Obstructive Sleep Apnea
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
central sleep apnea (Cheyne Stokes syndrome)
break in respiratory effort secondary to improper central command
uncommon
severe - up to 20% mortality rate w/in 5y of dx
obstructive sleep apnea
soft tissues of the throat collapse & occlude airway, continually during sleep cycle → occlusion of airway leads to decreased blood O2
brain then signals the body to wake up & breathe
T
T/F: not everyone who snores has sleep apnea, but almost everyone w/ sleep apnea snores
gestational sleep apnea
sleep apnea that develops during pregnancy or post-partum
thought to be due to increased edema in airway tissues &/or hormonal factor
overweight men with large necks
what is the habitus of OSA patients?
apnea
each complete, 100% stop in breathing that lasts at least 10 seconds
hypopnea
each low, shallow breathing event of at least 10 seconds & at least 30% reduced air flow
17
a neck circumference of __in or larger for men increases the risk of OSA
16
a neck circumference of __in or larger for women increases the risk of OSA
snoring, tiredness, observed stop in breathing, pressure (HTN), BMI (35kg/m2 & up), age >50, neck size, gender (male)
what is the STOP BANG acronym?
0-2
a score of _____ on STOP BANG indicates low risk for OSA
3-4
a score of _____ on STOP BANG indicates intermediate risk for OSA
5-8
a score of _____ on STOP BANG indicates high risk for OSA
snoring that stops
what is a very sensitive sign of OSA?
heart disease, HTN, stroke & atrial fibrillation, VTE, increased LDL/triglycerides/total cholesterol, decreased HDL, gout
what systemic complications are associated w/ OSA?
T
T/F: OSA pts who have a non-fatal heart attack often have less residual damage
80, 90
___% of men & ___% of women are undiagnosed w/ OSA
2.5
cancer incidence was found to be ____x higher w/ OSA
3.4
cancer mortality was found to be ___x higher w/ OSA
86
untreated OSA was found to have a ___% higher mortality risk compared to non-OSA
35
CPAP treated OSA was found to have a ___% higher mortality risk compared to non-OSA
Epworth sleepiness scale
scale that uses self-report of likelihood of falling asleep during separate activities
Epworth sleepiness scale
pulse oximetry
polysomnography
apnea hypopnea index
respiratory disturbance index
cardiosomnography (not commercially available yet)
what can be used to dx OSA?
weight loss
smoking cessation
alcohol avoidance
sleeping pill avoidance
sleep on side instead of back
acetazolamide
dental appliances
Pillar procedure
CPAP, auto-titrating CPAP, BiPAP
surgery (MMA, UPPP, tongue reduction)
Provent
Winx
Inspire
Vivos DNA
dronabinol
ADI09
Mounjoro
Zepbound
Didgeridoo
what are the tx options for OSA?
move the lower jaw forward to keep airway open
how do dental appliances for OSA work?
Pillar procedure
tx option for OSA; performed in office w/ anesthetic & syringe, inserts Dacron strips into soft palate to keep airway open
CPAP
tx option for OSA: a machine & mask combine to provide a continuous flow of air to force airway open; poor pt compliance due to being uncomfortable, noise, difficulty traveling, & no point of use satisfaction
auto titrating CPAP
CPAP that continually adjusts flow pressure automatically
BiPAP
CPAP that develops higher dosing & has a different pressure b/t inhaling & exhaling
Provent
tx option for OSA: band-aid like device covering each nostril w/ center valve creating pressure
Winx
tx option for OSA: small mouthpiece that rests inside the mouth & creates suction to open airway
Inspire
tx option for OSA: upper airway stimulation: stimulates nerves to keep airway open; surgical procedure
Vivos DNA
tx option for OSA: daytime-nighttime appliance; looks like a retainer; worn for 9-18mo & expands the airway by lengthening the palate & trains the tongue to lie in a position that does not block the airway
floppy eyelid syndrome
keratoconus
NAION
glaucoma (NTG)
papilledema
ICSC
CPAP side effects
increased CRVO risk
increased risk of ME & PDR in diabetics
increased risk of AMD
what are the ocular SE of OSA?
deep retinal hemorrhages
CWS
vessel tortuosity
isolated peripheral retinal hemorrhages
what are the retinal changes associated w/ just having OSA?
dry eye & irritation, bacterial conjunctivitis risk
what are the SE associated w/ CPAP use?
5
less than __% of people w/ OSA have FES, but a very large percentage of people w/ FES have OSA
floppy eyelid syndrome
most commonly in overweight men
lids are loose & rubbery & evert easily w/ minimal pressure
associated w/ keratoconus
high rate of substantial conjunctivochalasis
lash ptosis common
pt will describe irritation as improving throughout day
weight loss & OSA management
nighttime lubricating ointment
sleep w/ cylinder pillow
firm sleep mask
taping of lids
sleep tite/sleep rite adhesive pads
surgical resection
what are the tx options for floppy eyelid syndrome?
FES
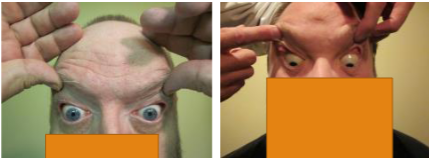
FES
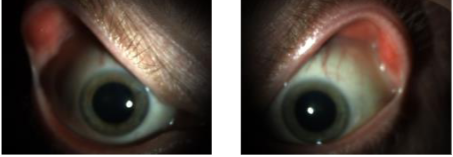
lash ptosis
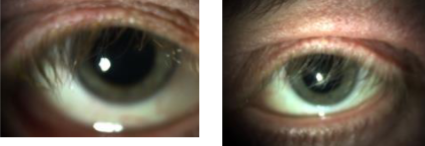
lash ptosis