Anaerobic fermentation & Photosynthesis
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
missed stuff
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
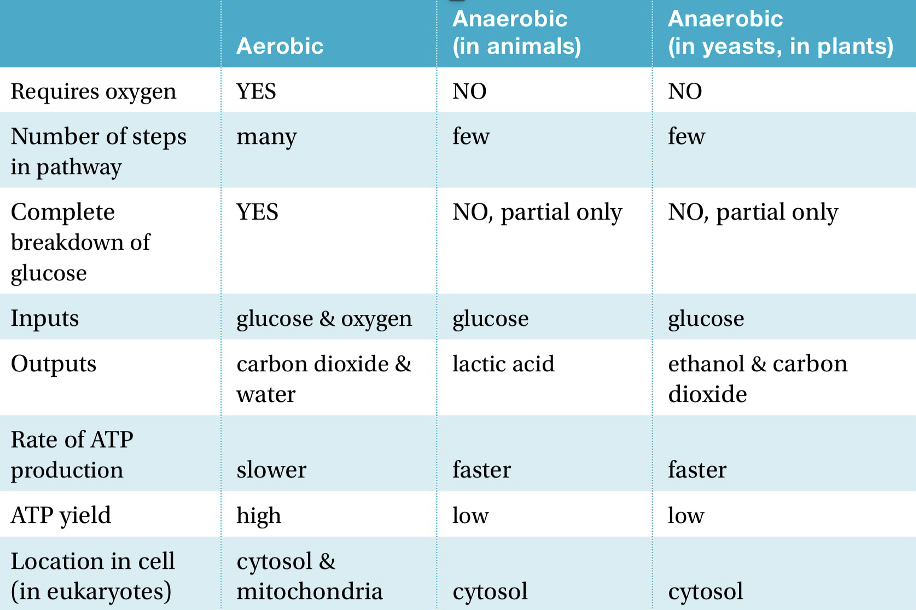
Anaerobic vs Aerobic
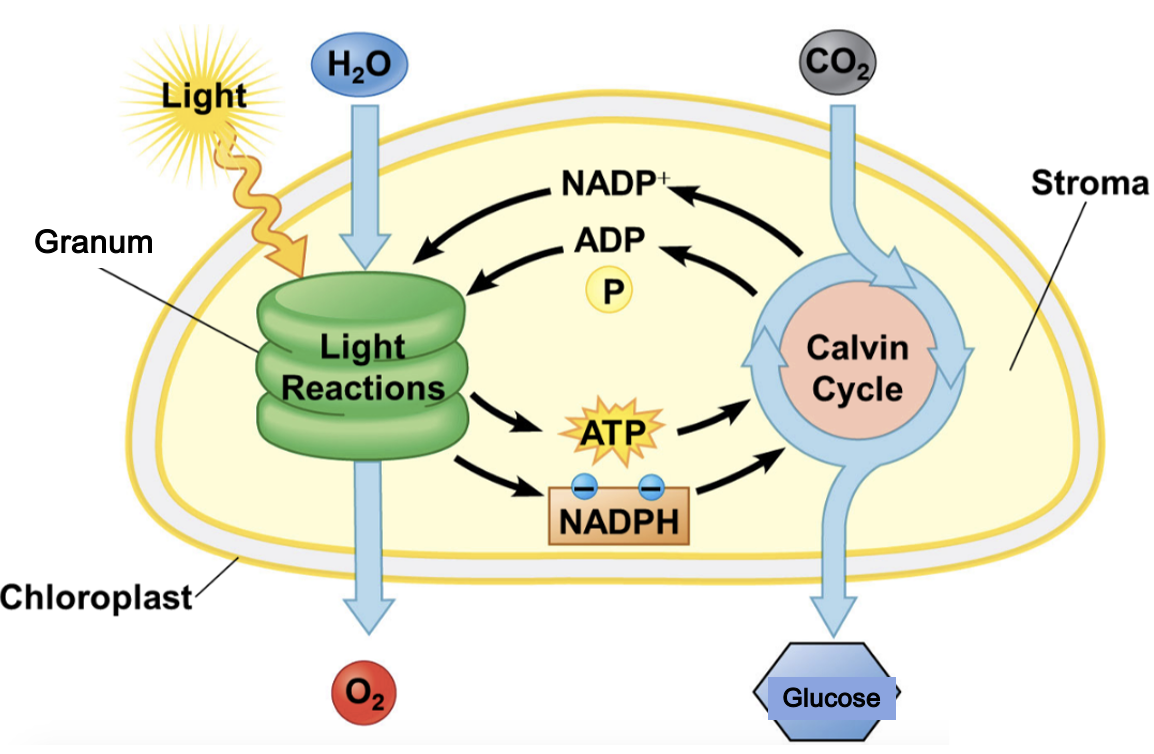
Photosynthesis
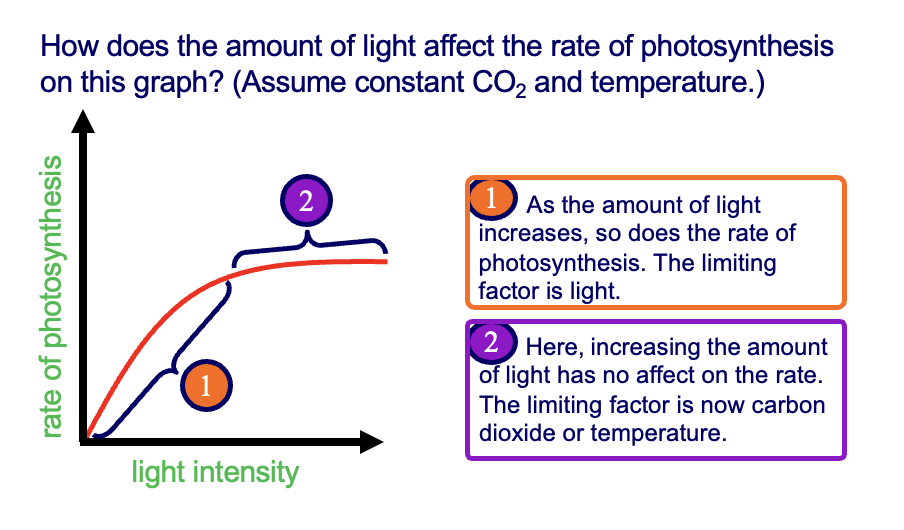
effect of light intensity
CO2 concentration
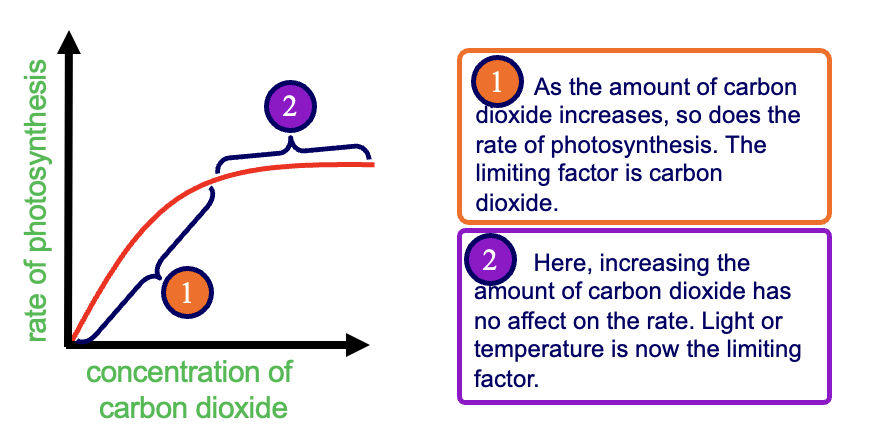
temperature
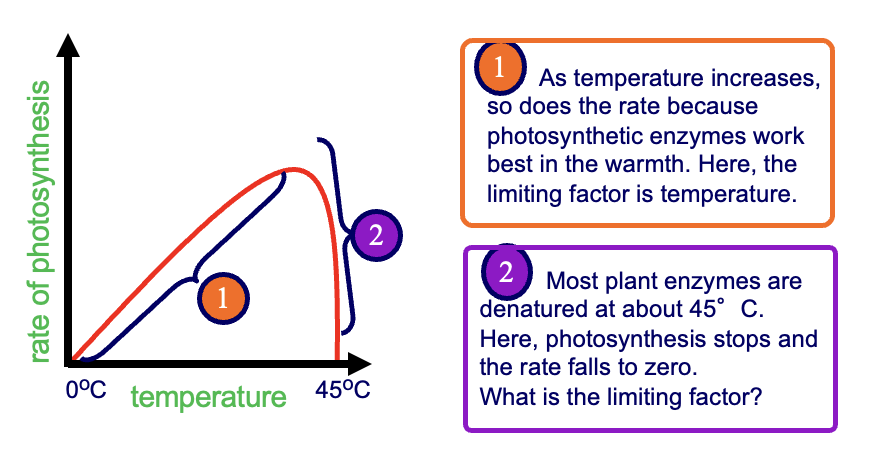
effect of water availability
source of water is the soil in which the plants are growing
uptake of water depends on an efficient root system
live cell that are respiring
branching roots/root hairs to max surface area
water is lost from the leaves through the stomata, when the stomata are open
water deficit
when water lost from leaves is greater than the uptake of water
plants closes stomata
reduces uptake of CO2 into the leaves
CO2 levels within the mesophyll cells falls
calvin cycle reduced/stopped
water logging
when more rain falls that the plant can absorb
air spaces surrounding the roots gets filled with water
oxygen availability to the roots is limited
root cells are not able to respire
root cells can become permanently damaged
water uptake fro the leaves reduced
photolysis reduced/stopped
do plants intake oxygen?
However, plants also require oxygen for their respiration process. They take in oxygen through small openings in their leaves called stomata, especially at night when photosynthesis does not occur.
limiting factors
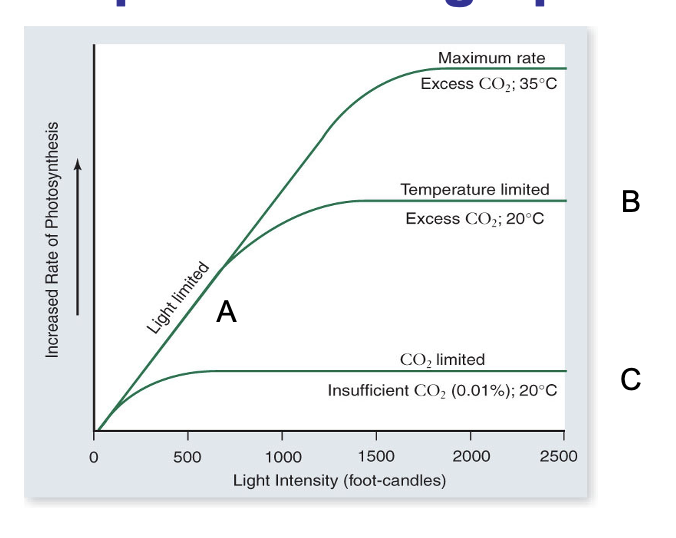
why is water not a limiting factor?
Cus they have a lot of water in the plant already
But lack of water → stomata close (to reduce the loss of water) → not getting CO2 → rate of photosynthesis
Too much water → roots can’t respire anymore
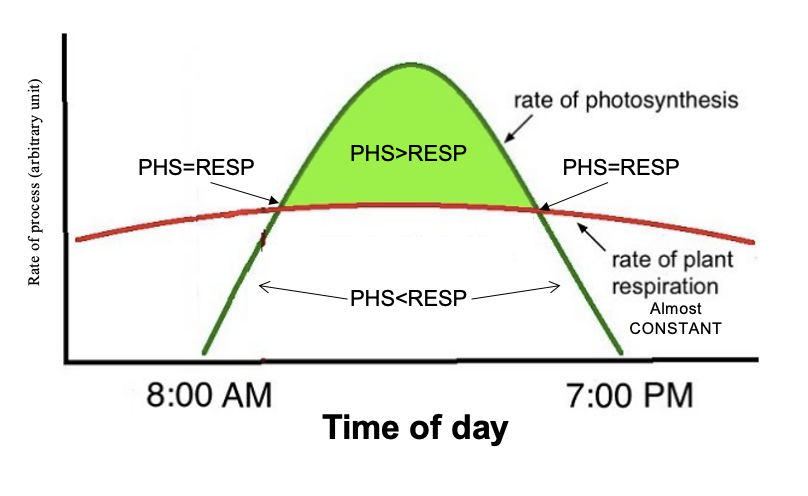
Compensation point
When PHS = RESP
Below - using more O2 than produced - decrease in O2 levels
Above - O2 level increasing (more PHS than RESP) - CO2 levels decrease
Below = decrease mass change
Compensation point = no mass change
Above = increase in mass (photosynthesis)