Unit 8: World War II - Isolationism, Pearl Harbor, & Japanese Internment
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Joseph Stalin
WWII dictator of the Soviet Union (USSR)

Benito Mussolini
WWII dictator of Italy

Adolf Hitler
WWII dictator of Nazi Germany

Appeasement
-giving into a hostile power in order to preserve peace (illustration - giving into bratty child to keep them quiet)
-one of the causes of WWII

Munich Pact
-Britain tried to appease Hitler by giving Germany the Sudetenland around Czechoslovakia as long as he promised not to take any more land.
-It didn't work. 6 months later Hitler invaded and conquered the rest of Czechoslovakia.

3 Reasons Germans wanted revenge for the Treaty of Versailles (which ended WWI)
(1) took 13% of Germany's land
(2) took away Germany's military
(3) forced Germany to admit they caused WWI and had to pay reparations for all damages done in WWI

America First Committee
-organization founded in 1940 to keep the U.S. from participating in WWII
-Had many famous members like Charles Lindbergh & Walt Disney

Charles Lindberg
-member of America First Committee
-Originally opposed U.S. involvement in WWII because he didn't think the U.S. could defeat Nazi Germany

Nye Committee
Congressional committee that concluded America entered WWI to keep American munitions (weapons) makers and bankers from losing their investments in Great Britain.
Good Neighbor Policy
-example of American isolationism during 1930s
-U.S. promised not to intervene in affairs of Latin American nations.

How did the Neutrality Acts (1935-37) try to keep the U.S. out of WWII?
-made it illegal for Americans to sail on ships owned by nations at war
-made it illegal to loan or sell weapons to nations at war
-example of American isolationism during 1930s

Kellogg-Briand Pact
international treaty signed by over 60 nations in the 1920s to outlaw the use of war as a solution for international controversies

Lend-Lease Act
-allowed America to "loan" weapons to Great Britain to defeat Nazi Germany.
-Great Britain was supposed to return these weapons after the war.
-Example of an action that moved America toward involvement in WWII BEFORE Pearl Harbor was bombed

Cash & Carry Policy
-allowed nations at war to buy goods and arms in the United States if they paid cash and carried the merchandise on their own ships.
-Example of an action that moved America toward involvement in WWII BEFORE Pearl Harbor was bombed

Destroyers for Bases Agreement
-FDR transferred 50 American destroyers to Great Britain in exchange for 99-year leases on eight British bases in the Western Hemisphere.
-Example of an action that moved America toward involvement in WWII BEFORE Pearl Harbor was bombed

Atlantic Charter
-joint declaration made by the U.S. and Britain, which endorsed an international system of general security.
-became basis for the creation of the United Nations (1945).
-Example of an action that moved America toward involvement in WWII BEFORE Pearl Harbor was bombed

Why did Japan attack Pearl Harbor?
get natural resources (oil, steel, etc...) to enable Japan to expand empire without being opposed by U.S. sanctions and Navy in the Pacific
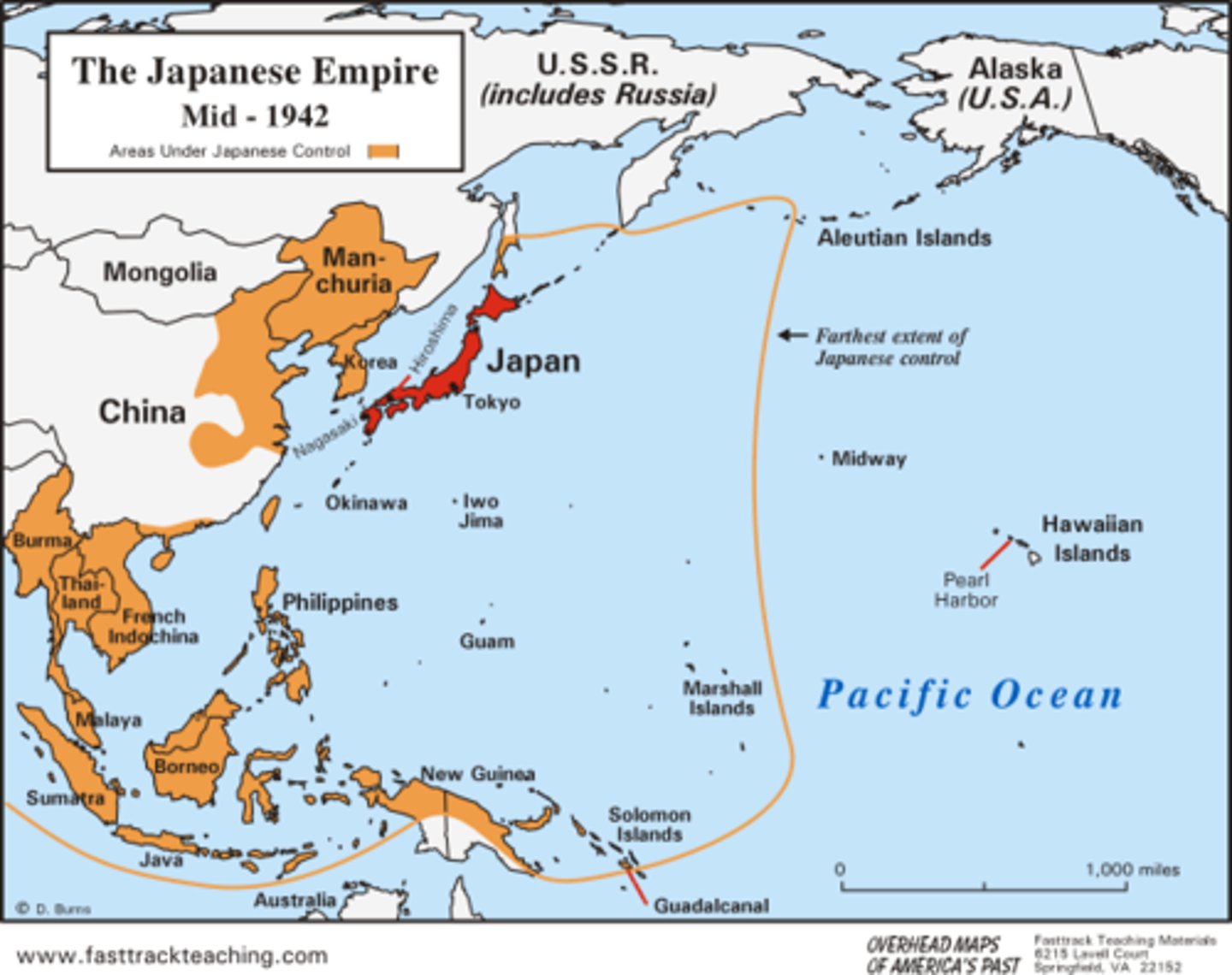
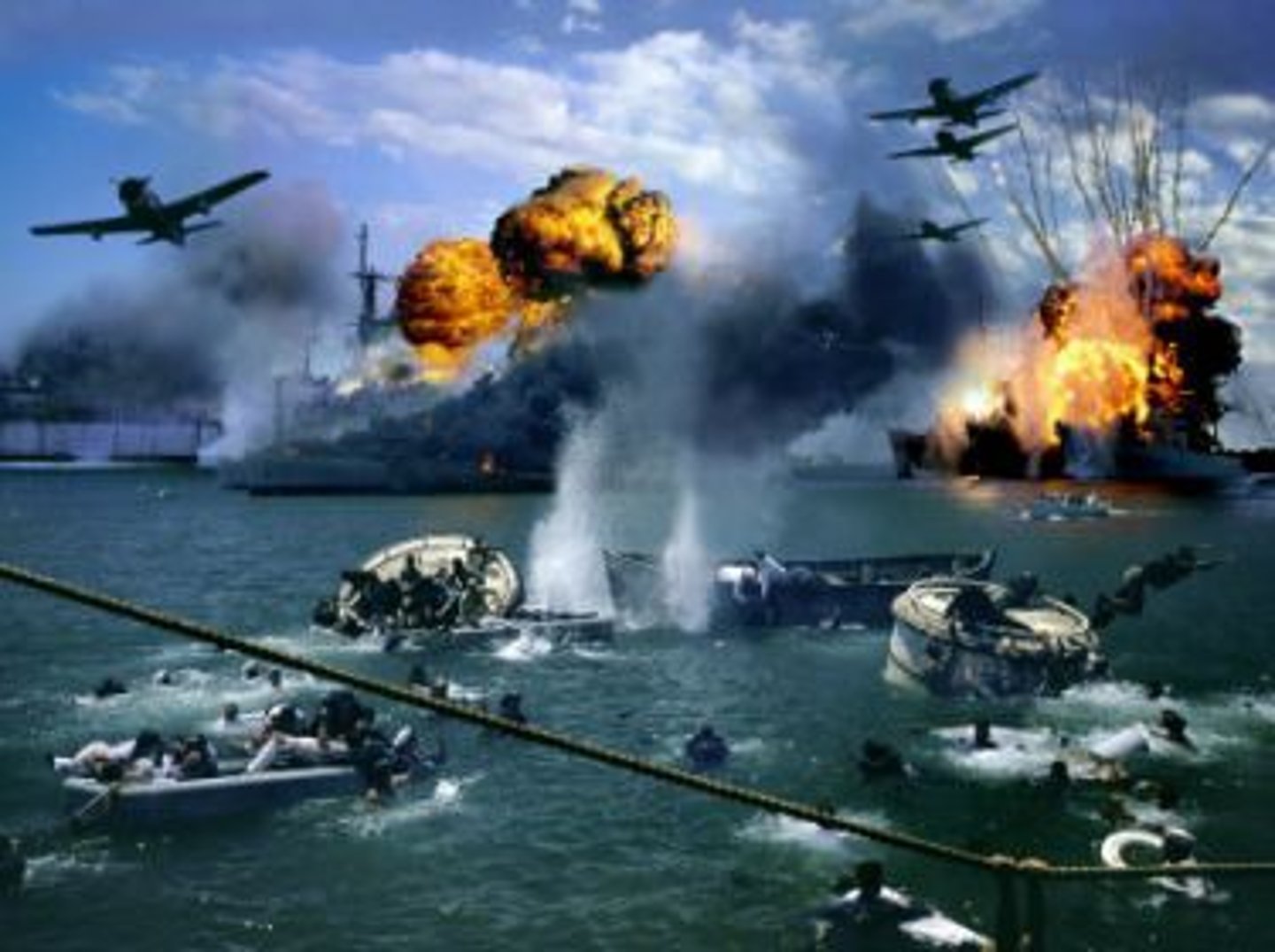
What were the results of Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor?
approximately 2400 Americans died and the U.S. was officially pulled out of isolationism when it entered WWII.

Executive Order 9066
allowed the U.S. military to place Japanese-Americans in concentration camps within the U.S.

For what reasons did the U.S. place people of Japanese ancestry in internment camps?
-Fear of sabotage or spying for Japan
-Fear they might help Japan in a possible land invasion of the west coast of the U.S.
Korematsu v. United States (1944)
-the Supreme Court upheld a conviction against a Japanese-American man for breaking curfew. This decision said it was okay for the government to intern Japanese out of a military necessity to protect Americans. -Korematsu's conviction was overturned in 1984 and reparations were awarded to those interned

442nd
-all Japanese-American combat-unit was the
-most highly decorated combat regiment in WWII.
-Many of the men had family members in internment camps, but still fought bravely for their country - demonstrating their loyalty to the nation.
