Integumentary System
1/62
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What does the integumentary system consist of?
skin
accessory structures
hair
sebaceous glands
sweat glands
ceruminous glands
mammary glands
nails
List the functions of the integumentary system (5)
protection
body temperature regulation
sensation
excretion
vitamin D production
Describe the function of the integumentary system: protection
protects against
ultraviolet light
bacterial invasion
dehydration
Describe the function of the integumentary system: body temperature regulation
regulates body temperature by way of blood flow and sweating
Describe the function of the integumentary system: sensation
nerve endings and receptors that detect
temperature
touch
pressure
pain
Describe the function of the integumentary system: excretion
removal of waste through secretion
Describe the function of the integumentary system: vitamin D production
produces vitamin D with the help of UV light
Describe the skin
protective barrier
7% of total body weight
divided into two regions
epidermis
dermis
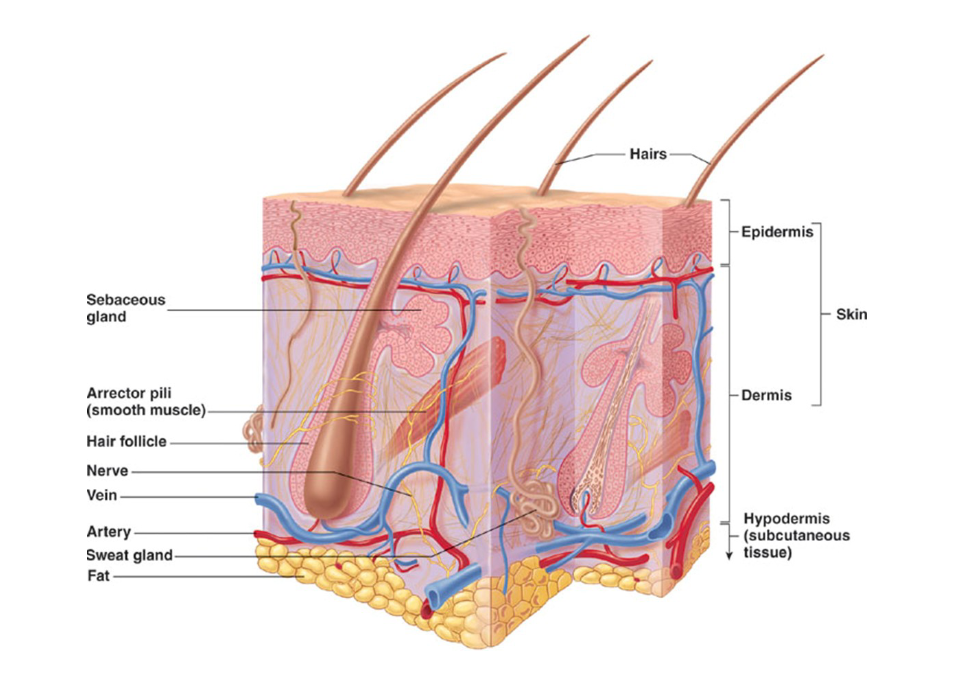
Describe the hypodermis
located just below the dermis
made up of subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia
Describe the epidermis
composed of stratified squamous keratinized epithelial tissue
avascular
contains cells
keratinocytes
melanocytes
4-5 layers (depends on type of skin)
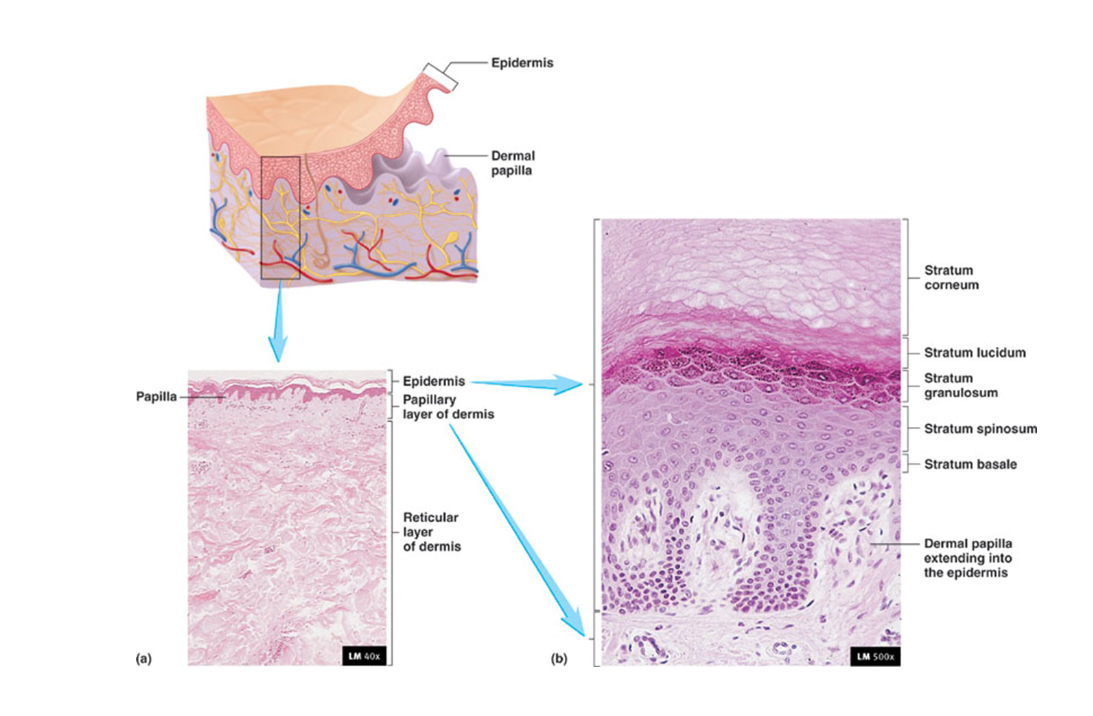
Describe keratinocytes
found in epidermis
majority of cells
epithelial cells that produce keratin
Describe melanocytes
found in stratum basale of epidermis
produce melanin
melanin sits on top of nuclei of cells and protects them from UV radiation
all races have the same number of melanocytes
Describe how we have different skin colors
all races have the same number of melanocytes
differences in skin color may be due to difference in melanocyte activity or the speed of melanin breakdown in keratinocytes
darker skin may have more melanocyte activity
paler skin breaks down melanin faster in keratinocytes
What characteristics determine the type of skin?
number of layers in the epidermis
thickness of these layers
if hair is present
What are the two types of skin?
thick skin
thin skin
Describe thick skin
5 layers form the epidermis
DO NOT contain hair follicles or oil glands
found in
palms of hands
soles of feet
finger tips
Describe thin skin
4 layers form the epidermis
found everywhere thick skin isn’t
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis of thick skin?
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
stratum corneum
What are the 4 layers of the epidermis of thin skin?
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum corneum
Describe stratum basale
found in thick and thin skin
one layer thick
mitosis occurs here
newer cells at bottom
older cells at top
Describe stratum spinosum
found in thick and thin skin
several layers thick
lots of desmosomes present
Describe stratum granulosum
found in thick and thin skin
2-5 cell layers thick
contains granules for strength and waterproofing
keratohyalin granules give the epidermis its strength
lipid filled lamellated bodies give the epidermis is waterproof property
Describe stratum lucidum
found in thick skin only
“clear layer”
Describe stratum corneum
found in thick and thin skin
20-30 cells thick
provides protection from external environment
dead cells
thicker in thick skin
What gives the epidermis its strength?
keratohyalin granules
What gives the epidermis its waterproof property?
lipid filled lamellated bodies
Describe the dermis
deep to the epidermis
connective tissue of skin
thicker than epidermis
richly supplied with
nerves
blood vessels
lymphatics
oil & sweat glands
divided into two regions
papillary
reticular
Describe the papillary layer of the dermis
superficial layer of the dermis (on top)
composed of areolar connective tissue
has projections called dermal papillae
indent the dermis (makes it harder to separate the layers)
separation of the papillary layer of the dermis from the epidermis can result in a blister
Describe the reticular layer of the dermis
deep to the papillary layer (deepest layer of dermis)
composed of dense irregular connective tissue
Describe hair
found on all surfaces except
palms of hands
soles of feet
fingertips
lips
made up of the
hair follicle
root
shaft
Describe the hair follicle of hair
contains the matrix
germinal layer where hair growth is initiated
pushes other cells distally
cells keratinize as they move up
contains melanocytes
brown and black eumelanin (brown and black hair)
small amount of brown eumelanin (blonde hair)
pheomelanin (red hair)
Describe the root of hair
portion of hair within the hair follicle
Describe the shaft of hair
portion of hair that extends from the hair follicle
functions
protection
eyebrows prevent sweat from entering eyes
eyelashes prevent debris from entering eyes
nose and ear hair prevent debris from entering the body
sense orgain
Describe nails
protects ends of fingers and toes
fingernails grow at a rate of about 1-4 inches per year
grow twice as fast as toenails
made up of the
matrix
lunula
quick/nail bed
nail root
nail body / nail plate
hyponychium
Describe the matrix of the nail
germinal layer where nail growth is initiated
push other cells distally
cells keratinize as they move up
Describe the lunula of the nail
white, crescent-shaped, visible region of the nail matrix
white in color because it is thick and blood vessels do not show
Describe the quick / nail bed of the nail
layer of epithelial cells where the nail attaches to the fingers and toes
well vascularized
therefore, appears pink
adds to the growth of the nail
thickens the nail
Describe the nail root of the nail
area of the nail that is hidden by the eponychium / cuticle
cuticle fuses nail root to the skin and provides a waterproof barrier
Describe the nail body / nail plate
visible area of the nail
Describe the hyponychium of the nail
area of skin at the tip of the fingers
fuses nail plate to the skin
provides a waterproof barrier
Describe glands
sebaceous glands
eccrine / merocrine sweat gland
apocrine sweat gland
Describe sebaceous glands
generally attached to hair follicle by ducts
most numerous on face and scalp
secrete oily substance called sebum
sebaceous glands “appear” at puberty
due to an increase in hormones
Describe sebum
oils the hair and lubricates the skin
helps prevent water loss
inhibits growth of certain bacteria
Describe eccrine / merocrine sweat gland
contain a duct that extends through the epidermis to the skin surface
secrete sweat
everywhere on the body
excreted onto the skin via a duct
aids in regulating body temperature
excretes nitrogenous waste
Describe the apocrine sweat gland
contains a duct that extends into the hair follicle
secrete thick, sticky sweat into hair follicles
sweat makes its way onto the skin
decomposed by skin bacteria and becomes odorous
this scent is used as a form of communication in other animals
bacteria is killed by deodorants
antiperspirants inhibit sweat production
found in
armpits
around areola
anus
genitals
these glands “appear” at puberty
due to an increase in certain hormones
What are the three types of skin cancer?
basal cell carcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant melanoma
Describe basal cell carcinoma
least malignant and most common
cells of the stratum basale proliferate and invade the dermis and hypodermis
appears as shiny dome shaped nodules
can be surgically removed
99% cure
Describe squamous cell carcinoma
arises in keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum
appears as small, scaly, red elevation
metastasizes (spreads to other sites in the body)
Describe malignant melanoma
cancer of the melanocytes
VERY dangerous, spreads faster
rarer of the skin cancers, but it is on the rise
survival rate depends on how early you catch it and metastasis
What is the function of the Meissner’s corpuscle?
detects light/soft touch
What type of cell junction can you find in the stratum spinosum?
desmosomes
cell to cell attachment
What is the function of the Pacinian corpuscle
detects deep touch
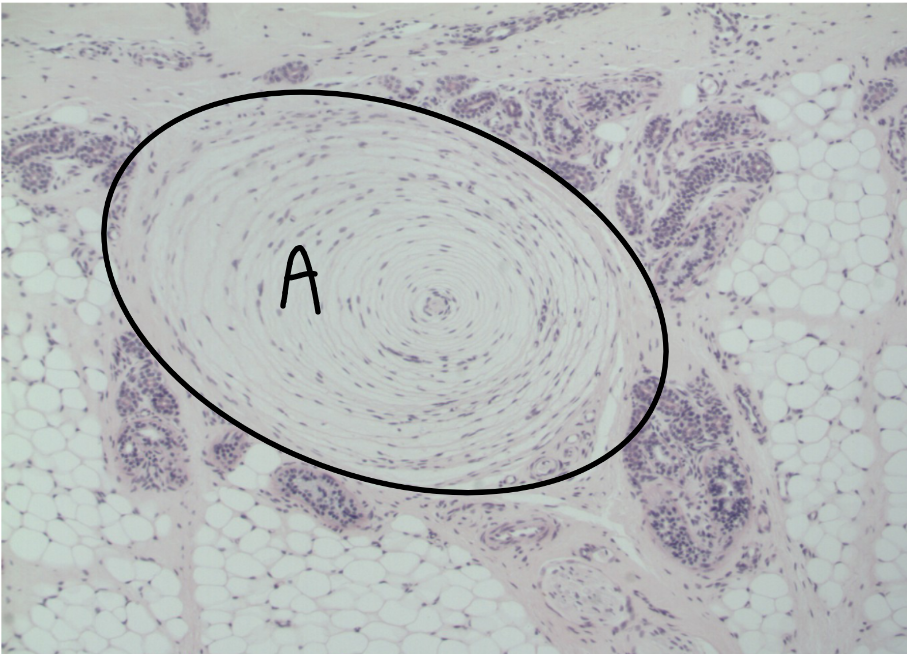
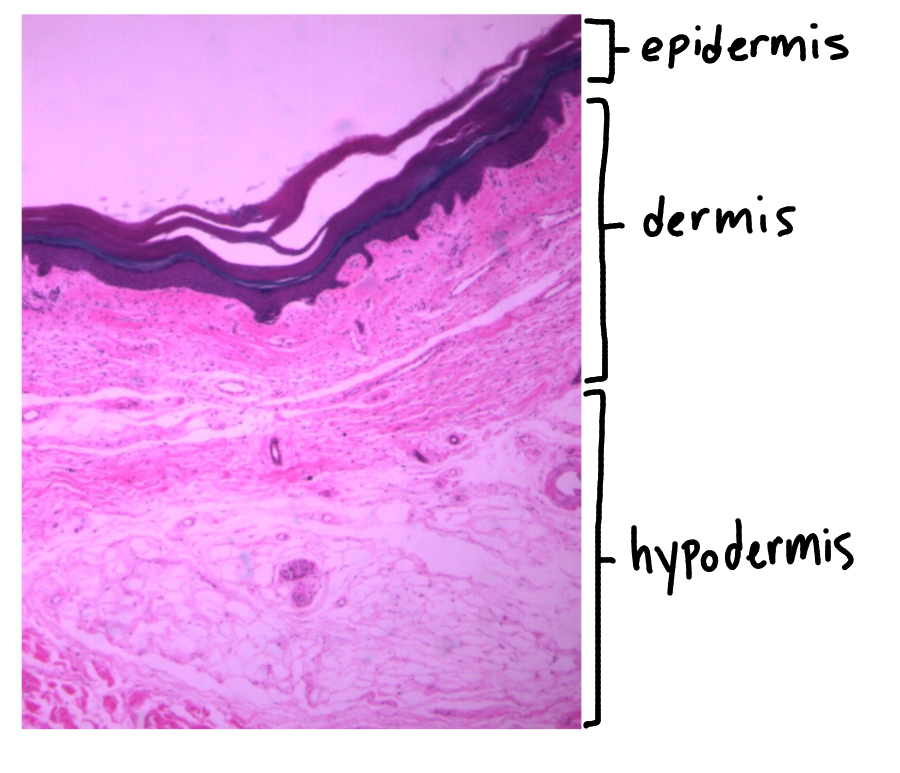
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Thick skin
from palm
A: Epidermis
composed of stratified squamous keratinized epithelial tissue
B: Dermis
composed of areolar connective tissue (papillary layer) and dense irregular connective tissue (reticular layer)
C: Hypodermis
composed (mainly) of adipose tissue
NOT PART OF SKIN
What is the difference between thick and thin skin?
thick skin has 5 layers, thin skin has 4 layers
thick skin does not contain hair follicles or oil glands, thin skin does
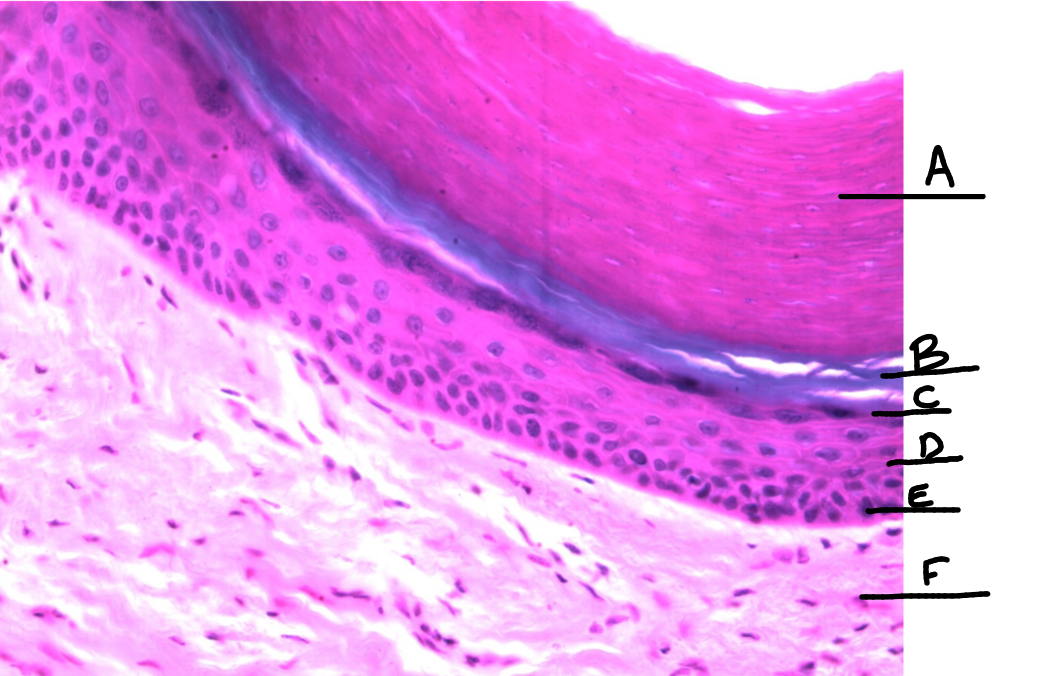
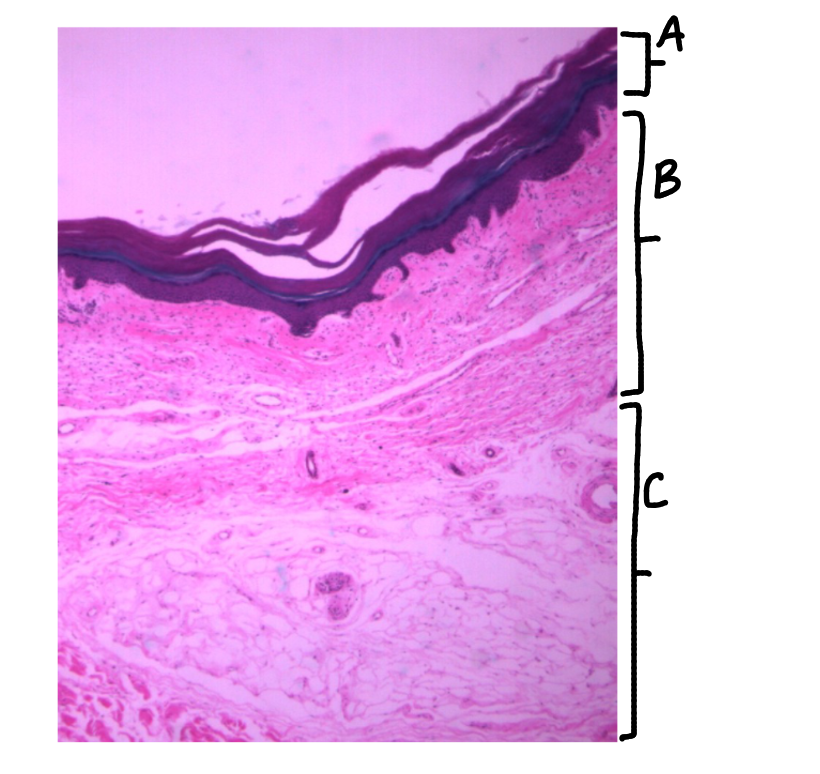
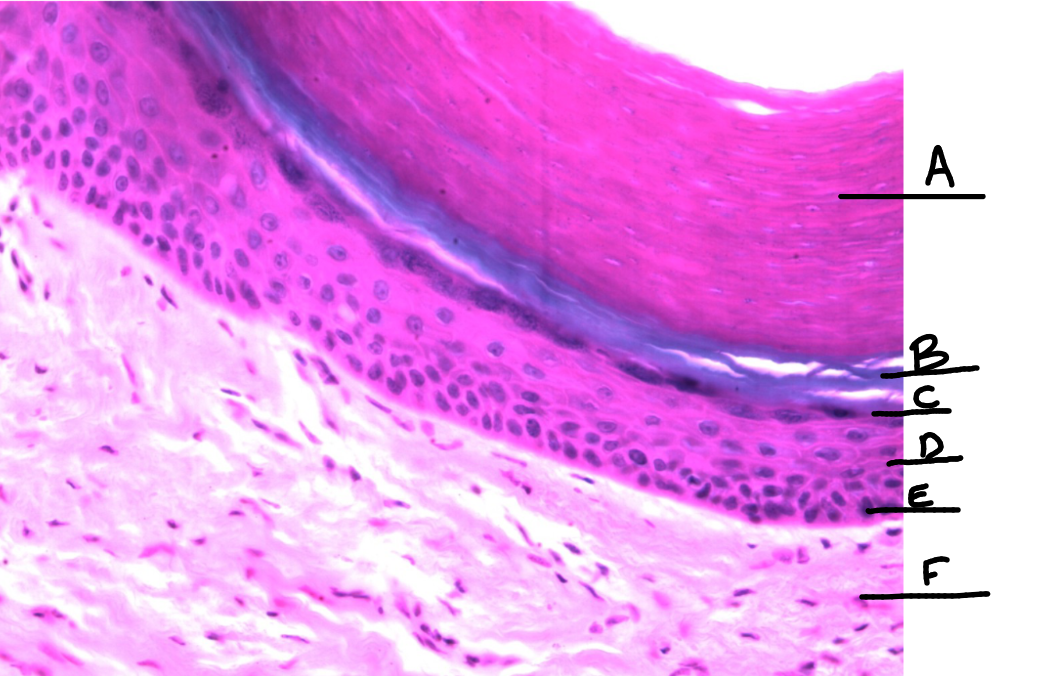
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Thick skin
A: Stratum Corneum
top layer of epidermis
B: Stratum Lucidum
2nd layer of epidermis
only in thick skin
C: Stratum Granulosum
3rd layer of epidermis
D: Stratum Spinosum
4th layer of epidermis
E: Stratum Basale
bottom layer of epidermis
F: Dermis
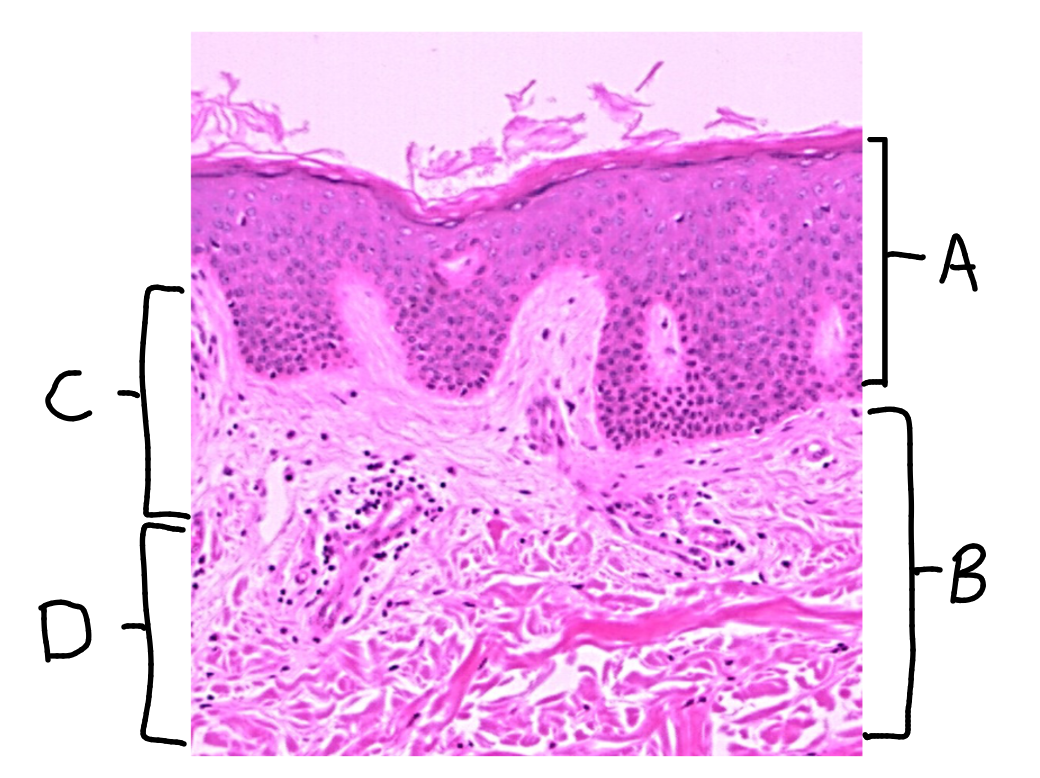
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Think Skin
A: Epidermis
composed of stratified squamous keratinized epithelial tissue
B: Dermis
composed of two layers
C: Papillary layer
top layer of the dermis
composed of areolar tissue
D: Reticular layer
bottom layer of the dermis
composed of dense irregular connective tissue
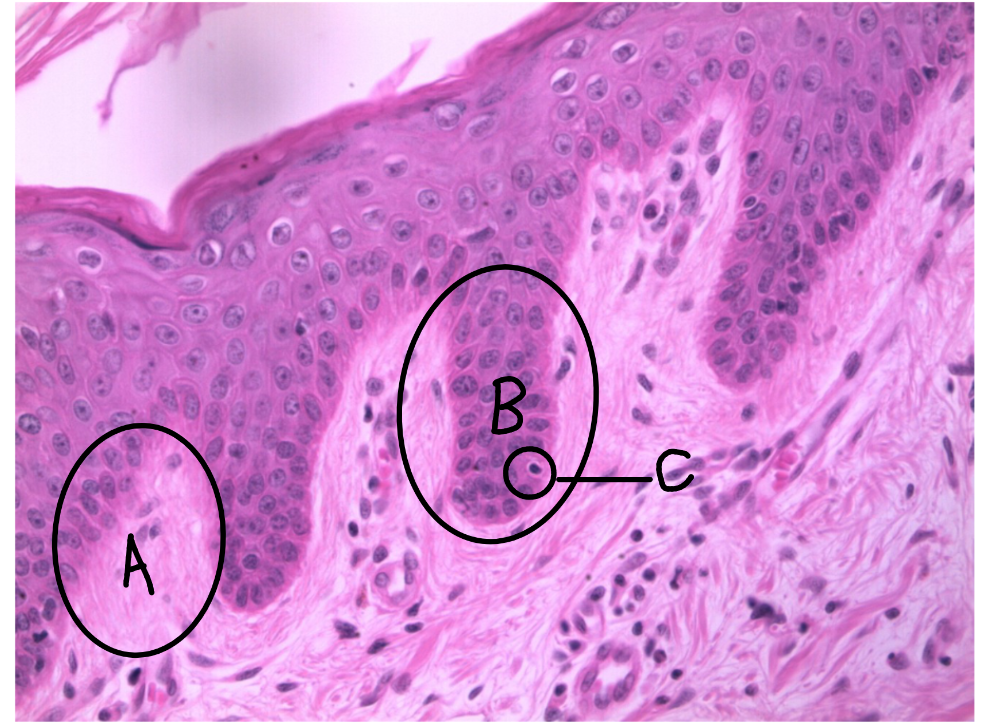
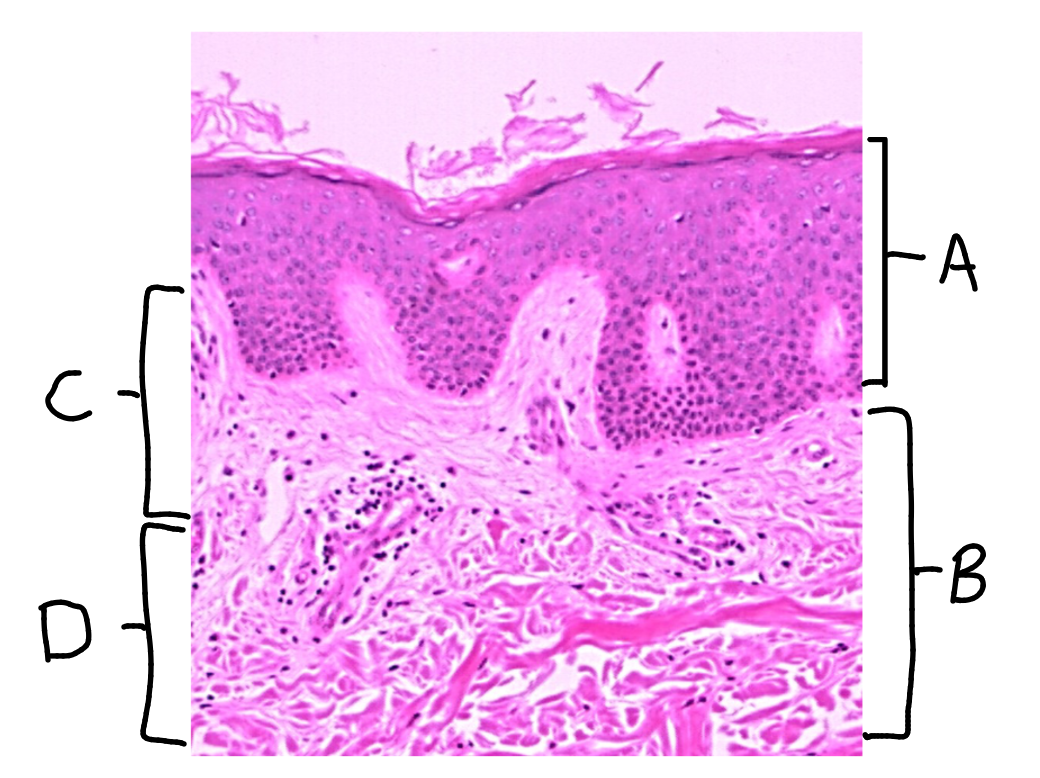
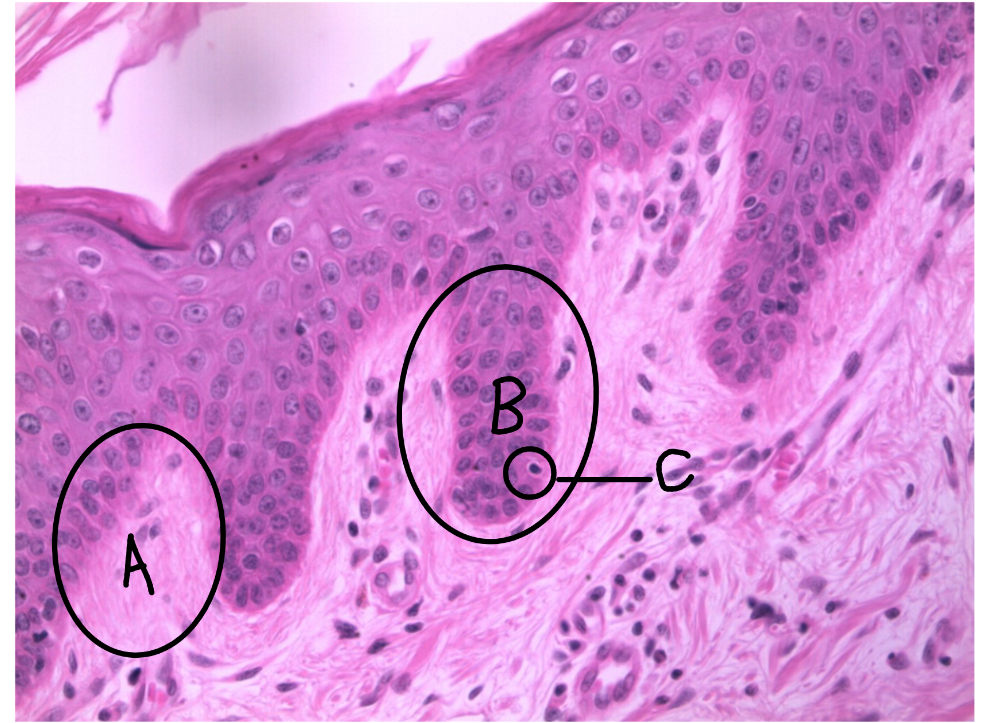
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Thin skin
A: dermal papillae
protrusion of the papillary layer of dermis into the stratum basale of the epidermis
B: rete peg
protrusion of the stratum basale layer of the epidermis into the papillary layer of the dermis
C: melanocyte
cell that produces melanin
located in the stratum basale of the epidermis
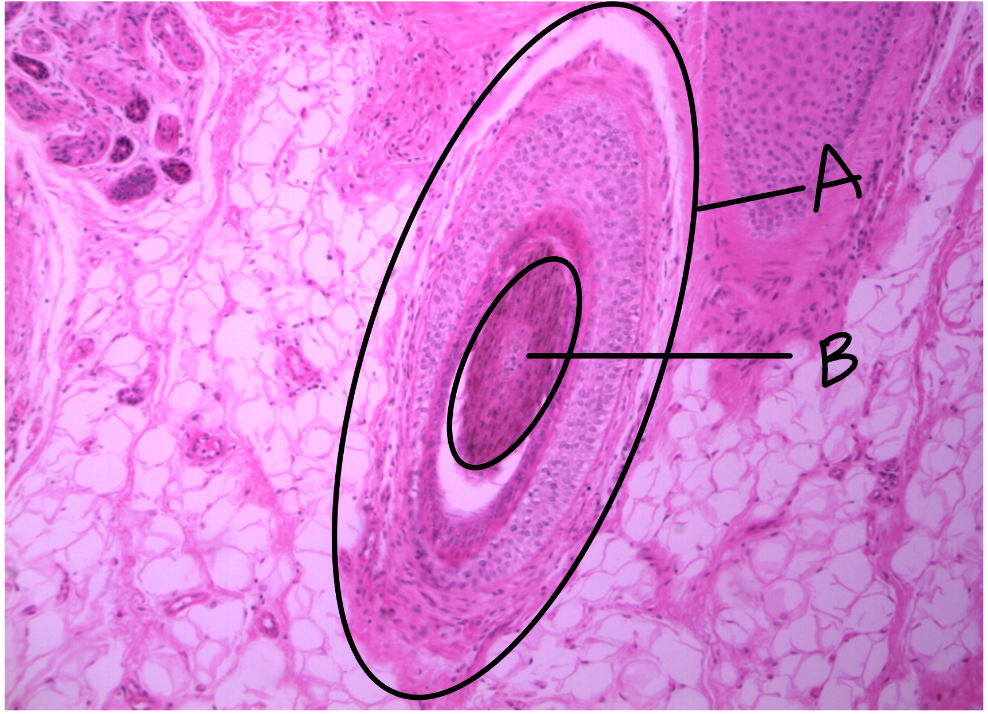
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Thin skin
from scalp
A: hair follicle
B: root of hair follicle
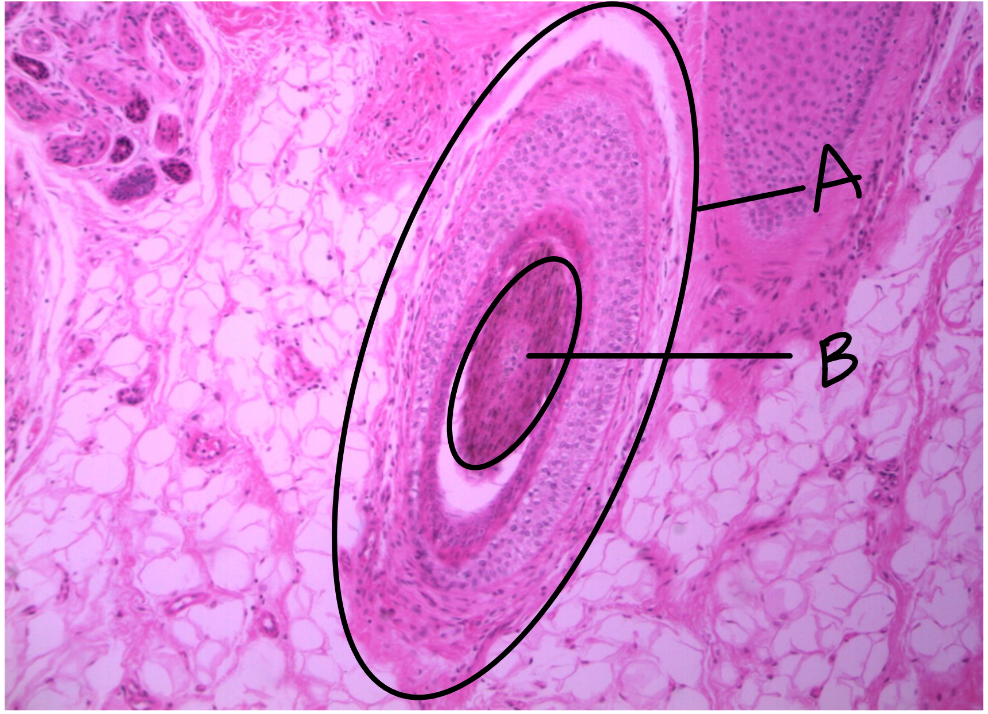
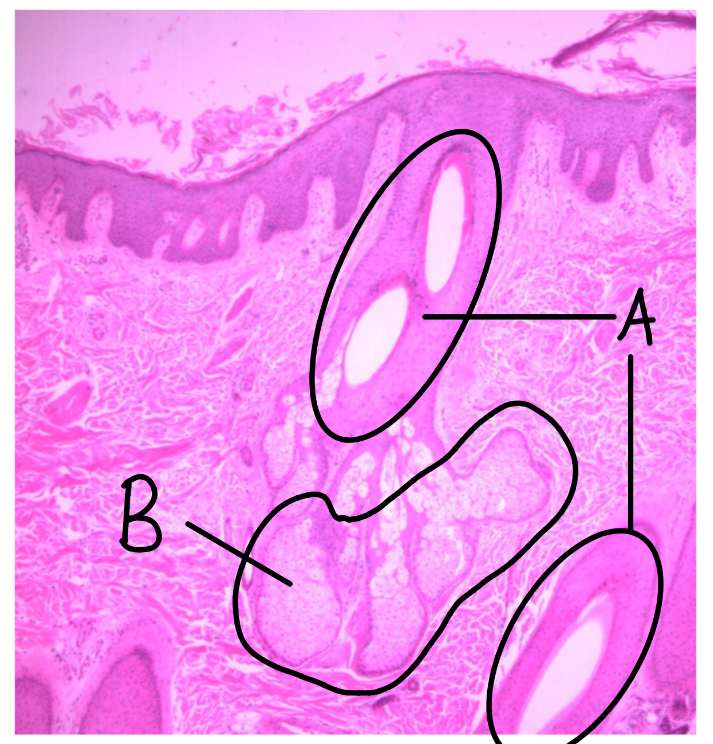
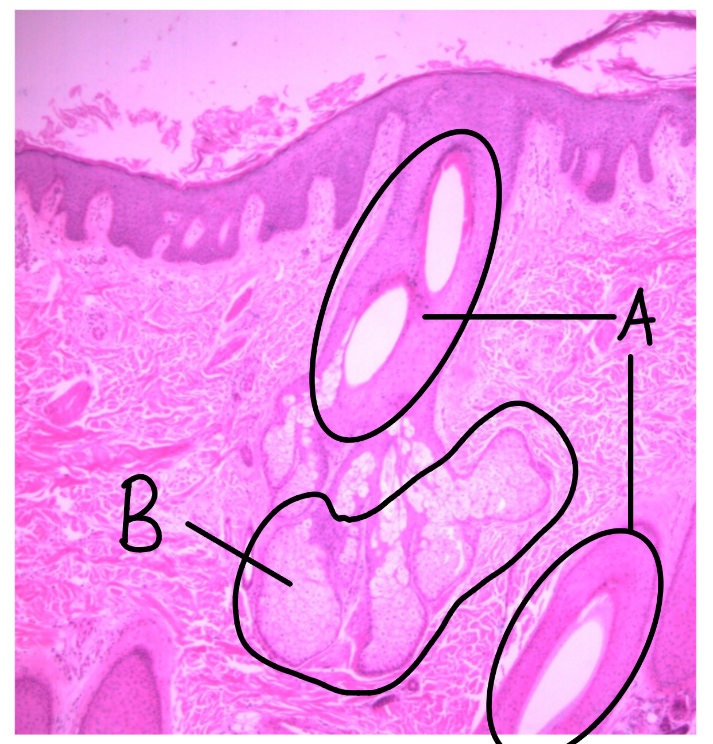
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Thin skin
from scalp
A: hair follicle
B: sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oily substance)
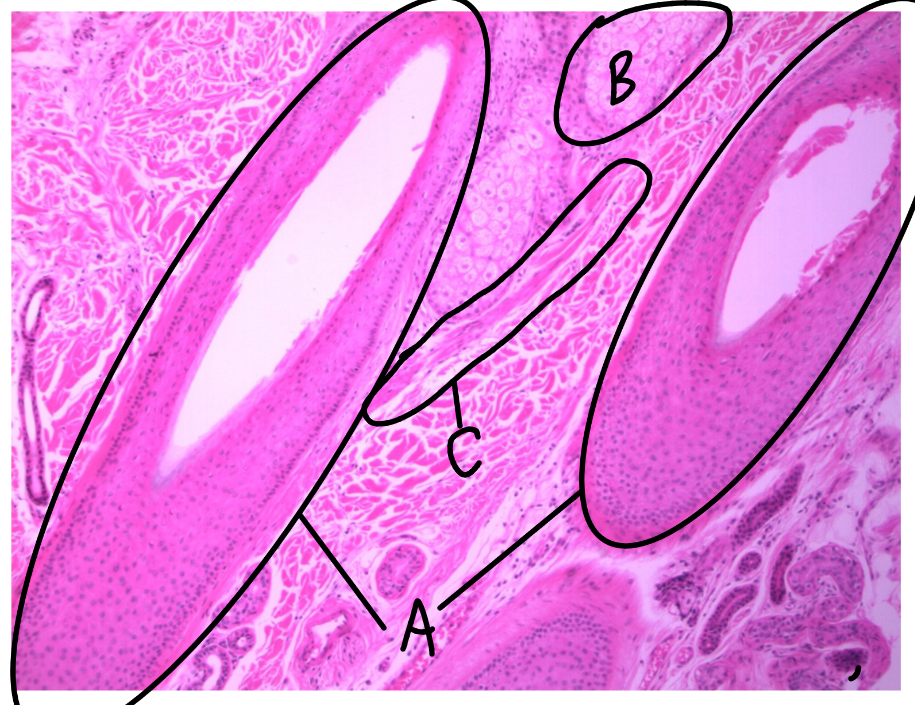
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Think skin
from scalp
A: hair follicle
B: sebaceous gland
secretes sebum
C: arrector pili muscle
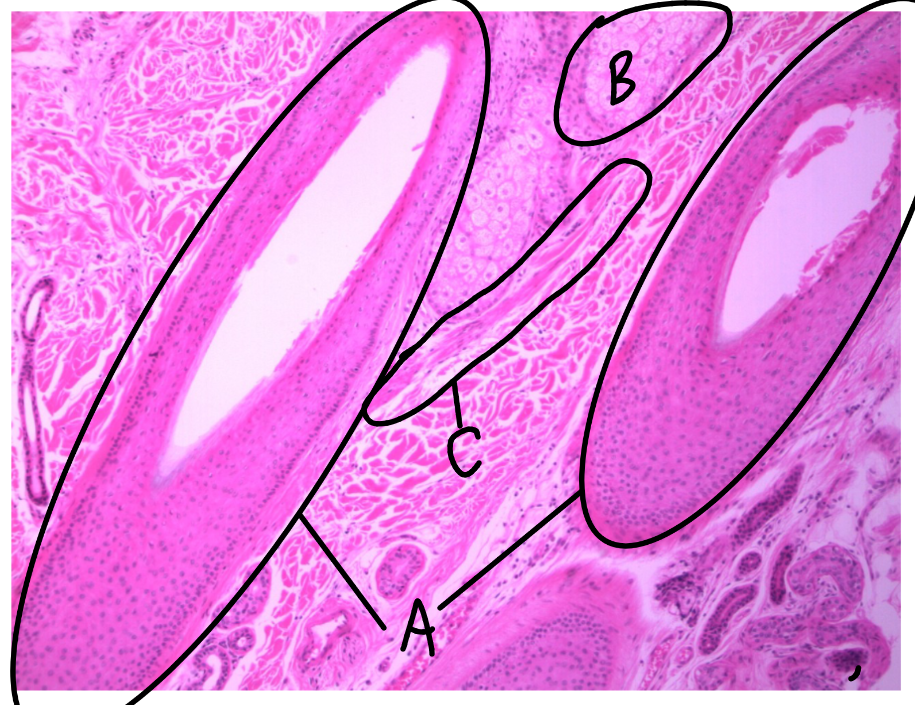
What is the function of arrector pili muscles, and what type of muscle tissue do they contain?
create goose bumps (make hair stand up)
contain smooth muscle tissue
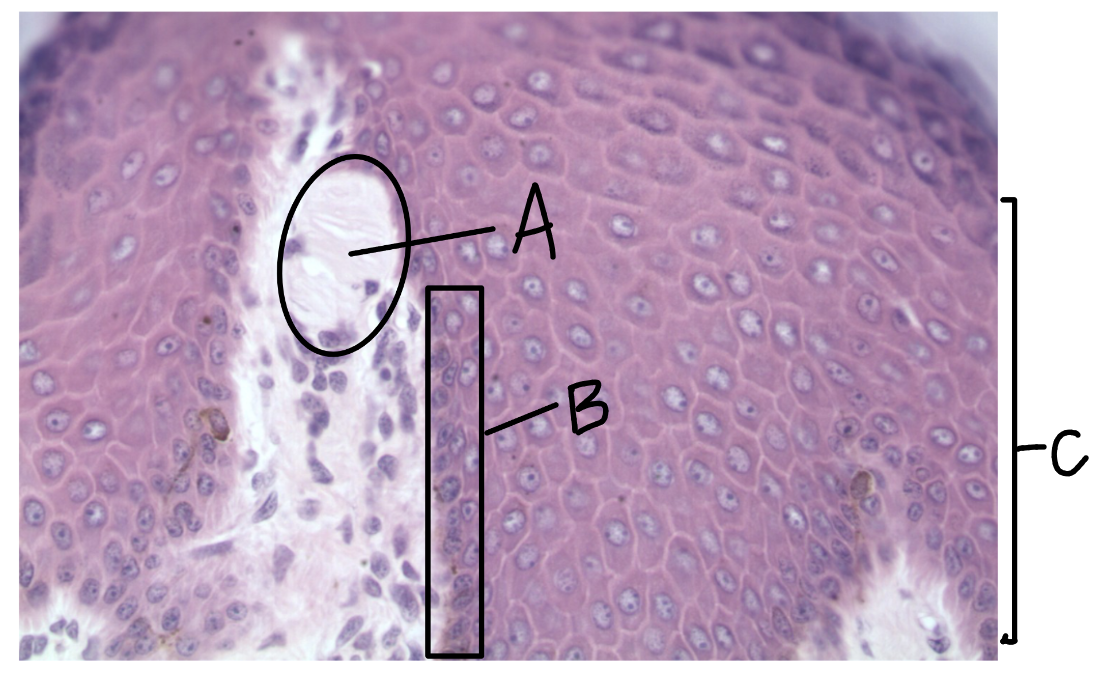
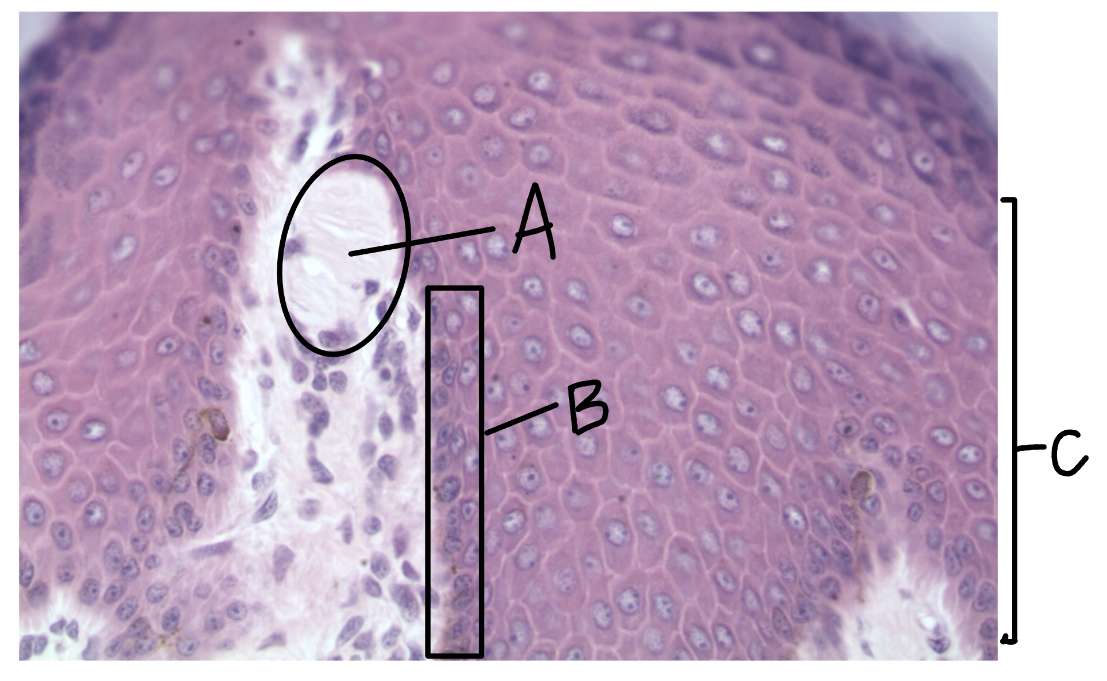
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Skin
A: Meissner’s corpuscle
detects light/soft touch
located in the dermal papillae
B: stratum basale
C: stratum spinosum
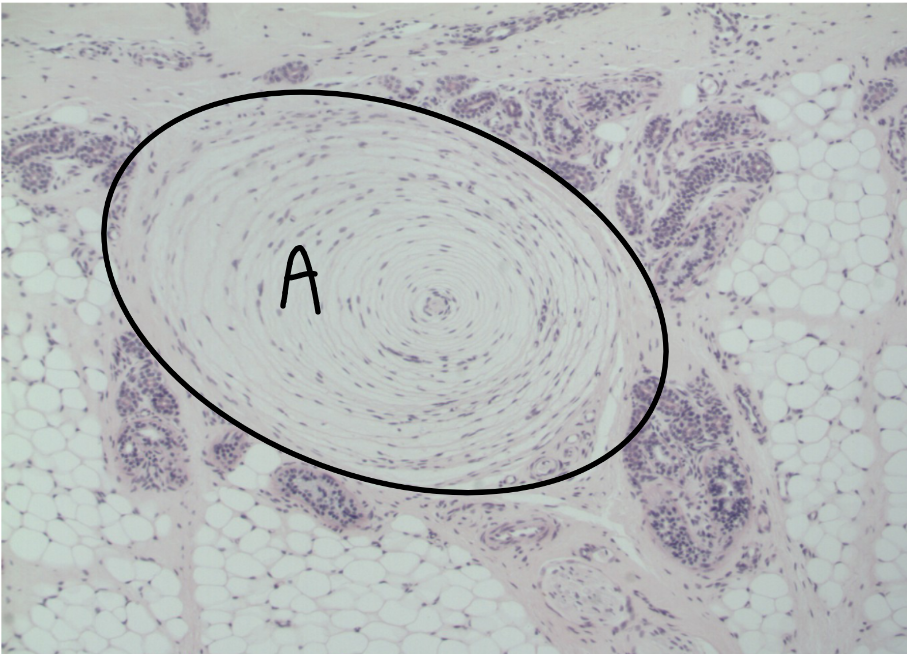
What is this a picture of? Identify the highlighted structures and describe them.
Hypodermis
A: Pacinian corpuscle
detects deep touch
located in the hypodermis
surrounded by fat cells