NET 126 CISCO QUIZ 2025SP.NET.126.0001 CCNA: Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Which two statements are correct with respect to SVI inter-VLAN routing? (Choose two.)
There is no need for a connection to a router.
Switching packets is faster with SVI.
SVIs can be bundled into EtherChannels.
SVIs eliminate the need for a default gateway in the hosts.
Virtual interfaces support subinterfaces.
Switching packets is faster with SVI.
There is no need for a connection to a router.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator wants to configure Switch1 to allow SSH connections and prohibit Telnet connections. How should the network administrator change the displayed configuration to satisfy the requirement?
Use SSH version 1.
Reconfigure the RSA key.
Configure SSH on a different line.
Modify the transport input command.
Modify the transport input command.
Which solution would help a college alleviate network congestion due to collisions?
a firewall that connects to two Internet providers
a high port density switch
a router with two Ethernet ports
a router with three Ethernet ports
a high port density switch
Switches provide microsegmentation so that one device does not compete for the same Ethernet network bandwidth with another network device, thus practically eliminating collisions. A high port density switch provides very fast connectivity for many devices.
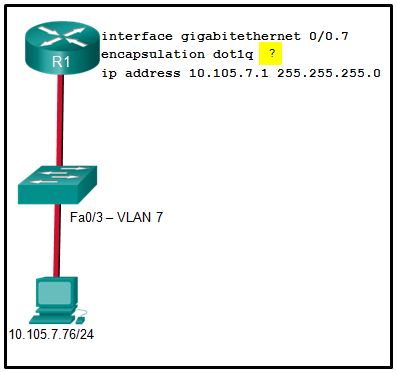
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring inter-VLAN routing on a network. For now, only one VLAN is being used, but more will be added soon. What is the missing parameter that is shown as the highlighted question mark in the graphic?
It identifies the subinterface.
It identifies the VLAN number.
It identifies the native VLAN number.
It identifies the type of encapsulation that is used.
It identifies the number of hosts that are allowed on the interface.
It identifies the VLAN number.
The completed command would be encapsulation dot1q 7. The encapsulation dot1q part of the command enables trunking and identifies the type of trunking to use. The 7 identifies the VLAN number.
A network administrator issues the show vlan brief command while troubleshooting a user support ticket. What output will be displayed?
the VLAN assignment and membership for device MAC addresses
the VLAN assignment and membership for all switch ports
the VLAN assignment and trunking encapsulation
the VLAN assignment and native VLAN
the VLAN assignment and membership for all switch ports
Which type of VLAN is used to designate which traffic is untagged when crossing a trunk port?
native
management
data
default
native
What is a characteristic of an IPv4 loopback interface on a Cisco IOS router?
It is a logical interface internal to the router.
It is assigned to a physical port and can be connected to other devices.
Only one loopback interface can be enabled on a router.
The no shutdown command is required to place this interface in an up state.
It is a logical interface internal to the router.
Which command is used to set the BOOT environment variable that defines where to find the IOS image file on a switch?
config-register
boot system
boot loader
confreg
boot system
The boot system command is used to set the BOOT environment variable. The config-register and confreg commands are used to set the configuration register. The boot loader command supports commands to format the flash file system, reinstall the operating system software, and recover from a lost or forgotten password.
If one end of an Ethernet connection is configured for full duplex and the other end of the connection is configured for half duplex, where would late collisions be observed?
on both ends of the connection
on the full-duplex end of the connection
only on serial interfaces
on the half-duplex end of the connection
on the half-duplex end of the connection
Full-duplex communications do not produce collisions. However, collisions often occur in half-duplex operations. When a connection has two different duplex configurations, the half-duplex end will experience late collisions. Collisions are found on Ethernet networks. Serial interfaces use technologies other than Ethernet.
Refer to the exhibit. A switch receives a Layer 2 frame that contains a source MAC address of 000b.a023.c501 and a destination MAC address of 0050.0fae.75aa. Place the switch steps in the order they occur.
switch adds frame
switch forwards frame to all ports bc destination is unknown
switch adds frame
switch forwards frame to all ports bc destination is unknown
Which switching method ensures that the incoming frame is error-free before forwarding?
cut-through
FCS
fragment free
store-and-forward
store-and-forward
Two methods used by switches to transmit frames are store-and-forward and cut-through switching. The store-and-forward method performs error checking on the frame using the frame check sequence (FCS) value before sending the frame. In contrast, cut-through switching sends the frame as soon as the destination MAC address part of the header has been read and processed.
What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
source MAC address and incoming port number
destination MAC address and incoming port number
source IP address and incoming port number
destination IP address and incoming port number
source MAC address and incoming port number
A switch “learns” or builds the MAC address table based on the source MAC address as a frame comes into the switch. A switch forwards the frame onward based on the destination MAC address.
How do switch buffers affect network performance?
They provide error checking on the data received.
They store frames received, thus preventing premature frame discarding when network congestion occurs.
They provide extra memory for a particular port if autonegotiation of speed or duplex fails.
They hold data temporarily when a collision occurs until normal data transmission resumes.
They store frames received, thus preventing premature frame discarding when network congestion occurs.
Switches have large frame buffers that allow data waiting to be transmitted to be stored so the data will not be dropped. This feature is beneficial especially if the incoming traffic is from a faster port than the egress port used for transmitting.
Which statement is correct about Ethernet switch frame forwarding decisions?
Frame forwarding decisions are based on MAC address and port mappings in the CAM table.
Cut-through frame forwarding ensures that invalid frames are always dropped.
Only frames with a broadcast destination address are forwarded out all active switch ports.
Unicast frames are always forwarded regardless of the destination MAC address.
Frame forwarding decisions are based on MAC address and port mappings in the CAM table.
Cut-through frame forwarding reads up to only the first 22 bytes of a frame, which excludes the frame check sequence and thus invalid frames may be forwarded. In addition to broadcast frames, frames with a destination MAC address that is not in the CAM are also flooded out all active ports. Unicast frames are not always forwarded. Received frames with a destination MAC address that is associated with the switch port on which it is received are not forwarded because the destination exists on the network segment connected to that port.
Which switch component reduces the amount of packet handling time inside the switch?
ASIC
dual processors
large buffer size
store-and-forward RAM
ASIC
Application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are used in Cisco switches to speed up switch operations so that the switch can have an increased number of ports without degrading switch performance.
Which characteristic describes cut-through switching?
Error-free fragments are forwarded, so switching occurs with lower latency.
Frames are forwarded without any error checking.
Only outgoing frames are checked for errors.
Buffering is used to support different Ethernet speeds.
Frames are forwarded without any error checking.
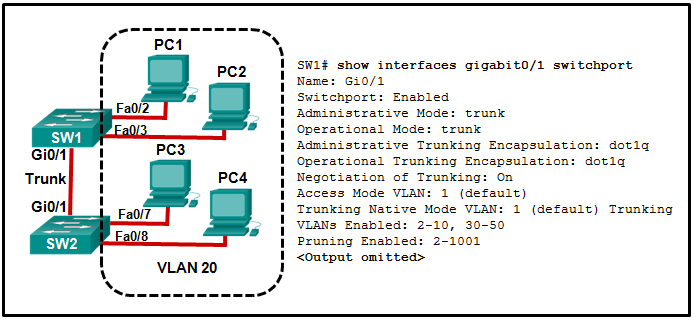
Refer to the exhibit. All workstations are configured correctly in VLAN 20. Workstations that are connected to switch SW1 are not able to send traffic to workstations on SW2. What could be done to remedy the problem?
Allow VLAN 20 on the trunk link.
Enable DTP on both ends of the trunk.
Configure all workstations on SW1 to be part of the default VLAN.
Configure all workstations on SW2 to be part of the native VLAN.
Allow VLAN 20 on the trunk link.
Enabling DTP on both switches simply allows negotiation of trunking. The “Negotiation of Trunking” line in the graphic shows that DTP is already enabled. The graphic also shows how the native VLAN is 1, and the default VLAN for any Cisco switch is 1. The graphic shows the PCs are to be in VLAN 20.
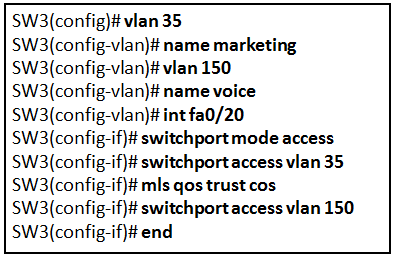
Refer to the exhibit. A technician is programming switch SW3 to manage voice and data traffic through port Fa0/20. What, if anything, is wrong with the configuration?
There is nothing wrong with the configuration.
Interface Fa0/20 can only have one VLAN assigned.
The mls qos trust cos command should reference VLAN 35.
The command used to assign the voice VLAN to the switch port is incorrect.
The command used to assign the voice VLAN to the switch port is incorrect.
The voice VLAN should be configured with the switchport voice vlan 150 command. A switch interface can be configured to support one data VLAN and one voice VLAN. The mls qos trust cos associates with the interface. Voice traffic must be trusted so that fields within the voice packet can be used to classify it for QoS.
Which two characteristics describe the native VLAN? (Choose two.)
Designed to carry traffic that is generated by users, this type of VLAN is also known as the default VLAN.
The native VLAN traffic will be untagged across the trunk link.
This VLAN is necessary for remote management of a switch.
High priority traffic, such as voice traffic, uses the native VLAN.
The native VLAN provides a common identifier to both ends of a trunk
The native VLAN traffic will be untagged across the trunk link.
The native VLAN provides a common identifier to both ends of a trunk
The native VLAN is assigned to 802.1Q trunks to provide a common identifier to both ends of the trunk link. Whatever VLAN native number is assigned to a port, or if the port is the default VLAN of 1, the port does not tag any frame in that VLAN as the traffic travels across the trunk. At the other end of the link, the receiving device that sees no tag knows the specific VLAN number because the receiving device must have the exact native VLAN number. The native VLAN should be an unused VLAN that is distinct from VLAN1, the default VLAN, as well as other VLANs. Data VLANs, also known as user VLANs, are configured to carry user-generated traffic, with the exception of high priority traffic, such as VoIP. Voice VLANs are configured for VoIP traffic. The management VLAN is configured to provide access to the management capabilities of a switch.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is reviewing port and VLAN assignments on switch S2 and notices that interfaces Gi0/1 and Gi0/2 are not included in the output. Why would the interfaces be missing from the output?
There is a native VLAN mismatch between the switches.
There is no media connected to the interfaces.
They are administratively shut down.
They are configured as trunk interfaces.
They are configured as trunk interfaces.
Interfaces that are configured as trunks do not belong to a VLAN and therefore will not show in the output of the show vlan brief commands.
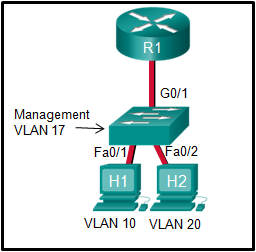
Refer to the exhibit. In what switch mode should port G0/1 be assigned if Cisco best practices are being used?
access
trunk
native
auto
trunk
The router is used to route between the two VLANs, thus switch port G0/1 needs to be configured in trunk mode.
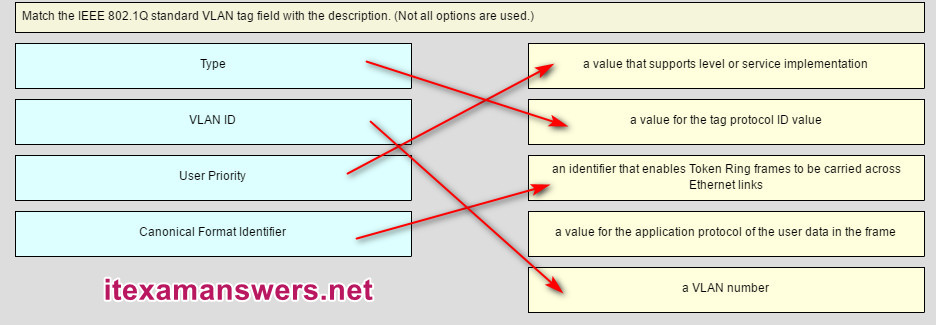
formatMatch the IEEE 802.1Q standard VLAN tag field with the description.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is verifying the configuration of inter-VLAN routing. Users complain that PCs on different VLANs cannot communicate. Based on the output, what are two configuration errors on switch interface Gi1/1? (Choose two.)
Gi1/1 is in the default VLAN.
Voice VLAN is not assigned to Gi1/1.
Gi1/1 is configured as trunk mode.
Negotiation of trunking is turned on on Gi1/1.
The trunking encapsulation protocol is configured wrong.
Gi1/1 is in the default VLAN.
Gi1/1 is configured as trunk mode.
With legacy inter-VLAN routing methods, the switch ports that connect to the router should be configured as access mode and be assigned appropriate VLANs. In this scenario, the Gi1/1 interface should be in access mode with VLAN 10 assigned. The other options are default settings on the switch and have no effect on legacy inter-VLAN routing.
A high school uses VLAN15 for the laboratory network and VLAN30 for the faculty network. What is required to enable communication between these two VLANs while using the router-on-a-stick approach?
A multilayer switch is needed.
A router with at least two LAN interfaces is needed.
Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
A switch with a port that is configured as a trunk is needed when connecting to the router.
A switch with a port that is configured as a trunk is needed when connecting to the router.
With router-on-a-stick, inter-VLAN routing is performed by a router with a single router interface that is connected to a switch port configured with trunk mode. Multiple subinterfaces, each configured for a VLAN, can be configured under the single physical router interface. Switches can have ports that are assigned to different VLANs, but communication between those VLANs requires routing function from the router. A multilayer switch is not used in a router-on-a-stick approach to inter-VLAN routing.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured router CiscoVille with the above commands to provide inter-VLAN routing. What type of port will be required on a switch that is connected to Gi0/0 on router CiscoVille to allow inter-VLAN routing?
routed port
access port
trunk port
SVI
trunk port
To allow a router-on-a-stick configuration to function, a switch must be connected to the router via a trunk port to carry the VLANs to be routed. An SVI would be used on a multilayer switch where the switch is performing inter-VLAN routing.
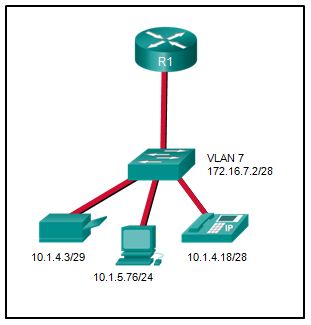
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure router-on-a-stick for the networks that are shown. How many subinterfaces will have to be created on the router if each VLAN that is shown is to be routed and each VLAN has its own subinterface?
1
2
3
4
5
4
Based on the IP addresses and masks given, the PC, printer, IP phone, and switch management VLAN are all on different VLANs. This situation will require four subinterfaces on the router.
A technician is configuring a new Cisco 2960 switch. What is the effect of issuing the BranchSw(config-if)# shutdown command?
It disables a virtual or physical switch interface.
It saves the running configuration to NVRAM.
It activates a virtual or physical switch interface.
It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
It saves the startup configuration to the running configuration.
It disables a virtual or physical switch interface.
What type of VLAN is initially the management VLAN?
default VLAN
native VLAN
data VLAN
management VLAN
default VLAN