Physics: Work, Energy and Power
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

18 Terms
energy
the capacity or ability to do work

work
the product of the component of a force along the direction of displacement and the magnitude of displacement

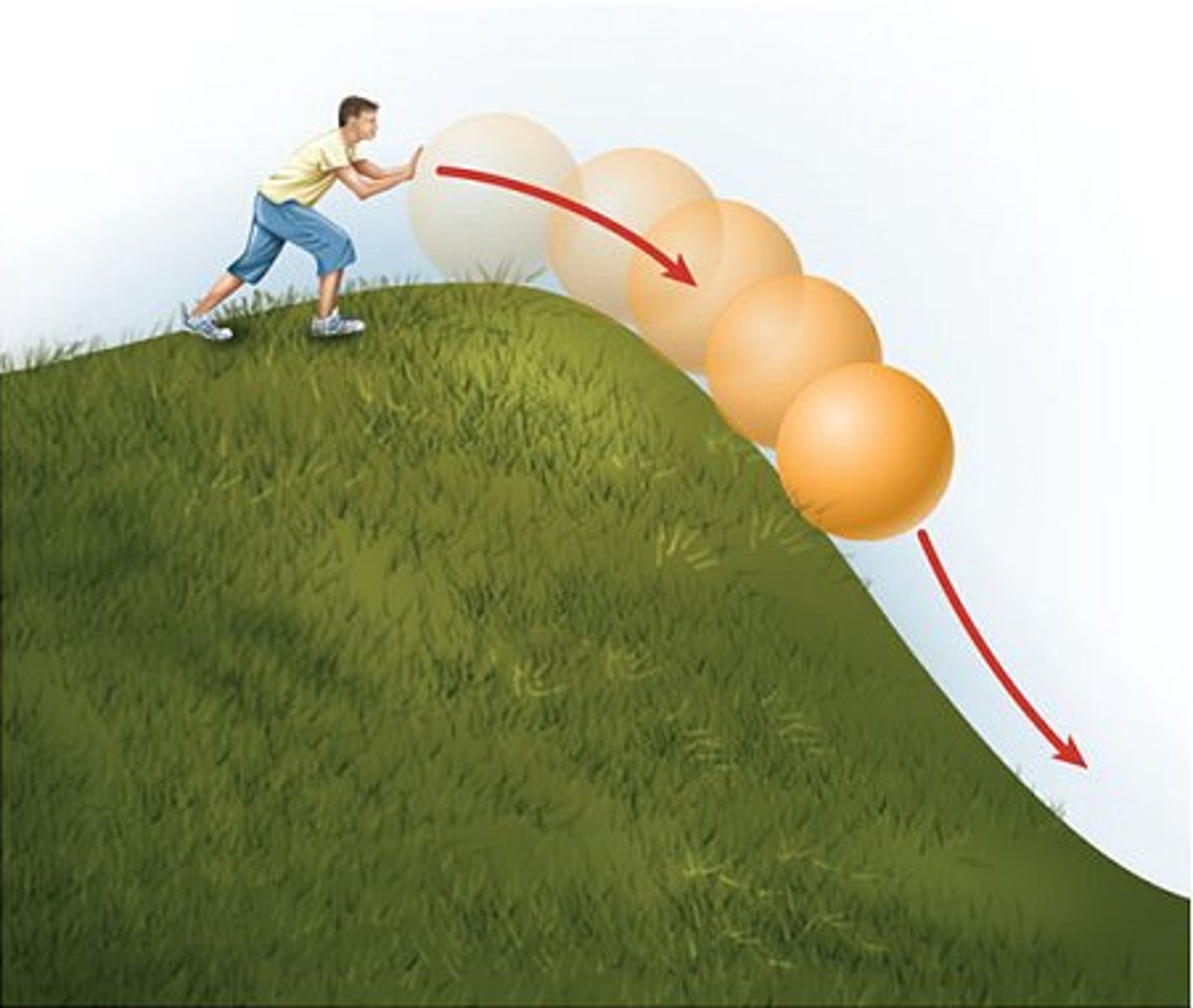
kinetic energy
Energy of motion; the energy available as a result of the motion of a body.

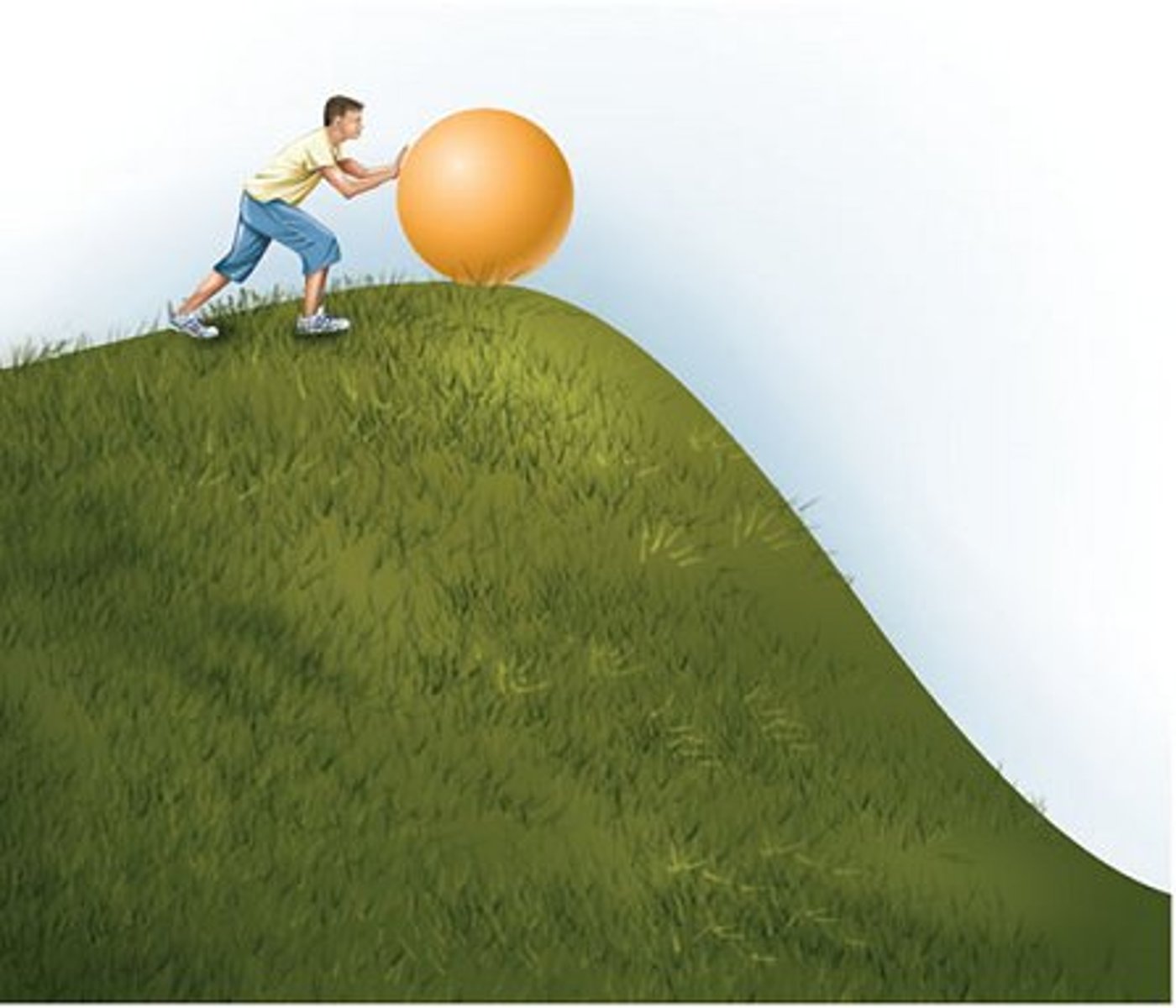
potential energy
stored energy; energy associated with an object due to its position, shape, or condition

conservation
energy can only be transferred not elimated, is the law of ________ energy
mechanical energy
the sum of kinetic and all forms of potential energy

power
The rate at which work is done over time
joule
unit of work or energy

watt
unit of power

gravitational potential energy
potential energy that is stored in the gravitational fields of interacting bodies
elastic potential energy
the energy available for use when a deformed elastic object returns to its original configuration
scalar
What type of quantity are work and power?
0 J
A young lad carries a small bucket of water that weight 1 N to his firefighter dad with a constant velocity for 4 m/s. How much work did he do?
spring constant
a parameter that is a measure of a spring’s resistance to being compressed or stretched
true
T or F; total energy is always conserved.
work-kinetic energy theorem
the net work done by all the force acting on an object equal to the change in the object’s kinetic energy
negative work
the product of when force and displacement are in opposite directions, resulting in a decrease in energy.
positive work
the product of when force and displacement are in the same direction, resulting in an increase in energy