is a risk for overcrowding.
What type of stress do poor people experience?
Poor people experience long-term stress.
Are poor people homeless?
Yes, poor people are sometimes homeless.
What do less favored races experience in a clinical setting?
Black and brown people are more likely to be ill and die.
What two terms are used to describe inaccessibility to food?
Food desserts
food insecurity
What about someone’s insurance could make them have less access to quality healthcare?
Someone could have less access to quality healthcare if they are uninsured or underinsured, or if they live an area with less healthcare providers and facilities.
What two types of factors does vulnerability result from?
Individual and social factors result in vulnerability.
What are two individual factors that could make a person vulnerable?
age, preexisting illness
what are three social factors that could make a person vulnerable?
education, employment, housing
what does vulnerability increase the likelihood of?
more vulnerable people are more likely to develop health problems
what are more vulnerable people at a greater risk of?
more vulnerable people are at a greater risk of health disparities
what is the most common illness present in prisons?
incarcerated people are more likely to experience mental health disorders in prison
what are three risk factors that impact the health of incarcerated people?
violence
crowded living conditions
limited treatment options
what is the nurses responsibility when caring for incarcerated folk
the nurse must maintain professionalism and care without unconscious bias
what are the homeless at higher risk of (5)?
HIV
alcohol drug use
mental illness
tuberculosis
chronic illness
what is the nurse’s role when caring for the homeless? (what is the nurse’s three step plan)
outreach
advocacy
care coordination
what are three common mental disorders common in veterans?
depression, PTSD, anxiety
what are three things that a veteran is at increased risk for?
substance abuse
physical diseases (amputation)
somatic complaints (chronic pain)
what organization helps veterans gain healthcare access?
veterans affairs
what are two common mental disorders amongst LGBTQIA+ populations?
depression
anxiety
what are three things LGBTQIA+ folk are at risk for?
substance abuse
STIs
suicide
what do nurses need to do when treating LGBTQIA+ patients? (4-step process)
awareness
sensitivity
knowledge
skills
who does adolescent pregnancy pose health risks to?
adolescent pregnancy poses risks to the mother and baby
why does adolescent pregnancy pose health risks to the mom and baby? (4)
lack of prenatal care is common
high blood pressure
premature-birth
low-birth-weight infants
where do adolescently pregnant mothers end up/ who are adolescently pregnant mothers?
mothers in foster system are common teen pregnancies
what three options should nurses discuss with adolescent pregnancies?
termination, adoption, parenthood
do rural populations usually have poor perception of health/functional status?
yes, people from rural populations typically have a poor perception of health/functional status
what type (high/low) of incidence of chronic illness do people living in a rural area experience?
rural people experience high incidence of chronic illness
are people in rural areas more or less likely to seek care?
people in rural areas are less likely to seek health care
what is a good option for rural populations who want to seek healthcare?
telehealth
what can nurses do to improve healthcare in rural areas?
advocate
are migrant populations typically poor?
yes, migrant populations are typically poor
what do migrant populations have limited access to?
migrant populations have limited access to healthcare
what working conditions do migrant populations typically endure?
hazardous working conditions are endured by migrant populations
are there a lot of or less regulations when working with migrant populations?
there is a lack of regulations for migrant populations
what should be the nurse’s focus when treating migrant populations, why?
infection prevention, because migrants typically live in crowded spaces
what do pediatric patients do to fulfill basic needs?
pediatric patients depend on others to fulfill their needs
what three environments affect a pediatric patient?
family (parents, caregivers, siblings)
social environment
physical environment
what circumstances affect a pediatric patient?
economic circumstances and access to healthcare
what is the most important relationship for pediatric development?
caregiver relationship is the most important relationship for pediatric patients’ development
what beliefs play a role in pediatric development and health care? (3)
cultural, ethnic, and religious beliefs
what is important to watch out for in the home of a pediatric patient?
stress level
what are adverse childhood events (ACEs). give six examples of ACE
ACEs are events occurring in childhood that cause physical or emotional trauma
abuse
neglect
household challenges
exposure to substance abuse
watching intimate partner violence
death of a caregiver
what are ACEs linked to?
ACEs are linked to toxic stress
what do ACEs alter? what does this result it
ACEs alter brain development, which leads to issues with decision making, forming relationships, and chronic illness
how could a caregiver put a child at risk for ACEs? (5)
caregivers who:
were abused as children
have less than a high school education
have no reliable support system
lack financial resources
are sole caregivers for the family
what are a nurses roles within vulnerable groups? (3)
patient advocacy
equal treatment despite social factors
culturally sensitive care
address social determinants of health
list 8 vulnerable populations
incarcerated
homelessness
veterans
lgbtqia+
adolescent pregnancy
rural population
migrant population
pediatric patient
define health disparities
differences in medical conditions or health outcomes in a specific population
which groups do health disparities happen most often with?
marginalized groups are most likely to experience health disparities
what are health disparities rooted in?
systemic racism
what directly influences health disparities?
social determinants of health
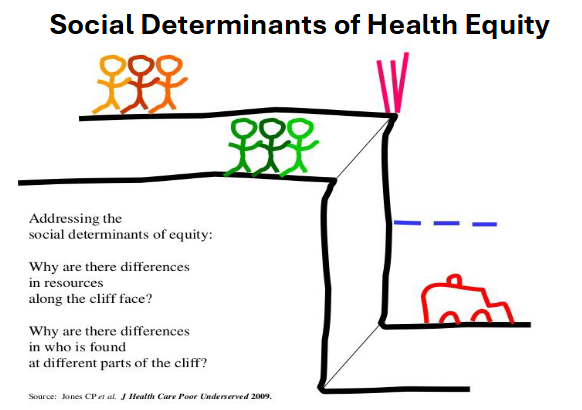
draw out the cliff analogy
what type of nursing workforce is needed to address health disparities? why?
a diverse nursing workforce can address health disparities, because cultural similarities between nurses and clients improves outcomes
what should nurses develop to prevent health disparities?
nurses should develop cultural competency
what is implicit bias? is it good or bad? how long does it take to develop? what does it drive? what are common examples?
unconscious assumptions we hold
can be good or bad
developed over a lifetime
drive our actions towards other people
often about race, gender, age, sexual orientation, and religion
what are nurses for individuals in the healthcare system?
nurses are usually the point of entry for patients into the healthcare system
what does not addressing implicit bias lead to?
implicit bias leads to health disparities
what should a nurse do to stop implicit bias?
self reflection
list 8 ways to counteract stereotypes
stereotype replacement
counter stereotypic imaging
perspective taking
inter group contact
doubt objectivity
increase motivations to be fair
thinking slow (engaging in mindful, deliberate processing)
count patterns and decisions or behavior and disparate outcomes that may be linked to bias
what is provision 9 in the ANA code of ethics?
provision 9 in the ANA code of ethics is the social justic statement
nurses should:
address the history of racism in nursing
take accountability for ongoing harm
identify specific, measurable plans for creating more inclusive, diverse, and equitable professional organizations that meet the needs of all people
condemn all forms of oppression
demonstrate intentional efforts to reflect and act upon social justice issues
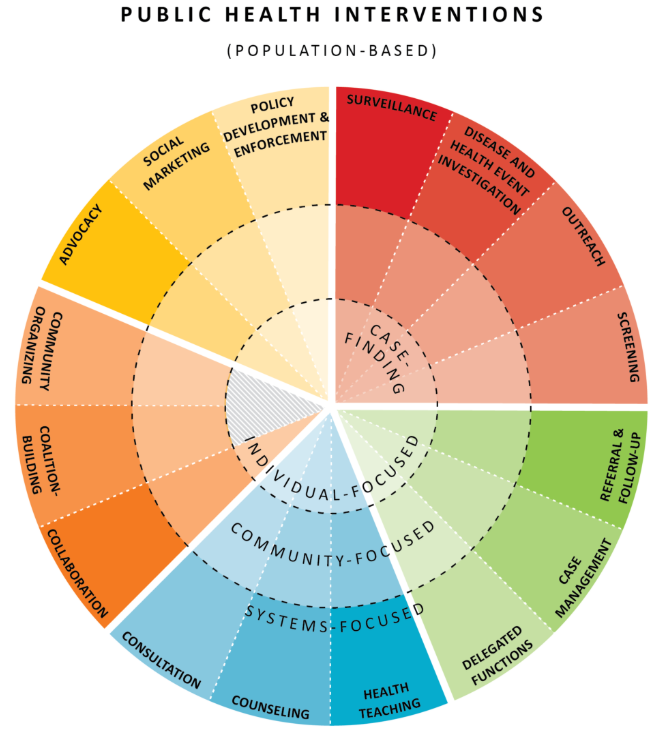
minnesota public health wheel: use it to identify 3 public health nursing interventions for each of the following vulnerable populations: veterans, LGBTQIA, adolescent pregnancy, migrant populations, rural populations, pediatric populations