Six Principles found in the Constitution
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP gov
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
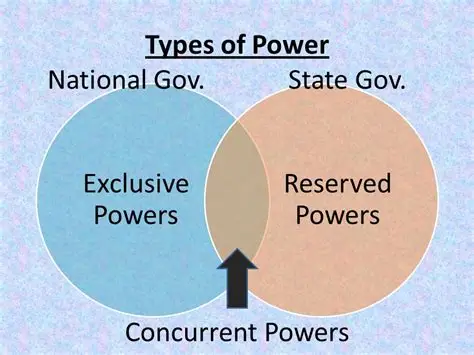
1) Principle of the Constitution: federalism
A) Powers delegated to the national government
B) Powers reserved to the state government
C) Concurrent powers shared between them
2) Principle of the Constitution: Limited Government
The Bill of Rights limits the governments
3) Principle of the Constitution: Popular Sovereignty
The government derives its power from the people
4) Principle of the Constitution: Separation of Power
Legislative
Executive
Judicial
5) Principle of the Constitution: Judicial Review
The Supreme Court can declare an act of Congress unconstitutional.
6) Principle of the Constitution: Checks & Balance
Makes sure one branch cannot get too powerful
How are powers delegated to the federal government?
Articles 1 section 8
What is listed in Articles 1 section 8
The powers of the national government are:
-collect tax
-regulate commerce
-coin money
-declare war
-post offices
-ability to pass “necessary and proper” laws to carry out enumerated powers
Enumerated
Powers granted to Congress by the Constitution
Delegated
Specific authorities granted to the federal government
Reserved
Powers not specifically granted to the federal government by the Constitution, nor prohibited to the states. It is retained by the people. (Tenth Amendment)
Concurrent power
Powers shared by states and the federal government
legislative
makes laws in Congress
-House of Representatives
-senate
Executive
enforce laws
-white house
Judicial
interprets laws
-supreme court