Unit 1 Ana/Phys Key Terms
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Nucleolus
Dense, spherical structure made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
Area where ribosomes are assembled
Helps regulate the cell cycle
Golgi Apparatus
Membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells made up of flattened sacs (cisternae)
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins + lipids received by the ER
Packages into vesicles for transport
Lysosome
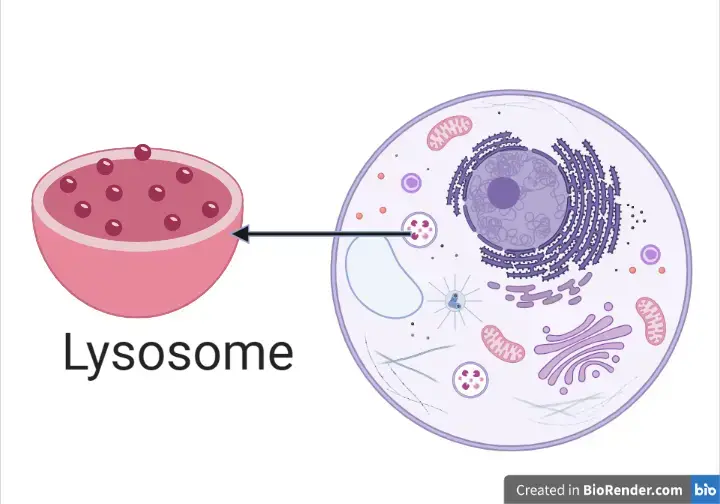
Membrane-bound organelle filled with digestive enzymes that break down waste, cellular debris, and foreign substances
Helps break down substances, destroy invaders, and remove damaged organelles
Can trigger apoptosis
Peroxisomes
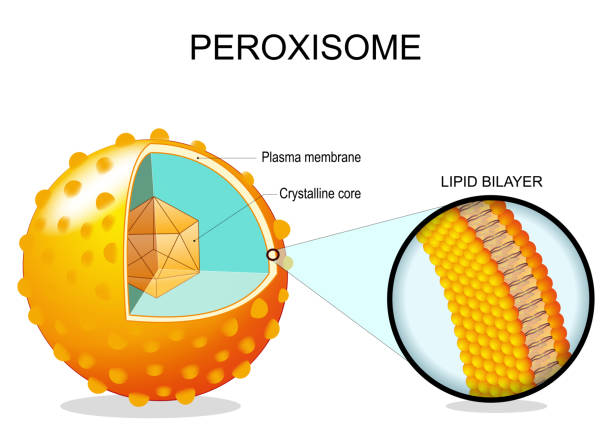
Small, membrane-bound organelle containing enzymes (oxidases and catalase) to break down toxic substances
Metabolizes fat
Helps break down harmful substances and detoxification
Microtubules
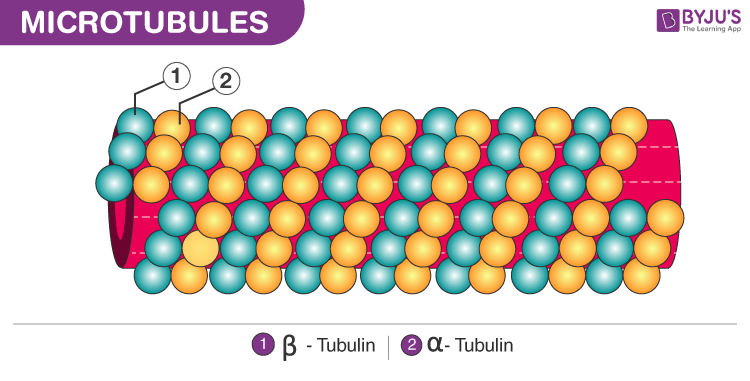
Hollow, cylindrical structures made up of the protein tubulin
Part of the cytoskeleton, giving the cell its shape and framework
Also important in intracellular transport, cell division, and movement
Microfilaments
Thin, solid protein fibers made up of actin
Part of the cytoskeleton, helping maintain the cell’s shape
Assist in endocytosis + exocytosis
Forms the ring that splits the cell apart during cytokinesis
Intermediate filaments
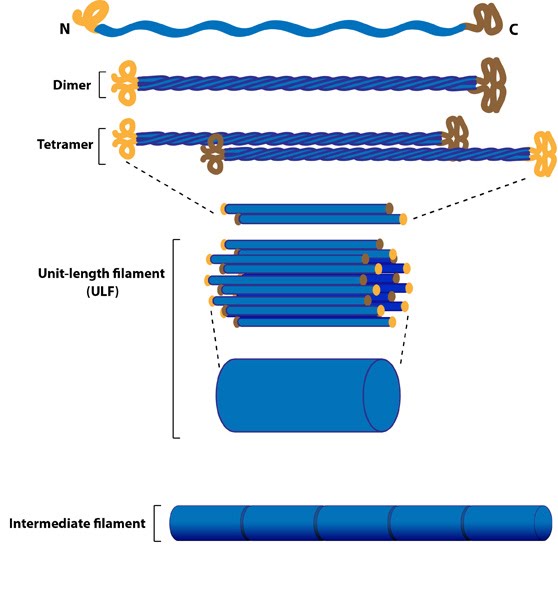
Rope-like protein fibers that provide mechanical strength and structural stability to cells
Important in the formation of cell junctions (especially desmosomes)
Help resist tension, preventing cells from being ripped apart
Centrioles
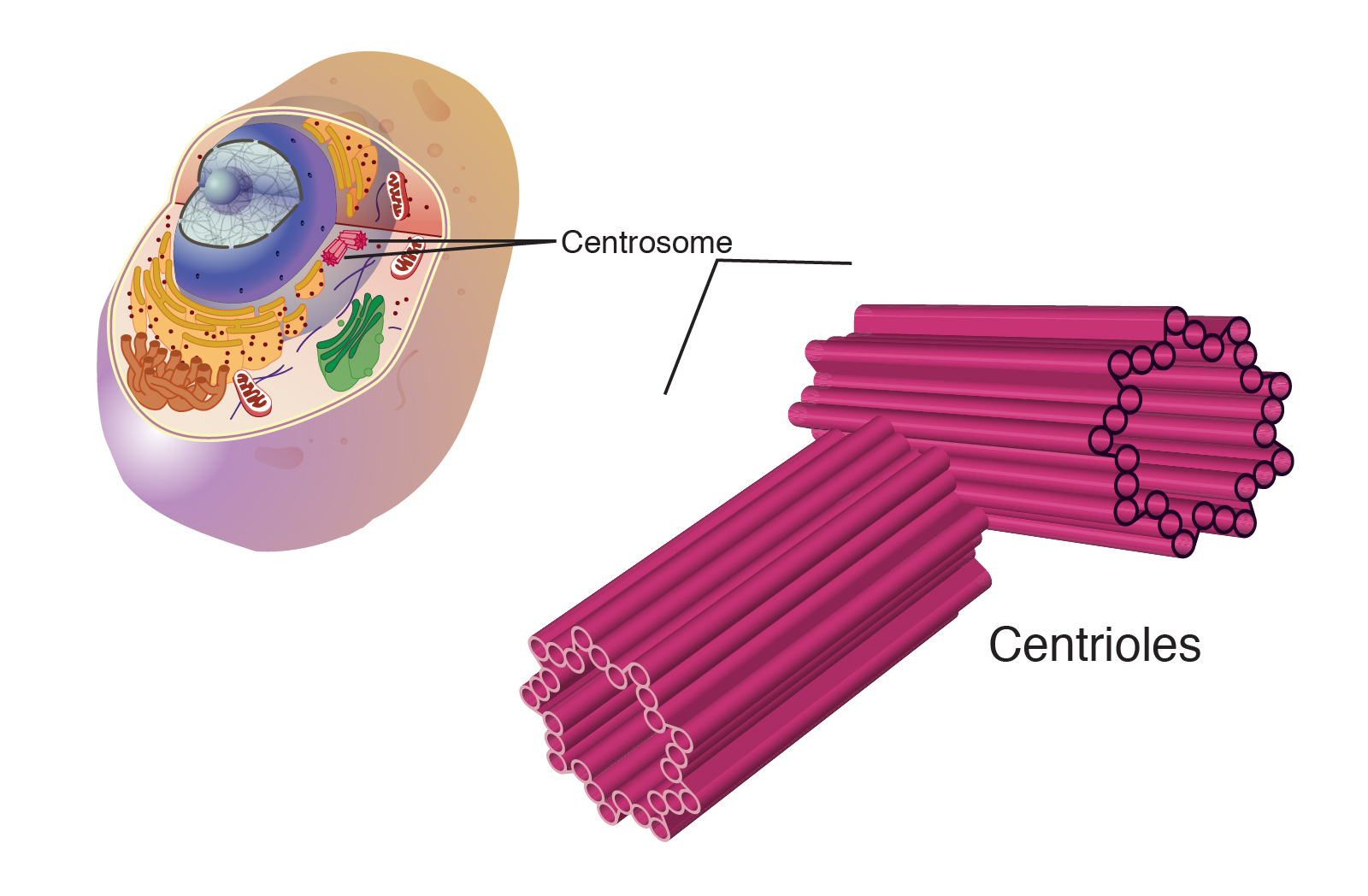
Small, cylindrical structures made up of microtubule
Found in pairs in the centrosome of animal cells
Help organize microtubules in mitotic spindle during mitosis
Helps form cilia and flagella
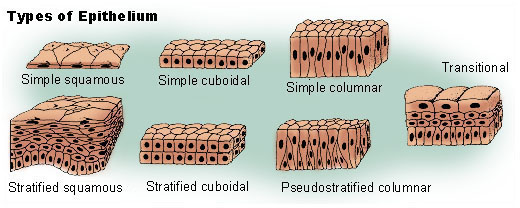
Characteristics of Epithelium
Cells fit closely together and bounded by tight junctions + desmosomes
Cell surface is exposed
Cells are anchored to basement membrane, which holds them like glue
Cells have no blood supply (avascular) - rely on underlying tissue for nutrients + blood
Simple squamous epithelia
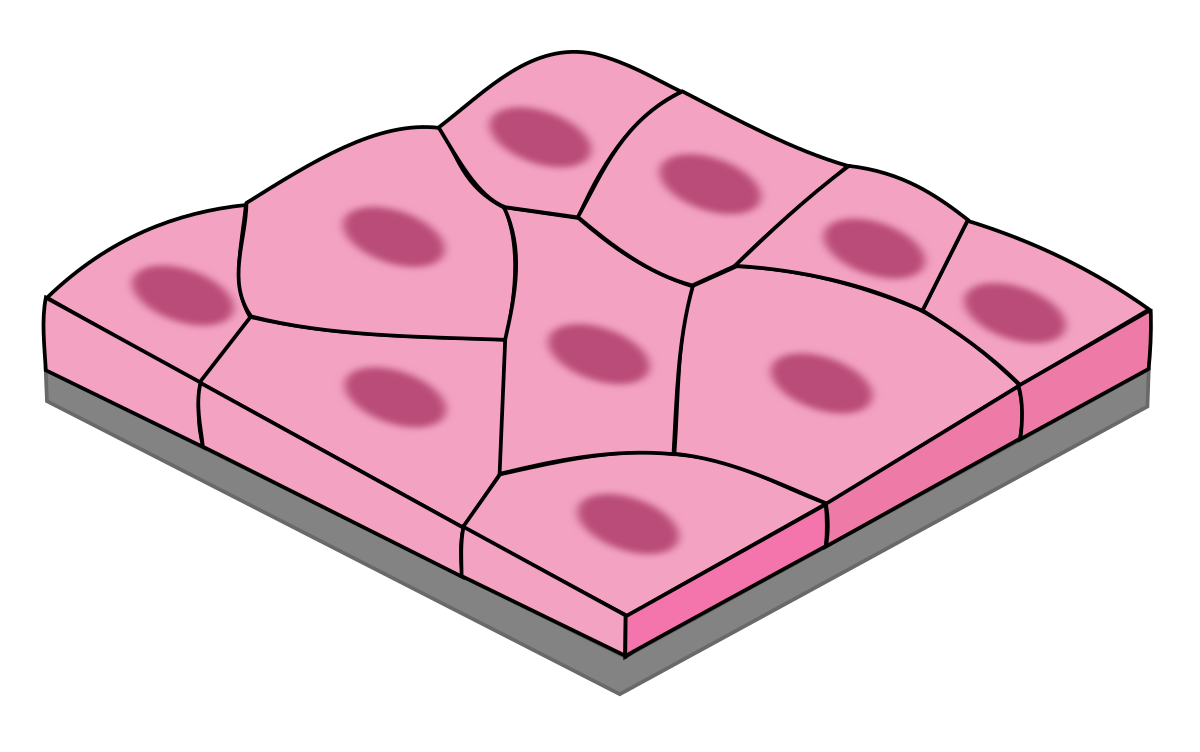
Single layer of flat, thin cells with centrally located nuclei
Allows for rapid diffusion, filtration, and exchange of materials
Found in lungs and kidneys
Also secretes in serious membranes as well
Stratified squamous epithelia
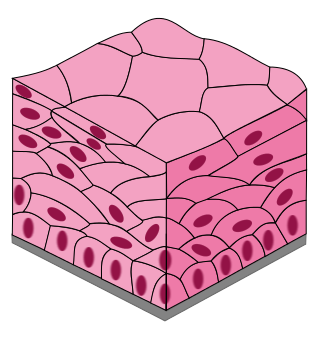
Multiple layers of cells, with topmost layer flat (squamous) while deeper layers can be cuboidal or columnar
Most common stratified epithelium
Provides protection against friction and abrasion
Lines surface of skin, mouth, and esophagus
Simple cuboidal epithelia
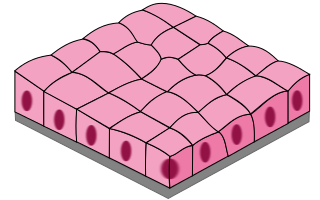
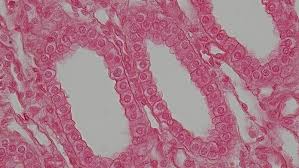
Single layer of cube-shaped cells with centrally located nuclei
Specializes in absorption and secretion
Common in glands and ducts (salivary glands, sweat glands and pancreas)
Simple columnar epithelia
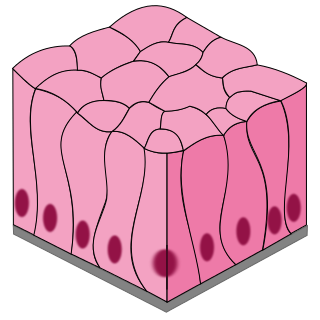
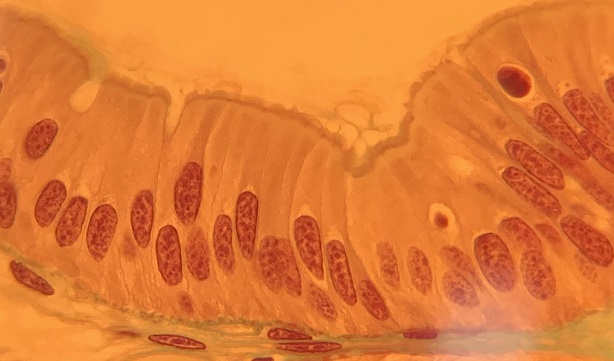
Single layer of tall, rectangular (column-shaped) cells with nuclei located near base of cell
Specializes in secretion, absorption, and protection
Found through the digestive tracts and includes goblet cells (produce mucus)
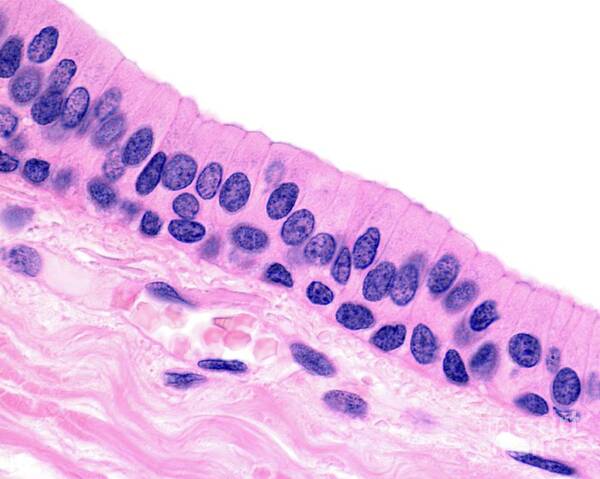
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia
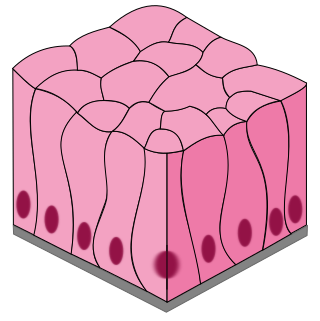
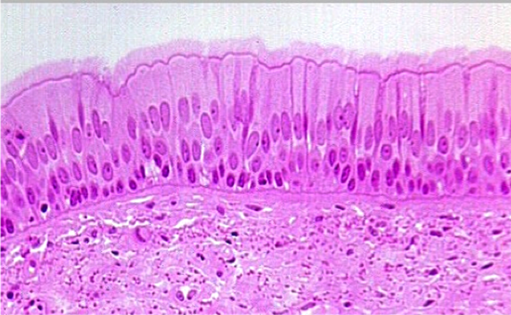
Single layer of columnar cells that appears multilayered b/c nuclei are at varying heights, but every cell touches basement membrane
Specializes in secretion and movement of mucus
Found in respiratory tracts (trachea, bronchi)
Has goblet cells (produces mucus) and cilia (moves mucus)
Stratified cuboidal epithelia
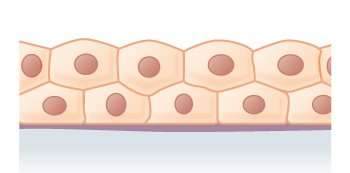
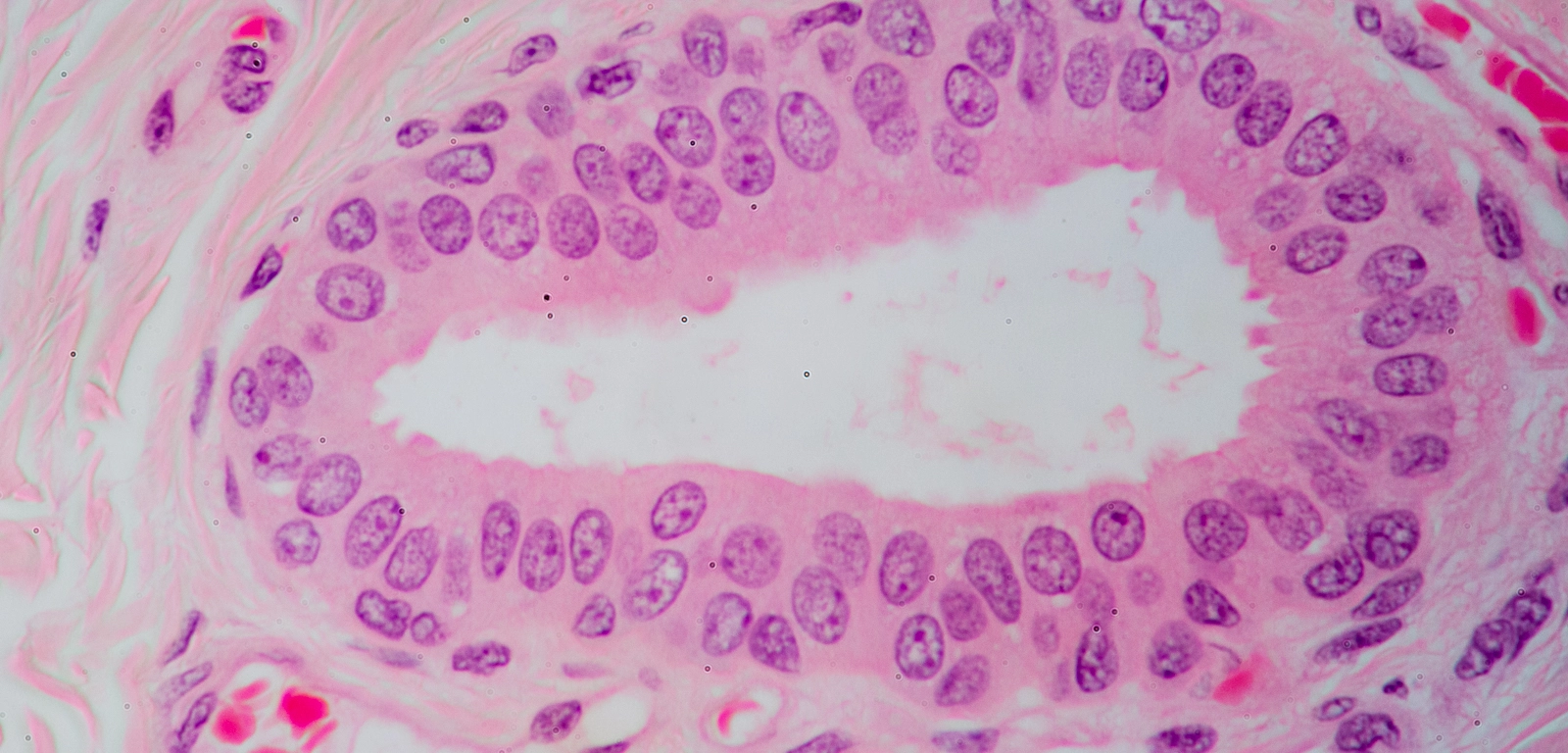
Multiple layers of cube-shaped cells, top layer is cuboidal
Provides protection and some secretion
Found in ducts of swear glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands
Not common
Stratified columnar epithelia
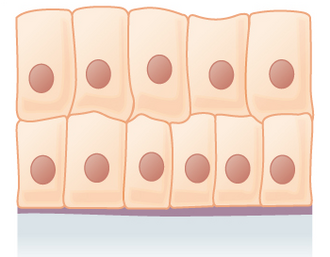
Multiple layers of cube-shaped cells; top layer is columnar (lower layers can be cuboidal)
Provides protection and some secretion
Found in lining of large ducts in large glands (salivary glands, parts of male urethra)
Not common
Bone/Osseous (Connective Tissue)
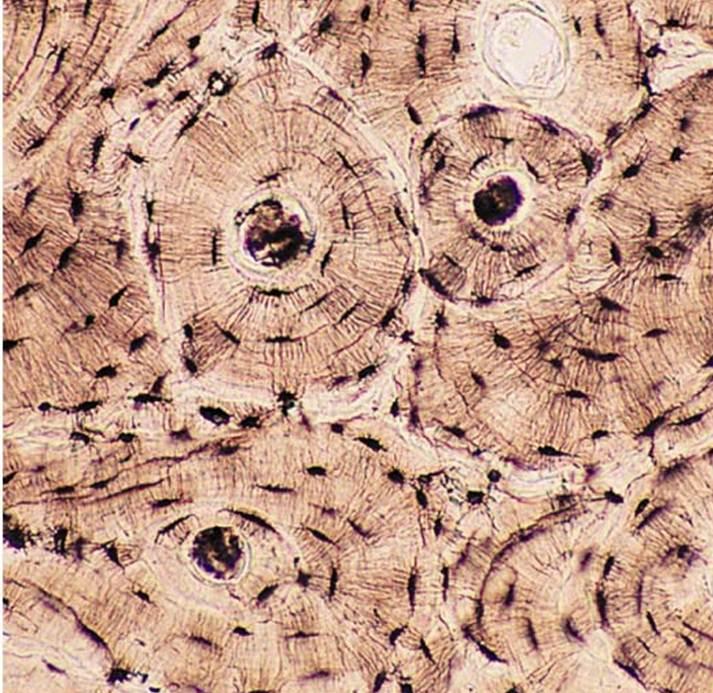
Connective tissue that provides structural support and protection for body
Can be soft or hard
Osteocytes found within cavities (lacunae)
Lacunae surrounded by hardened matrix (due to calcium salts) with large amount of collagen fibers
Cartilage (Connective Tissue)
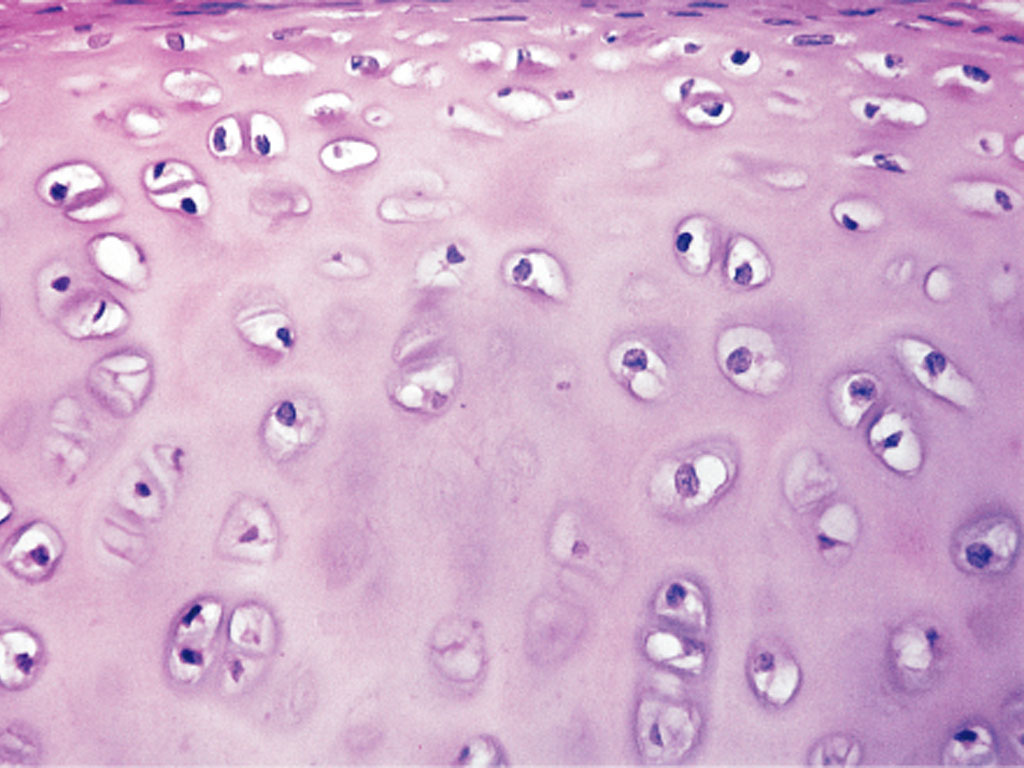
Flexible, semi-rigid connective tissue providing support and cushioning of body
Chondrocytes found within cavities (lacunae)
Types of cartilage depends on protein fibers/density of matrix
Three types: hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
Dense/Fibrous (Connective Tissue)
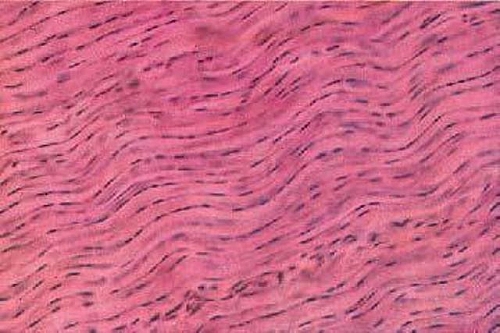
Connective tissue with high density of collagen fibers, making it strong and resistant to stretching
Fibroblasts (cells) produce collagen fibers
Forms tendons and ligaments
Areolar/loose (Connective Tissue)
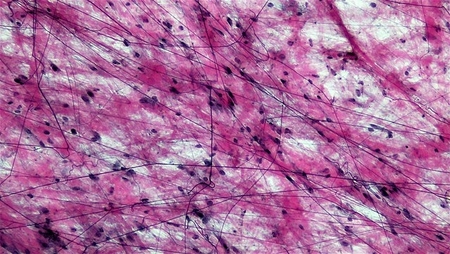
Loosely organized connective tissue with cells (fibroblast. macrophage), fibers, and ground substances that fills space and cushions organs
Provides flexible support, cushioning, and diffusion of nutrients/waste
Rich in nutrients and blood vessels
Most common connective tissue
Adipose (Connective Tissue)
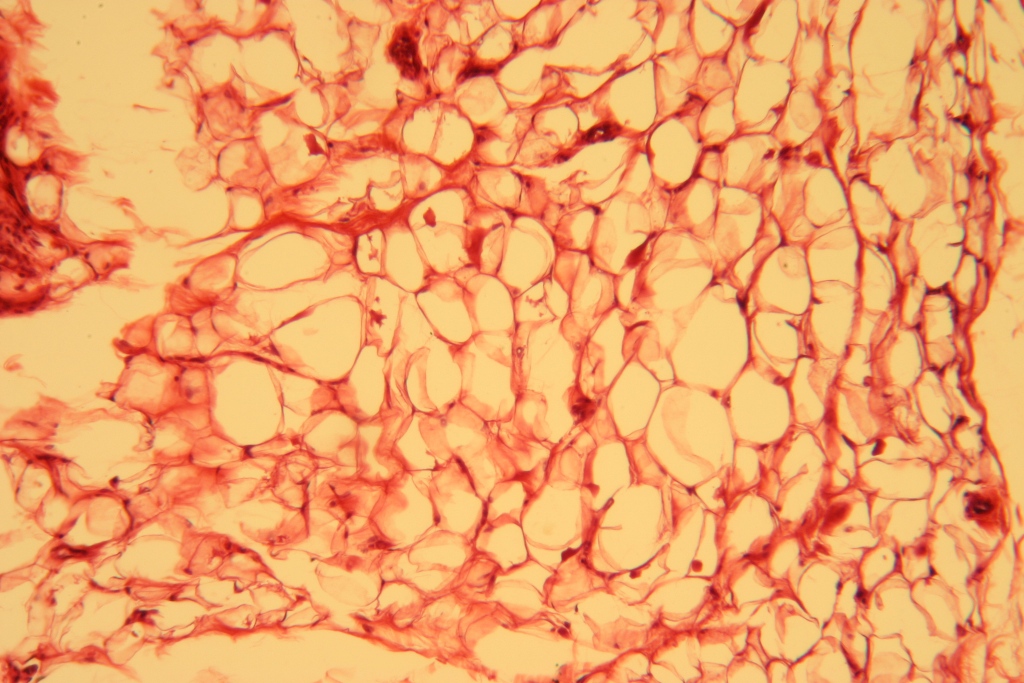
Type of connective tissue specialized for storing lipids and energy storage, cushioning, and insulation
Adipocytes (fat cells) found within matrix
Found in subcutaneous layers beneath skin and around major organs (hearts and kidneys)
Secretes leptin (hormone) to regulate appetite
Reticular (Connective Tissue)
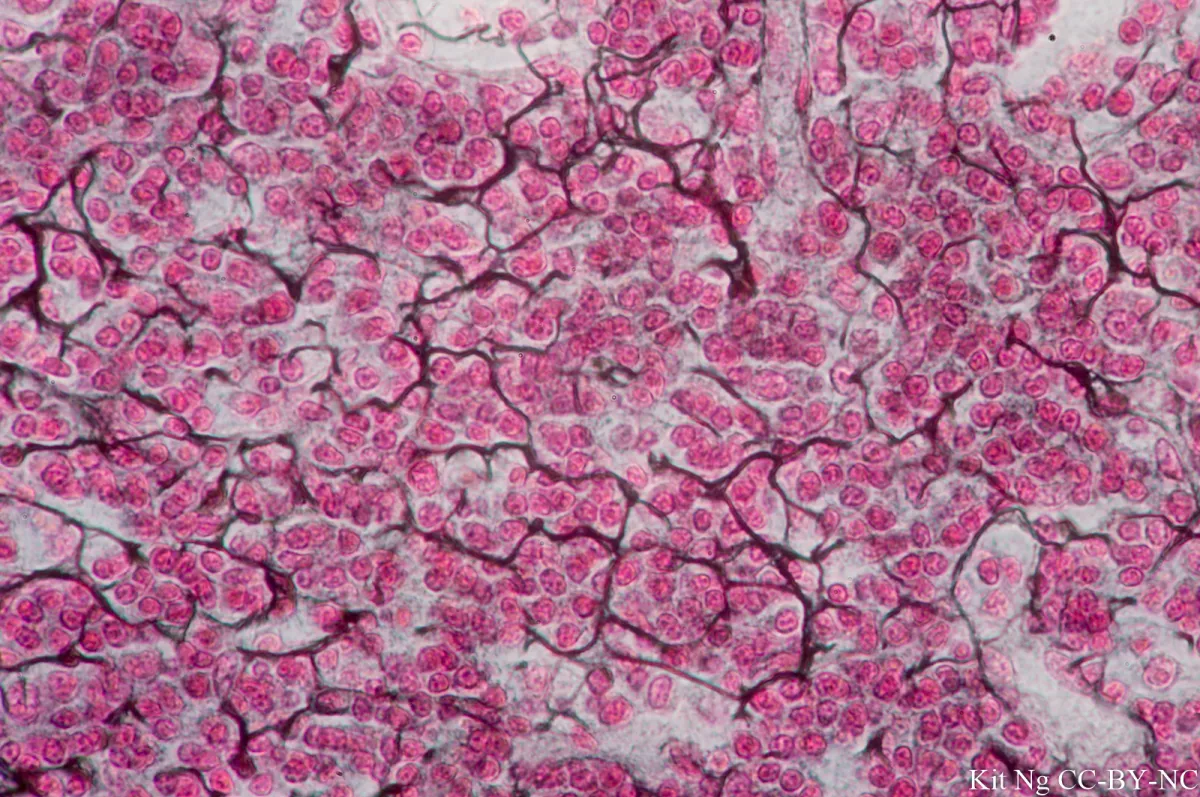
Delicate network of reticular fibers, providing support and framework for soft organs
Reticular cells produce reticular fibers which form web-like network within hollow organs
Found in lymph tissues, spleen, kidney, liver, and pancreas
Vascular Tissue (Blood)
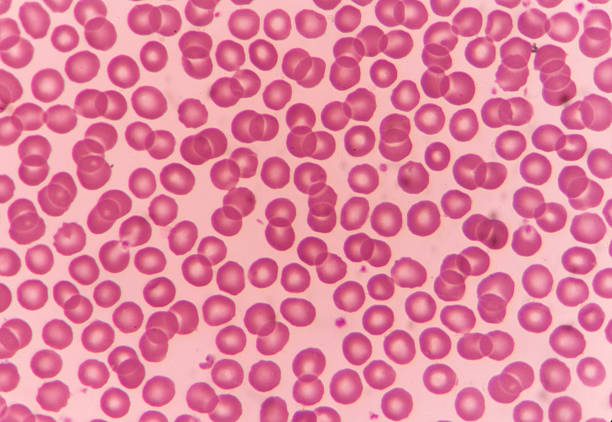
Connective tissue specialized for transporting fluids, nutrients, gases and wastes throughout body
Blood cells found within fluid matrix (plasma)
Red blood cells (oxygen) and white blood cells (defense)
Lymph Tissue
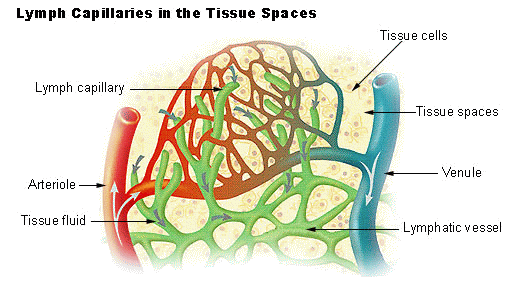
Connective tissue specialized in immune cell activation, proliferation, and filtration of pathogens
Contains no red blood cells. White blood cells are in a fluid matrix (lymph)
Found in spleen, tonsils, thymus, and lymph node
Part of the immune (lymphatic) system
Skeletal Muscle (Tissue)
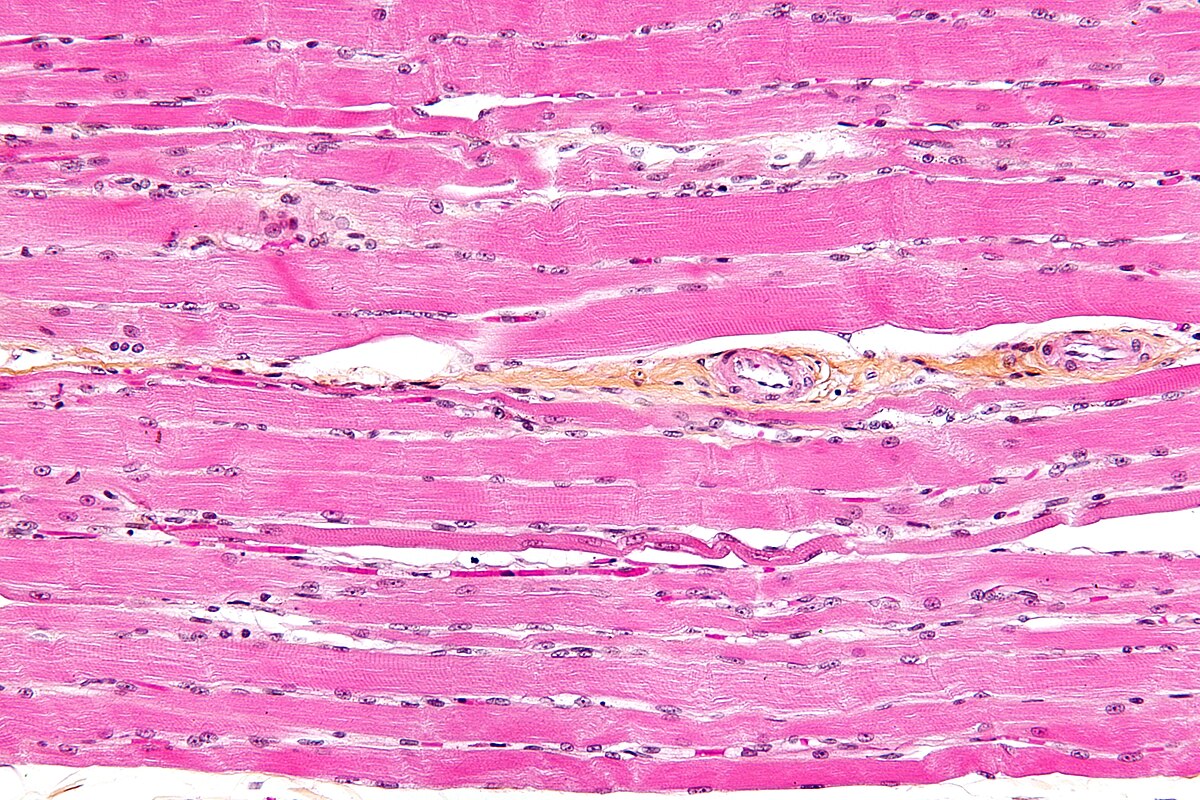
Voluntary, striated muscle tissue attached to bones for movement
Cells are long, cylindrical, and multinucleated
Contains protein fibers (actin and myosin) that form the vertical “striations” within muscle tissue
Forms Muscular System
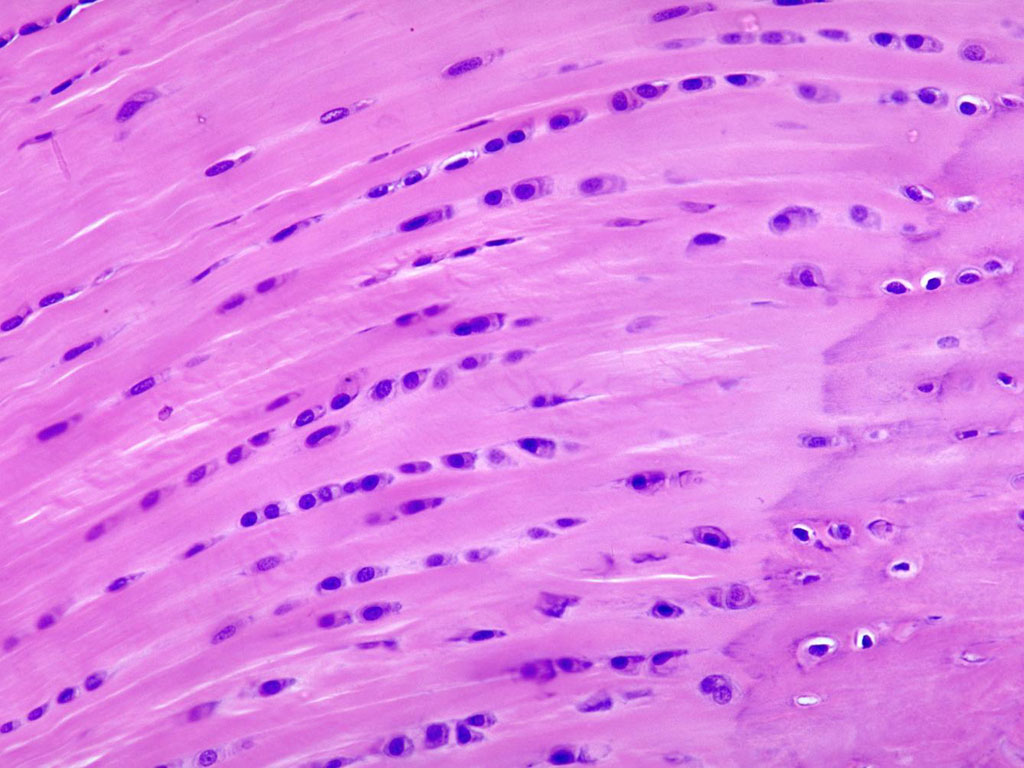
Cardiac Muscle (Tissue)
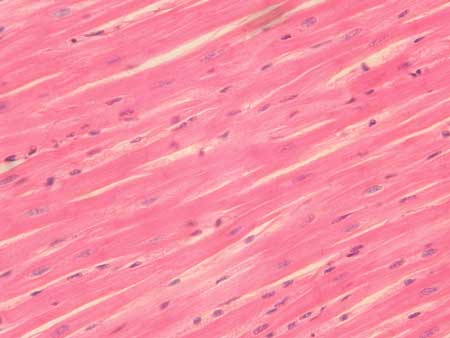
Involuntary muscle tissue that is striated and found only in the wall of heart
Short cells that have a single nucleus and branch
Cells fit tightly together through junctions (intercalated discs) that allow free movement of ions between cells
Contracts rhythmically to pump blood
Smooth Muscle (Tissue)
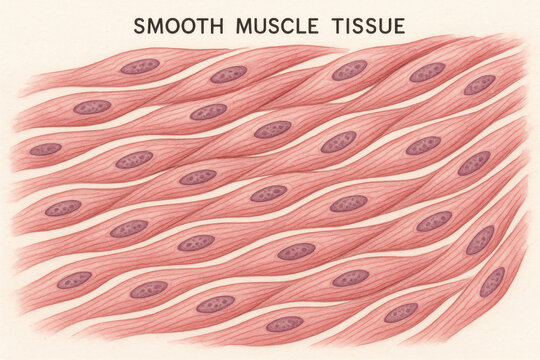
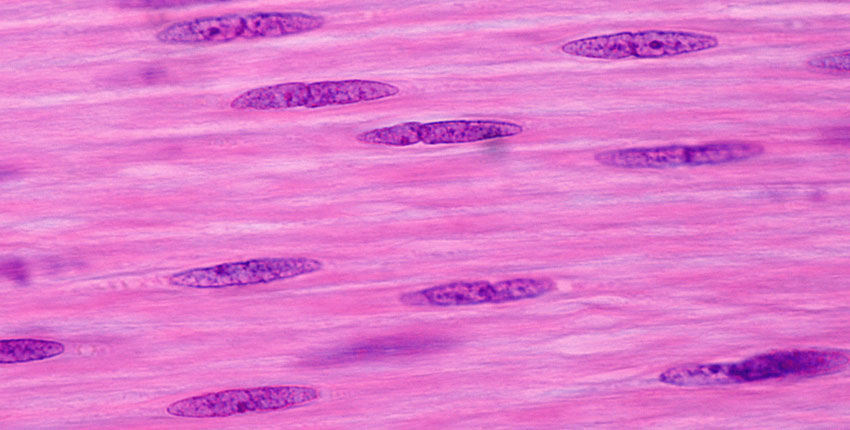
Muscle tissue that has no striations and is responsible for involuntary muscle control
Causes constriction or dilation of organs
Found in walls of hollow organs (stomach, blood vessels (arteries + veins), intestines, and uterus)
Cells have a single nucleus and are tapered at each end
Nervous Tissue
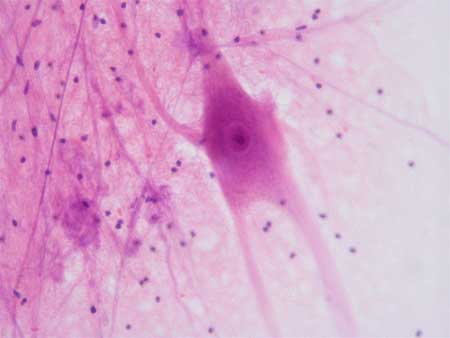
Tissue specialized to produce, conduct, and received electrical impulses
Cells are long and large (neurons)
Also contains neuroglia (glial cells) that support the neurons
Found in Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System
Osteocytes
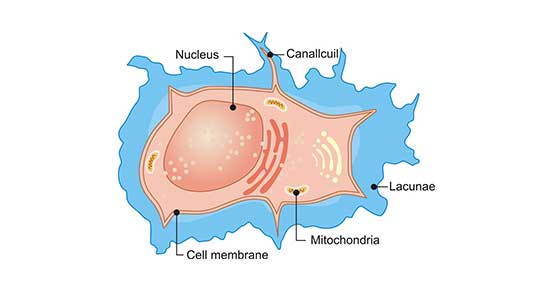
Mature bone cells that maintain bone matrix
Monitors and maintain mineral content of bone, helping repair bone damage
Found within lacunae in bone tissue
Lacunae
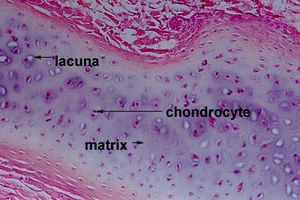
Small spaces/cavities within cartilage or bone tissue that house and protect cells
Protects chondrocytes in cartilage, osteocytes in bone
Allow cells to maintain extracellular matrix around them
Collagen
Most abundant protein in body, forming strong fibers in connective tissue
Gives strength and shape to tissues, resists stretching forces, and supports skins, bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and organs
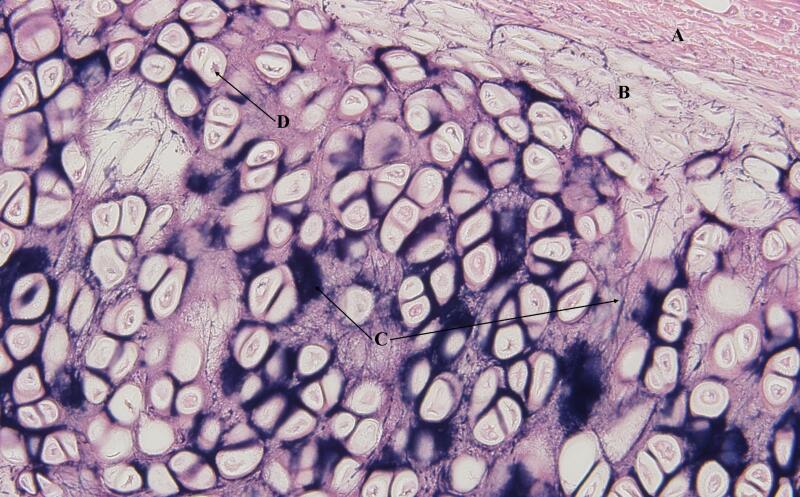
Chondrocytes
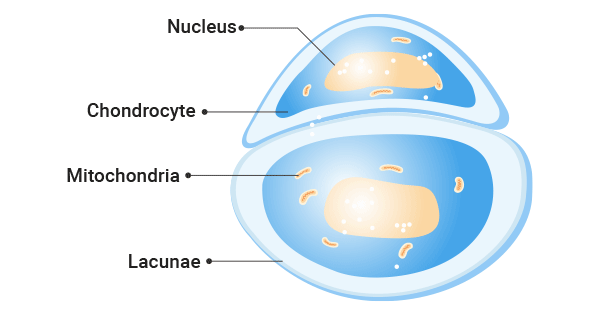
Mature cartilage cells that maintain and produce cartilage extracellular matrix (fibers and ground substances)
Produces collagen for cartilage structure
Maintains health of cartilage tissue
Found in cartilage tissue
Hyaline cartilage
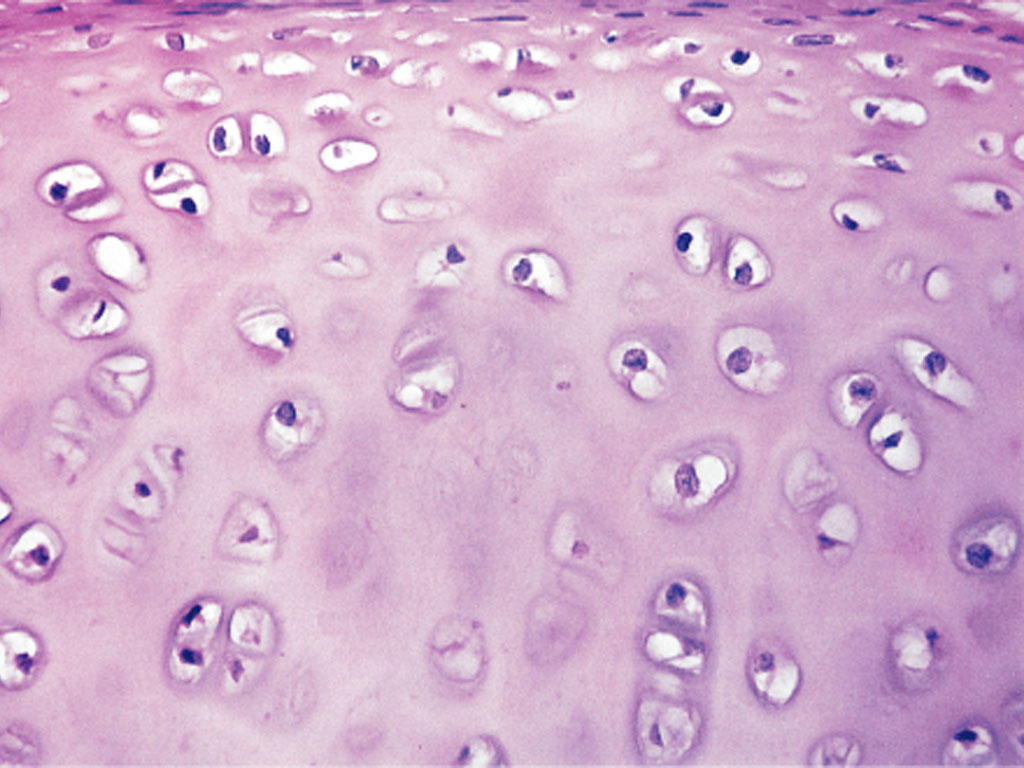
Most common type of cartilage, with glossy, smooth matrix made up of collagen
Provides flexible support, smoother surfaces for joint movement, and growth of bones
Found in nose, trachea, bronchi, and larynx
Fibrocartilage
Type of cartilage that is very tough and durable, containing thick bundles of collagen fibers
Provides strong support + absorbs force
Found in discs between vertebrae, between pelvic bones
Elastic cartilage
Type of cartilage that is flexible and resilient
Contains dense network of elastic fibers + collagen fibers
Consists of chondrocytes housed in lacunae
Found in external ear, larynx, epiglottis
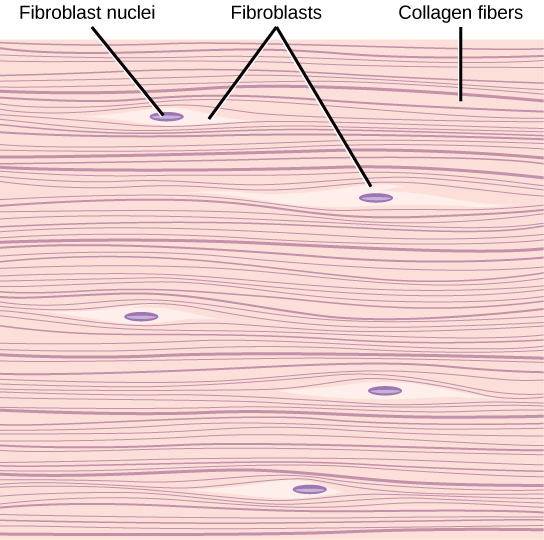
Fibroblasts
Type of connective tissue that produces and maintains extracellular matrix
Synthesizes fibers + ground substances (gel-like material between cells and fibers) that form framework of tissues
Creates fibers (collagen, elastic fibers, reticular, etc.)
Found every in connective tissues around body
Subcutaneous tissue
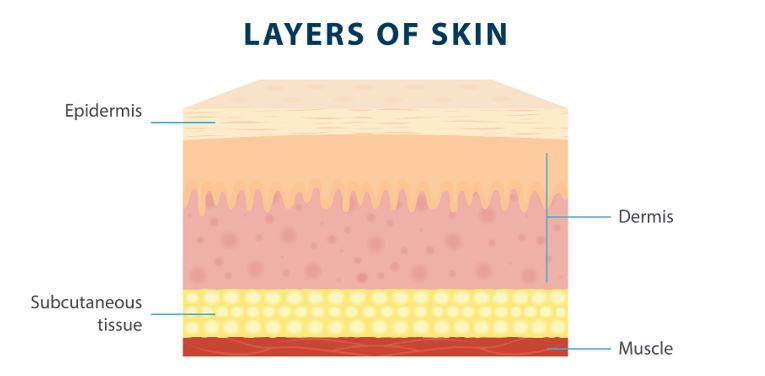
Layer of connective tissue and fat beneath dermis of skin
Consists of adipose tissue (fat), loose connective tissue, and fibrous bands
Helps maintains body temperature, protecting underlying muscles/organs/bones
Fat acts as reserve for energy
Reticular fibers
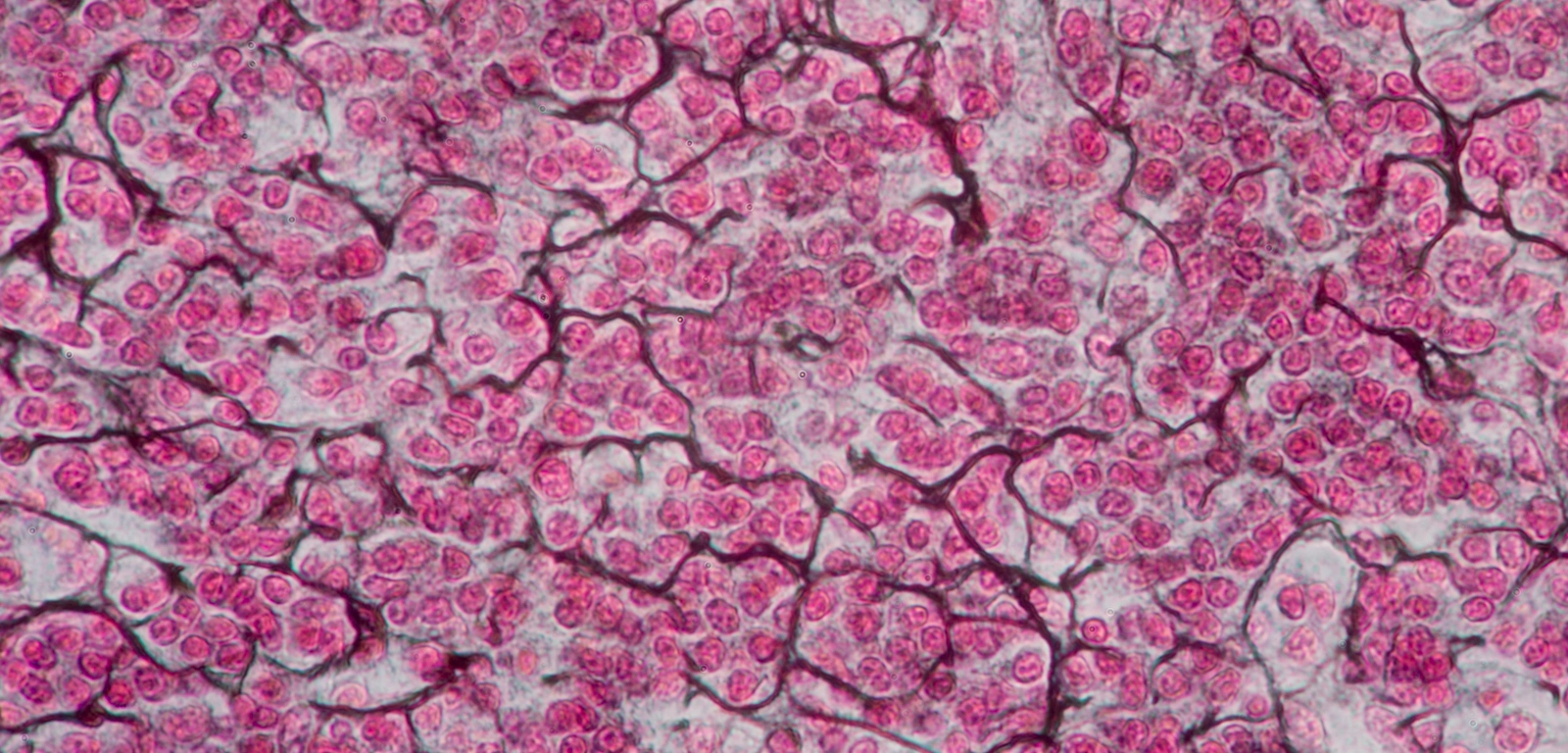
Thin, branching fibers of connective tissue made up of collagen to provide supportive network in soft tissues
Forms reticulum (network) rather than bundles
Support organs’ structures while allowing flexibility
Found in bone marrow, liver, pancreas, spleen
Myofibrils
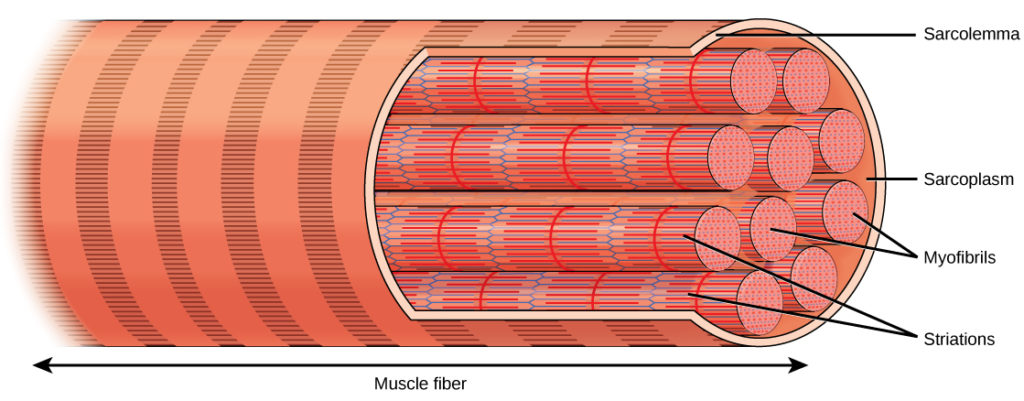
Long, cylindrical contractile structures inside muscle fibers
Responsible for muscle contraction
Generates force and movement by shortening during contraction
Neuroglia (Glial Cells)
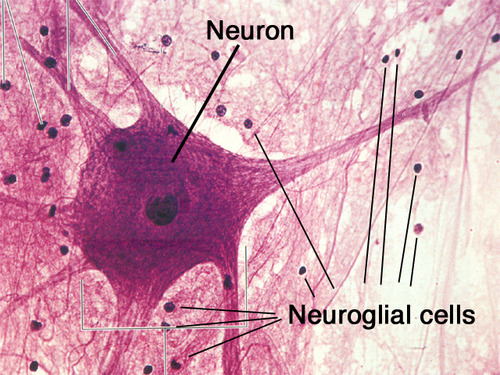
Supporting cells of nervous system
Do not conduct nerve impulse, but help neurons function
Maintains homeostasis, protects neurons, and assist in signal transmission
Globular proteins
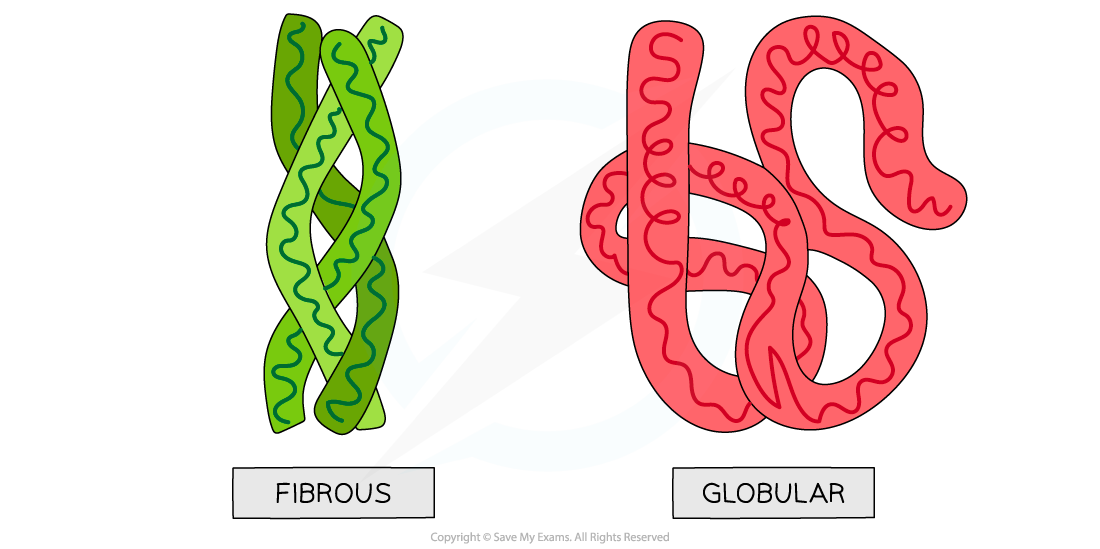
Proteins that are globular (spherical) in shape
Soluble in water
Helps in catalysis, transport, and regulation
Elastic fibers
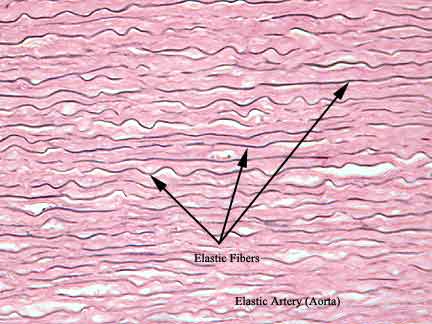
Fibers in connective tissue that are stretchable/flexible
Returns to original length after being stretched
Made up of elastin protein
Found in skin, lungs, blood vessels, ligaments
Tendon
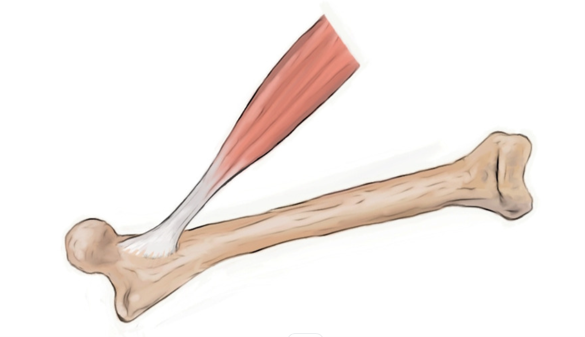
Tough, fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone
Composed of collagen fibers
Transmits force generated by muscles to move bones
Ligaments
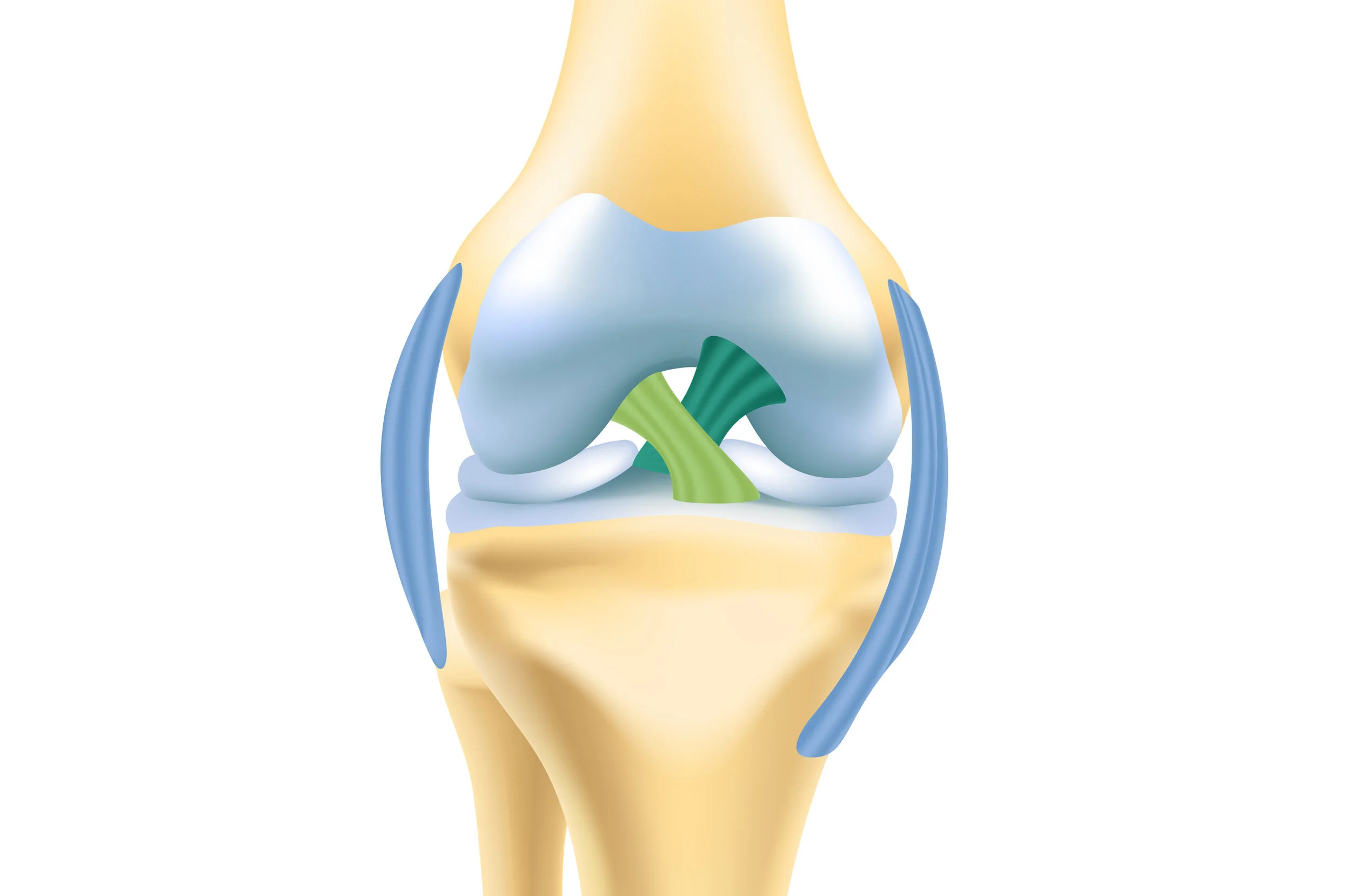
Tough, fibrous connective tissue that connects bone to bone at a joint
Provides stability to joints + prevents excessive movement
Composed of collagen fibers
Arteries
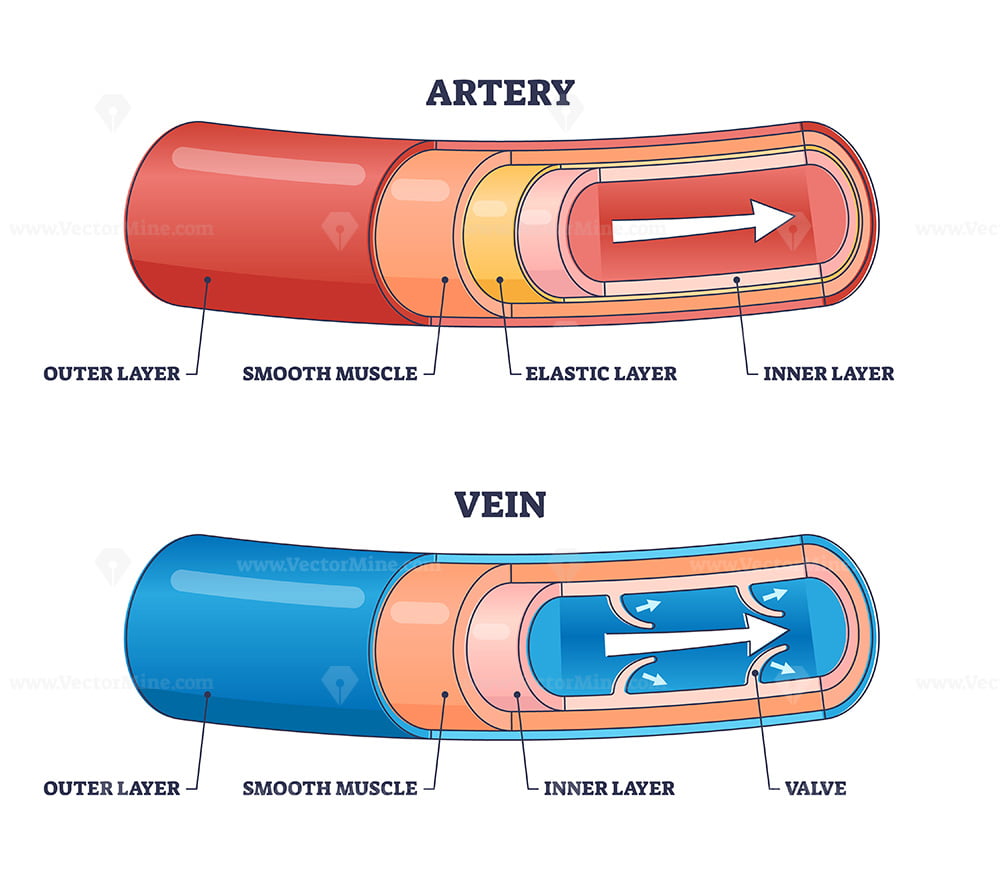
Blood vessels that carry blood away from heart
Thick, muscular, and elastic walls to handle high pressure from heart
Carry oxygen-rich blood
Distribute blood throughout body
Vein
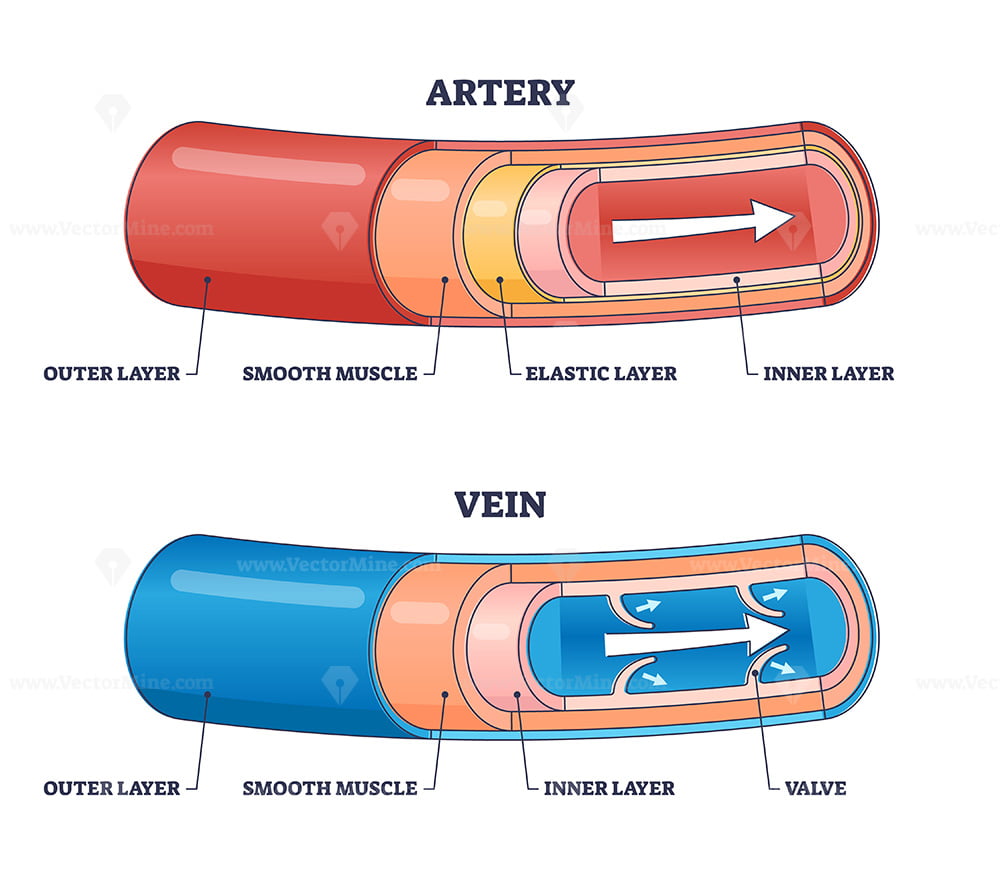
Blood vessels that carry blood toward heart
Thinner walls, less muscular
Carry oxygen-poor blood
Have valves to prevent backflow
Involuntary muscle tissue
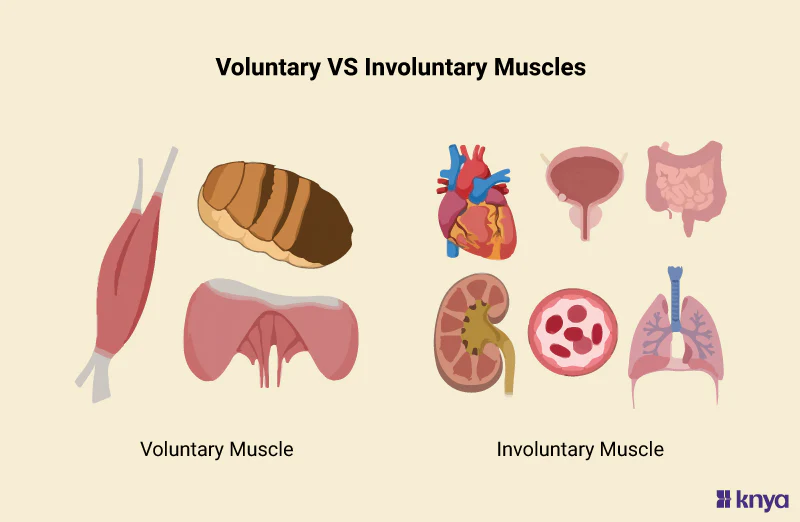
Muscle tissue that works automatically, w/o conscious control
Controls internal organ functions like heartbeat, digestion, and blood flow
Ex. walls of intestine, uterus, bladder walls, respiratory airways
Voluntary muscle tissue
Muscle tissue that you can consciously control
Striated, attached to bones via tendons, and responsible for body movement + posture
Ex. biceps, triceps, facial muscles, tongue
Striations
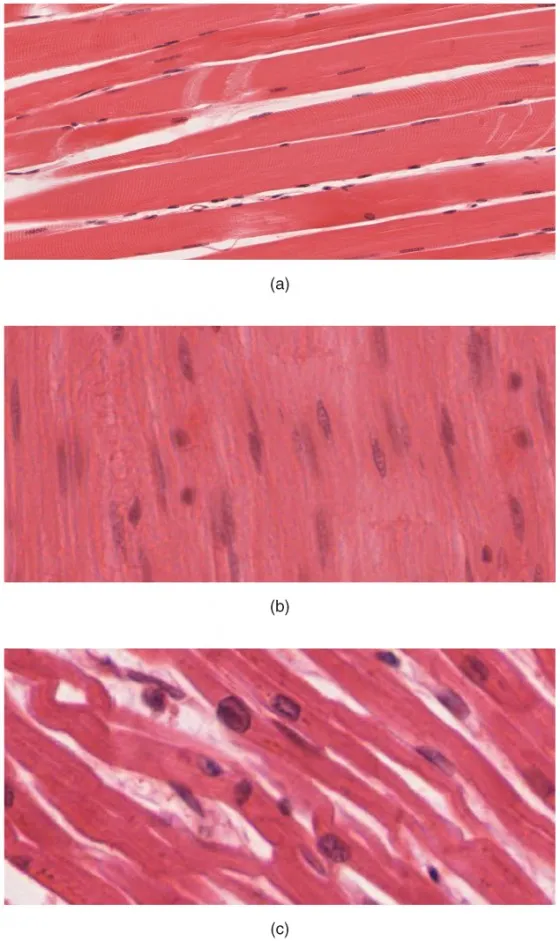
Alternating bands seen in certain types of muscle tissues
Due to arrangement of actin and myosin filaments within muscle fibers
Found in skeletal and cardiac muscle tissues (not in smooth muscle)
Intercalated disc
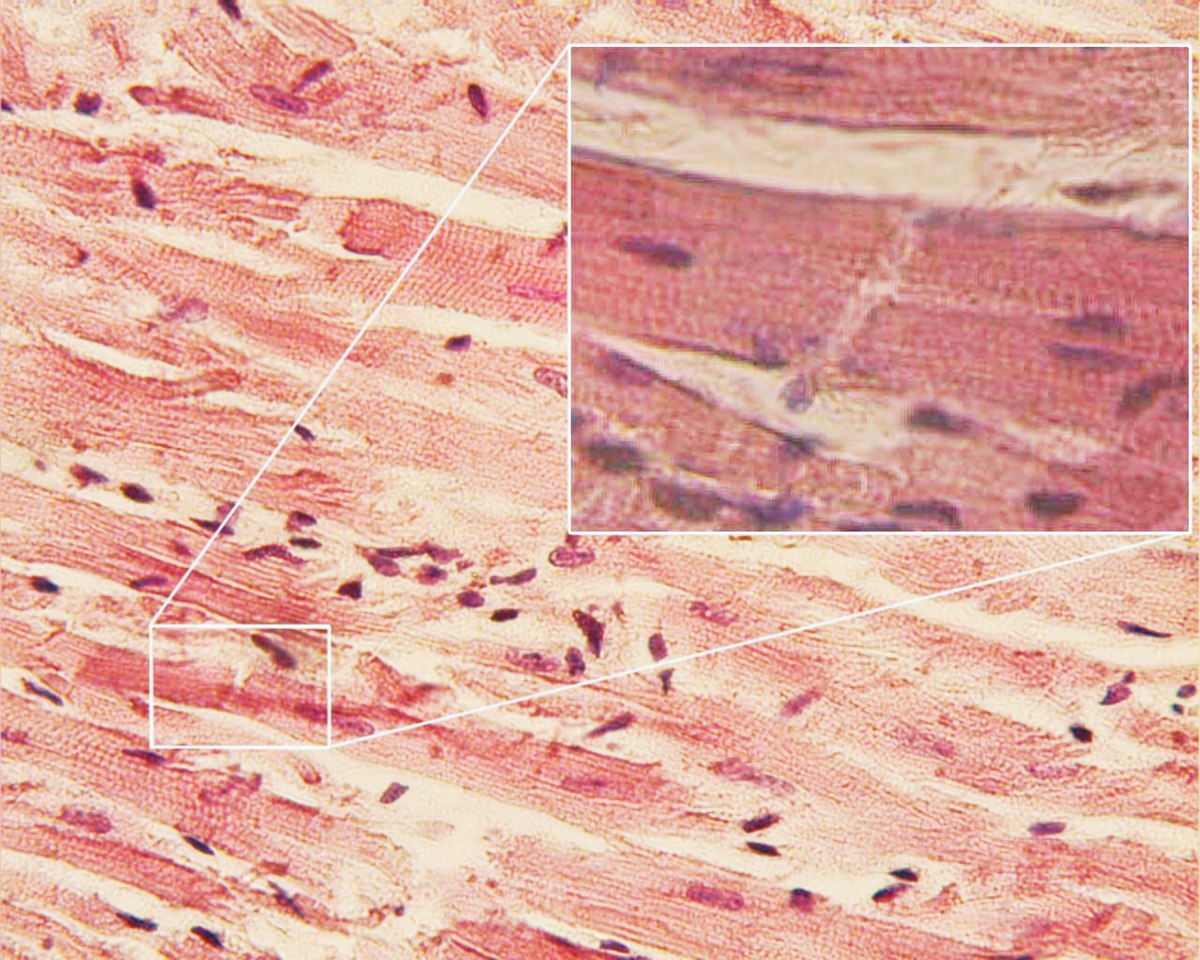
Specialized connections between cardiac muscle cells
Allows for heart to work as a coordinated unit
Keeps cardiac cells attached so they don’t pull apart during contraction, allowing for heart to beat
Found only in heart muscles
Goblet cells
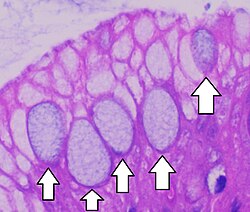
Cell that works by itself to produce mucus (Designed for one job only)
Releases secretion through duct or onto surface
Mucus traps dust, microbe, debris, and protects lining of organs
Found in trachea, bronchi, lining of intestines and stomach
Contractile Tissue
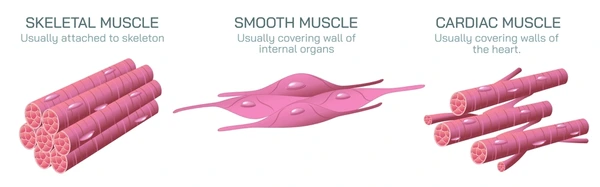
Tissue specialized to shorten (contract) and generate force, enabling movement
3 types: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Use actin and myosin filaments that slide past each other to shorten cell
Attached to bones, heart wall, walls of blood vessels + digestive tracts
Myosin
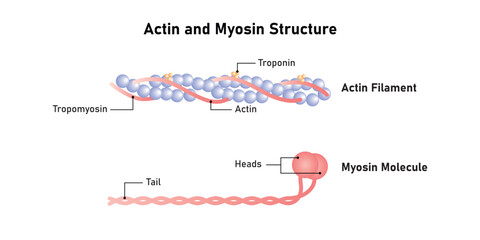
Thick filament protein function
Has a “head” region that binds to actin and uses ATP for energy
Works with actin to help with muscle contraction
Actin
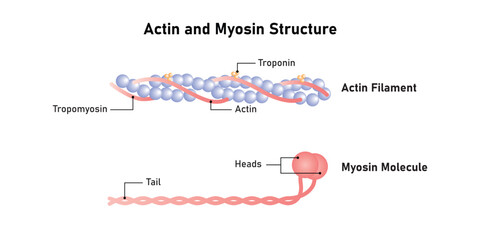
Thin filament protein found in muscle fibers
Filamentous and forms part of cytoskeleton
Works with myosin to help with muscle contraction
Fibrosis
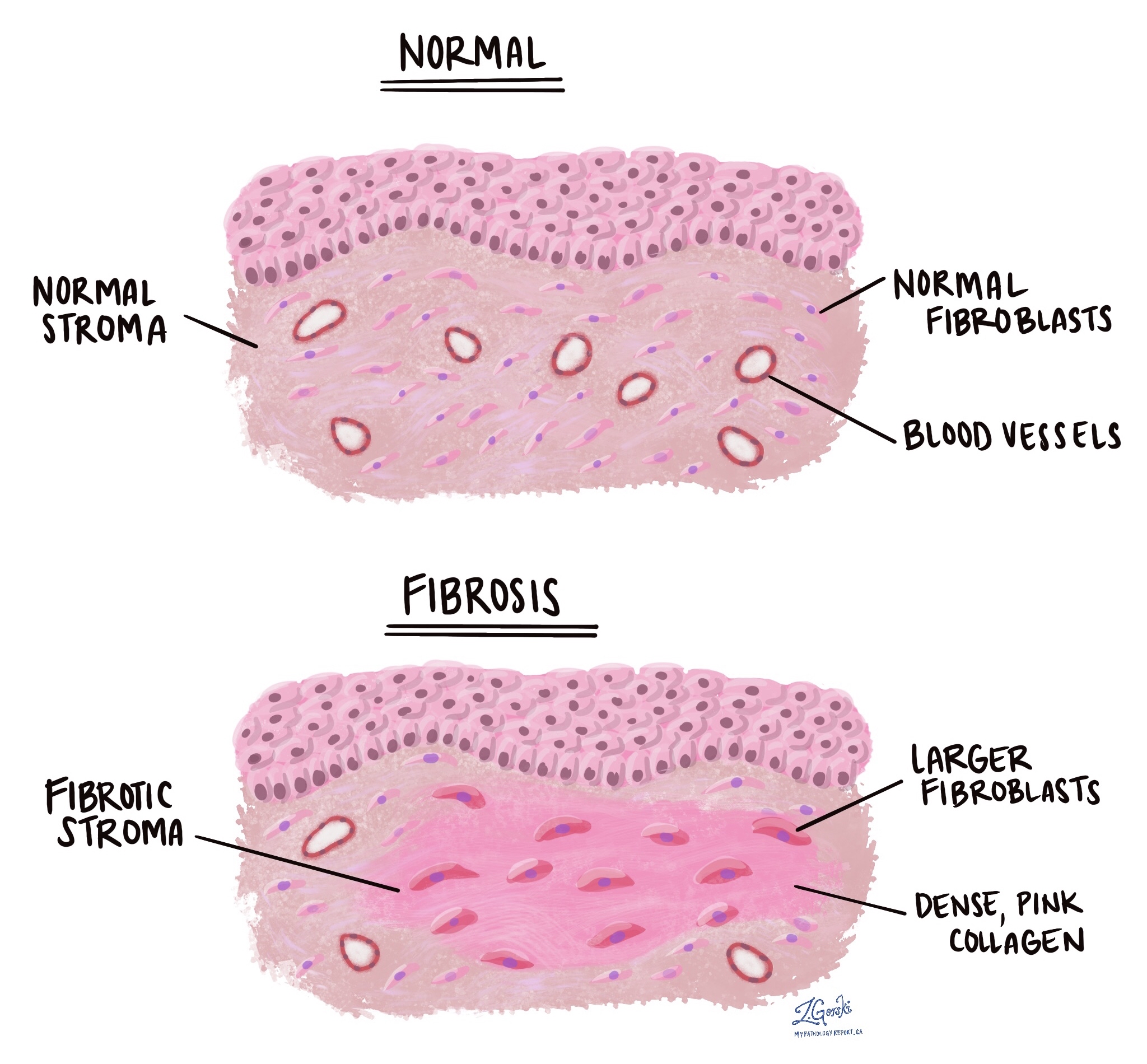
The formation of excess fibrous connective tissue during wound healing
Occurs when tissue is severely damage and cells cannot regeneration
Tissue becomes less flexible and might lose function
Granulation tissue
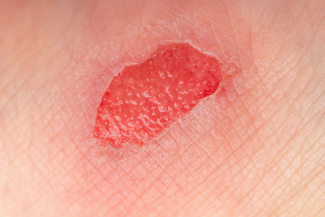
Connective tissue and blood vessels that form during the process of healing a wound
Helps fill the wound bed and provide a foundation for new tissue growth and skin (epithelization)
Looks pink/red, moist, and bumpy
Junctions
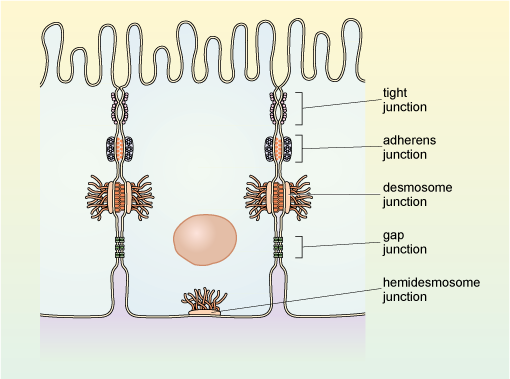
Specialized structures that connect cells together or link them to extracellular matrix
Critical for communication, adhesion, and maintaining tissue integrity
Tight junctions seal cells together to prevent leakage between them
Desmosomes
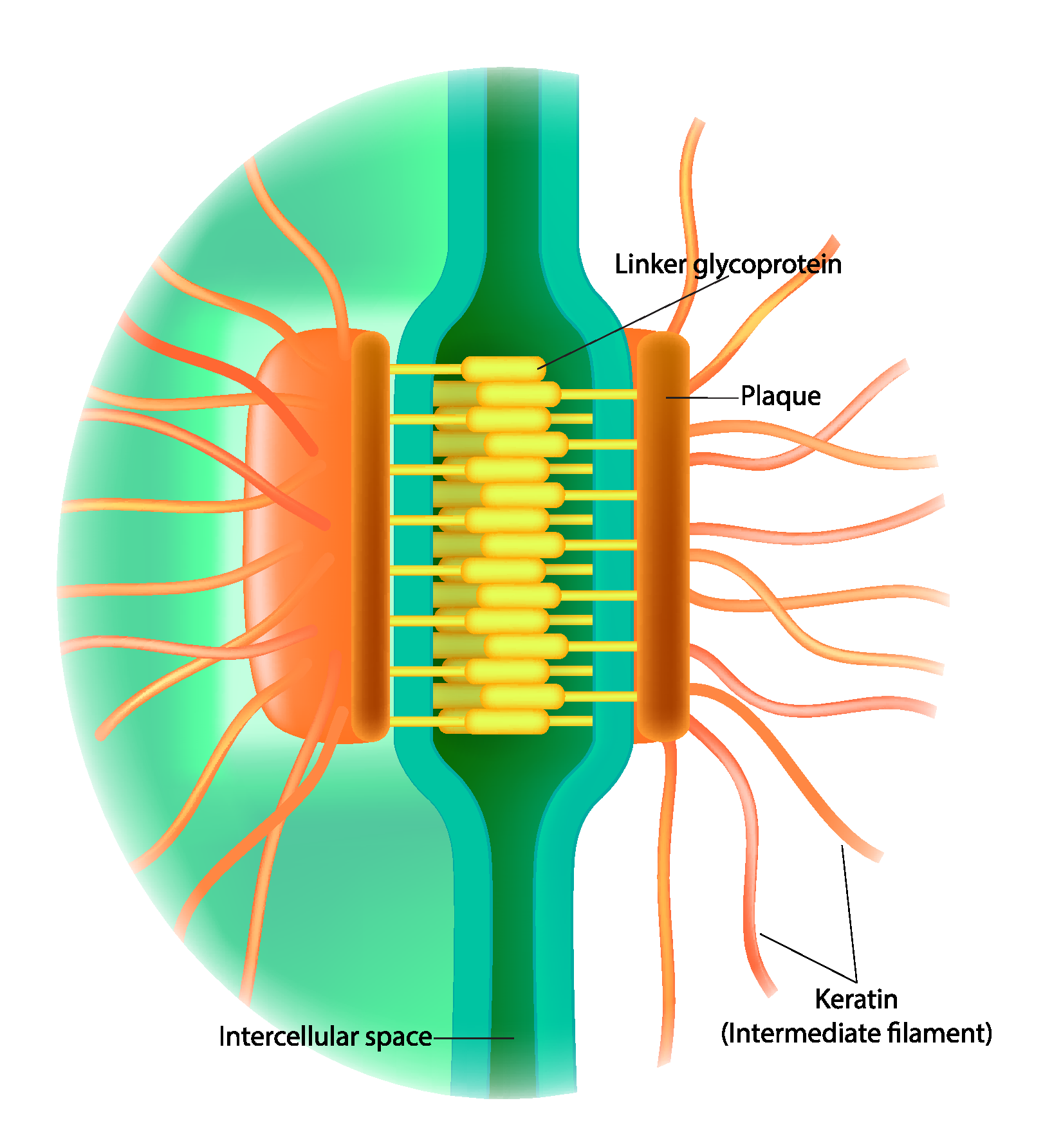
Type of cell junction that holds adjacent cells together
Intermediate filaments inside cells hold them together (think of the desmosome as a coupler that connects train cars together)
Keeps them from breaking apart under stress
Avascular

Tissue of structure that does not contain blood vessels
Relies on diffusion from nearby vascularized tissues (tissues with blood vessels) for nutrients and for removing waste
Epithelial tissue is avascular, and they rely on basement membrane and connective tissue to get nutrients
Basement membrane
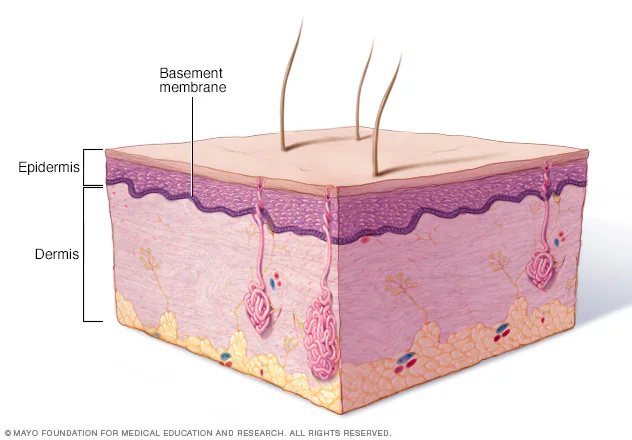
Thin, specialized sheet of extracellular matrix lying between epithelial tissue and underlying connective tissue
Provides support, anchors, and filtrates epithelium
“Glues” epithelial tissue (tiles) to connective tissue (floor)
Transitional epithelium
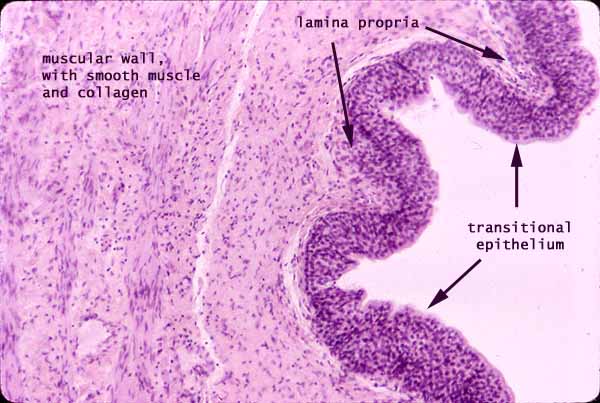
Type of tissue that can stretch and change shape without tearing
Found in organs that expand and contract (ureters, urinary bladder)
Cells near surface are rounded when relaxed, flattened when stretched
Endocrine + Exocrine glands
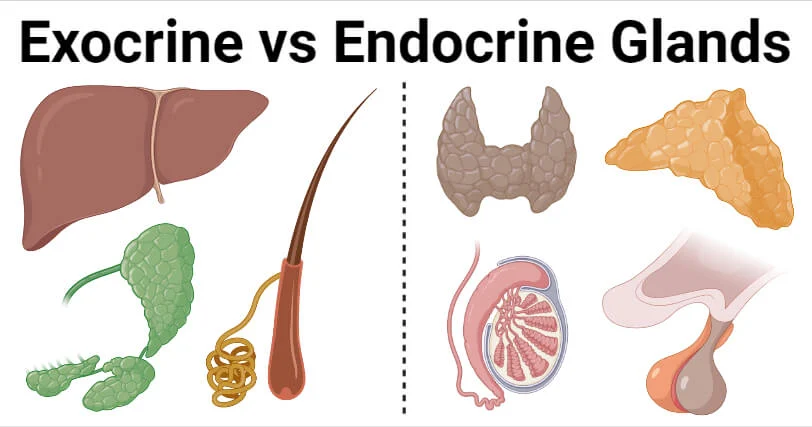
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into bloodstream
- No tubes, hormones travel directly though blood to target organs
- Pituitary gland, thyroid glands, adrenal glandsExocrine glands secrete substances through ducts or to surface of body or into cavities
- Have ducts (tubes) to carry secretions
- Sweat glands, salivary glands
Phagocytes (White Blood Cells)
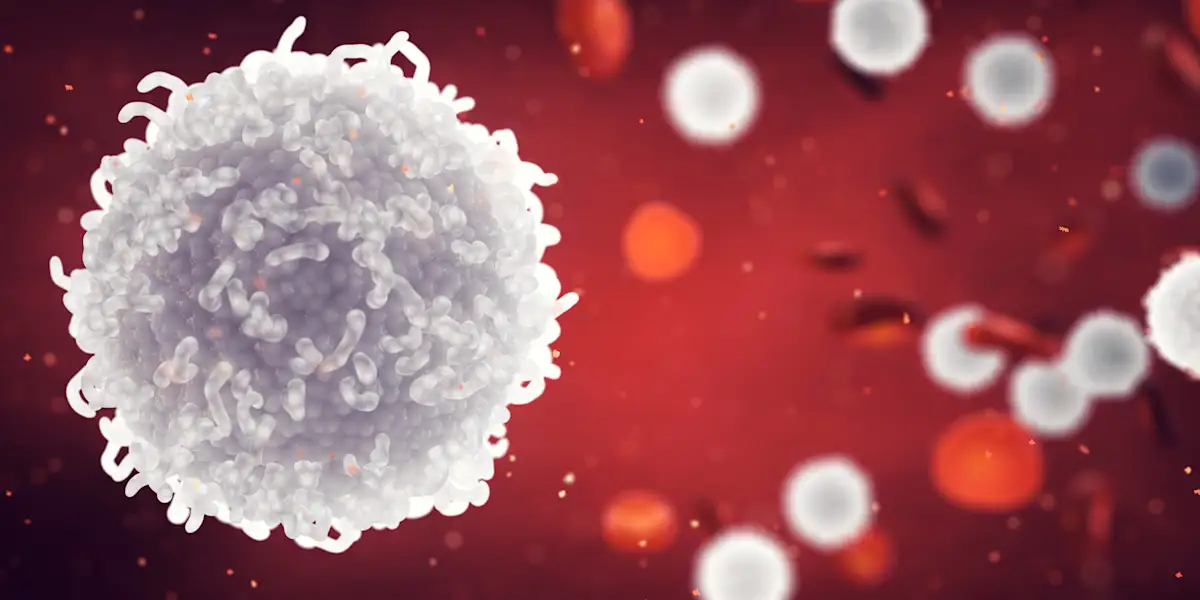
Type of white blood cells that ingests (“eats”) and destroys foreign particles, bacteria, and dead/dying cells
Part of the immune (lymphatic) system
Engulf and digest harmful particles through phagocytosis (endocytosis)
Contain a lot of lysosomes
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
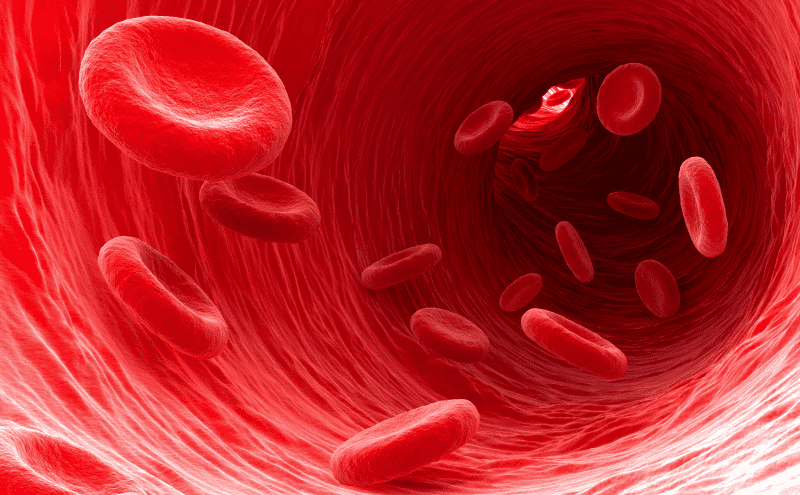
Type of red blood cell that specialize in transporting oxygen from lungs to body tissues and carry CO2 from tissues back to lungs
Shaped like discs with a caved in center to increase surface area for exchange and flexibility
Lacks a nucleus to carry more hemoglobin (oxygen-carrying protein)
Oocytes
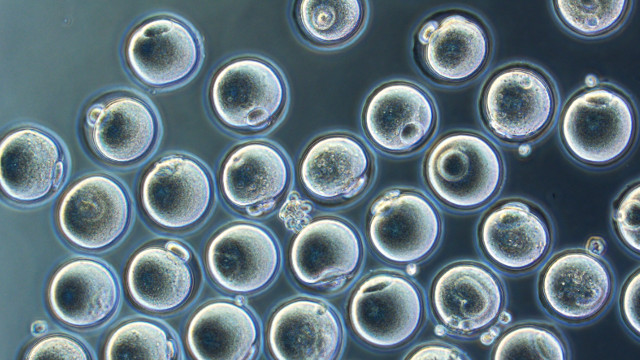
Immature female egg cell that develops in ovaries
Develops into ova (eggs)
Found in ovarian follicles in ovaries
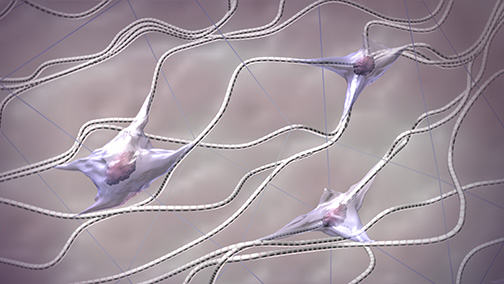
Neurons (Nerve cells)
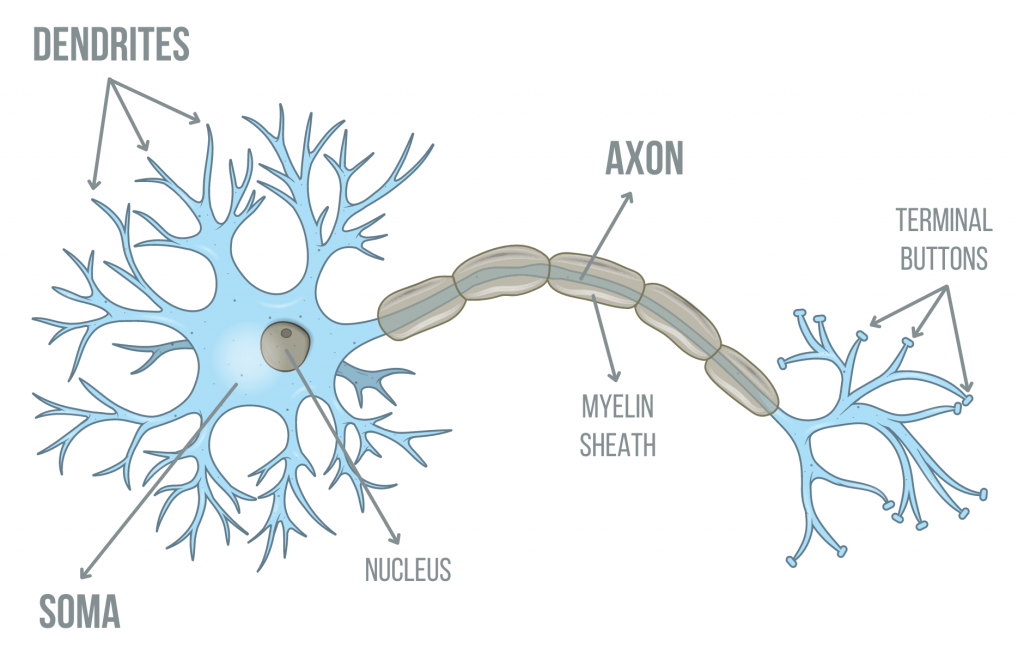
Specialized nerve cells that transmit electrical + chemical signals through body
Part of nervous system
Soma (body), dendrites (receives input), axon (long fiber carrying impulses away from soma), myelin sheath (insulates/protects axon), axon terminals (releases neurotransmitters)