LAL 3) Further learning Theories with animals
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and concepts from the lecture on Learning Theory, focusing on various learning mechanisms, behaviors, and psychological theories.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Associative Learning
The most basic learning mechanism involving the simple pairing of two stimuli/events.
Behaviourism
A psychological approach focusing on objectively observable, quantifiable events and behavior while discounting mental activity.
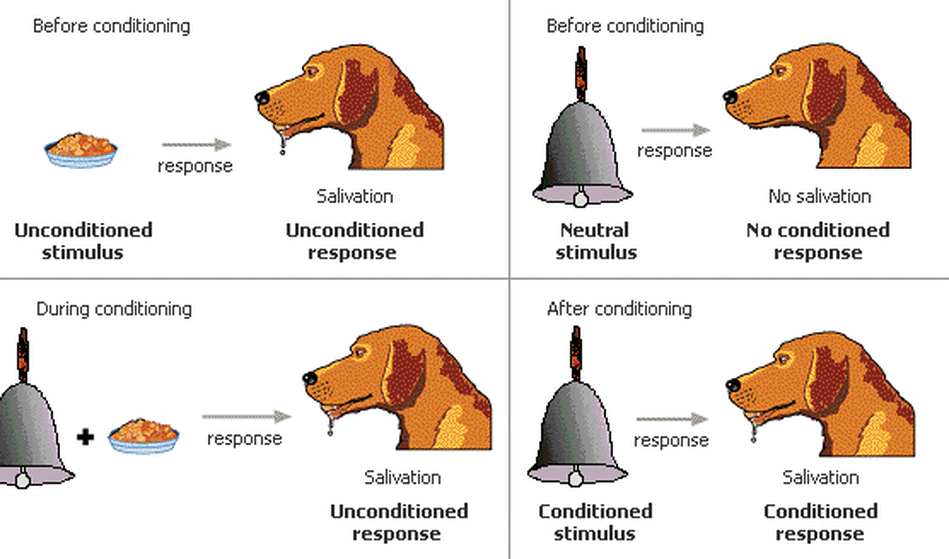
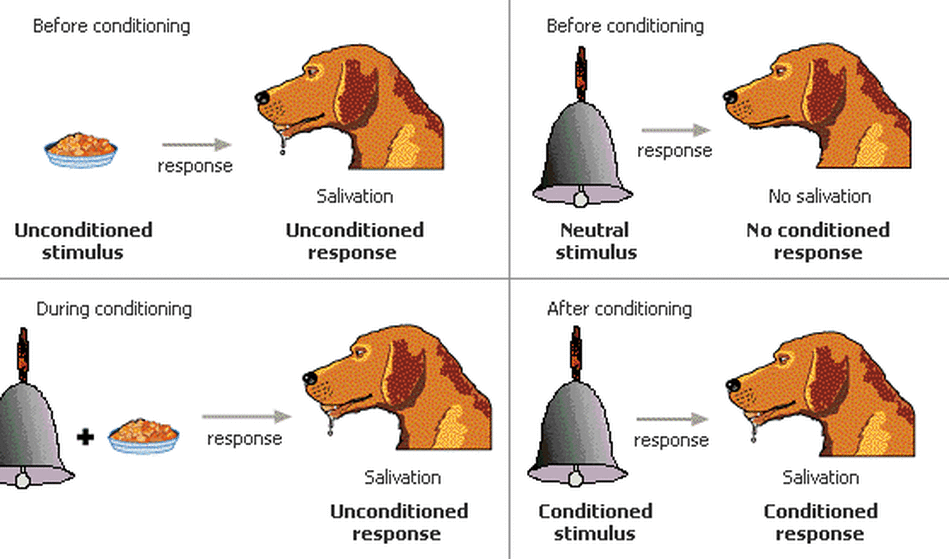
Classical Conditioning
A learning process through which an association is made between a neutral stimulus and a biologically important stimulus.
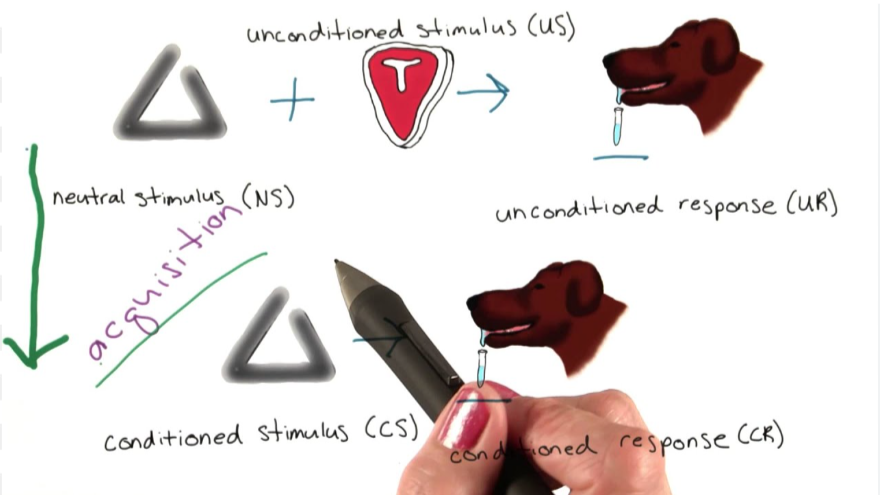
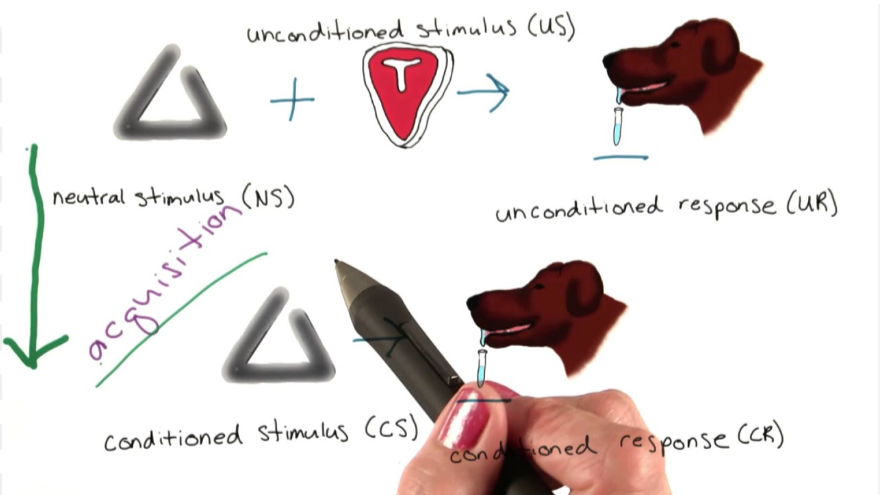
Acquisition
The strengthening of the connection between a conditioned stimulus (CS) and an unconditioned stimulus (US) that leads to a conditioned response (CR).
Extinction
The weakening of the CS-US association when the US is no longer presented with the CS.
Generalisation
The elicitation of the CR by stimuli resembling the original CS.
Discrimination
The ability to differentiate between the CS and other similar stimuli.
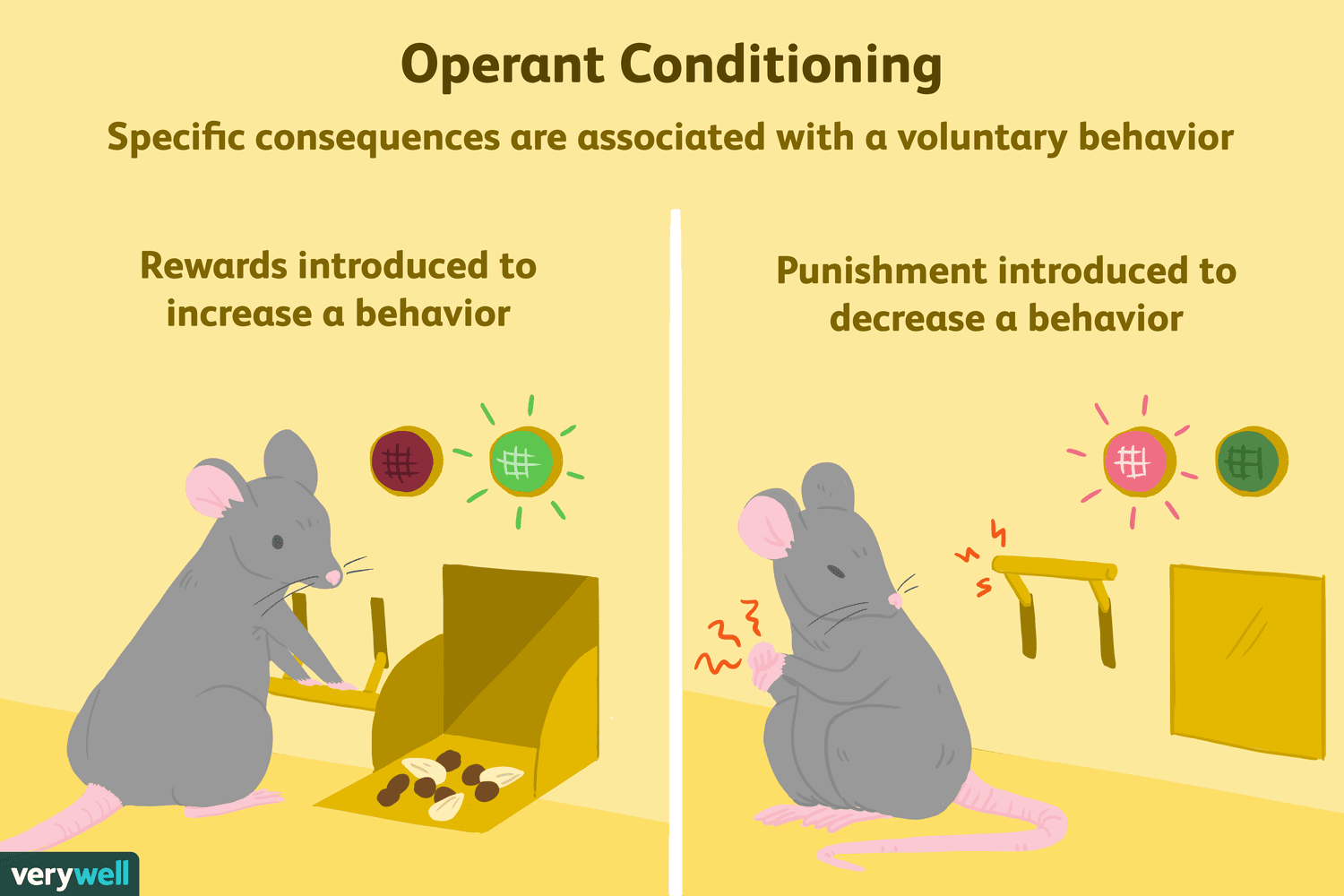
Operant Conditioning
A learning process where associations are made between a response (or action) and a biological stimulus (a consequence).
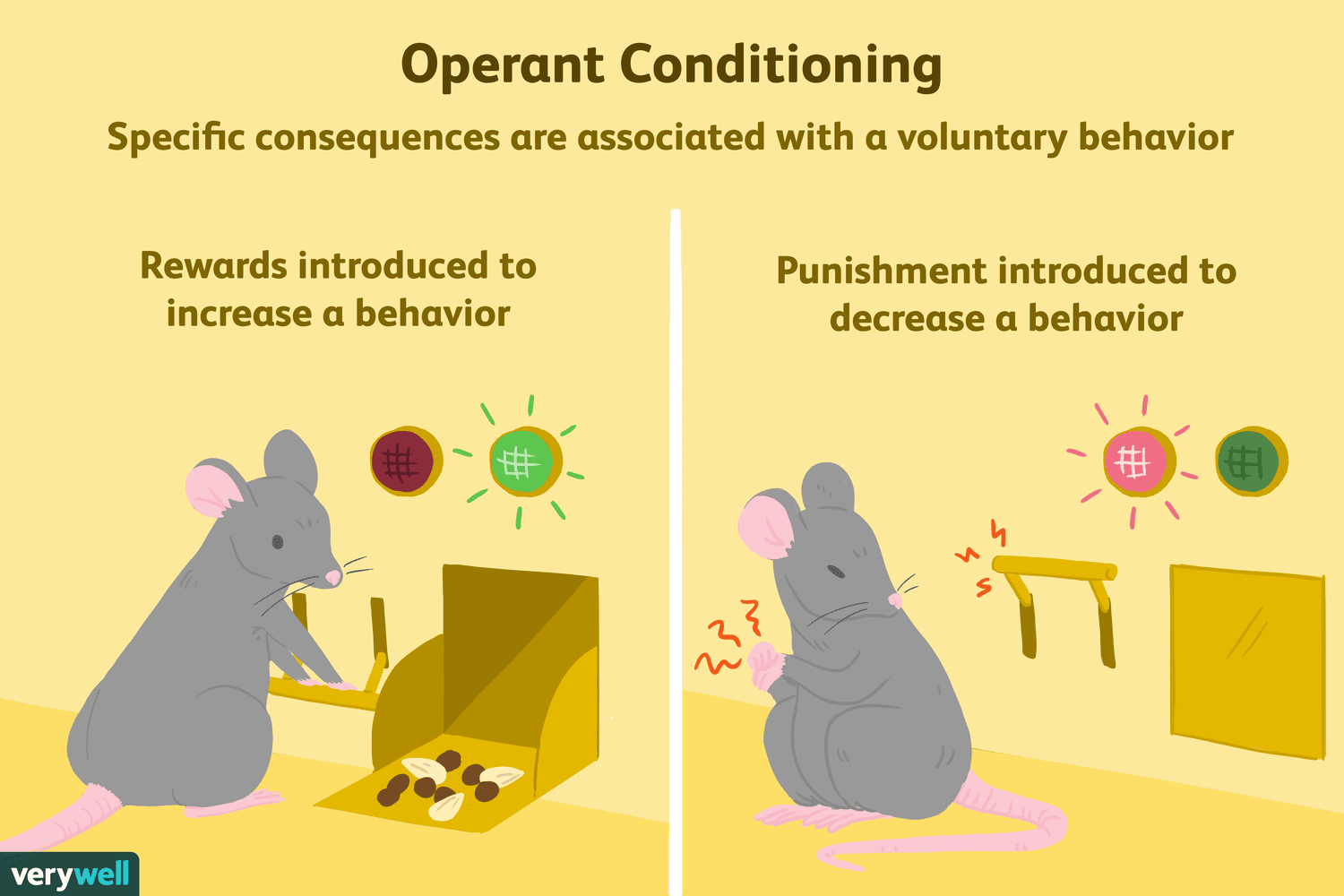
Reinforcer
An effect that follows an operant response, increasing the likelihood of that response being repeated.
Punishment
An effect that decreases the frequency of an operant response due to its consequences.
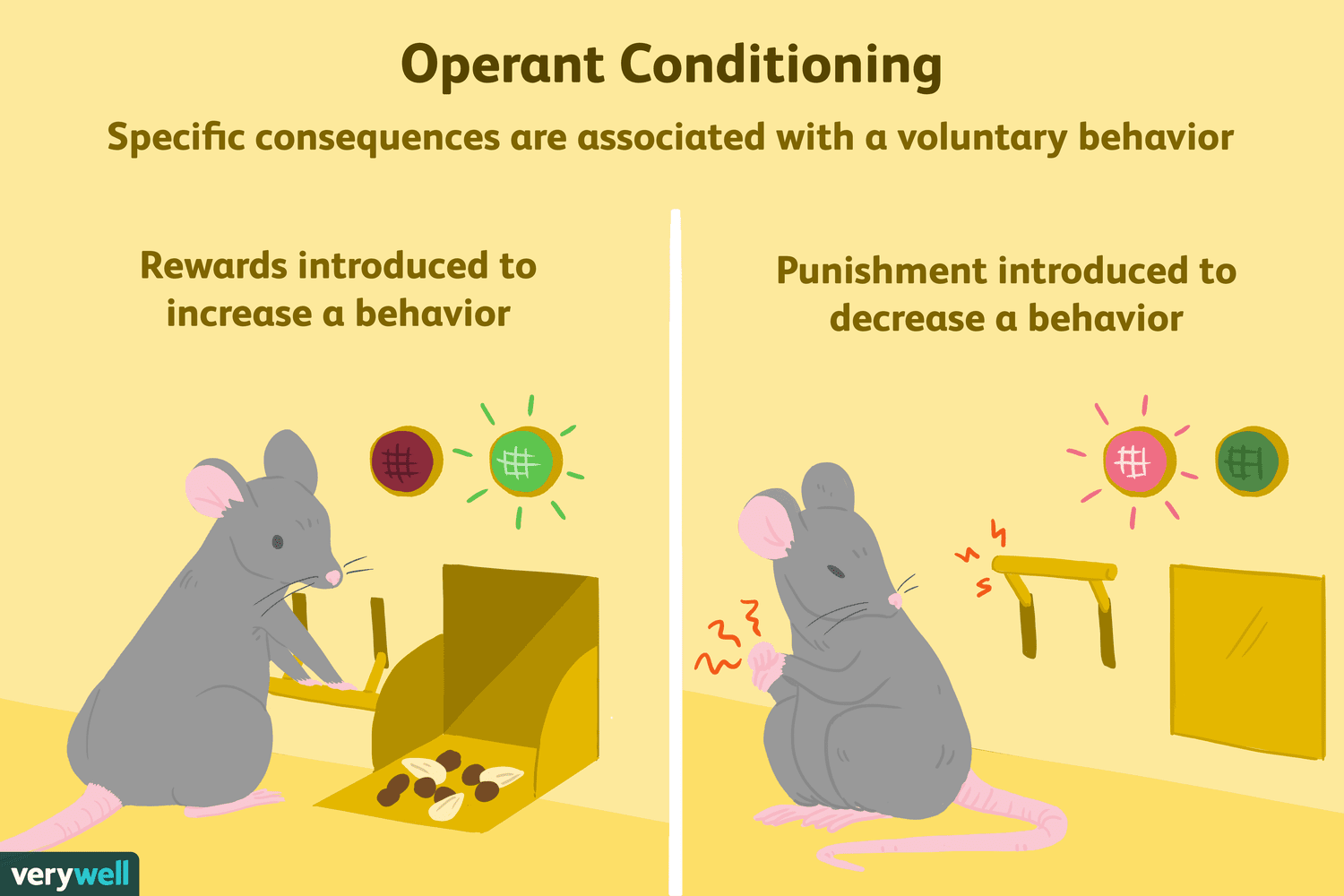
Skinner Box
A controlled environment used to study operant conditioning, typically involving a lever for food reinforcement.
Repetition
A crucial aspect in conditioning that helps establish associations necessary for learning.
Behavioural Therapy
A therapeutic approach that focuses on reconditioning fear responses through exposure and extinction, such as systematic desensitisation.

Systematic Desensitisation
A behavioral therapy technique that replaces fear responses with relaxation through gradual exposure to feared stimuli.

Active Learning
An educational approach that engages students actively in the learning process, emphasizing higher-order thinking and group work.
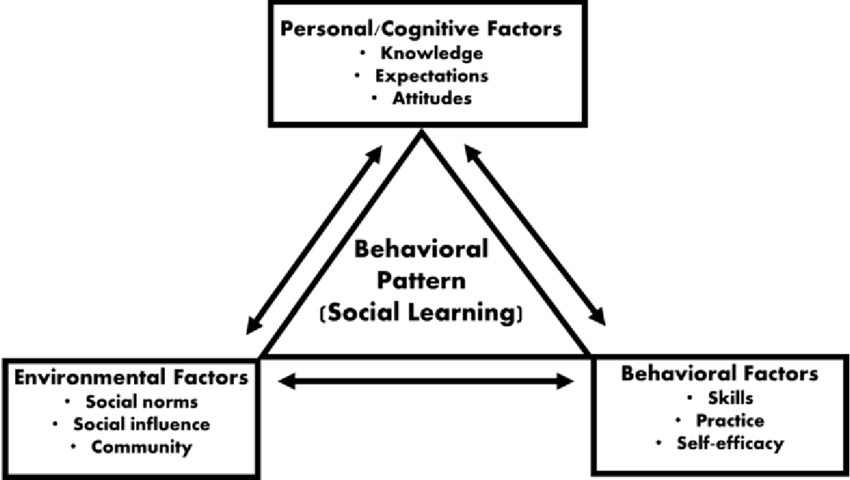
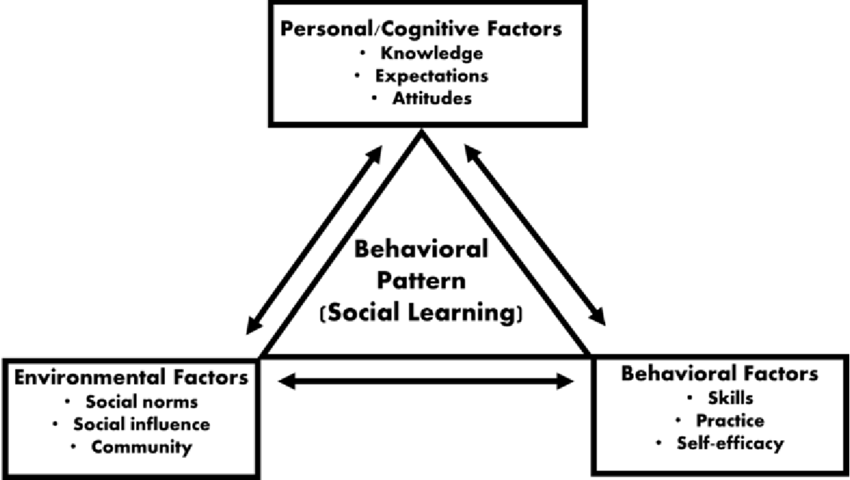
Social Learning Theory
A theory that proposes learning occurs through observation of others and the consequences of their behaviors.
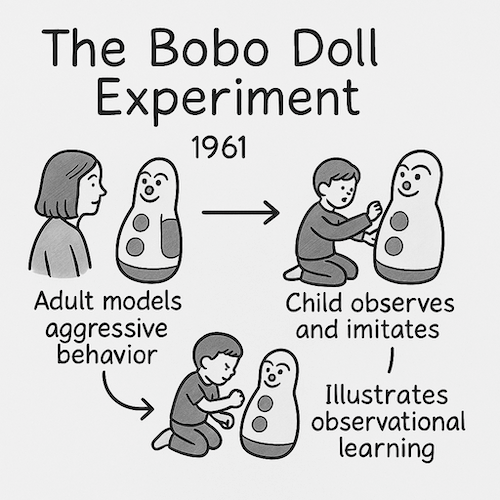
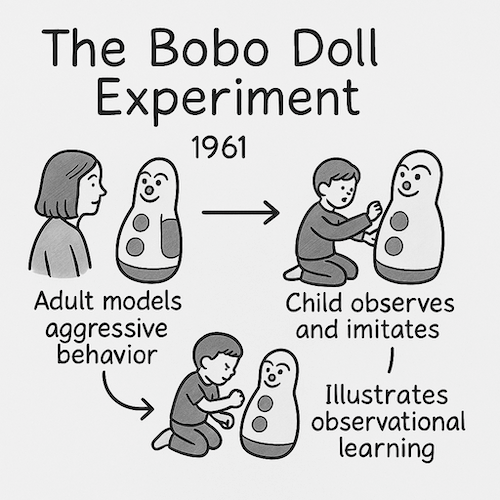
Bobo Doll Experiment
An experiment by Bandura demonstrating that children learn aggressive behaviors through observation of adults.
Triadic Reciprocal Determinism
The interaction of behavior, environment, and cognition, proposed by Bandura in his social learning theory.
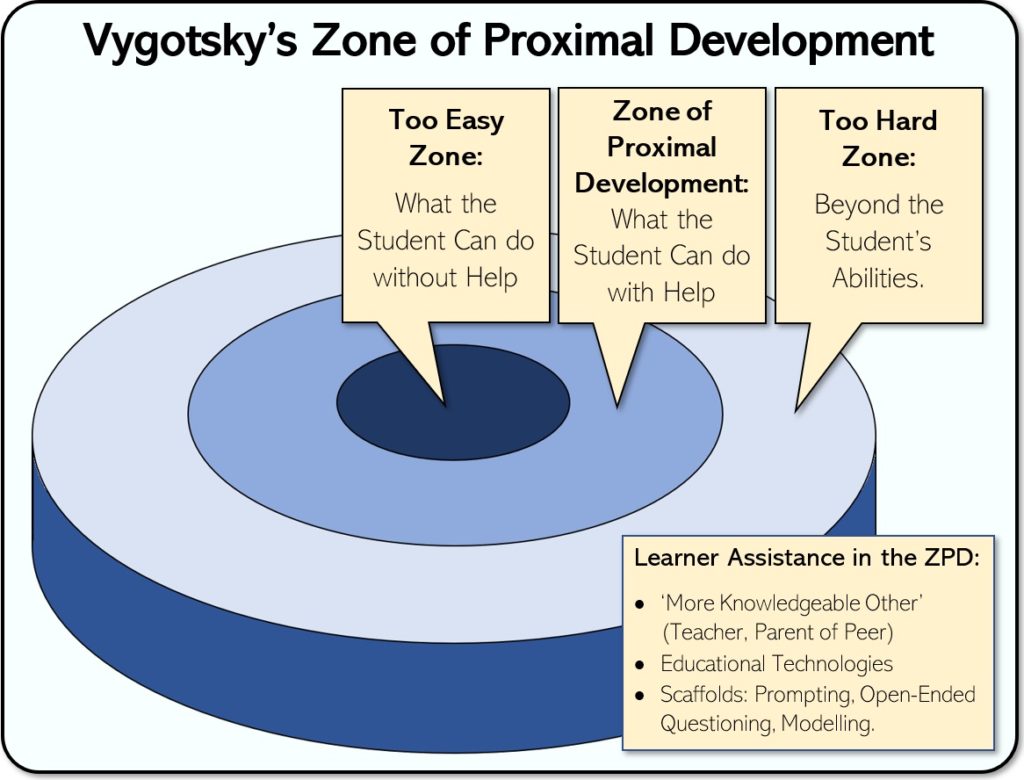
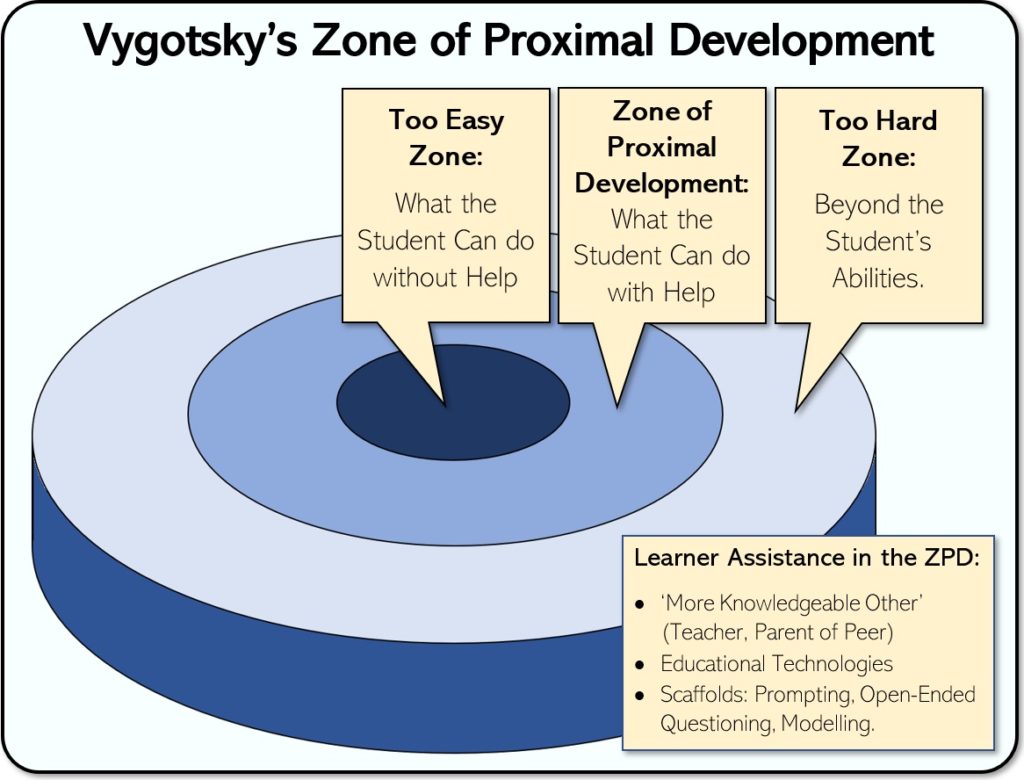
Zone of Proximal Development (Lev Vygotsky et al)
The gap between what a learner can do independently and what they can achieve with guidance.
Observational Learning
Learning that occurs through observing the actions of others and the results of those actions.

Intrinsic Motivation
The drive to engage in an activity for its inherent satisfaction rather than for some separable consequence.


Extrinsic Reward
A tangible benefit given for a behavior, which may diminish intrinsic motivation.

Cognitivism
A learning theory emphasizing mental processes and active participation in learning.
Constructivism
A philosophical perspective suggesting knowledge is personally constructed based on beliefs and experiences.
Taste Aversion
A learned avoidance of a specific flavor after it is associated with illness.

Animal Models
Using animal behavior to understand human learning and cognition.

Neophobia
The fear of new or unfamiliar things, particularly seen in children's aversion to trying new foods.

Social Learning in Primates (van Leeuwen, E.J.C., DeTroy, S.E., Haun, D.B.M. et al (2024))
Evidence showing that non-human animals can learn socially, which is similar to human social learning such as observation of their companions.

Observational Conditioning
A form of learning where an individual's response is influenced by observing others.
Imitation
The act of copying the behavior of others, said to be an important aspect of social learning.
Cognitive Processes
Mental actions or processes underlying the acquisition of knowledge and skills.
Emotional Processing
The neurological mechanisms involved in understanding and managing emotions.