fungi notes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
are fungi unicellular or multicellular?
unicellular. they are made of a collection of hyphae and can only be built one cell at a time
2
New cards
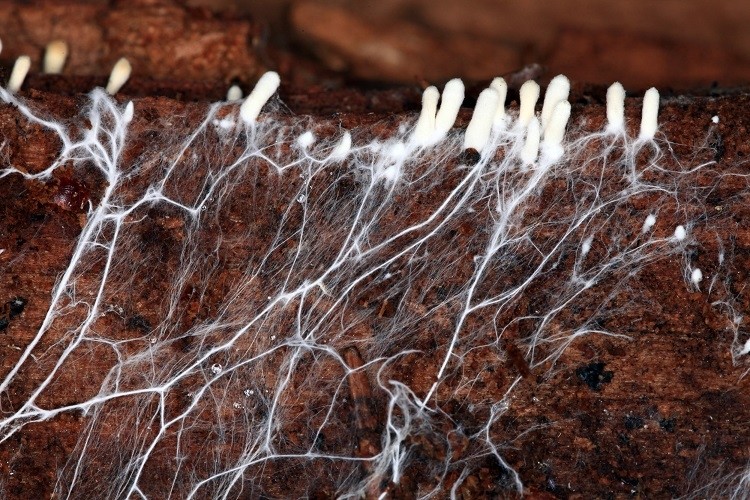
what is mycelium?
the collections of hyphae cells
3
New cards
sclerotium
hardened mass of mycelium that generally serves as an overwintering stage
4
New cards
both the ___ and ___ are made of hyphae
mushrooms and mycelium
5
New cards
how do fungi get their food?
they are heterotrophs, so they get their food by consuming other organisms
6
New cards
how do saprophytes/saraprobes get their food?
by decomposing and feeding on decaying organisms or organic material
7
New cards
how do symbiont fungi get their food?
through mutually beneficial relationships with other organisms
8
New cards
symbiont
an organism that lives in symbiosis with another
9
New cards
how do parasitic fungi get their food?
they feed on the living tissue of a host, which causes it harm
10
New cards
fungi are heterotrophic by…
…absorption
11
New cards
components of absorption
* carbon taking from organic material
* hyphal tip releases enzymes that break down the substrate
* the products diffuse back into the hyphae
* hyphal tip releases enzymes that break down the substrate
* the products diffuse back into the hyphae
12
New cards
components of hyphae
* tubular
* grows from the tip
* hard cell wall made of chitin
* cross walls may form compartments
* grows from the tip
* hard cell wall made of chitin
* cross walls may form compartments
13
New cards
what is mycorrhizae?
the fungal roots of a fungus organism that have a symbiotic relationship with plants
14
New cards
what do plants and fungi receive from their symbiotic relationship through mycorrhizae
* plants receive minerals, water, and carbohydrates from the fungi
* fungi receive up to 80% of their nutrients and carbohydrates from plants
* fungi receive up to 80% of their nutrients and carbohydrates from plants
15
New cards
types of mycorrhizae
Zygomycota, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota
16
New cards
Zygomycota…
…invade cell roots
17
New cards
Ascomycota & Basidiomycota are…
…hyphae that invade the root but don’t penetrate cells
18
New cards
lichen
the product of a mutualistic relationship between fungi and algae. they have fungus-like structures but the algae provided food for the organism
19
New cards
main three types of lichen
crustose, foliose, fruticose
20
New cards
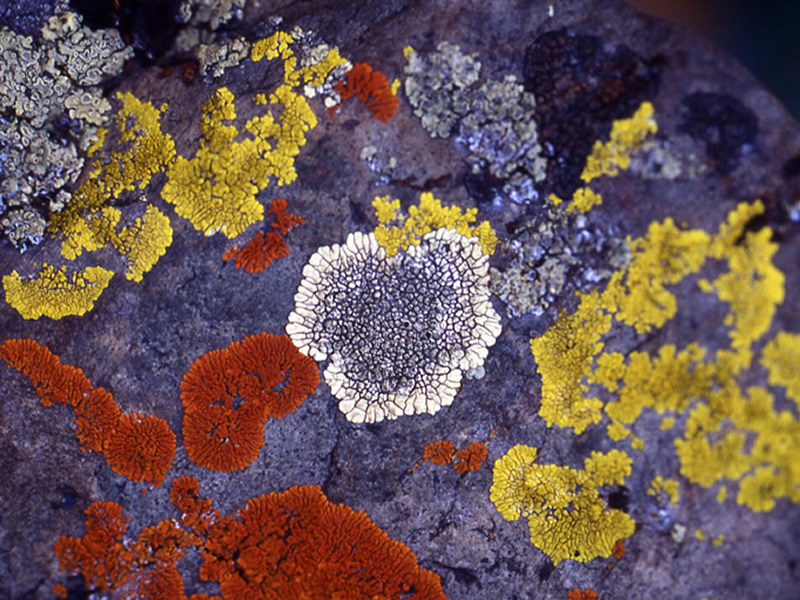
crustose lichen
lichen that forms flat crusty plates
21
New cards
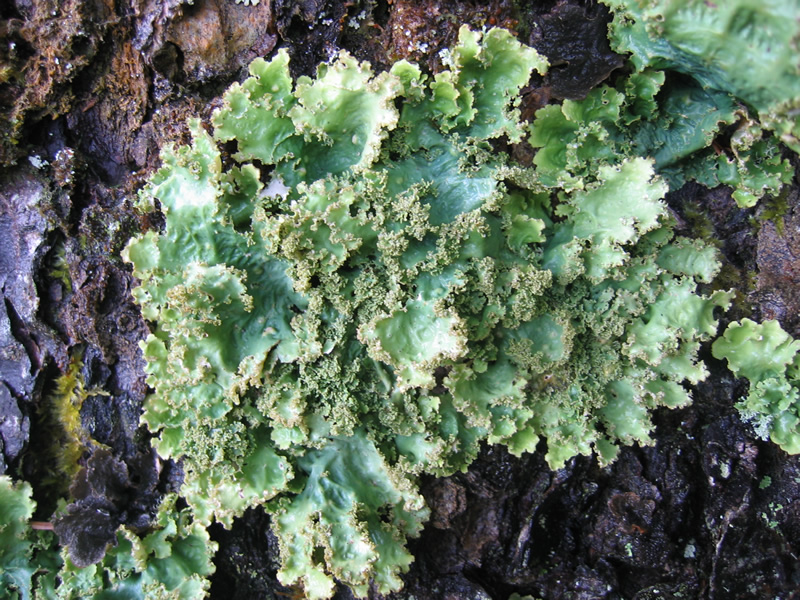

foliose lichens
leafy-like appearance with lobed or branched structures
22
New cards

fruticose lichen
very finely branched, they hang from trees like beards or grow in shrub-like formations
23
New cards
what are spores?
the asexual product of mitosis or the sexual product in origin
24
New cards
what is the purpose of spores?
* allows the fungus to move to a new food source
* spores are extremely resistant to environmental factors and allow the organism to survive for long periods of time
* allows for the introduction of new genetic information
* spores are extremely resistant to environmental factors and allow the organism to survive for long periods of time
* allows for the introduction of new genetic information
25
New cards
how do fungus reproduce?
by producing and spreading spores
26
New cards
where are spores formed?
directly on hyphae, inside of sporangia, and inside fruiting bodies(mushrooms)
27
New cards
where do fungi grow from?
they grow from their food source and ex
28
New cards
what are fungi’s cell walls made of?
their cell is made of chitin and cellulose
29
New cards
what macromolecules do fungi store their food as?
glycogen(sugar) and lipids(fat)
30
New cards
are fungi eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
eukaryotes
31
New cards
Chytridiomycota or “chytrids”
* simple fungi
* produces motile spores or zoospores
* Mostly saprobes and
parasites in aquatic habitats
\
* produces motile spores or zoospores
* Mostly saprobes and
parasites in aquatic habitats
\
32
New cards
Zygomycota or “zygote fungi”
* reproduces asexually and sexually\\
* rapid growers
\
* rapid growers
\
33
New cards
Ascomycota or “sac fungi”
* reproduces sexually and asexually
34
New cards
Basidiomycota or “club fungi”
* reproduces mainly through asexual reproduction
35
New cards
beneficial effects of fungi
* decomposition
* used in biosynthetic factories to make alcohol, drugs, and acids
\
* used in biosynthetic factories to make alcohol, drugs, and acids
\
36
New cards
harmful effects of fungi
* animal, plant, and human diseases, including allergies
* toxins produced
* toxins produced