chapter 12 - alcohols, aldehydes, thiols, ethers, keytones
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
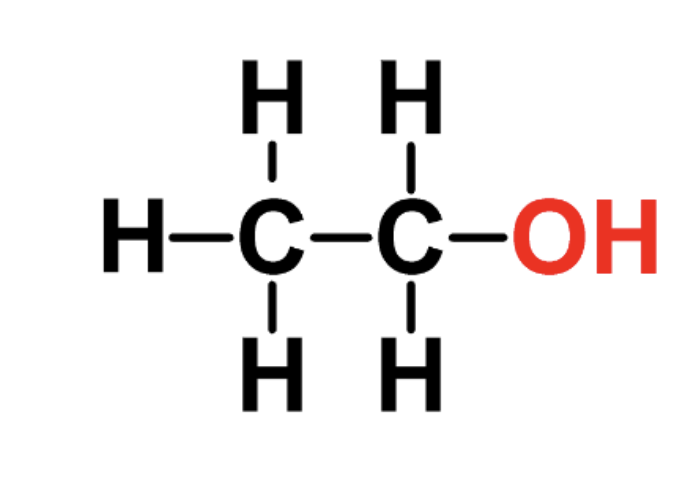
identify the fxn group
alcohols
has an -OH attached (single bonds)?
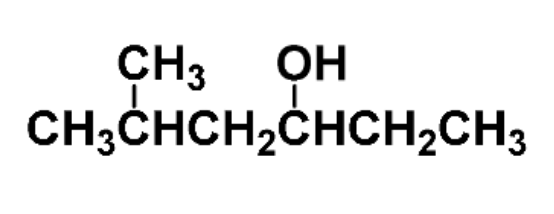
example: name the following
5-methyl-3-hexanol
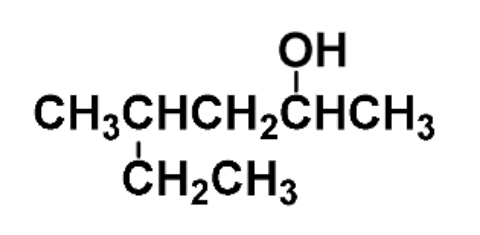
example: name the following
4-methyl-2-hexanol
how are alcohols classified?
with degrees
1 degree, 2 degrees, 3 degrees
fxn group with a -OH and single bonds
alcohol
what is a 1 degree alcohol?
1 carbon directly attached to the carbon of the -OH
what is a 2 degree alcohol?
2 carbons directly attached to the carbon of the -OH
what is a 3 degree alcohol?
3 carbons directly attached to the carbon of the -OH
another term for a 1 degree alcohol?
primary alcohol
another term for a 2 degree alcohol?
secondary alcohol
another term for a 3 degree alcohol?
tertiary alcohol
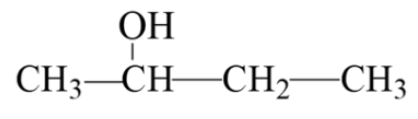
example: classify the alcohol
secondary
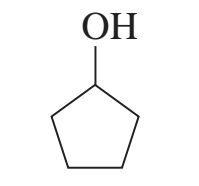
example: classify the alcohol
secondary
how does the number of carbons effect solubility?
as the number of carbons increases, solubility decreases
what is the relative boiling points of alcohols, and why?
relatively high boiling points
they have hydrogen bonding
H covalently bonded to unshared pair on an O,N, or F
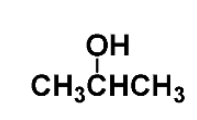
example: name the following
isopropyl alcohol
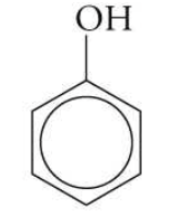
which fxn group has an -OH attached to an aromatic ring (benzene)?
phenol
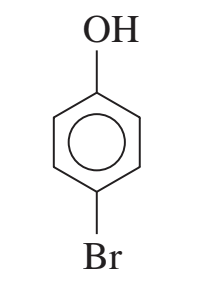
example: name the following
4-bromophenol
what is the solubility of phenols, and why?
slightly soluble in water
the OH makes hydrogen bonds when reacted with water
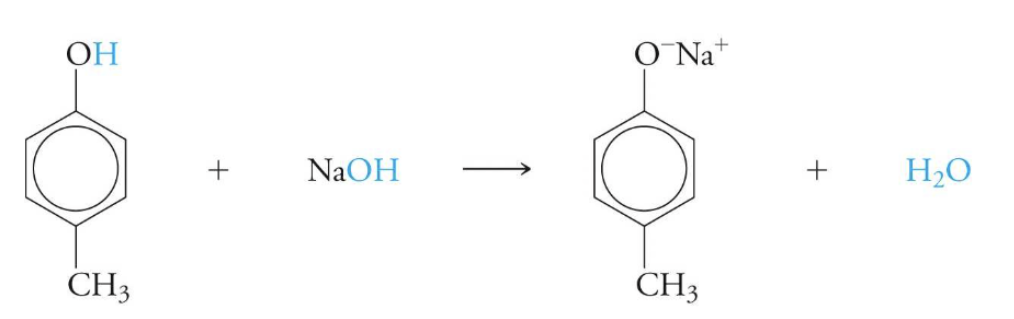
what do phenols act as in a reaction?
weak acids
acids are the H+ donor
acid/conj. base…
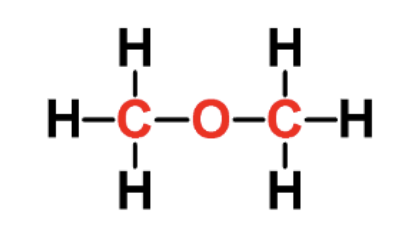
identify the fxn group
ether
has a C-O-C linkage
fxn group with a C-O-C linkage?
ethers
what type of connectivity to ethers have?
dipole-dipole
are ethers or alcohols more soluble in water?
alcohols
they have hydrogen bonds and ethers do not
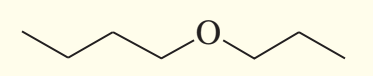
example: name the following
butyl propyl ether
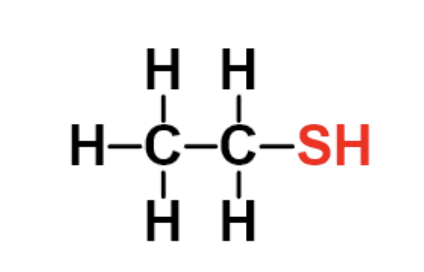
identify the fxn group
thiol
has an SH attached to an alkane
what is the polarity and solubility of thiols?
nonpolar
don’t have H bonds bc no H covalently bonded to O,N,F
limited solubility in water as a result
which fxn group has an SH attached to alkanes?
thiols
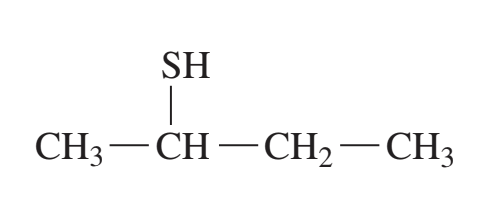
example: name the following
2-butanethiol
what fxn group has CSC linkage?
sulfides
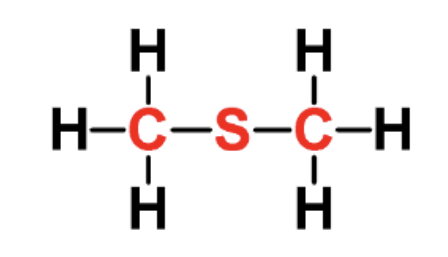
identify the fxn group
sulfide
has CSC linkage
what is the solubility and polarity of sulfides/disulfides?
limited solubility
nonpolar
do not have H bonds
when does an alcohol chain become insoluble?
if it has 5 or more carbons
the OH can no longer make it soluble as the carbons increase
what fxn group has CSSC linkage?
disulfides
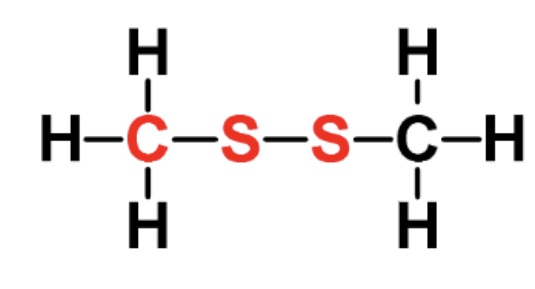
identify the fxn group
disulfide
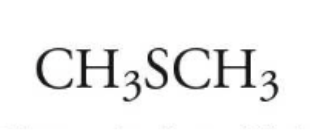
example: name the following
dimethyl sulfide
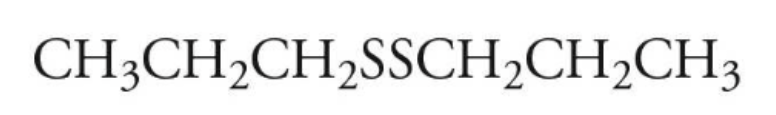
example: name the following
dipropyl disulfide
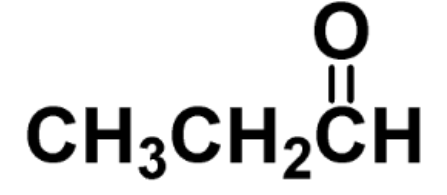
identify the fxn group
aldehyde
carbonyl group (C=O) is on the end of a carbon chain
which fxn group has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached on the end of the carbon chain?
aldehydes
which fxn group has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached in the middle of carbon chain?
ketones
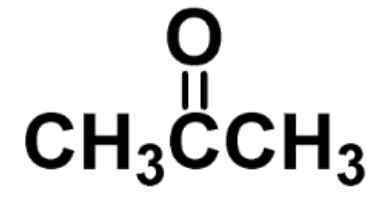
identify the fxn group
ketone
the carbonyl (C=O) is in the middle of two carbons
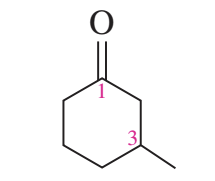
example: name the following
3-methylcyclohexanone
what does solubility look like for aldehydes and ketones?
it varies
bc of the amount of carbons
5+ carbons = insoluble
less than 5 = soluble
what parts of aldehydes and ketones makes them polar (sometimes)?
carbonyl group has partially negative oxygen atom and a partially positive carbon atom
makes it polar
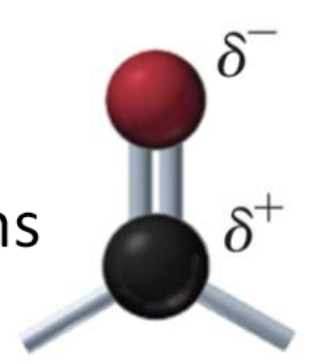
what type of forces do aldehydes and ketones have?
london
dipole-dipole
how does the boiling point for aldehydes/ketones compare that of alcohols?
lower boiling point than alcohols
they don’t have hydrogen bonding
nucleophile def
electron rich atom/group
electron pair donor
negatively charged/neutral
electrophile def
electron poor atom/group
electron pair acceptor
positively charged

what type of reaction is this?
nucleophilic substitution reaction
describe what happens during a nucleophilic substitution reaction
element attached to the long carbon chain switches places with the element that is being added
one pair of electrons from the original element moves to the other element
the other element gains a negative charge

name the products of the following reaction
diethyl sulfide
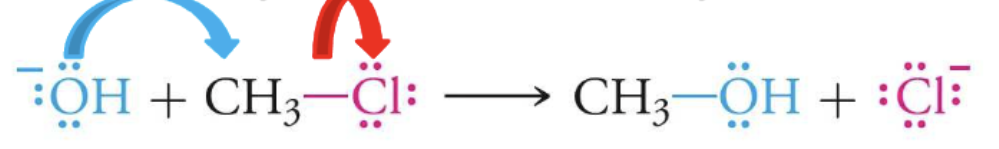
identify the nucleophile in the following reaction
the OH
it is donating electron pair, its electron rich
what happens during oxidation?
gaining of O bonds
losing of H bonds
when an alcohol is oxidized, what fxn group is formed?
a carbonyl group (C=O)
either aldehyde or ketone
describe what happens during primary alcohol oxidation
the OH loses the H
a double bond forms to the O
this makes it into an aldehyde/ketone
when aldehyde/ketone is oxidized, and O is added to one of the H’s
this makes a carboxylic acid (C=O with and OH group attached to the same carbon)
describe what happens during secondary alcohol oxidation
the OH loses the H
H under the carbon leaves
double bond is formed
what group cannot oxidize?
tertiary alcohols
what is the product of two thiols being oxidized?
disulfides
the H’s are removed from the SH’s to make a H2O
carboxylic acid is a acid or base?
weak acid
H+ donor
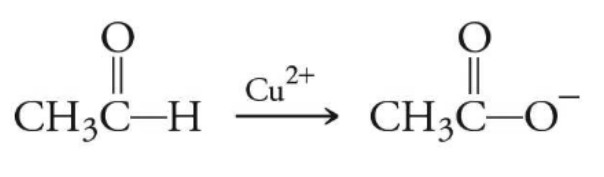
identify the reaction type
benedicts reagent oxidation
only affecting an aldehydes, not primary/secondary alcs
uses copper (Cu2+)
which type of reaction involves using copper as the oxidizing agent (on the arrow in the reaction)?
benedicts reagent
“benedict took some copper”
which type of reaction only effects aldehydes, and not alcohols?
benedicts reagent
describe what happens during benedicts reagent reaction
the H that is attaches to the C or the carboxylic acid of an aldehyde turns into an O-
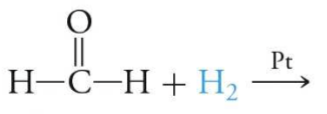
what’s the product of the following reaction?
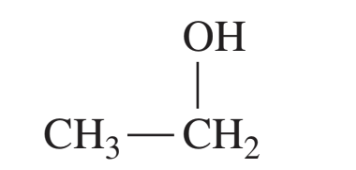
what is the relative boiling points of caboxylic acids?
relatively high
they have H bonds
how do carboxylic acids act in water?
weak acids
acids = H+ donors
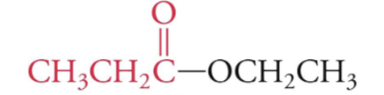
identify the fxn group
ester
C-O-C linkage where one carbon is a carbonyl (C=O)
what functional group has C-O-C linkage and one carbon has a carbonyl (C=O) group?
esters
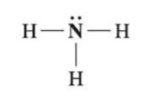
identify the fxn group
amine (ammonia)
has NH3
how are amines classified?
primary = 1 carbon directly attached to nitrogen
secondary = 2 carbon directly attached to nitrogen
tertiary = 3 carbon directly attached to nitrogen
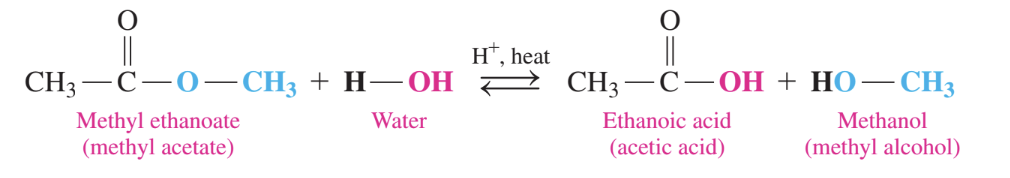
identify the reaction type
acid hydrolysis
there is an ester reacting with H+ and heat
think of it as HOH
what is different for an amine that is quarternary?
the nitrogen has a +1 charge
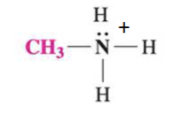
classify the following amine
quarternary
N has +1 charge
whats the ending for naming amines?
-amine
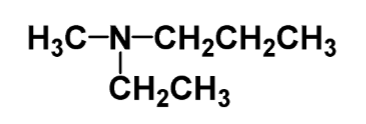
name the following
n-ethyl-n-methyl-ethanamine
what is a benzene ring with an amine on it called?
aniline
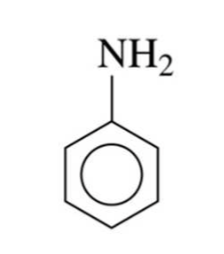
identify the fxn group
aniline
there is a benzene ring with an amine
which amines can hydrogen bond?
primary and secondary
which type of amines have the highest boiling points?
primary, seconday, and tertiary
what happens when an amine has more than 6 carbons?
decreased solubility
basically eliminates the effect of hydrogen bonding
what are amines when in a reaction?
weak bases
so they accept H+
describe an amide.
carboxylic acid group
instead of -OH, there -NH2