9b. gas exchange in mammals and plants
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
tissue
group of similar cells in one or more different types, where are specialised to carry out particular function
2
New cards
organ
structural and functional unit composed of a collection of tissues working totters to perform a particular function
3
New cards
epithelial tissue
tissue that line surfaces
4
New cards
connective tissue
tissue that holds structures together and provides support eg bone, blood and cartilage
5
New cards
muscle tissue
tissue that is able to contact to move parts of the body
6
New cards
nervous tissue
tissue that converts stimuli to electrical impulses and conducts impulses
7
New cards
squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells resting a basement membrane, gives smooth lining surface to reduce friction in blood vessels and heart chamber and provides a short diffusion dunce in alveoli and capillaries
8
New cards
ciliated epithelium
columnar epithelial cells extending from surface, interspersed with goblet cells to produce mucus, to trap dirt and bacteria in trachea, and beat with ATP to move mucus
9
New cards
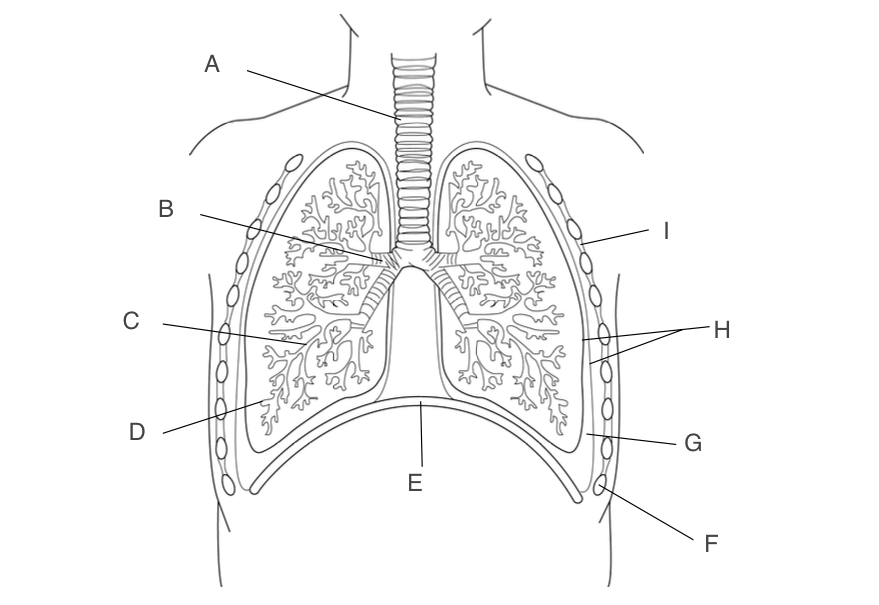
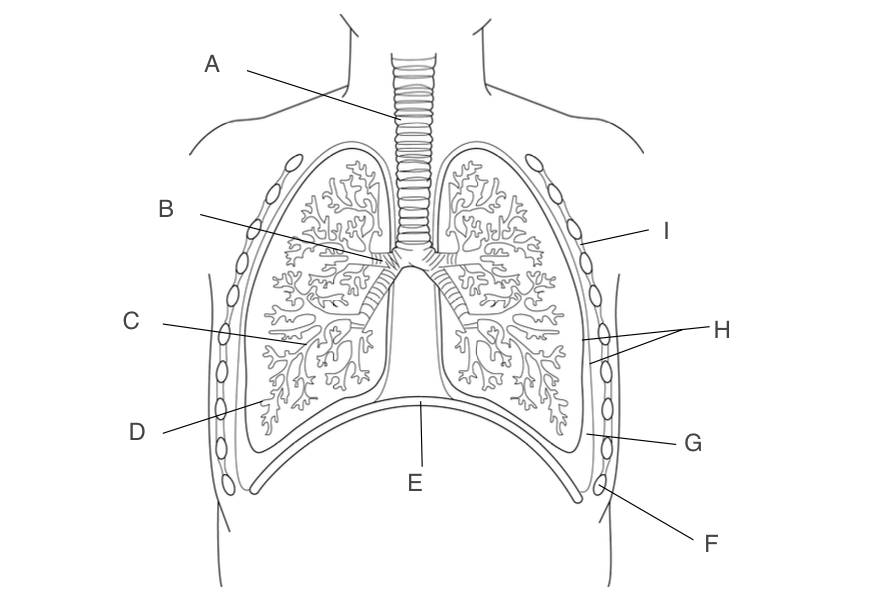
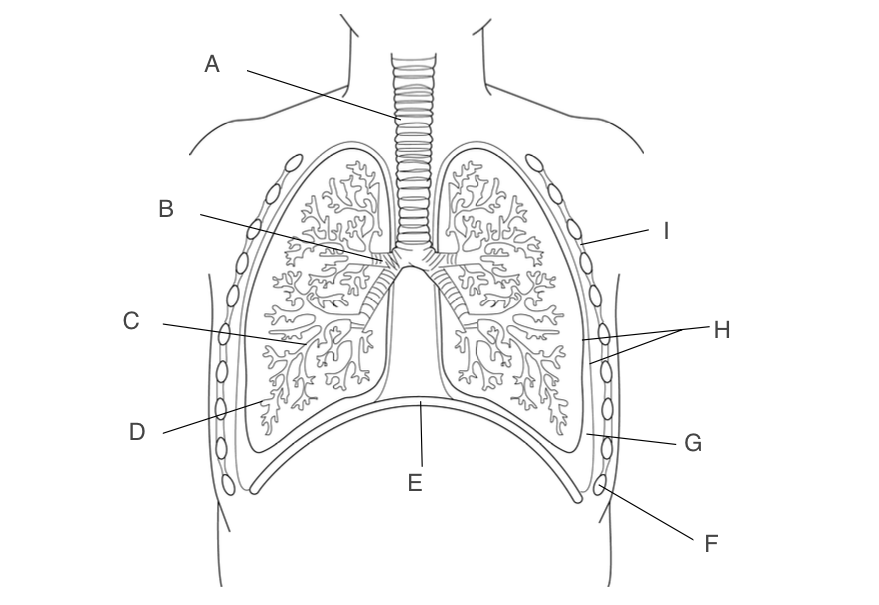
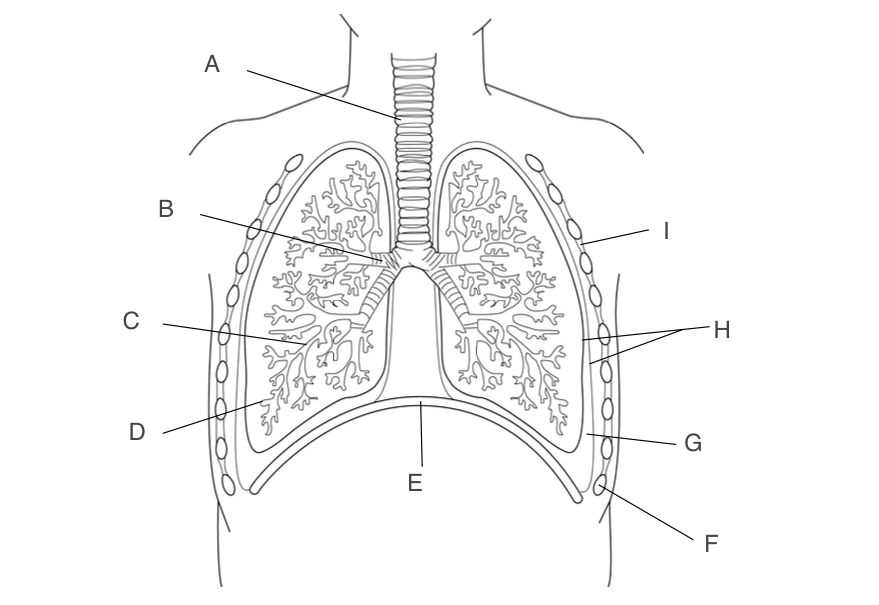
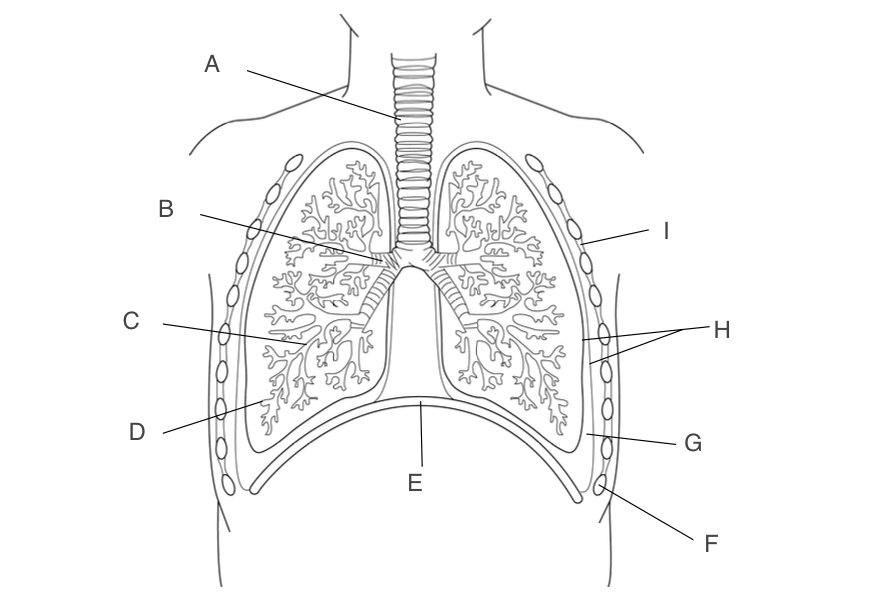
trachea
A, has a large lumen, lined with ciliated epithelium, supported by rings of cartilage
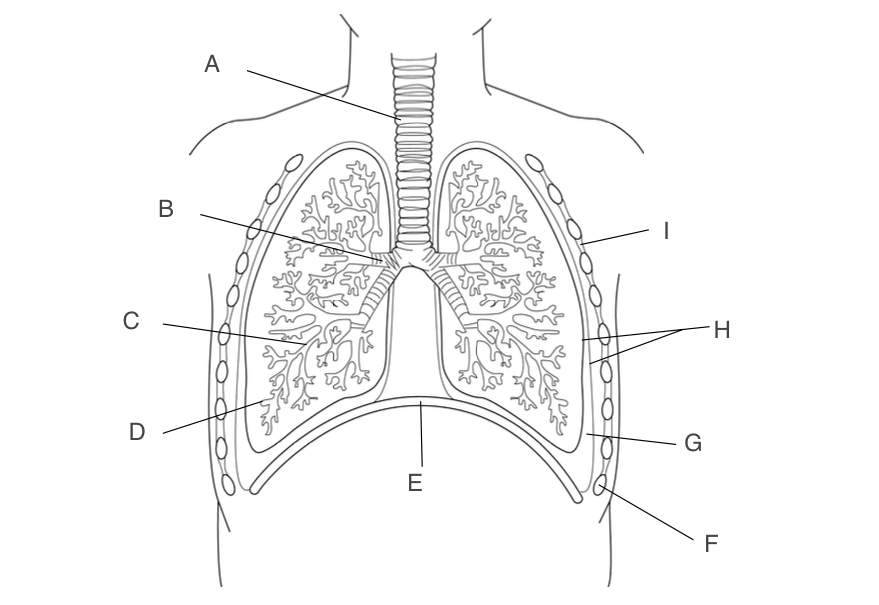
10
New cards
bronchus
B, one goes to each lung, narrower lumen, lined with ciliated epithelium, supported by rings of cartilage
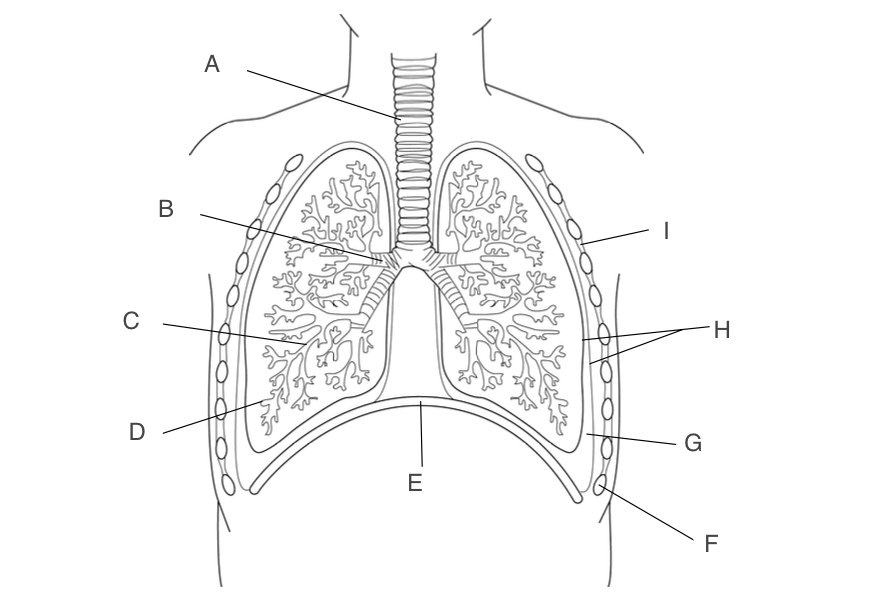
11
New cards
Bronchioles
C, smaller and more branched, may in each lung
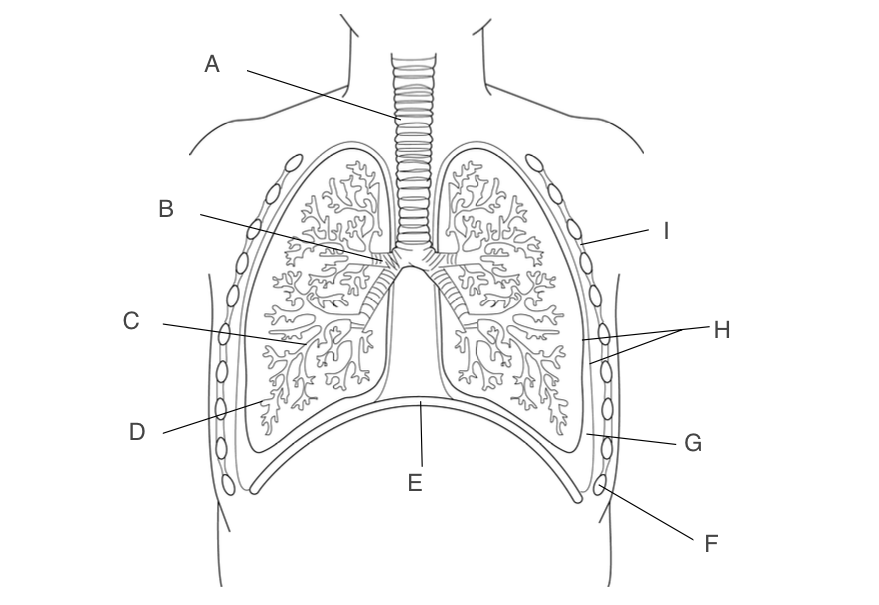
12
New cards
alveoli
D, small pockets where gas exchange occurs
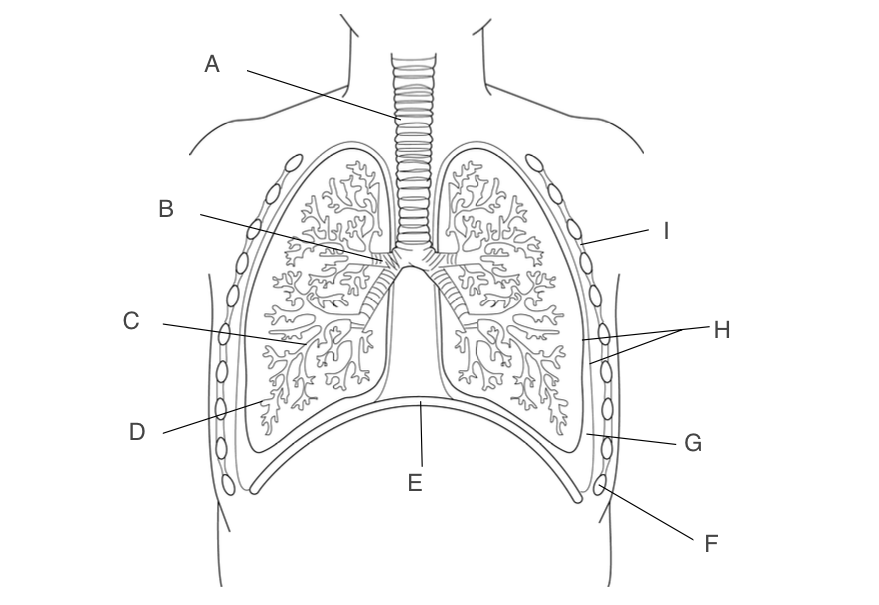
13
New cards
diaphragm
E, contracts and moves down when you inhale
14
New cards
Ribs
F, protects the lungs
15
New cards
pleural fluid
G, acts as a lubricant and protects lungs during ventilation
16
New cards
pleural membranes
H, forms an airtight cavity
17
New cards
intercostal muscles
I, antagonistic muscles that move the ribcage
18
New cards
C rings of cartilage
to prevent collapse of trachea during inhalation, allow back to bend and allow passage of food down oesophagus
19
New cards
smooth muscle
contacts to narrow lumen of bronchioles to reduce airflow an rent airborne particles entering lungs
20
New cards
electric fibres
recoil to original length when smooth muscle relaxes so widens lumen
21
New cards
short diffusion distance
due to alveoli walls been composed of one cell thick of squamous epithelium
22
New cards
expel air
elastic fibres recoil in alveolar walls
23
New cards
surfactant
secreted by alveoli walls to reduce surface tension of water to prevent alveoli collapsing during expiration
24
New cards
phagocytic cells
in the alveoli to engulf bacteria/foregin articles that reach there
25
New cards
efficient gass exchange surface
features include, large surface area, thin to allow a short diffusion distance, steep concentration gradient maintained by a fresh supply of molecules on one side and removal on the other
26
New cards
pulmonary ventilation
moment of diaphragm and ribcage during breathing
27
New cards
inspiration
movement of air into lungs by:
* diagram contracting and flattening
* external intercostal muscles contract to move rib cage upwards and outwards
* volume of chest vanity increases
* pressure in chest cavity decreases below atmospheric pressure
* diagram contracting and flattening
* external intercostal muscles contract to move rib cage upwards and outwards
* volume of chest vanity increases
* pressure in chest cavity decreases below atmospheric pressure
28
New cards
forced expiration
mount of air out lungs by:
* diaphragm relaxing and returning to domed shape,
* internal intercostal muscles contact to move ribcage downwards and inwards
* volume of chest cavity decreases
* pressure in chest cavity increases above atmospheric pressure
* diaphragm relaxing and returning to domed shape,
* internal intercostal muscles contact to move ribcage downwards and inwards
* volume of chest cavity decreases
* pressure in chest cavity increases above atmospheric pressure
29
New cards
punctured lung
causes the chest cavity to no longer be airtight so pressure cannot change relative to external pressure, preventing ventilation
30
New cards
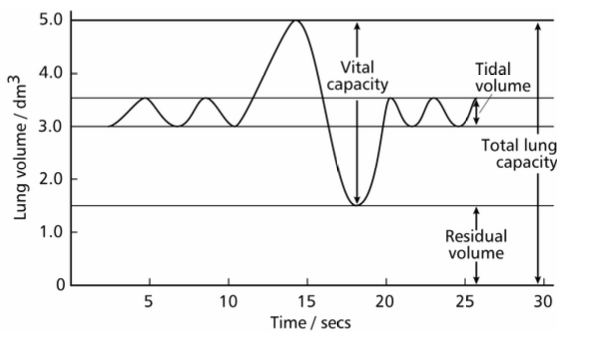
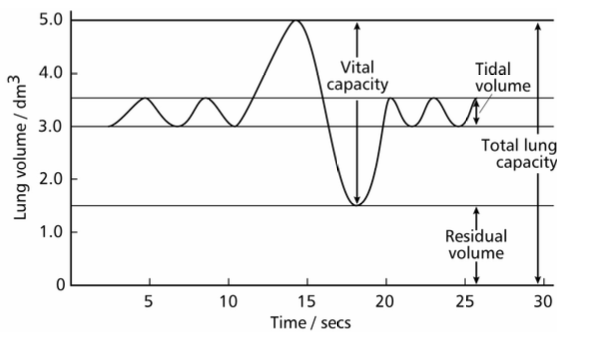
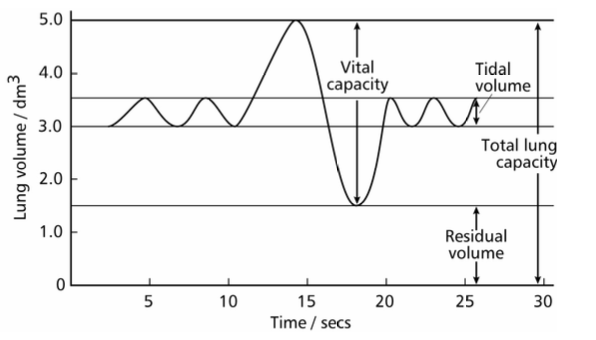
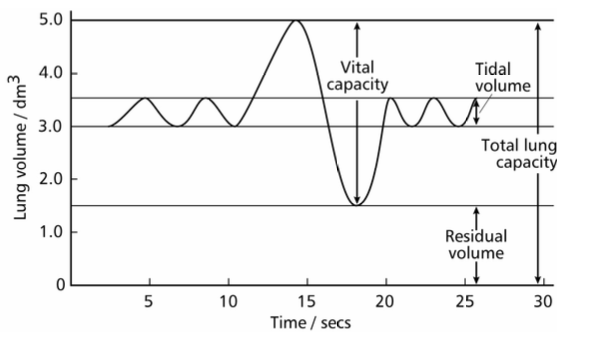
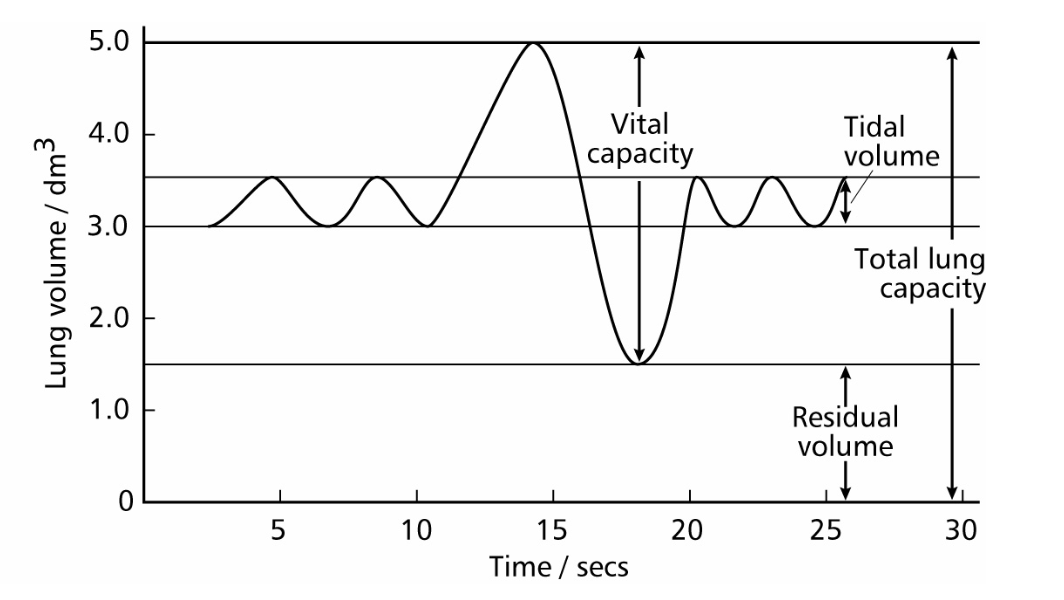
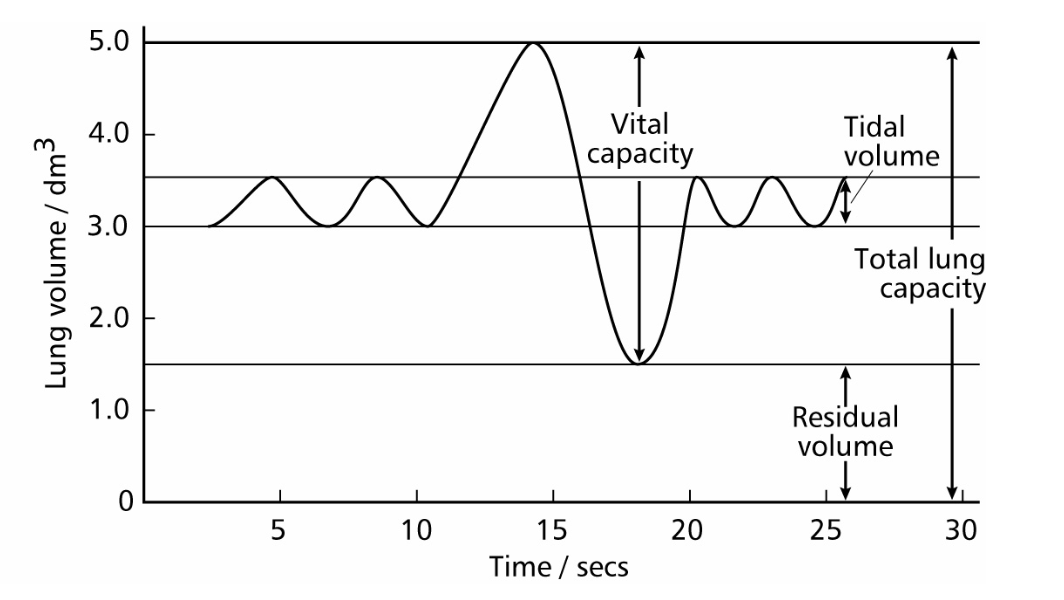
tital volume
volume of air inhaled in one breath during steady regular breathing typically 05.dm3.
31
New cards
breathing rate
number of breaths per minute
32
New cards
residual volume
volume of air that always remains in lungs after expiration, typically 1.5dm3
33
New cards
vital capacity
maximum volume of air exhaled after a deep breath in typically 5dm3, depends on age sex and fitness
34
New cards
total lung capacity
volume of lungs equals vital capacity plus residual volume
35
New cards
pulmonary ventilation rate
volume of air passing though lungs in one minute. breathing rate x tidal volume dm3 min-1
36
New cards
dead space
air present in trachea, branch and bronchioles where no gas exchange takes place with the blood
37
New cards
forces expiration volume (FEV1)
volume of air that can be breathed out in the first second of forced exhalation
= (4.3 x height (in mm) - 0.029 x age (in years)) - 2.49
= (4.3 x height (in mm) - 0.029 x age (in years)) - 2.49
38
New cards
peak expiratory flow rate PEFR
maximum rate of forcing air out the mouth measured with a peak flow meter, influenced by height, sex and age, greater at about 30-35 years old, effected by asthma or COPD
39
New cards
respiratory arrest
when a person stops breathing
40
New cards
causes of respiratory arrest
obstruction of airway blocking the trachea or bronchi
drug overdose that results in nervous system an the breathing system being depressed sufficiently to stop
asthma attack, sever pneumonia, severe shock, or heart attack
near drowning
drug overdose that results in nervous system an the breathing system being depressed sufficiently to stop
asthma attack, sever pneumonia, severe shock, or heart attack
near drowning
41
New cards
expired air resuscitation
emergency first aid procedure used if someone suffers respirator arrest
42
New cards
mechanical ventilation
used to assist or replace spontaneous breathing, may involve use of ventilator to push air into lungs or suck air out lungs (iron lung)
43
New cards
8, 1, 3, 4, 2, 6, 5, 7, 9
order statements for process of expired air resuscitation:
1. Roll person onto back
2. Pinch nostrils closed and make a tight seal over the patient’s mouth with your own
3. Remove any obstruction visible in mouth with finger
4. Push forehead back and tilt chin to open airway
5. Wait for chest to fall then blow again
6. Blow gently into mouth and watch chest rise
7. After two breaths check pulse
8. Call for help, wear sterile gloves and mask if available
9. If there is a pulse continue blowing through mouth. If there is no pulse perform CPR.
1. Roll person onto back
2. Pinch nostrils closed and make a tight seal over the patient’s mouth with your own
3. Remove any obstruction visible in mouth with finger
4. Push forehead back and tilt chin to open airway
5. Wait for chest to fall then blow again
6. Blow gently into mouth and watch chest rise
7. After two breaths check pulse
8. Call for help, wear sterile gloves and mask if available
9. If there is a pulse continue blowing through mouth. If there is no pulse perform CPR.
44
New cards
EAR resuscitate unconscious person
as expired air still contains about 16% oxygen and a higher level of carbon dioxide in expired air also stimulates breathing
45
New cards
EAR with a small child
don’t tilt head back as far
make a seal with mouth and nose
reduce volume of breaths but increase frequency
make a seal with mouth and nose
reduce volume of breaths but increase frequency
46
New cards
lenticels or stomata
where most gas exchange happens in plants
47
New cards
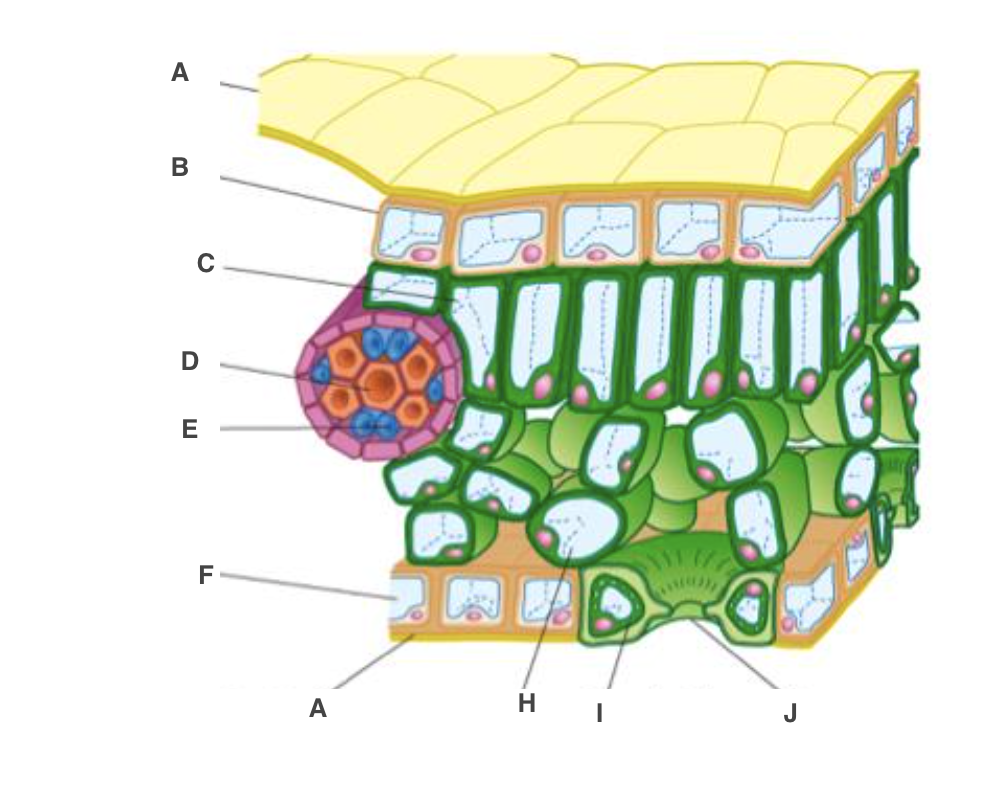
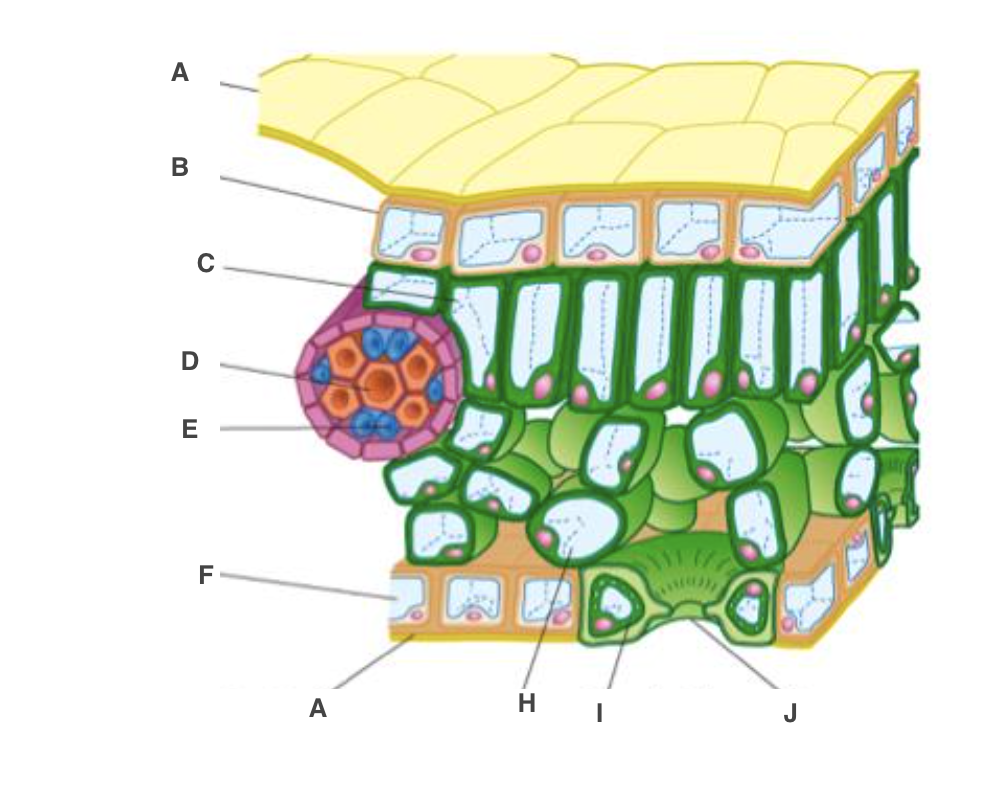
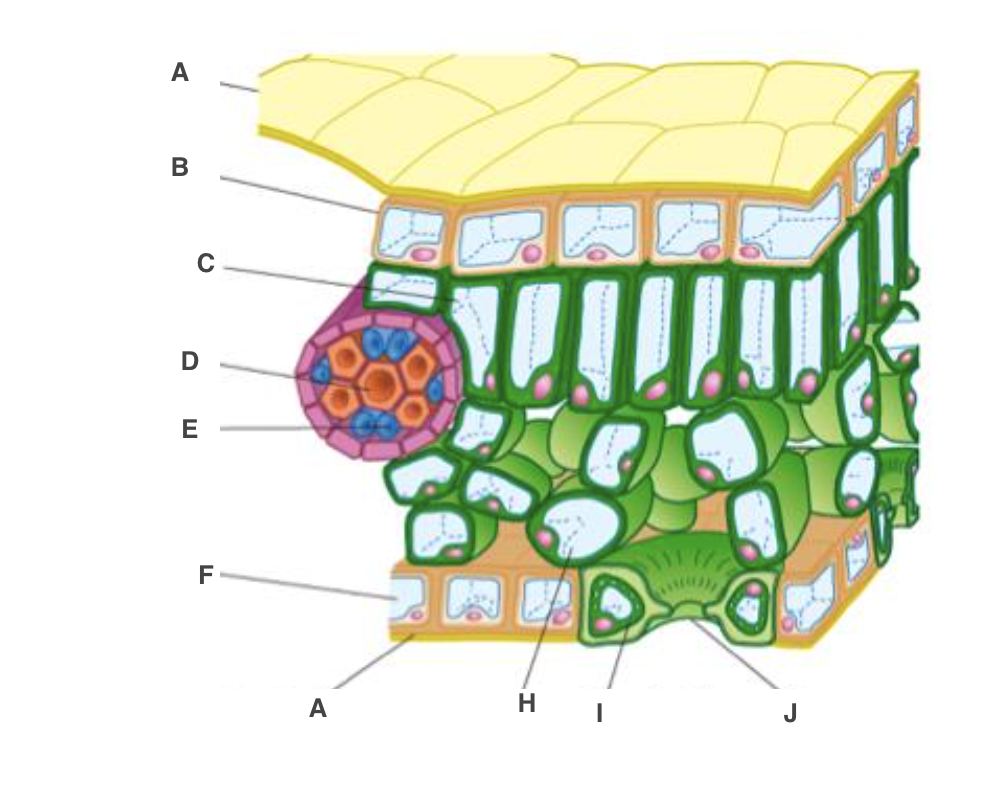
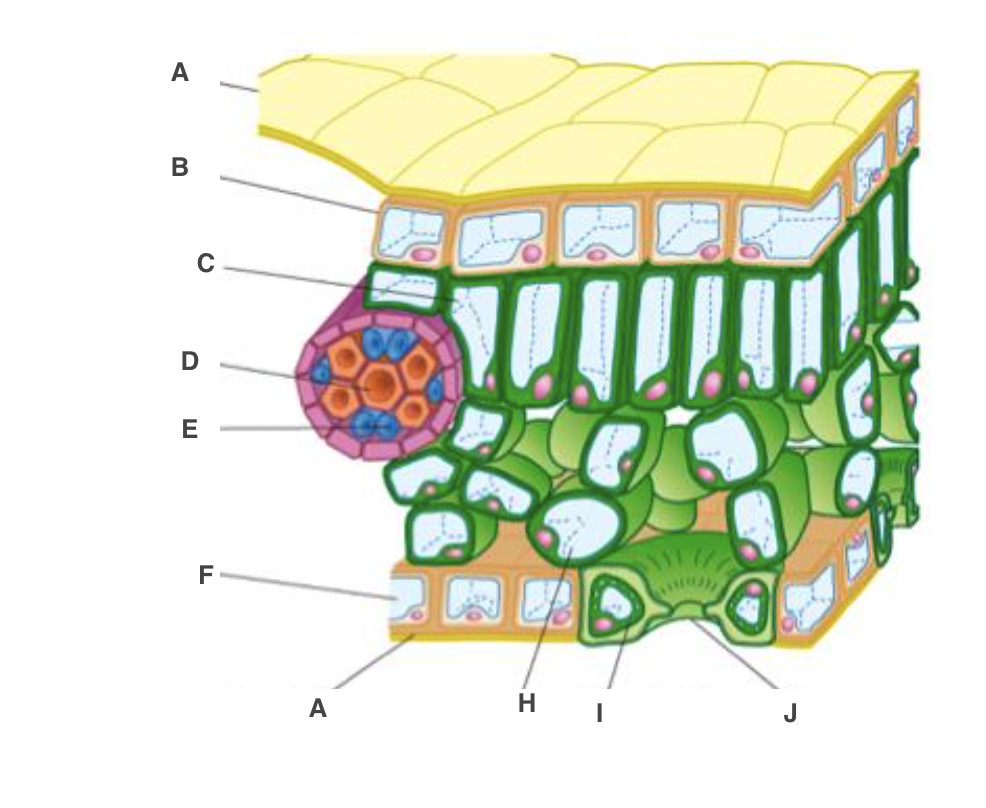
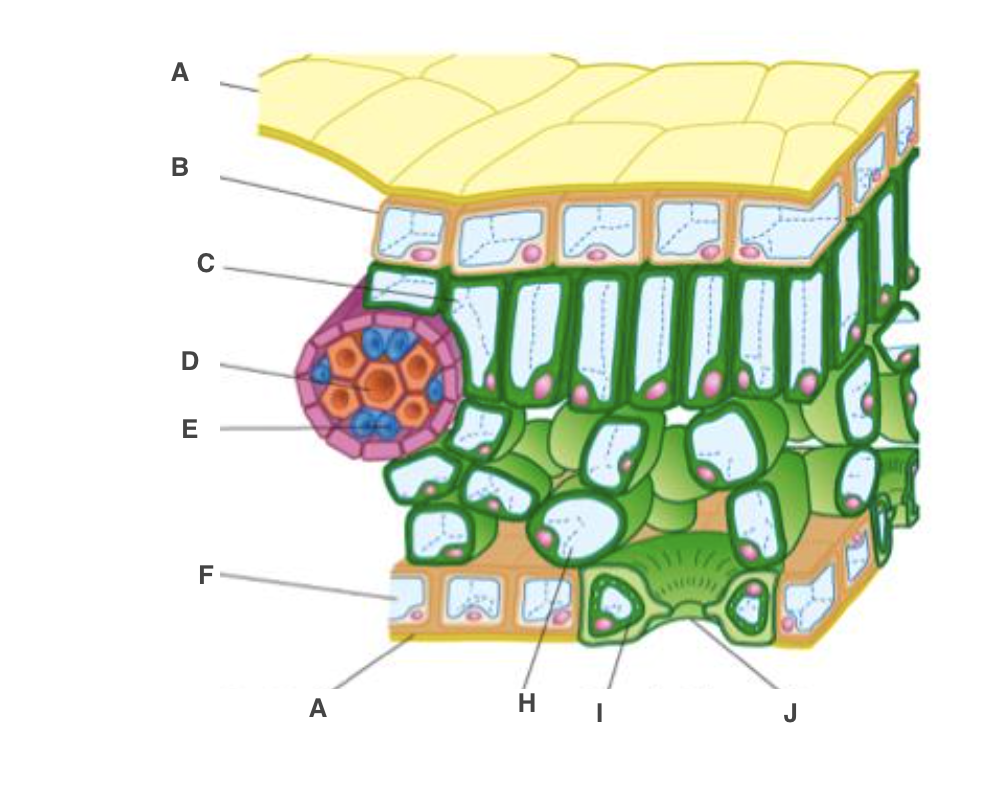
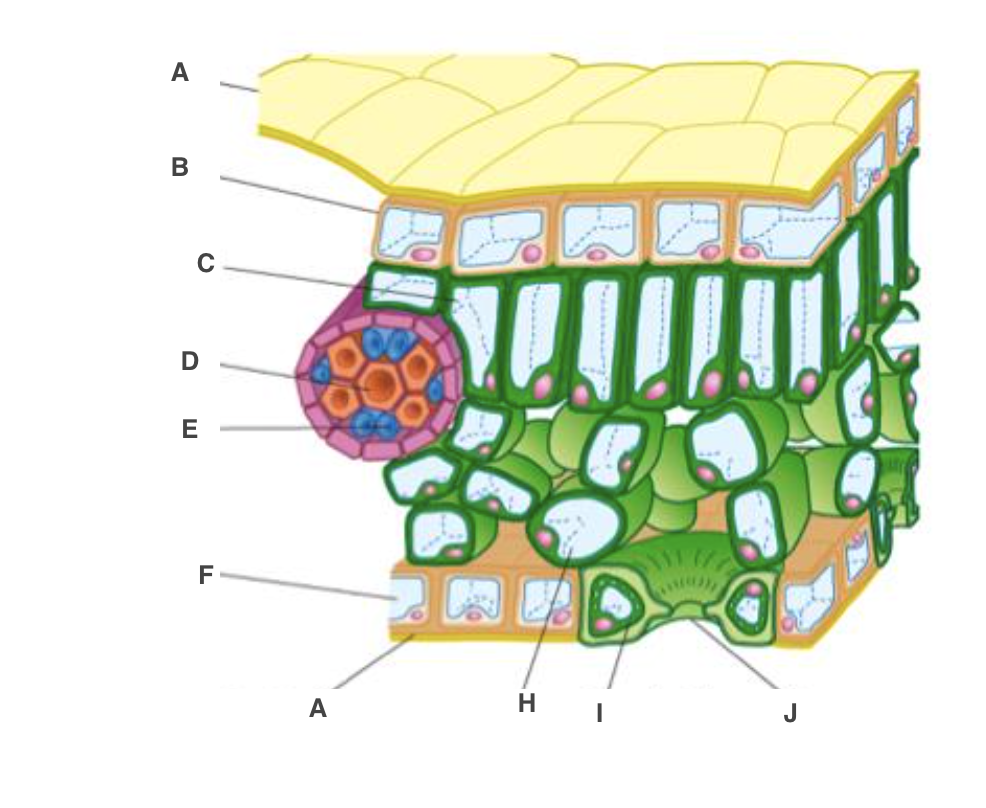
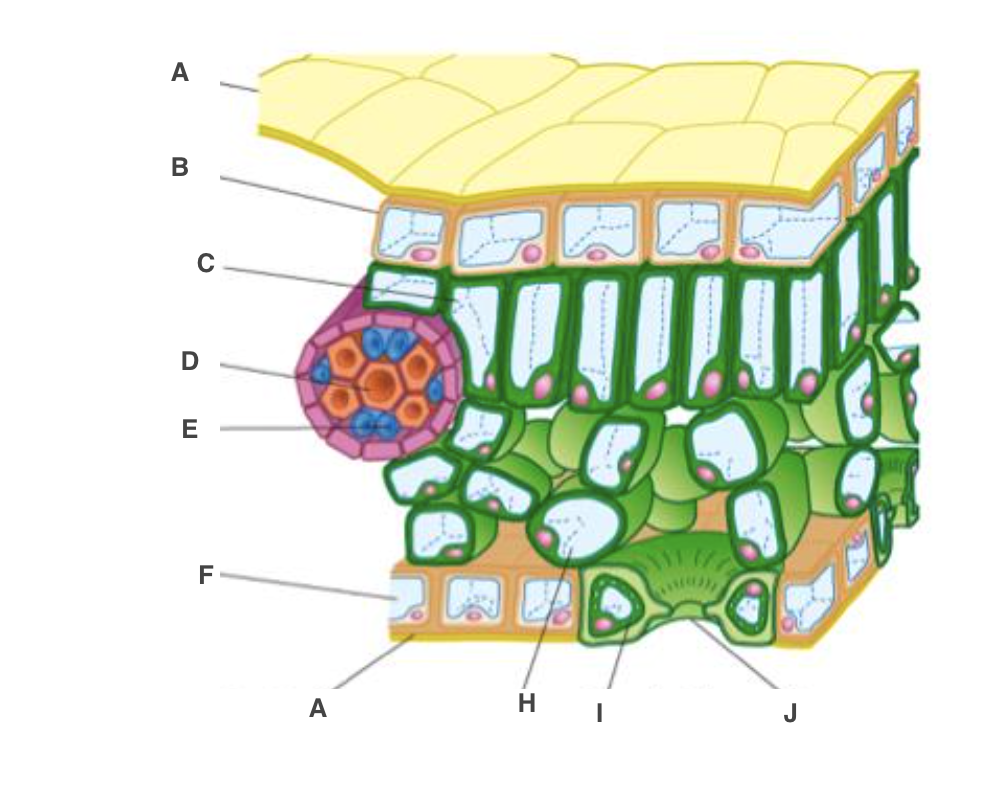
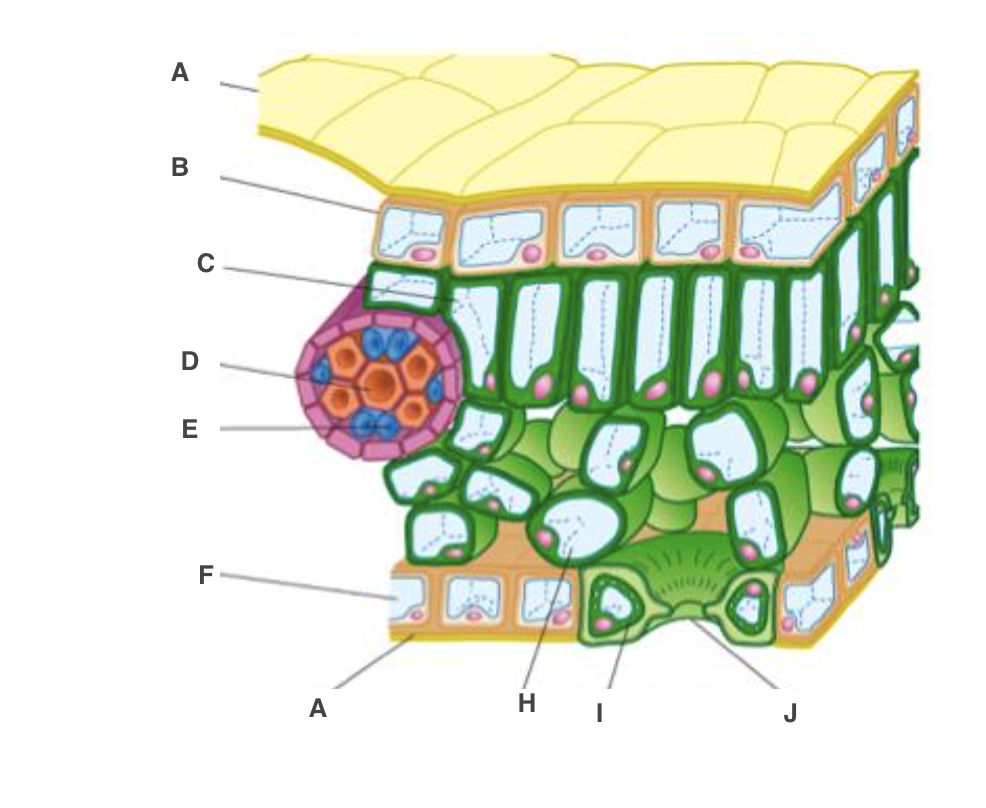
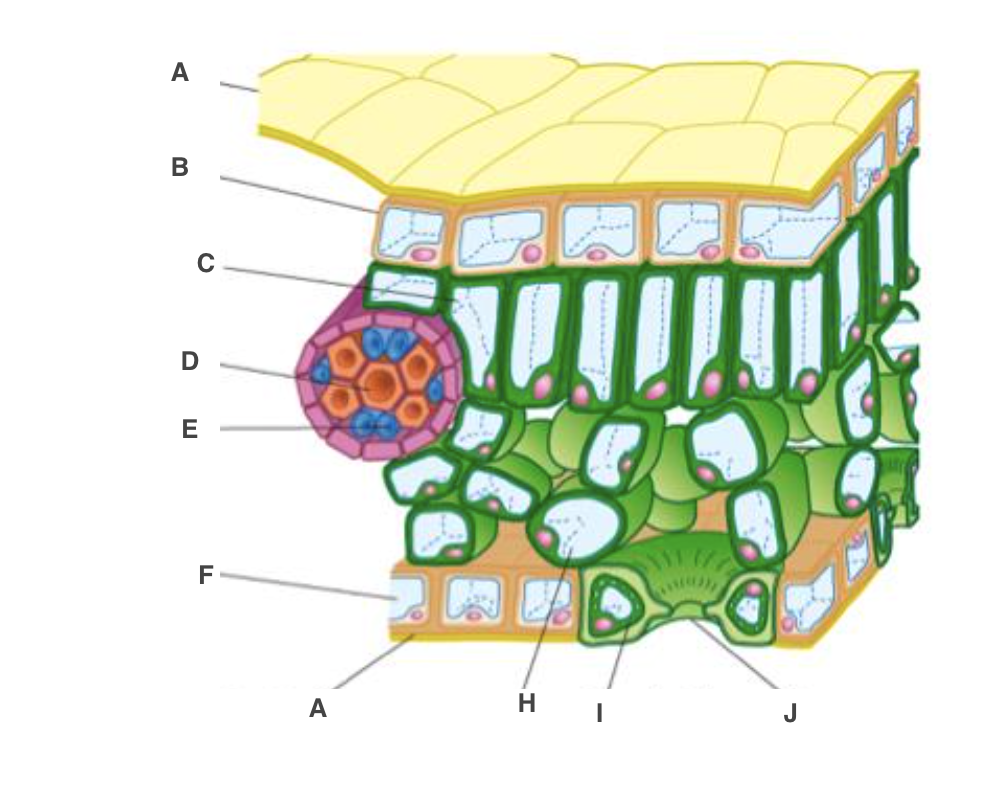
cuticle
A, waterproof to reduce water loss by evaporation
48
New cards
upper epidermis
B, transparent to allow light through
49
New cards
palisade mesophyll cel
C, many chloroplast to carry out photosynthesis
50
New cards
xylem
D, bring water and mineral ions from the roots
51
New cards
phloem
E, take the products of photosynthesis to other parts of the plant
52
New cards
spongy mesophyll cell
H, air spaces to allow circulation of gases
53
New cards
guard cell
I, open or close stoma
54
New cards
lower epidermis
F, transparent to allow light through, on underside
55
New cards
stoma
J, allow gases to diffuse in and out of leaf
56
New cards
stomata
pores in leaves which allow carbon dioxide in and oxygen out during the day
57
New cards
leaf adaptations
thin/cell have thin cell walls so short diffusion distance
large surface area for gas exchange
many stomas an large air spaces in spongy mesophyll to allow diffusion of gases
steep concentration gradient maintained by using carbon dioxide
large surface area for gas exchange
many stomas an large air spaces in spongy mesophyll to allow diffusion of gases
steep concentration gradient maintained by using carbon dioxide
58
New cards
transpiration
loss of water by evaporation from aerial parts of a plant, as water evaporates from cell walls of mesophyll into air spaces in leaf, then lost down water vapour potential gradient
59
New cards
prevent water loss
waxy cuticle- limits where can be lost
guard cells can close stomata
guard cells can close stomata
60
New cards
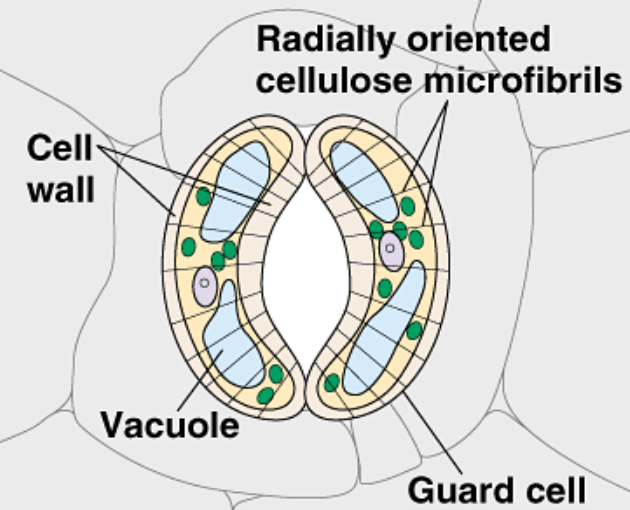
turgid
state where stomata open as the are vacuoles full
61
New cards
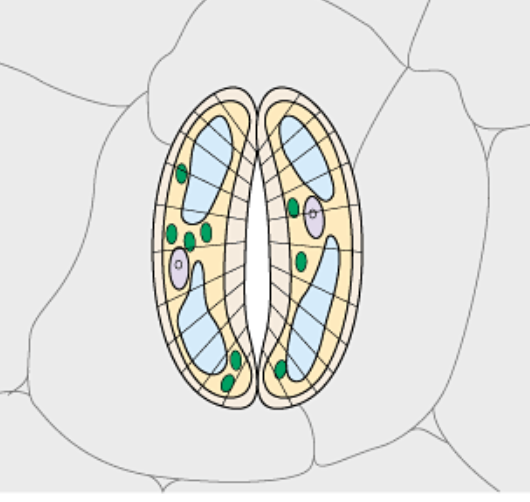
flaccid
state when stomata are closed as stomata aren’t full
62
New cards
cellulose microfibrils
arranged in hoops around cell so cell only increase in length when it becomes turgid
63
New cards
chloroplast
absorb light to produce ATP to open stoma
64
New cards
thick inner cell wall
compared to thin outer cell wall so guard cell bend more result to become banana shaped to open stoma
65
New cards
2, 3, 1, 4
order steps of stomata opening:
1. Water enters guard cell by osmosis down its water potential gradient
2. Active transport of K+ into the guard cells (using ATP produced in photosynthesis)
3. This lowers the water potential of the guard cell
4. Guard cell becomes turgid and stoma opens
1. Water enters guard cell by osmosis down its water potential gradient
2. Active transport of K+ into the guard cells (using ATP produced in photosynthesis)
3. This lowers the water potential of the guard cell
4. Guard cell becomes turgid and stoma opens
66
New cards
nail polish imprint
used to reveal distribution of stomata in upper and lower epidermis of plants, can be viewed under microscope
67
New cards
1, 6, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 3a
order steps for process of nail polish implant
1. Paint clear nail varnish onto the surface of a leaf
2. Examine using a light microscope at high magnification
3. Calculate the density of stomata per mm2
4. Count the number of stomata in the field of view
5. Repeat count at least five times and calculate mean
6. Peel off the dried layer of nail varnish
7. Measure the diameter of the field of view using a stage micrometer and calculate the area of the field of view
8. Calculate the area of the field of view
1. Paint clear nail varnish onto the surface of a leaf
2. Examine using a light microscope at high magnification
3. Calculate the density of stomata per mm2
4. Count the number of stomata in the field of view
5. Repeat count at least five times and calculate mean
6. Peel off the dried layer of nail varnish
7. Measure the diameter of the field of view using a stage micrometer and calculate the area of the field of view
8. Calculate the area of the field of view
68
New cards
advantage of high density of stomata
treated has exchange for photosynthesis
69
New cards
disadvantage of high density of stomata
greater water loss by transpiration