Necrosis
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
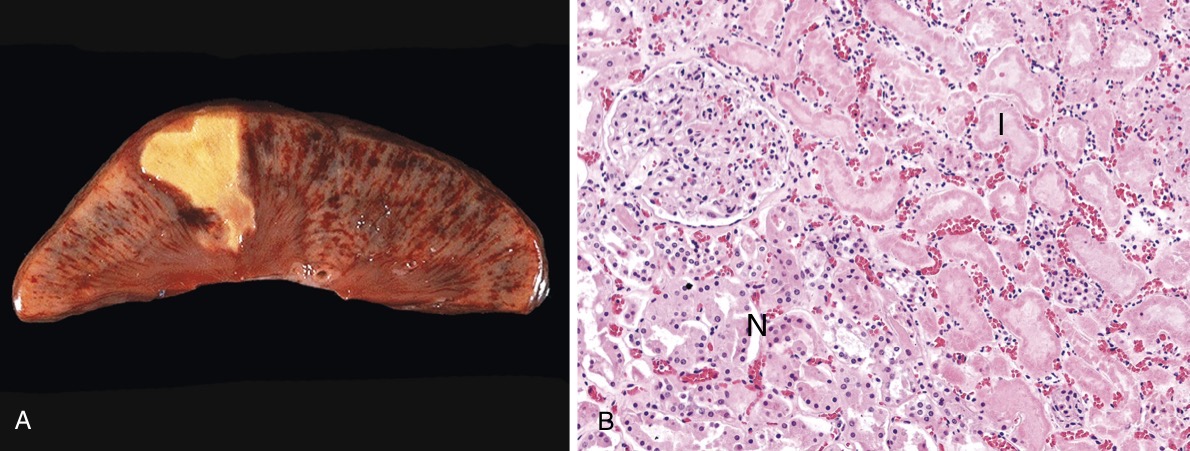
Coagulative necrosis
It’s caused due to denaturation of proteins, effecting organs such as liver, kidney, heart (mainly). It appears as a wedge shaped infarct on the organ so it preserves the architecture of the organ. Microscopically it appears as a tombstone (multiple ghost cells).
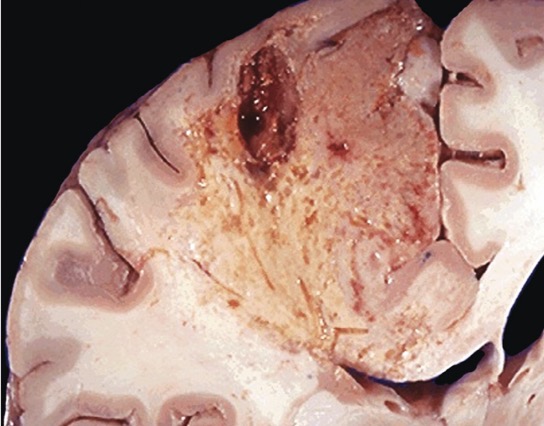
Liquefactive necrosis
It’s characterised by digestion of dead cells, so tissue architecture is lost. It’s mainly seen in fungal infections or due to focal bacteria, high enzymatic levels are seen. The main organs affected are brain and pancreas. The necrotic material is creamy yellow because of presence of leukocytes (pus).
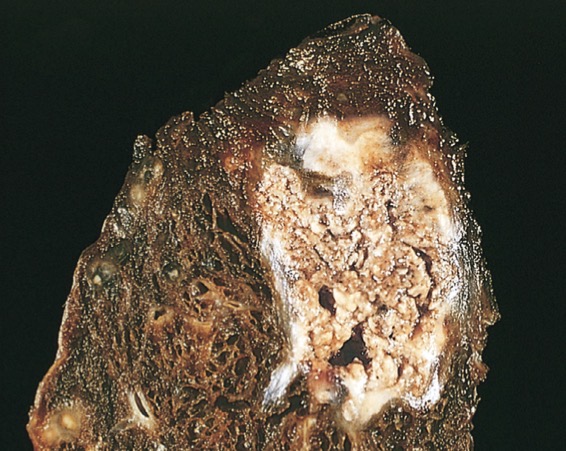
Caseous necrosis
Most commonly seen in foci of tuberculous infection. It’s a type of coagulative + liquefactive necrosis, the necrotic area appears cheese like, structure less collection of fragmented cells and amorphous granular debris enclosed within epitheloid cells. Seen in TB, fungal infection, granuloma, syphilis.
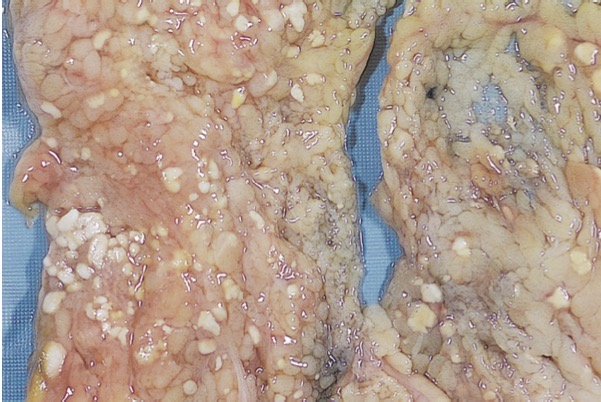
Fat necrosis
Results from release of activated pancreatic lipases into the substance of pancreas and peritoneal cavity. There is breakdown of fat by pancreatic lipases resulting in generation of fatty acids which further combine with ca2+ giving a chalky white appearance.
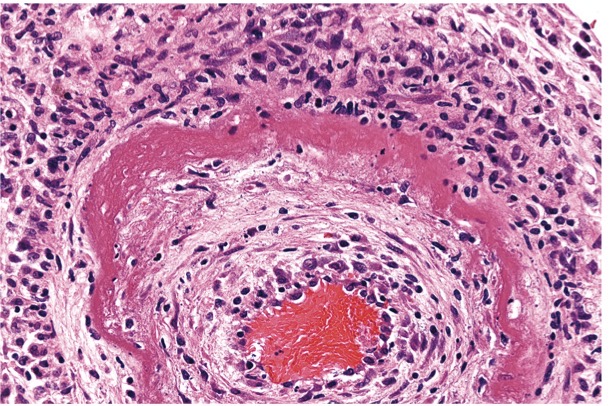
Fibroid necrosis
It’s a special form of vascular damage usually seen in immune reactions involving blood vessels. There is deposition of ag-ab in the wall of arteries along with plasma proteins that have leaked out of vessels, result in bright pink amorphous appearance in H&E stains called “fibrinoid”.
Eg: Rheumatic heart disease, malignant hypertension.