unit 3 aos 2 hhd
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
changes in aus health status over time
improved life expectancy males and females
decreased mortality rates
increased prevalence noncommunicable diseases
decreased prevalence communicable diseases
categories of disease
CRICI
cancers
respiratory diseases
infectious + parasitic diseases
cardiovascular diseases
injury and poisoning
disease categories and trends over time
cancers: decreased over time (e.g. lung cancer decreased prevalence as smoking rates decreased)
respiratory: general decrease then sudden increase bc COVID-19
infectious + parasitic: decreased over time as living conditions + tech improved → child mortality, overall mortality rates decreased
cardiovascular: have decreased but still high levels
injury and poisoning: public health actions have decreased this significantly e.g. compulsory wearing seatbelts
public health def
collective effort to improve popul’s health status and how govs monitor, regulate and promote it
why was health st from earlier times not optimal
poor living conditions
minimal access clean water
minimal access sanitation
less knowledge on good hygiene practices
overcrowding and poor housing quality
some initiatives with ‘old’ public health
improved clean water access
improved sanitation
mass immunisation programs (not discovery of vaccines themselves)
better quality housing
better quality food + nutrition
safer working conditions
health promotion def
process of letting ppl increase control over their health to improve it
biomedical approach to health def
physical aspects of disease and illness involving med practices by health professionals to diagnose, treat, cure disease
features of biomedical approach
focus on ill individuals
focus on treatment rather than cause (when cond already present)
involves disease, illness, disability
relies on health services by health professionals
relies on tech to diagnose, treat, cure
advances in med technology e.g. (biomedical approach)
discovery of antibiotics to treat and reduce mortality rates from infectious diseases
drug development to treat high bp → reduce morbidity + mortality rates from cardiovascular disease via hypertension management
scans
biomedical approach to health — strengths
allows many diseases effectively treated via tech improvements
extends life expectancy
improves life quality → HALE
biomedical approach to health — limitations
relies on health professionals and tech → costly → not always affordable to all
may not always promote good h&w — bc focused on solutions rather than causes of conditions
not all conditions can be cured/treated → hence optimal h&w may not be restored
social model of health def
approach recognises improvements in popul h&w achieved by addressing physical, sociocultural, political envos
focuses on cause rather than solution
ottawa charter for health promotion
approach by WHO aims to reduce health inequalities by 5 action areas used as basis to improve health outcomes
the 5 action areas of the Ottawa Charter
BCSDR (bad cats smell dead rats)
build healthy public policy
create supportive envos
strengthen community action
develop personal skills
reorient health services
OTTAWA CHARTER — build healthy public policy
decisions by govs and orgs about laws and policies to improve popul’s health
e.g, compulsory wearing of seatbelts
OTTAWA CHARTER - create supportive envos
promote healthy physical + sociocultural envo for comm so it’s safe, stimulating, satisfying and enjoyable to promote h&w
e.g. providing shaded areas in school playgrounds
OTTAWA CHARTER - strengthen community action
comm involved in planning or implementing a program to achieve common goals of improving their h&w
e.g. parents working with school and canteen staff to serve healthier foods
OTTAWA CHARTER - develop personal skills
gaining education of health-related knowledge and skills that let ppl act in specific ways to
affectimprove their h&we.g. ability to read food labels and find the energy contents of diff foods to compare them
OTTAWA CHARTER - reorient health services
changing health system so it promotes h&w → like focus on prevention instead treatment of conditions and considering factors apart from disease as h&w from health professionals — more holistically
e.g. docs discuss regular exercise to pre-diabetic patients for prevention of development
— changing health system by encouraging health profs to focus on prevention over treatment and to consider h+w more holistically
social model of health — strengths
promotes good h&w through prevention rather than treatment
can be less expensive
more holistic approach to h&w (focus on all dimensions)
focus on vulnerable popul grps
health education can be passed generationally
responsibility for h&w is shared
social model of health — limitations
not every condition can be prevented (doesn’t benefit those already diagnosed)
doesn’t promote medical advancements e.g. tech
may not address specific h&w concerns of inds e.g. those sick not focused on
health promotion messages may be ignored — relies on public cooperation
lung cancer as an example of health approaches improving health outcomes — social model of health + health promotion
anti-smoking campaigns as a health promotion campaign
making tobacco products more expensive
lack of tobacco adverts + sold in plain packaging
health warnings on cig packets
banning smoking in pubs + clubs
has caused effective reduction in smoking rates
lung cancer as an example of health approaches improving health outcomes — biomedical approach
early diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer important bc has high fatal risk
improvements in med tech → has increased chance of ind surviving 5 years after diagnosis + better palliative care
diagnosed by ways like chest x-rays, CT scans, PET scans, bone scans
treatment by ways like chemotherapy, radiotherapy, removing affected lung parts
palliative care def
improvement of life quality for patients with life-threatening illness → manage symptoms, relieve pain and suffering
old public health def
gov actions that were focused on changing physical envo to prevent disease spread e.g. via improved sanitation and access to clean water
the role of health promotion in improving popul health
create conditions that encourage healthier lives and prevent ill health
diff to biomedical model that treats conditions already formed
why are some issues targeted by health promotion more than others
contribute more to aus burden of disease
cause great economic cost e.g. through health care, absenteeism
have modifiable component that can be addressed to improve
why health promotion > biomedical model
why biomedical > health promotion
lower cost for govs to prevent ill health than treat
not all diseases/conditions like injuries can be prevented
— hence important to invest in both
health promotion focus — Quit campaigns for smoking and vaping
develops personal skills: provide advice and practical strategies for quitting → increase ability of ppl to manage cravings
creates supportive envo: provide support throughout quitting process by telephone service that anyone can access
strengthen community action: Aboriginal Quitline has Aboriginal Australian specialists and community members with training to assist ppl with smoking/vaping cessation in culturally appropriate way
build healthy public policies: Quit advices govs on smoking and vaping laws e.g. no smoking in certain public places
reorient health services: Quit has online training program for health professionals so they can advise clients in quitting (before disease develops? prevent > treat)
e.g. how Quit campaigns can impact health outcomes
health status impact: decrease prevalence of smoking related conds like cardiovascular disease and cancer
h+w impact: reduced smoking rates → higher levels fitness in popul → promote physical h+w
health promotion focus — the Good Sports program for alcohol and drug misuse
build healthy public policy = gives expert advice on developing illegal drug policies in sport clubs
creates supportive environment = moves away from alcohol culture and create fam friendly sporting clubs
develops personal skills = promotes positive behaviour around alcohol so young club members can increase ability in decision making skills to reduce alcohol related harms
strengthens community action = parents and clubs reduce junior players exposure to alcohol and create positive playing envo + older players act as role models
reorient health services = gives support networks and assistance for members with mental illness to access health professionals before issue escalates
e.g. how Good Sports program can impact health outcomes
health status impact: reduce risk of members driving drunk hence reduced mortality rates from road trauma
h+w impact: members can socialise freely knowing it’s a safe envo to do so → form support networks and meaningful relationships → promote social h+w
health promotion focus — Victorian Road Safety Strategy for road safety
strengthens community action = collective response by govs, industry and vic community to allow safer roads by planning and implementing strategies
create supportive envo = AI cam systems can detect seatbelt absence and illegal phone use to allow safer roads and drivers
build healthy public policies = creating new laws and penalties to remove risky drivers from roads e.g. alcohol driving limit laws
develop personal skills = makes signs that can be seen along roads advising safe behaviour → increase drivers ability to assess if they are fit to drive safely
e.g. how Victorian Road Safety Strategy can impact health outcomes
health status impact: safer roads means less risk road accidents hence fewer deaths and increased life expectancy
h+w impact: safer roads means less risk road accidents → less risk injury → ppl can spend time with friends and form meaningful relationships → promote social h+w
health promotion focus — SunSmart for skin cancer
develops personal skills = media education campaigns increase ppl ability to recognise conditions for extra sun protection like wearing sunscreen
create supportive envos = promote building shades and using UV app thru day so ppl away from direct sun when dangerous conds
strengthens comm action = assists orgs like schools to implement sun safety measures like having sunscreen for kids to use at break times
build healthy public policies = assists schools in policies like no hat no play when outdoors during breaks
reorient health services = promotes GPs to increase awareness on UV exposure effects
social justice
fairness in society based on principles like
human rights (freedoms every person entitled to despite individual characteristics)
equity (disadvantaged grps have their challenges addressed, more support to those who need it) — consider diff situations of inds so those disadvantaged that need more support can get it
access (all ppl have adequate resource access)
participation (everyone has voice and opportunity)
e.g. health inequalities of ATSI vs non-ATSI
higher mortality rates
higher rates underweight babies and infant mortality
higher burden of disease rates
health promotion focus for First Nations — Closing the Gap
strengthen community action: ATSI consulted and help plan + implement agreement alongside govs
build healthy public policy: has targets formed by govs that influence policies to improve ATSI popul health
health promotion focus for First Nations — Deadly Choices initiative
develop personal skills: education programs provides cooking programs and tobacco cessation strategies for popul to gain ability to cook nutritious food and resist smoking cravings
reorient health services: health workers promote annual health check so they can identify risks of health concerns hence focus on preventing them prior to onset
strengthen community action: ATSI community members plan and implement health services in culturally appropriate way
health promotion focus for First Nations — Tackling Indigenous Smoking (TIS) initiative
reorients health services: Quitskills training program gives health workers knowledge to support ATSI people to quit smoking → focus on prevention > treatment of associated diseases
create supportive environment: regional tobacco grants allow local orgs to implement tobacco cessation activities and Quitline services
build healthy public policy: advises aus gov on policies to to reduce smoking among ATSI and close the gap
develop personal skills: developed a children’s book promoting healthy behaviour + lack of tobacco use → increase kids ability to refuse smoking opportunities as they are aware of negative effects
evaluating initiatives to improve First Nations health — considerations of whether effective or ineffective
make judgement statement about level of effectiveness (use format) — either start or end
identify action area ottawa charter for hp
outline how used in case study/program (quote and explain it)
outline how this increase program engagment (use format)
link to improved h&w (dimensions and key words) for inds
no. people that have accessed / participated
feedback from participants
action areas of Ottawa Charters evident
whether culturally appropriate
whether specific needs addressed
program effectiveness — ottawa charter for hp action areas format
develop personal skills = ‘knowledge learnt can be passed on to friends and fam, increasing program reach’
create supportive envo = ‘increase likelihood ppl feel comfortable accessing program, increasing no. participants’
strengthen community action = ‘comm involved may encourage others to engage in program by creating trust, increasing participation rates’
for step where state effectiveness: “ the (program name) is an effective program to promote h+w as it includes various action areas of the ottawa charter for health promotion” — either at start or end of response
federal gov initiatives to promote healthy eating
aus dietary guidelines
aus guide to healthy eating
ATSI guide to healthy eating
evaluating initiatives to promote healthy eating — considerations of whether effective or ineffective
ease of understanding (e.g. using visual guides for those with lower literacy levels, language range)
access (e.g. resources are free of charge, available online)
inclusiveness (relates to diff popul grps)
relevance (should work towards an imp need in community)
effectiveness (expected or already achieved objectives across popul grps)
sustainability (ability for program to continue in future)
the aus dietary guidelines notes
developed by NHMRC — fed gov body
addresses causes of the increase in diet-related conds and diseases in seen in aus population over time
used by health professionals, educators etc
promotes aus popul to develop healthy dietary patterns, reduce risk of developing diet-related conds,
and reduce risk developing chronic conds
the aus dietary 5 guidelines
to achieve + maintain healthy body weight, be physically active, choose amounts of nutritious foods and drinks to match your energy needs
enjoy wide variety nutritious foods from the five groups (veges, fruit, grain, protein foods, dairy foods — vital foods grow people daily) daily and drink plenty water
limit intake foods with sat fats, added salt, added sugar, alcohol (discretionary foods)
encourage, support and promote breastfeeding (promotes ideal infant growth and. development)
care for your food (prepare and store safely to avoid food-borne diseases, food poisoning)
strengths and limitations of aus dietary guidelines
strengths:
available free download online (no cost and geo barrier)
accounts for diff needs for diff inds e.g. diff life span stages, vegetarians and vegans, ppl of diff cultures, pregnant women etc
accessible in low vision format
provides serving sizes for food grps for more effectiveness
limitations:
written format hence low literacy levels hard to understand
only in eng
based on needs of average person hence not specific to all (e.g. those with serious diet conds not considered)
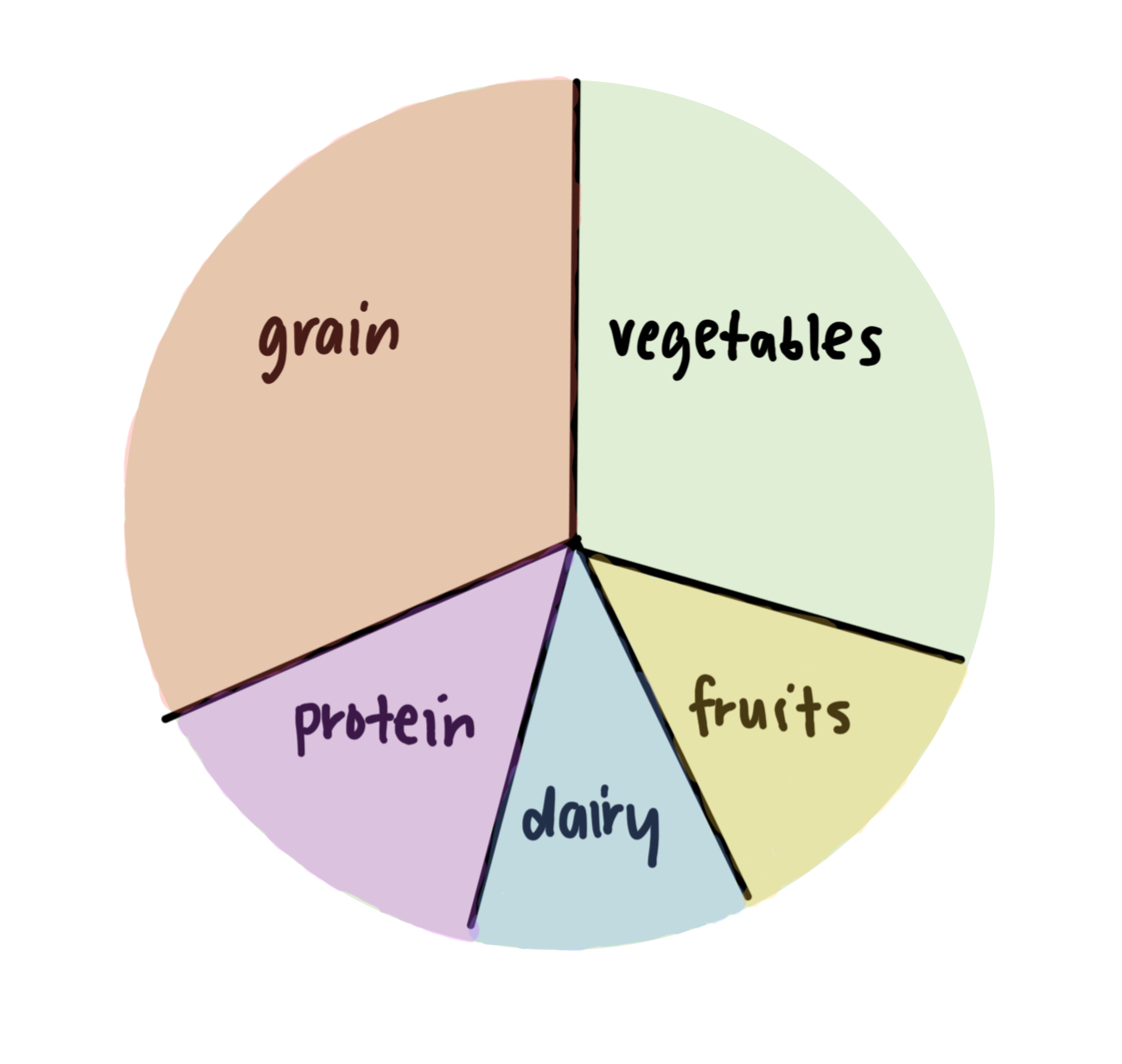
the aus guide to healthy eating
visual tool in aus dietary guidelines for ppl to plan + eat recommended food proportions daily
shows proportions of five food grps consumption
promotes water consumption
suggests limiting discretionary foods
recommends small amount healthy fats
label the aus guide to healthy eating proportions
+ plenty water
+ use small amounts discretionary foods, healthy fats
the ATSI guide to healthy eating
visual tool in aus dietary guidelines for ppl to plan + eat recommended food proportions daily that also has FN trad foods e.g. kangaroo meat, bush fruits
food selection models (aus and ATSI guide to healthy eating) strengths and limitations
strengths:
multiple languages available
applies to all ages
visual presentation allows those low literacy understand
based on latest scientific research → more effective
large range foods from diff cultures
limitations:
doesn’t show serving sizes → more subjective
doesn’t consider composite foods e.g. pizza (has multiple grps in it)
based on average popul needs → do not consider some ppl with specific dietary needs → not applicable to everyone
how has food intake in aus changed over time
less nutrient-dense whole foods → more energy-dense processed foods — has caused increased rates diet related conds
what are the main factors as challenges to nutritional change
personalsociocultural (commercial too)
environmental
personal factors as challenges to nutritional change — list
— relates to ind’s characteristics
willpower and taste prefs
attitudes and beliefs
h+w factors
personal factors as challenges to nutritional change — willpower and taste prefs
people prefer certain foods than others
e.g. foods high in fat, salt, sugar → flavour enhancers → stimulate taste buds and cause dopamine release → creates cravings for these foods hence removing these foods hard
taste prefs often form over time period hence can be hard to change
personal factors as challenges to nutritional change — attitudes and beliefs
can complicate diet changes
e.g. =
perception that healthy food is bland
ignorance of negative effects unhealthy foods for taste
beliefs like vegetarianism
restriction of certain foods (e.g. religion)
personal factors as challenges to nutritional change — h+w factors
e.g those with allergies may not be able to eat some healthy foods
those experiencing poor emotional / mental h+w may rely on dopamine release from unhealthy foods to enhance mood
sociocultural factors as challenges to nutritional changes — list
socioeconomic status
employment status
fam and peer grp
commercial factors (dppm)
sociocultural factors as challenges to nutritional change — socioeconomic status
education, income, occupation all influence foods
lack of nutritional knowledge and cooking skills = people eat unhealthy meals
lack of literacy = consumers may not accurately assess food labels and hence control their food intake patterns
if lower income = cannot afford more costly healthy food
some occupations may consume foods based on nearness to employment place → e.g. may access fast food and reduce ability to consume healthy diet
sociocultural factors as challenges to nutritional change — employment status
if both parents working full time then less time spent preparing healthy food → hence more ready-made foods consumed
when working outside people may eat from locations near employment area → affects regular diet
sociocultural factors as challenges to nutritional change — family and peer group
family may increase familiarity of certain foods (esp to kids) hence may be difficult to change to non-familiar foods
social settings can impact choices of food as people may be influenced by others choices
cultural background of family may influence typical foods consumed
sociocultural factors as challenges to nutritional change — commercial factors
private sector (economy not run by gov like companies) influence popul food intake:
distribution and affordability = prices set by retailers often influence affordability of foods + price generally increases if food has travelled larger distance
processing = addition of additives and preservatives to prolong foods shelf life and enhance flavour
packaging and labelling = foods packed to be more visually appealing can cause increased consumption + labelling may be misleading
marketing strategies = media like ads on television, in newspaper, on radio etc can increase people’s exposure to certain foods hence increasing likelihood of consumption (esp for kids that see specific ads between cartoons etc)
envo factors as challenges to nutritional changes — list
geographic location
workplaces
housing envo
transport
(green world happy tomorrow)
environmental factors as challenges to nutritional change — geographic location
— where ppl live influence food available to them
ppl outside major cities may have more limited food options
those in remote areas may rely on processed + non-perishable foods → not as healthy
suburbs with lower SES may have more fast-food outlets
environmental factors as challenges to nutritional change — workplaces
some workplaces offer food at canteens → influence ability to control diet
workplaces without cooking facilities can also decrease food preparation and diet control
environmental factors as challenges to nutritional change — housing envo
facilities available in house (e.g. fridges, microwaves etc) can influence meal options → if lack of facilities can limit food options as cannot prepare and store properly
environmental factors as challenges to nutritional change — transport
availability of roads, paths etc can influence access to food outlets
if lack of transport access (e.g. no vehicle, no public transport) → ppl may rely on foods closer to homes → reduce ability to make nutritional change
health system def
all activities that primary purpose is to promote, restore and maintain health
common elements of health systems
funding models
professional workforce
reliable info to base decisions + policies
up-to-date facilities
logistics for meds and tech
2 main components of aus health system
public health care
private health care
public health care def
aus gov provides services and schemes including public hospitals, Medicare, PBS, NDIS
private health care def
not funded by gov directly includes private health insurance, private hospitals, med professionals in private practices
medicare def
aus’s universal public health insurance scheme funded by fed gov to give all eligible (australians, permanent residents, those from countries with reciprocal agreement) access to subsidised health care
what does medicare cover overall
out of hospital expenses
in hospital expenses
medicare safety net
medicare cover — out-of-hospital expenses
COVERS SCHEDULE FEE OF ESSENTIAL HEALTHCARE SERVICES
pay all/some fees for essential healthcare services (e.g. GP consultation fees, specialist consultations, tests and examinations like blood tests, eye tests)
medicare benefits schedule lists services medicare gives schedule fee for
schedule fee: amount money gov finds suitable for specific med services based on reasonable average → a set amount given to that service (however depending on ind’s doctor this schedule may be less than actual fee → remainder paid by patient as patient co-payment)
if doc charge only schedule fee = no patient co-payment = service has been bulk-billed
when inds access specialist services = medicare contribute 85% of standard schedule fee (which may be diff to specialist actual fee) = patient co-payment required
medicare cover — in-hospital expenses
as a public patient in public hospital — accomodation and treatment covered
if ind chooses to admit in private hospital or if private patient in public hospital — cover 75% of schedule fee for treatment services but not to accomodation, meds, theatre fees etc
medicare cover — medicare safety net
once ind/family contributed significant amount out-of-pocket costs for medicare services in one year → gov gives more financial support → make medicare services cheaper for rest of year
services covered by medicare e.g.
GP and specialist consultations
optom eye tests
x-rays
some dental procedures + services for some children 2-17 yrs under child dental benefits scheme
what is not covered by medicare
in home nursing care and treatment
ambulance services
services not clinically necessary (e.g. cosmetic procedures usually not covered)
most private hospital costs (only cover 75% schedule fee)
most dental exams and treatments
most allied health services (unless GP referral or in public hospital)
alternative meds unless GP involved
health aids like glasses
meds
med costs when someone else responsible
advantages of medicare
choice of doctor for out-of-hospital services
available to all aus citizens
reciprocal between aus and other countries lets australians access free health care there
covers tests, exams, schedule fee for consultations etc
medicare safety net provides extra financial support to those need it
disadvantages of medicare
no choice of doctor for in-hospital treatment
waiting lists for many treatments
doesn’t cover alternative services
often doesn’t cover full doctor fee (only pay schedule fee)
how is medicare funded
medicare levy
medicare levy surcharge
general taxation (revenue from above doesn’t meet full medicare operating costs hence this helps to fund)
medicare levy def
2% tax placed on taxable income of most taxpayers to fund medicare
(special circumstances or low incomes exempted)
medicare levy surcharge def
EXTRA 1-1.5% TAX PLACED ON TAXABLE INCOMES OF THOSE WHO DON’T HAVE PRIV HEALTH INSURANCE ESP HIGH INCOME EARNERS
those without private health insurance earning more than certain amount pay extra tax → surcharge % increases as income increases from 1 to 1.5%
purpose: encourage inds to take out private health insurance to reduce demand hence financial pressure of medicare (esp high income earners)
the pharmaceutical benefits scheme def
fed gov contribution to aus public health system by subsidise essential meds so ppl only make patient co-payment
the PBS safety net
those paying more than certain amount out-of-pocket expenses for PBS-listed meds in a year provided extra support so they only have to pay concessional co-payment rate ($7.70 instead of usual $31.60)
which meds covered under PBS
most essential prescription meds (including diff brands of same med) → meds under this category reviewed thrice a year by PBAS → they consider conditions med used for, clinical effectiveness, safety, cost-effectiveness before making +ve rec to include in PBS
meds not covered by PBS need patient pay full amount
the national disability insurance scheme
national insurance scheme funded by fed gov that provides support for people with permanent significant disabilities + their carers to help them live normally
NDIS eligibility requirements
under 65
must live in aus and be citizen or have permanent visa or protected special category visa
condition likely to be permanent
condition significantly reduce ability to participate in tasks/activities so need assistance from others, or with assistive tech or can’t even with these things
condition affects capacity for social and economic participation
likely to require NDIS support for lifetime
NDIS process
if age, residency, disability requirements met → develop individualised plan with support for ind’s goals and aspirations (e.g. more independence, community involvement etc) → plan includes functional support for daily living, support for pursuing goals and assistance for ind to organise how to manage plan over time
what can NDIS plan help ind’s to do
access mainstream services and supports (e.g. accessing teachers in education system or accessing justice system — NDIS can provide resources like transport or carer assistance if needed)
access community services (e.g. sports clubs or libraries)
maintain informal support arrangements (help from fam and friends)
receive funded supports (NDIS can pay for supports to help ind live normal life and achieve goals, for assistive tech like mobility cane, wheelchair etc and for carers) → increase independence
private health insurance def
additional insurance type where members pay premium in return for payment towards healthcare costs not covered by Medicare
premium def
amount members pay for insurance
hospital separations def
episodes of hospital care that start with admission and end with transfer/discharge/death
insurers classify their hospital policies to one of four tiers for hospital cover
gold — covers most categories hospital treatment (rehab, brain and nervous, heart and vascular, assisted reproductive)
silver — covers second most categories hospital treatment (rehab, brain and nervous, heart and vascular)
bronze — covers second fewest categories hospital treatment (rehab, brain and nervous)
basic — covers fewest categories hospital treatment (rehab)
private health insurance coverages
private hospital cover
general treatment cover (services not covered by medicare like physios, dentists etc)
combined cover (hospital and gen treatment cover)
what does medicare cover for private hospital treatments
75% of treatment schedule fee
fees charged with private hospitals
they usually charge more than schedule fee → medicare covers 75% of schedule fee → priv health insurance can sometimes pay all reminder sometimes cannot → if not patient pay rest = the gap
private health insurance incentives types
private health insurance rebate
lifetime health cover
medicare levy surcharge
age-based discount