Introduction to Clinical Hematology: Hematopoiesis and Hematopoietic Organs
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is hematopoiesis?
The production and development of blood cells.
Where does hematopoiesis occur during different life stages?
In various locations throughout embryonic and fetal development, childhood, and adulthood.
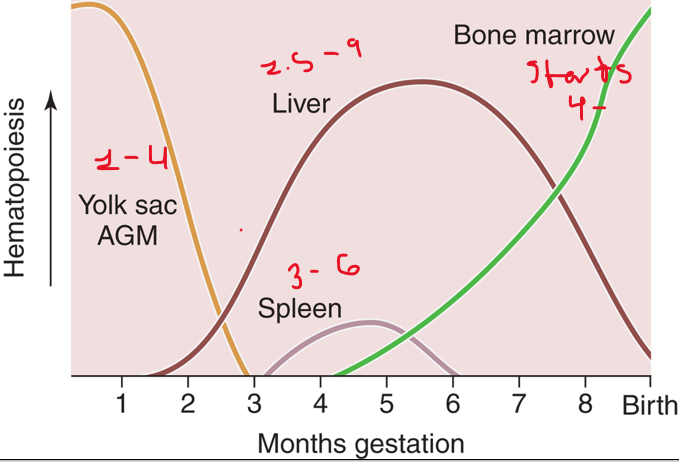

What are the primary lymphoid tissues?
Bone marrow and thymus.
where the precursors of lymphoid cells are made
What are the secondary lymphoid tissues?
Spleen and lymph nodes.
activation and proliferation of lymphocytes - basically, where cells go to be differentiated
What is the function of the bone marrow?
It is responsible for the production of blood cells.
•Two compartments:
–Vascular compartment
–Endosteal compartment
Stroma
Is supports Tissue and makes it a favorable environment for blood to mature
Stromal Cells Have
Scaffolding and Cytokines
Macrophages ( get of self reactive cells), lymphocytes, adipocytes
Yellow marrow vs red marrow
Osteoblast - Create Bone Tissue
Osteoclast - Break Down Bone Tissue
Found in the Endosteum and Produce Cytokines
•Hematopoietic niches
– specialized microenvironments within the bone marrow that support the self-renewal and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
- Diff. Groups and Diff. Locations
Erythroblast islands - are where red blood cell proliferate and mature
Granulocytic nests - a type of white blood cell including neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils—are produced.
Lymphoid aggregates - clusters of lymphoid cells, such as B-cells and T-cells, that can be found in the bone marrow and other organs
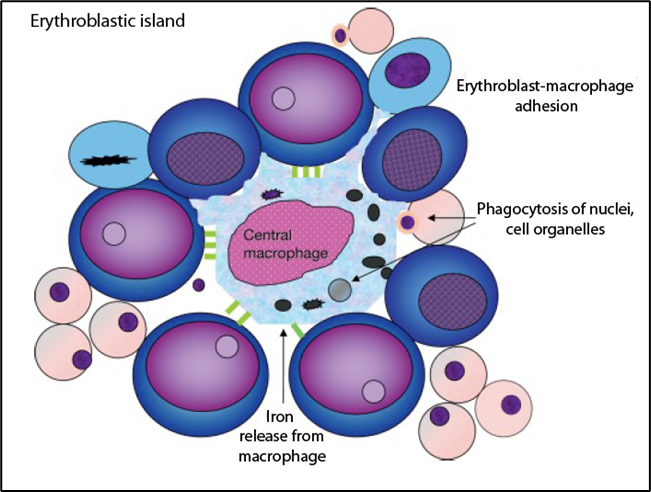
Adipose Tissue in the Bone Marrow
mechanically control he volume of the bone marrow
Hyperplastic Bone Marrow
Very Cellular - Often caused by Overproliferation (Cancer)
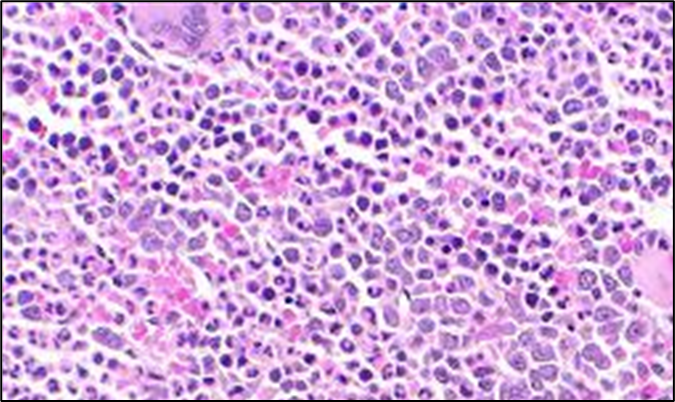
Hypoplastic bone marrow
Not Very Cellular - the bone marrow loses function, and Red is Replaced with Yellow
Blood Cell Egress
The process of a cell exiting or departing from its current location
–RBC move between reticular cells, through endothelial cells
–RBC is able to (deform) so they move Deformability (2-3 mcM wide pore)
–Cytokine regulates the process
* RBC will gather by the reticular sites and they essentially talk to endothelial cells so go through then RBC deform to squeeze through
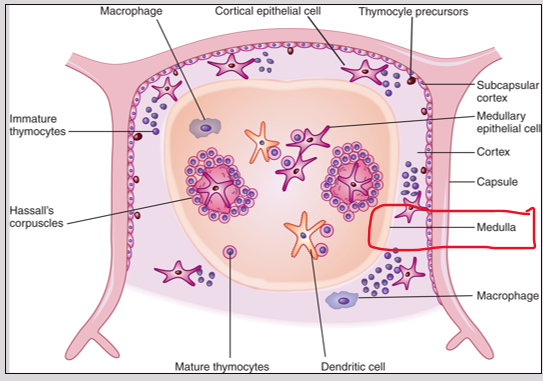
Thymus
Function is T Cell Maturation
It is fully developed at birth; atrophied by adulthood - (shrinks)
Lymphopoietic"- which is the process of generating lymphocytes.
Thymus Cortex
outer region of the thymus
Generation and proliferation: Immature T cells are produced and multiply in the cortex
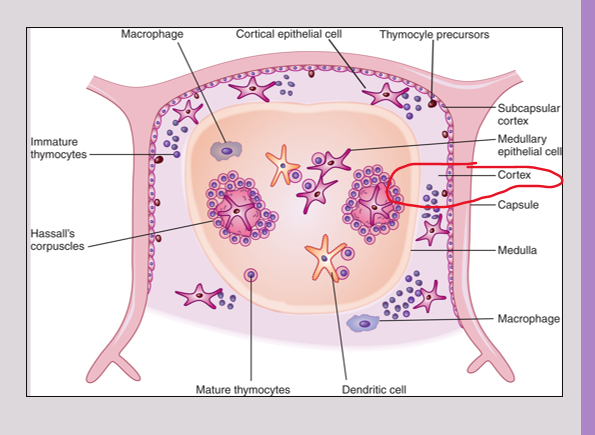
Thymus Medulla
Inner regions of Thymus
ensures that developing T cells do not attack the body's own tissues by eliminating self-reactive cells through negative selection.
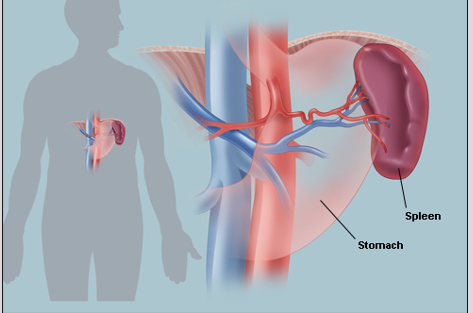
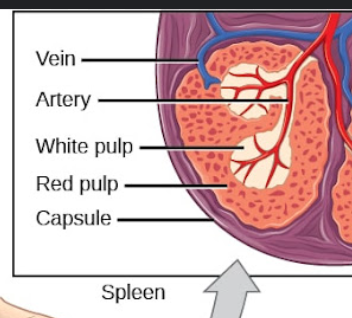
What is the function of the spleen?
To filter foreign substances and old RBCs, store platelets, and provide immune defense.
•Largest collection of lymphocytes and macrophages in body
•Upper-left quadrant
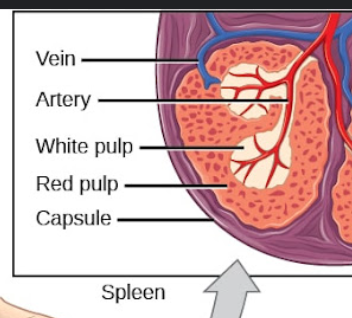
Spleen White Pulp
–Lymphocytes around central artery
–T-cells closest to artery
–B-cells within follicle germinal centers
Immune surveillance
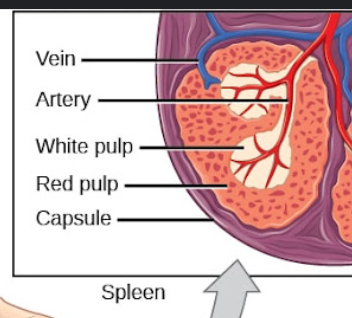
Spleen Red Puple
–Sinuses and cords - Have Macrophages and act to destroy
–Erythrocytes & platelets
Spleen Blood Flow
–5% of total cardiac output
–“sluggish” - is sluggish, so macrophages can destroy the old Red Blood Cells
–RBC obstacle course: hypoxic, acidic, hypoglycemic
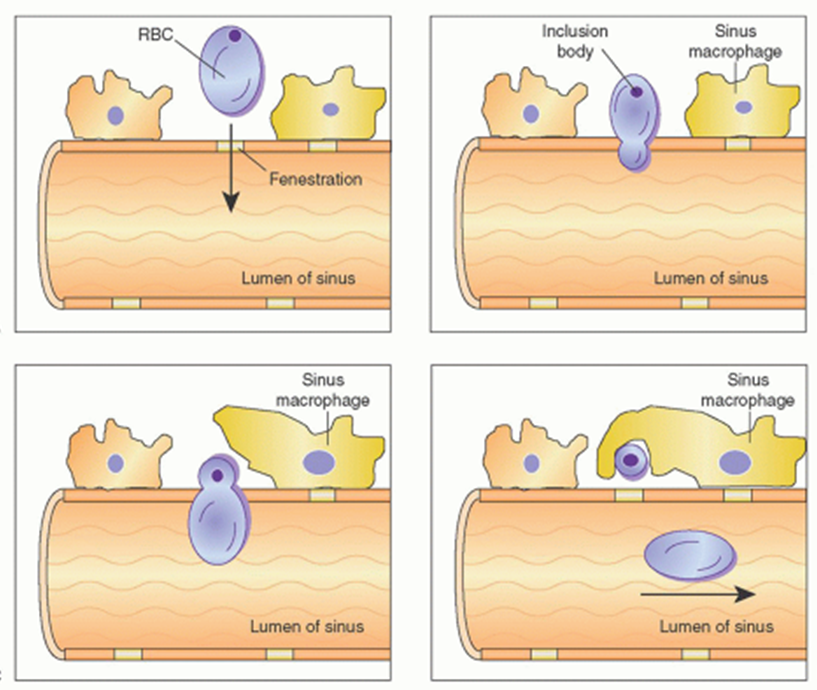
•Culling - Spleen
–Old RBCs phagocytized by macrophages
•Pitting - Spleen
–Removal of inclusions
–Removal of surface antibodies
–Damages cell but does not remove from circulation
Spleen:Function
•Immune sensitization and defense
•Platelet storage
–1/3 of total platelets
•Hypersplenism
Spleen is Enlarged
Splenectomy
•: surgical removal of spleen
–Removes site of RBC destruction
–Culling performed by liver (Kupffer cells)
Lymph Nodes
Filter Blood
•Function: removal of foreign particles from lymph and immune defense via B-cell stimulation
•B-cell follicles surrounded with germinal center by T-cell and macrophages
Lymphadenopathy
Swollen Lymph Nodes
What is the function of lymph nodes?
To remove foreign particles from lymph and provide immune defense via B-cell stimulation.
What is the difference between hyperplastic and hypoplastic bone marrow?`
Hyperplastic bone marrow has increased cellularity, while hypoplastic bone marrow has decreased cellularity.
What does pitting refer to in the spleen?
The removal of inclusions and surface antibodies from red blood cells without removing them from circulation.
What does culling refer to in the spleen?
The phagocytization of old RBCs by macrophages.
What are the two compartments of bone marrow?
Vascular compartment and endosteal compartment.
What is the role of stromal cells in the bone marrow?
They provide scaffolding and cytokines for hematopoiesis.
What is the primary function of the thymus?
T-cell maturation.
What is the largest collection of lymphocytes and macrophages in the body?
The spleen.
What are the components of the spleen's architecture?
White pulp (lymphocytes around central artery) and red pulp (sinuses and cords containing erythrocytes and platelets).
What is hypersplenism?
A condition characterized by splenomegaly.
What happens during a splenectomy?
The surgical removal of the spleen, which removes the site of RBC destruction.
What is the blood flow characteristic in the spleen?
It receives 5% of total cardiac output and has a sluggish blood flow.
What is the significance of the cortex and medulla in lymph nodes?
The cortex contains B-cell follicles, while the medulla contains T-cells and macrophages.
What is lymphadenopathy?
The enlargement of lymph nodes, often associated with immune response.