TAMU BIOL 319 (A&P Part 2)
1/466
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Set for the second practical of BIOL 319 at Texas A&M University. Made the summer of 2024.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
467 Terms
Where is smooth muscle?
Walls of hollow organs
How does smooth muscle move?
involuntary, slow and rhythmically to propel substances through channels of the body
How does cardiac muscle move?
involuntary, intrinsic contraction rhythm altered by nervous system
How much of the body’s mass is skeletal muscle?
40%
What do skeletal muscles do?
majority of locomotion and support of skeleton
What are skeletal muscles made up of?
muscle fibers/cells organized in fascicles
What is an upper motor neuron lesion?
loss of muscle function bc of stroke damaging neurons in the brain
How does skeletal muscle move?
voluntary, powerful, can rapidly contract but tires rapidly
What is excitability?
the electric charge differential in the cell membrane can be changes upon stimulation to produce an intracellular muscle response
What is contractility?
muscle cells shorten when stimulated
What is extensibility?
muscle cells can stretch, sometimes more than resting length
What is elasticity?
muscle cells can return to resting cell length after being stretched
Functions of muscles?
generate movement, maintain posture and balance, stabilize joints, generate heat to maintain body temperature
What is in a skeletal muscle?
muscle fibers, nerves, blood vessels, connective tissues
Where do blood vessels and nerves enter the skeletal muscle?
near the center, then branch out through connective tissue sheaths
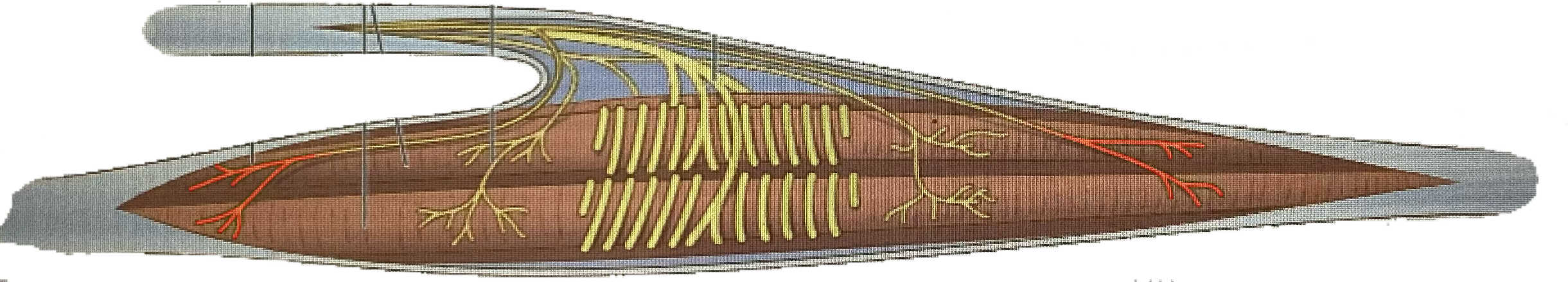
What is this?
Gamma efferent fibers
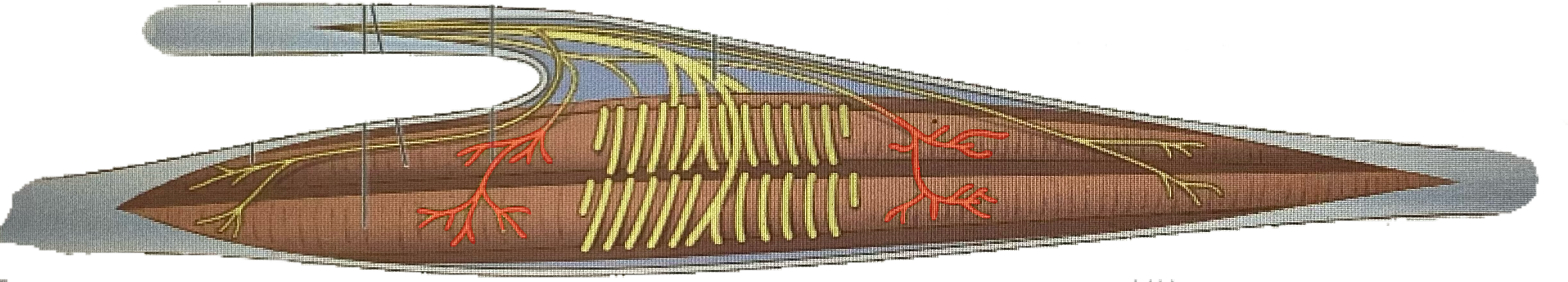
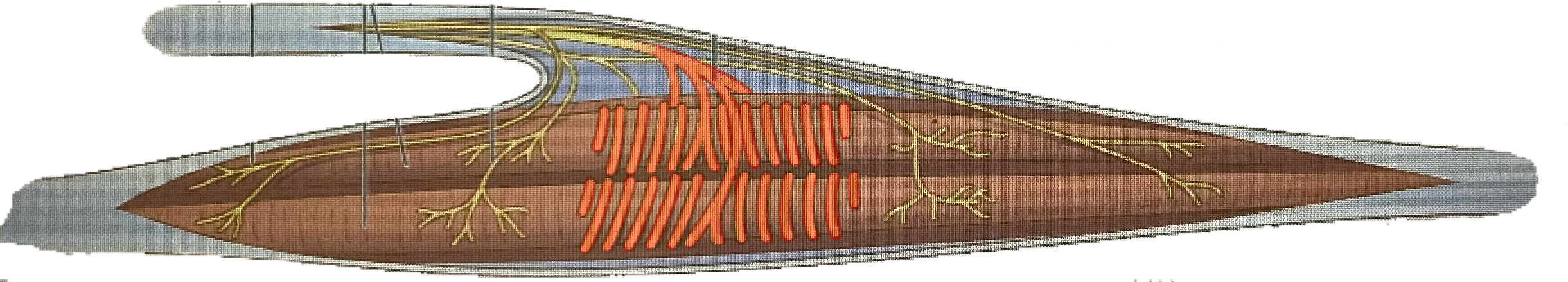
What is this?
Intrafusal muscle fibers
What is this?
Flower spray endings
What is this?
Annulospiral endings
What are annulospiral endings?
endings of large axons, wrap around center of muscle spindle, stimulated by degree and rate of stretch
What are flower spray endings?
small axons, ends of muscle spindles, stimulated by amount of stretch
What are gamma efferent fibers?
from small motor neurons of spinal cord, innervate contractile ends of intrafusal fibers, stimulate them to contract with rest of muscle
What are efferent fibers/alpha efferent fibers?
from large alpha motor neurons, stimulate contraction in extrafusal fibers
What is external stretch?
muscle spindle is stretched when muscle lengthens, eg. when weight is applied or antagonistic muscle contracts
What is internal stretch?
gamma motor neurons cause intrafusal fiber ends to contract which stretches spindle middle, increases rate of firing of anulospiral and flower spray endings
What is alpha-gamma coactivation?
descending motor pathway fibers synapse with alpha and gamma motor neurons so extrafusal and intrafusal fiber ends contract simultaneously
What type of muscle is autorhythmic?
Skeletal Muscle
Tendons
Connective tissues that attach muscle to bone; rope-like extensions that are made up of mostly collagen
Why are the connective tissue sheaths of muscles continuous with each other and with tendons?
To transfer the force of the contracting muscle fibers to the structure (like bone) to be moved
Direct Attachment
When the periosteum or perichondrium is fused with the muscle’s epimysium
Indirect Attachment
The more durable, smaller, and more common attachment type, like a tendon or aponeurosis; can blend into the fascia of other muscles to form an attachment
Interacting Joints or Articular Surfaces
Allows for an almost frictionless movement of the adjacent bones
Joints
Pivot points for motion when skeletal muscle contracts
Antagonistic muscle
The muscle that relaxes
Myofilament(s) that A Bands contain
Actin and Myosin
Myofilament(s) that I Bands contain
Actin
Myofilament(s) that H Bands contain
Myosin
Myofilament(s) that Z Line contain
Actin
Myofilament(s) that M Line contain?
Myosin
Alpha-Actin
The protein that the z line is mostly made up of
Titin
Protein that makes up elastic filaments and runs from the Z Line to the thick filaments
Agonist
Muscle that contracts
Terminal Cisterns
Large perpendicular cross channels of the sarcolemma that are always found in pairs
T Tubules
Elongated tube extensions of the sarcolemma that dive deeply into the cell
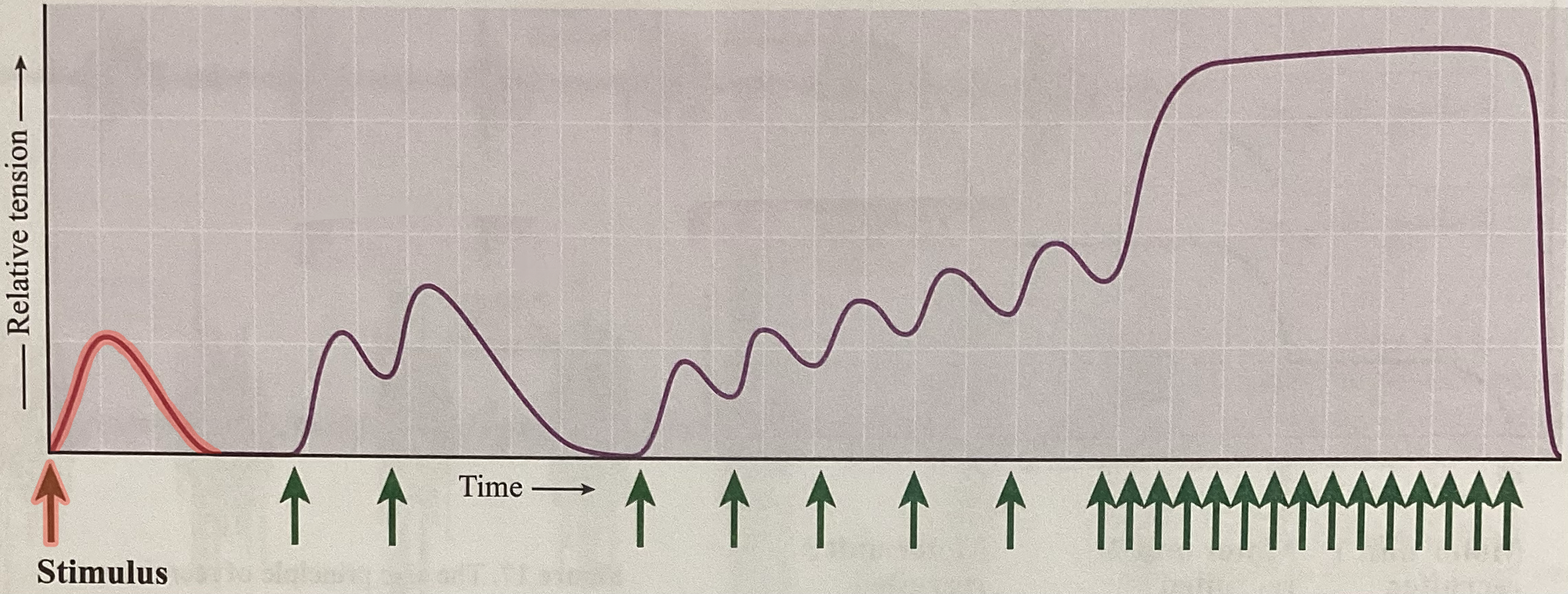
What type of contraction is this?
Twitch
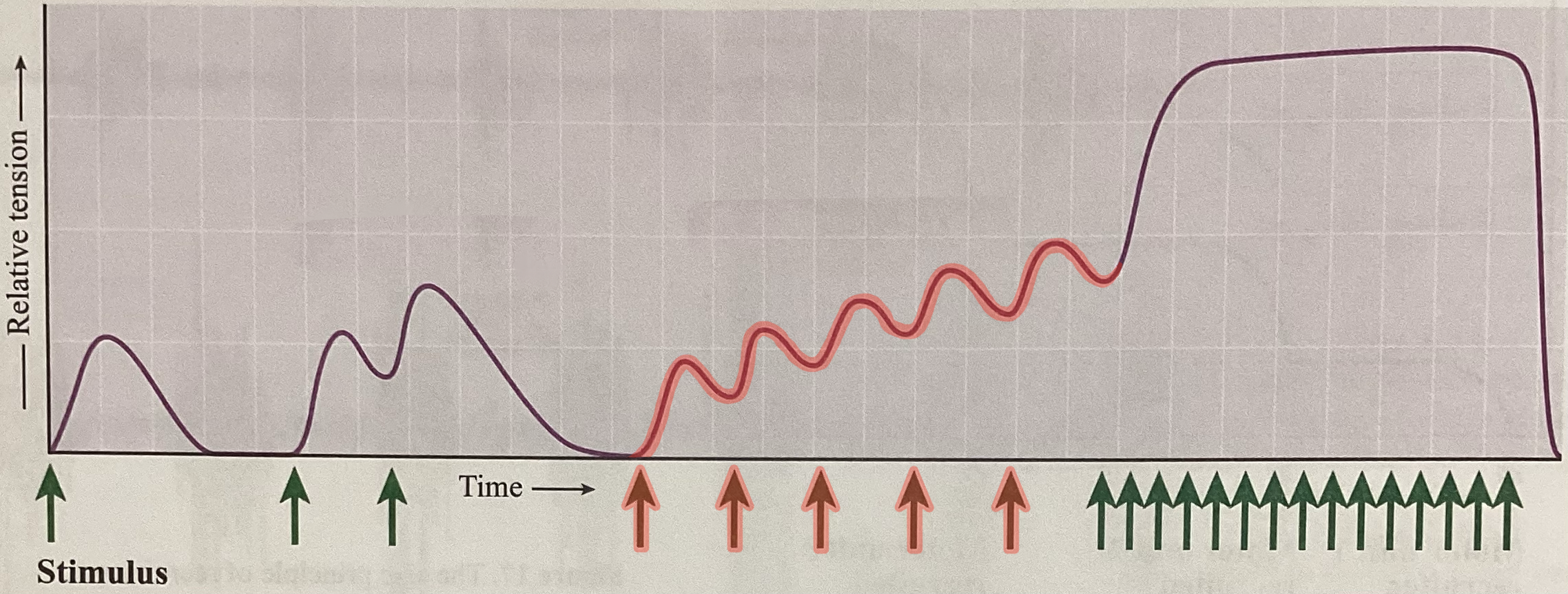
What type of contraction is this?
Unfused/incomplete tetanus
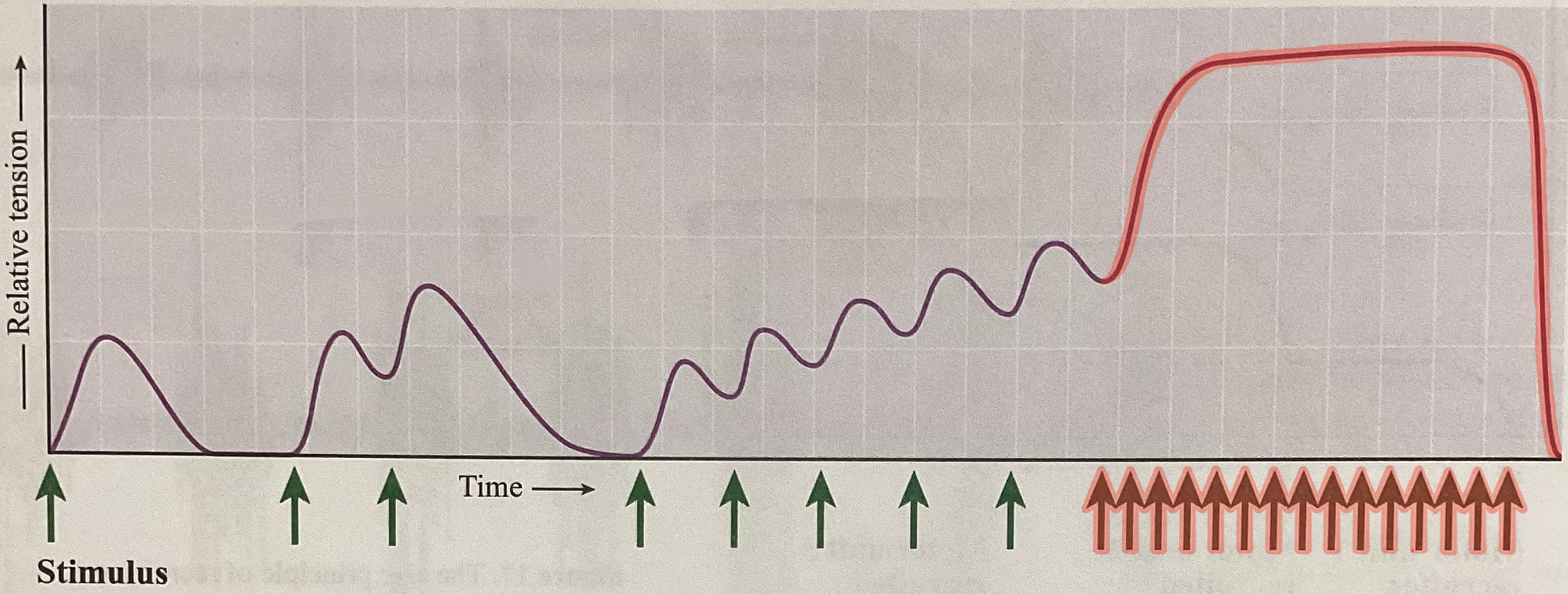
What type of contraction is this?
Fused/complete tetanus
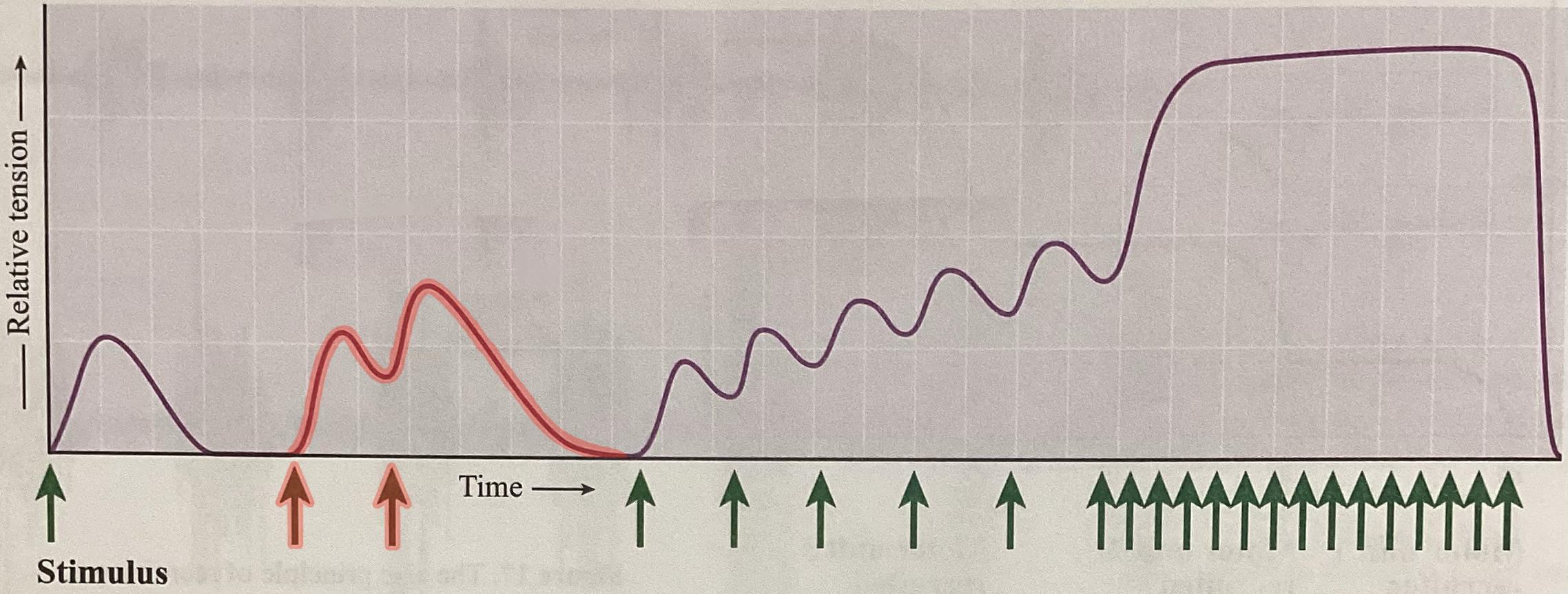
What type of contraction is this?
Wave summation
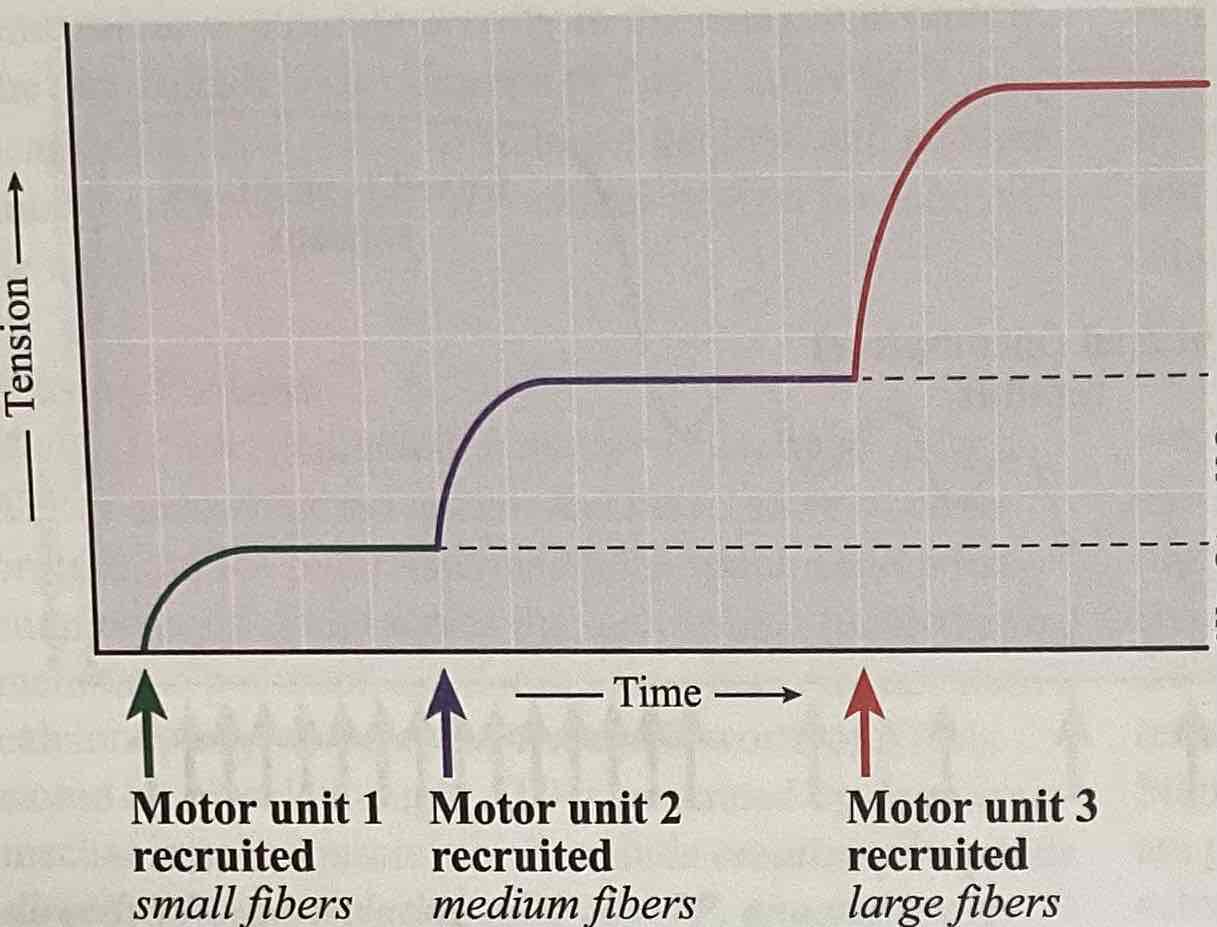
What is the order of neurons from least to most sensitive?
3 → 2 → 1
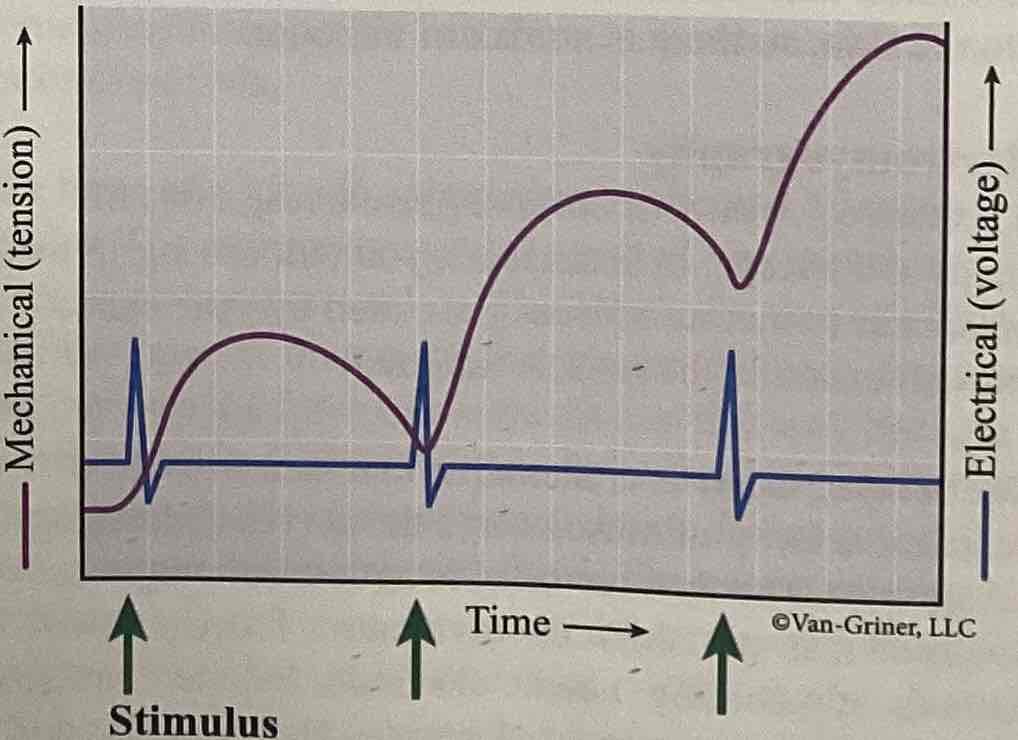
What does this image represent?
Summation
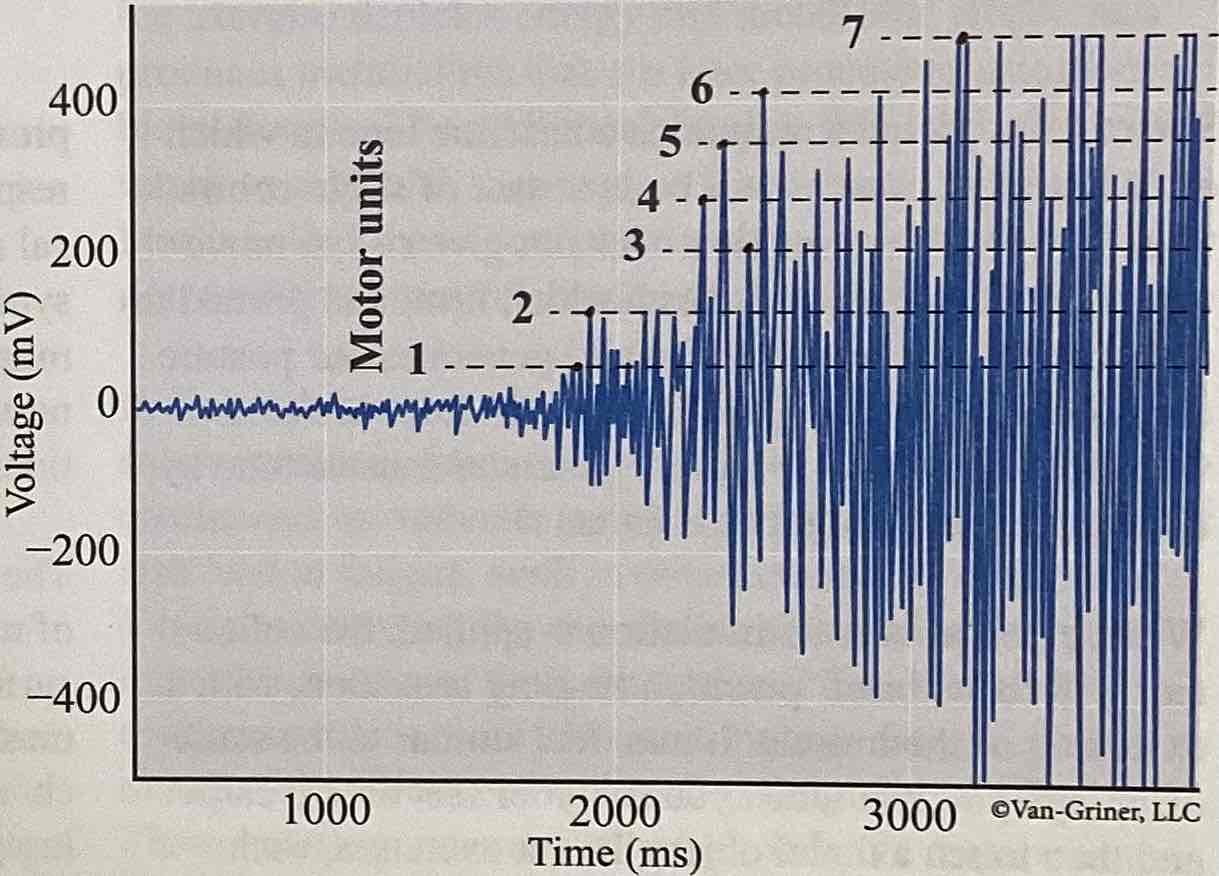
What does this image represent?
Size principal of recruitment (voltage)
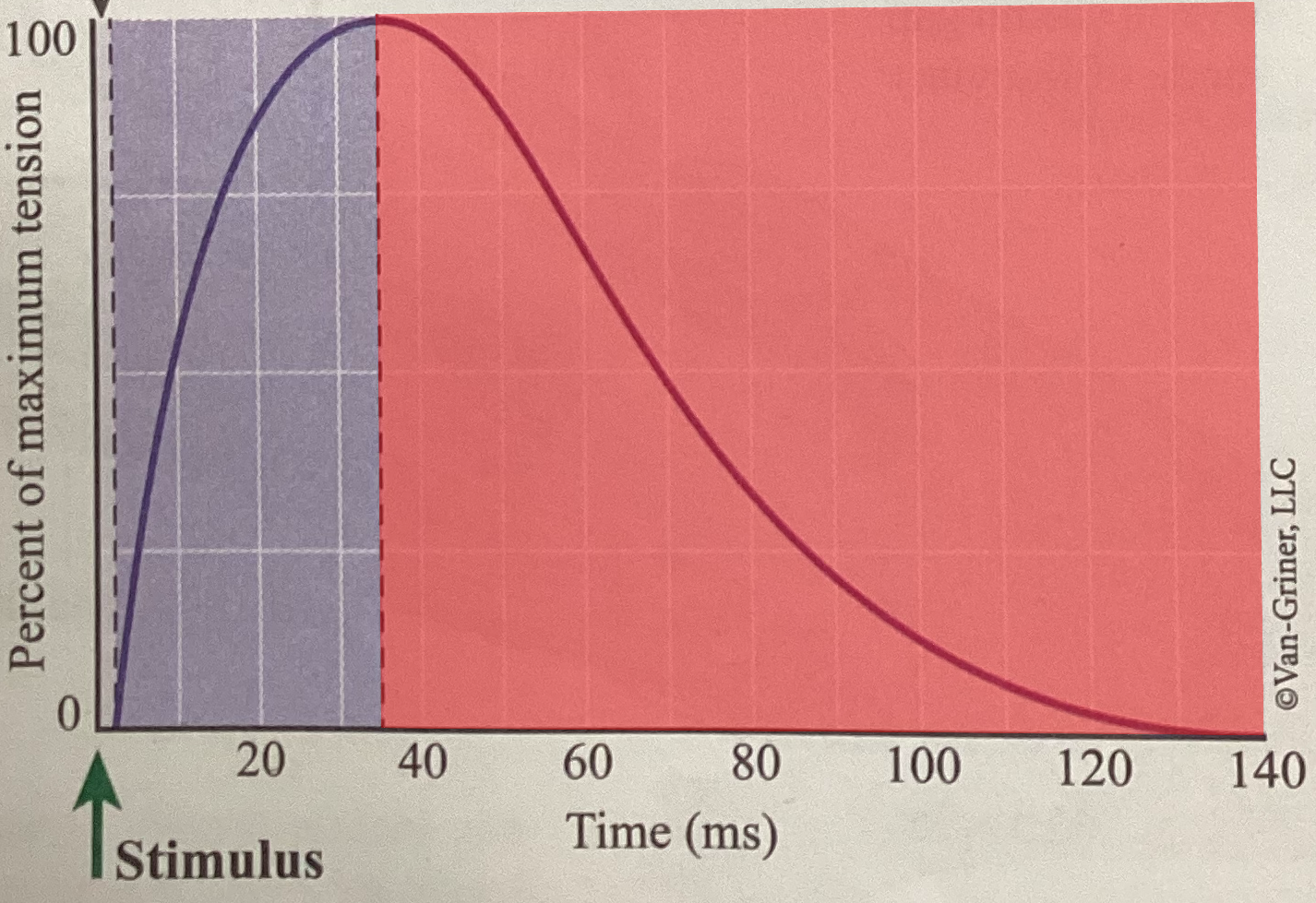
What phase of an isometric twitch is shown?
Period of relaxation
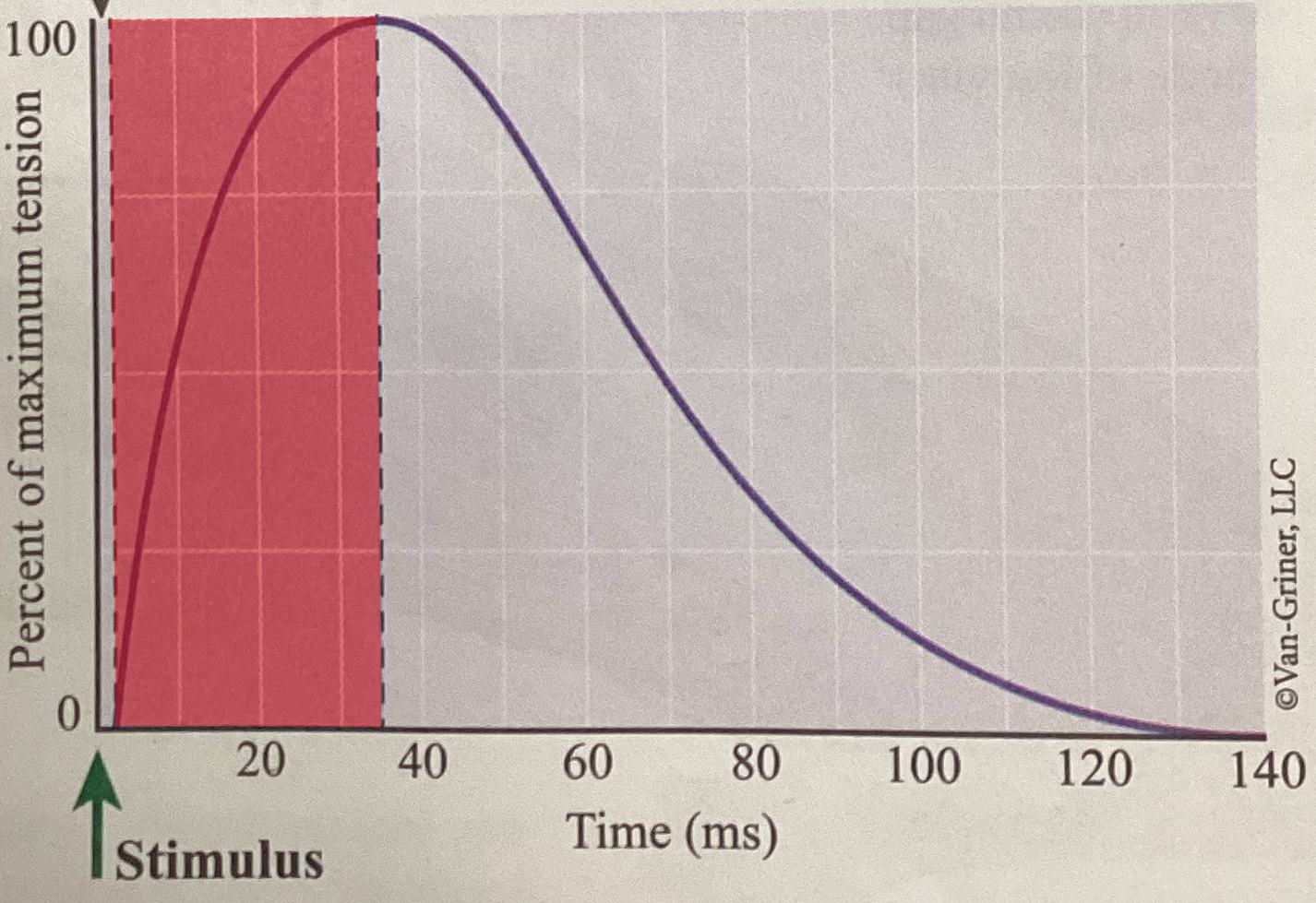
What phase of an isometric twitch is shown?
Period of contraction
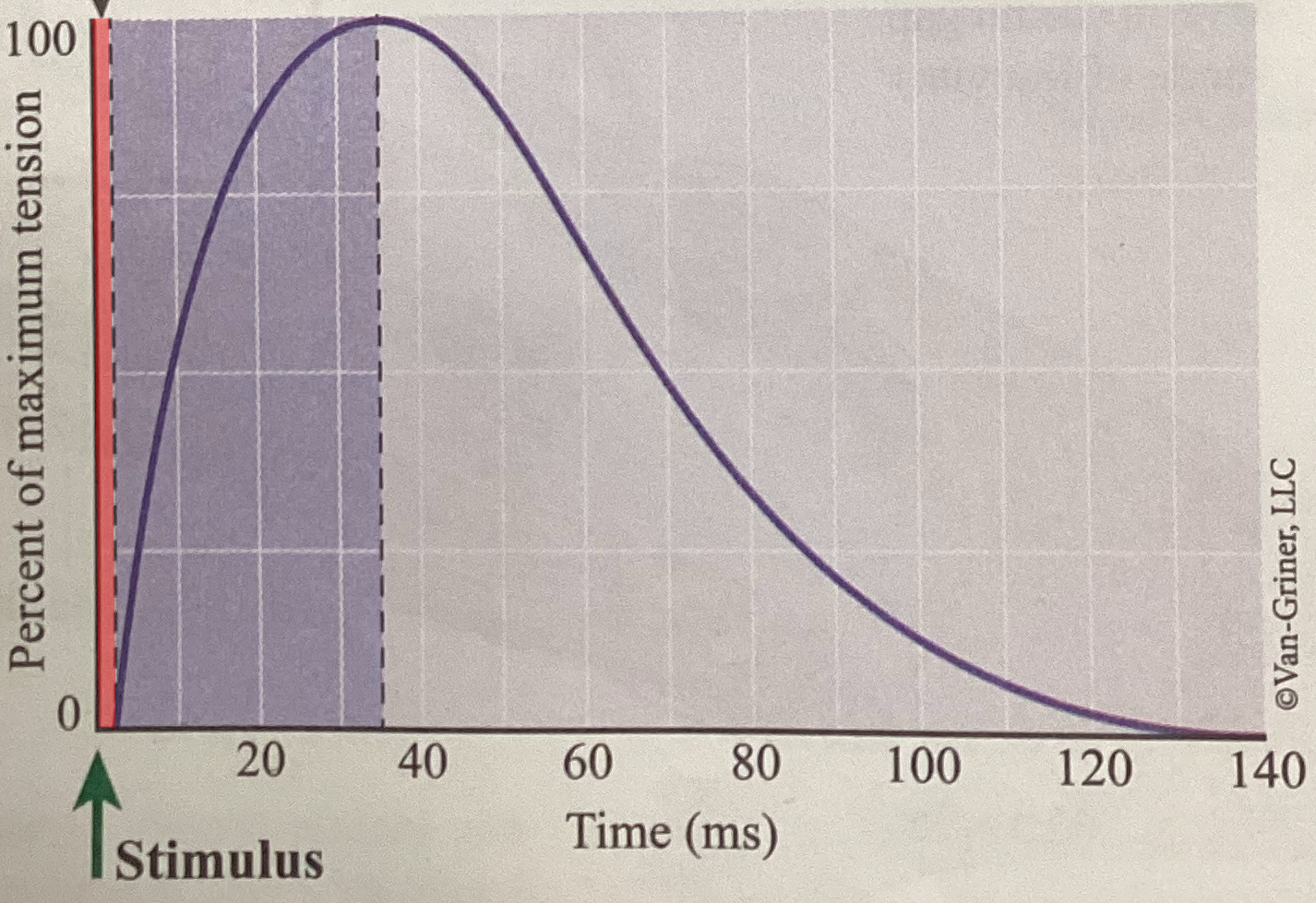
What phase of an isometric twitch is shown?
Period of latency
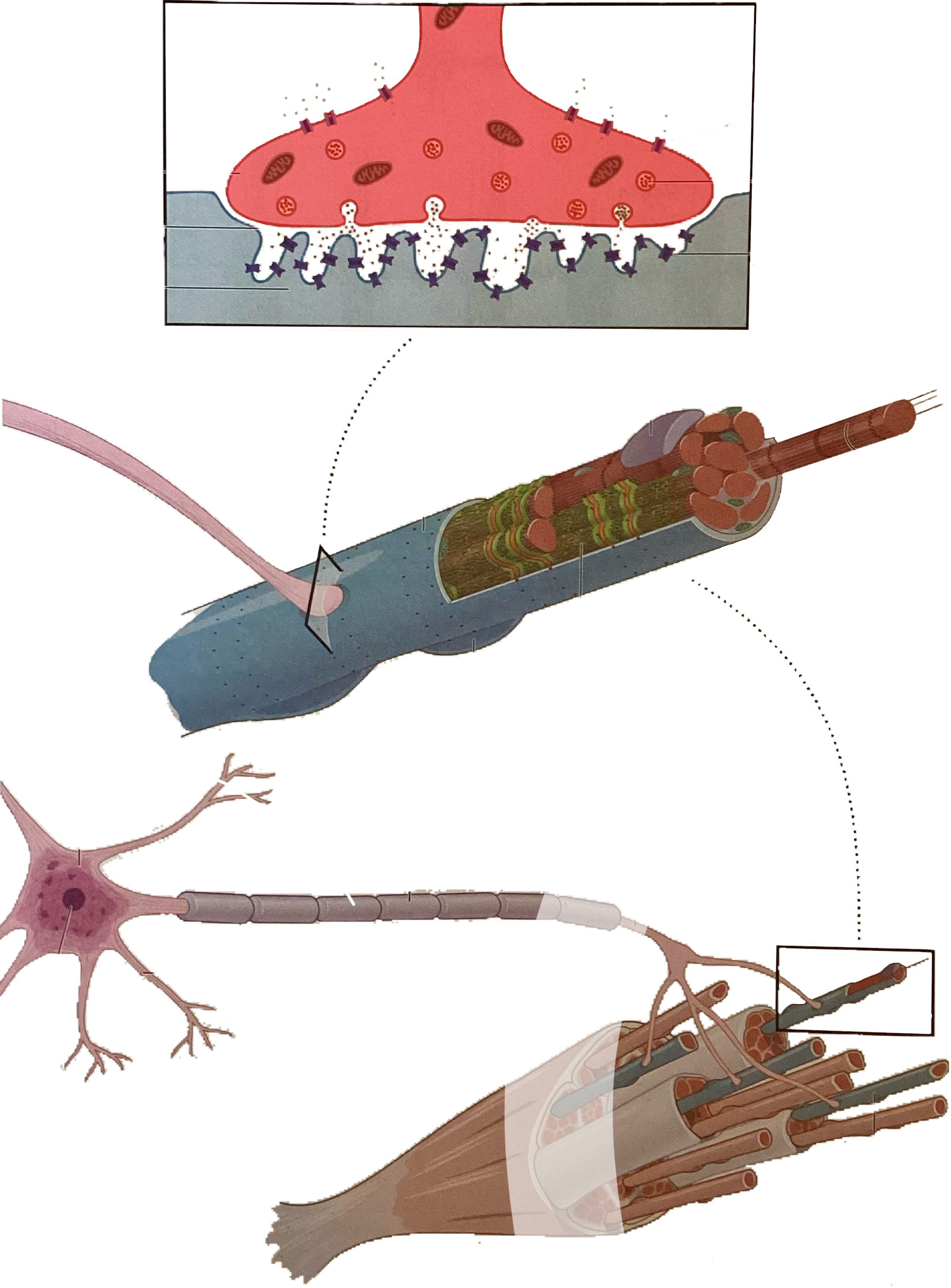
What is this?
Axon terminal
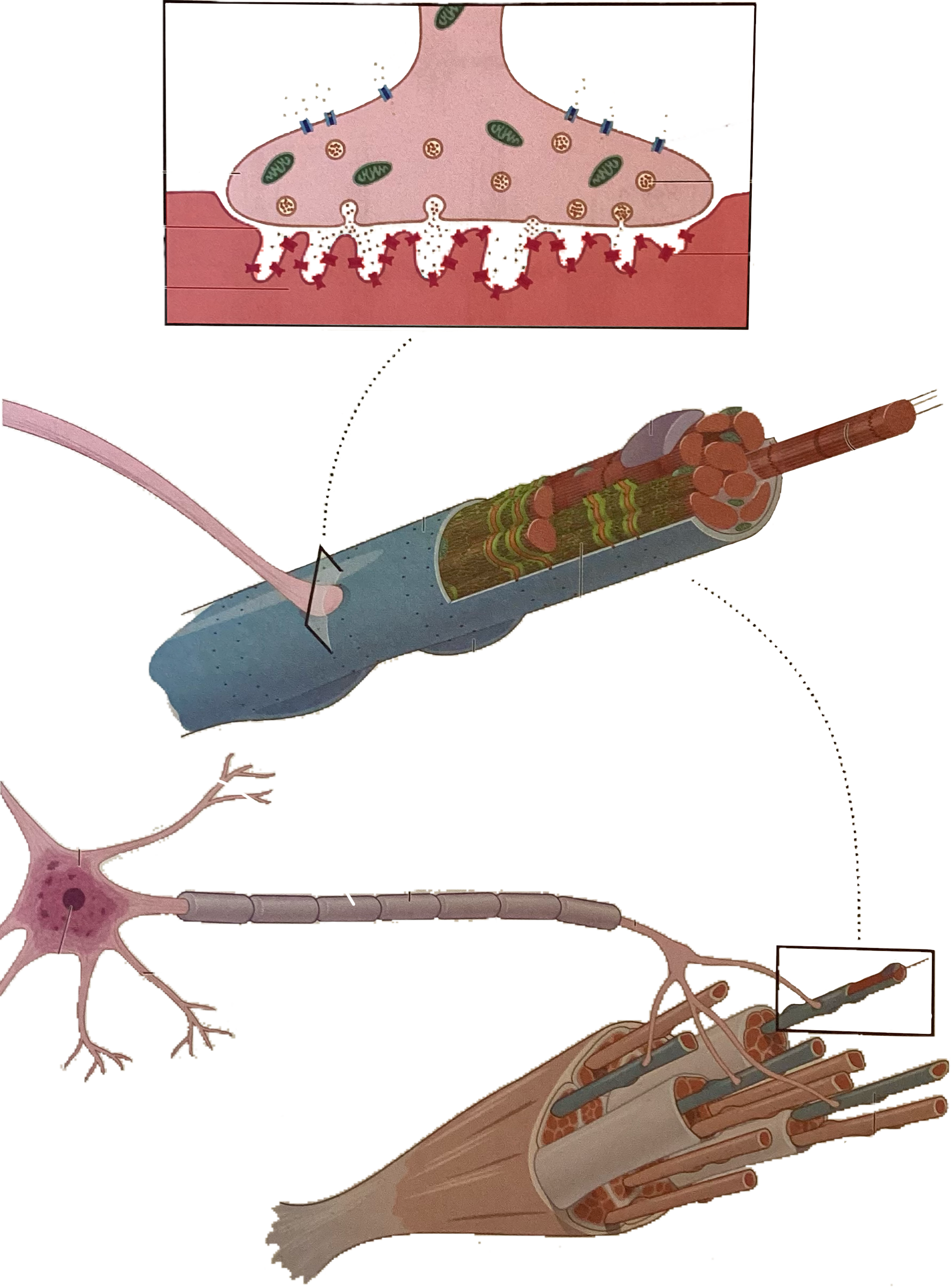
What is this?
Motor end plate
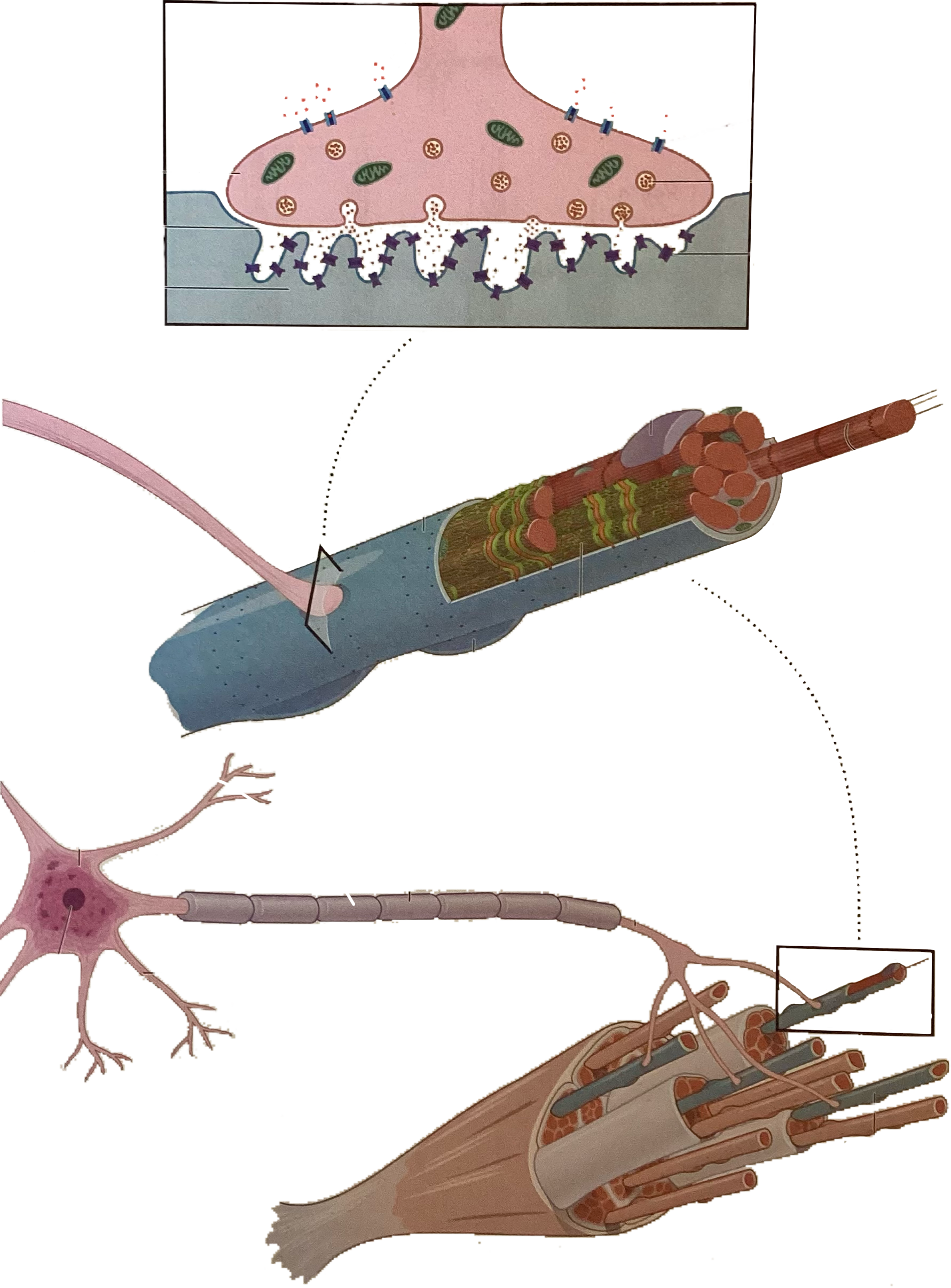
What is this?
Calcium
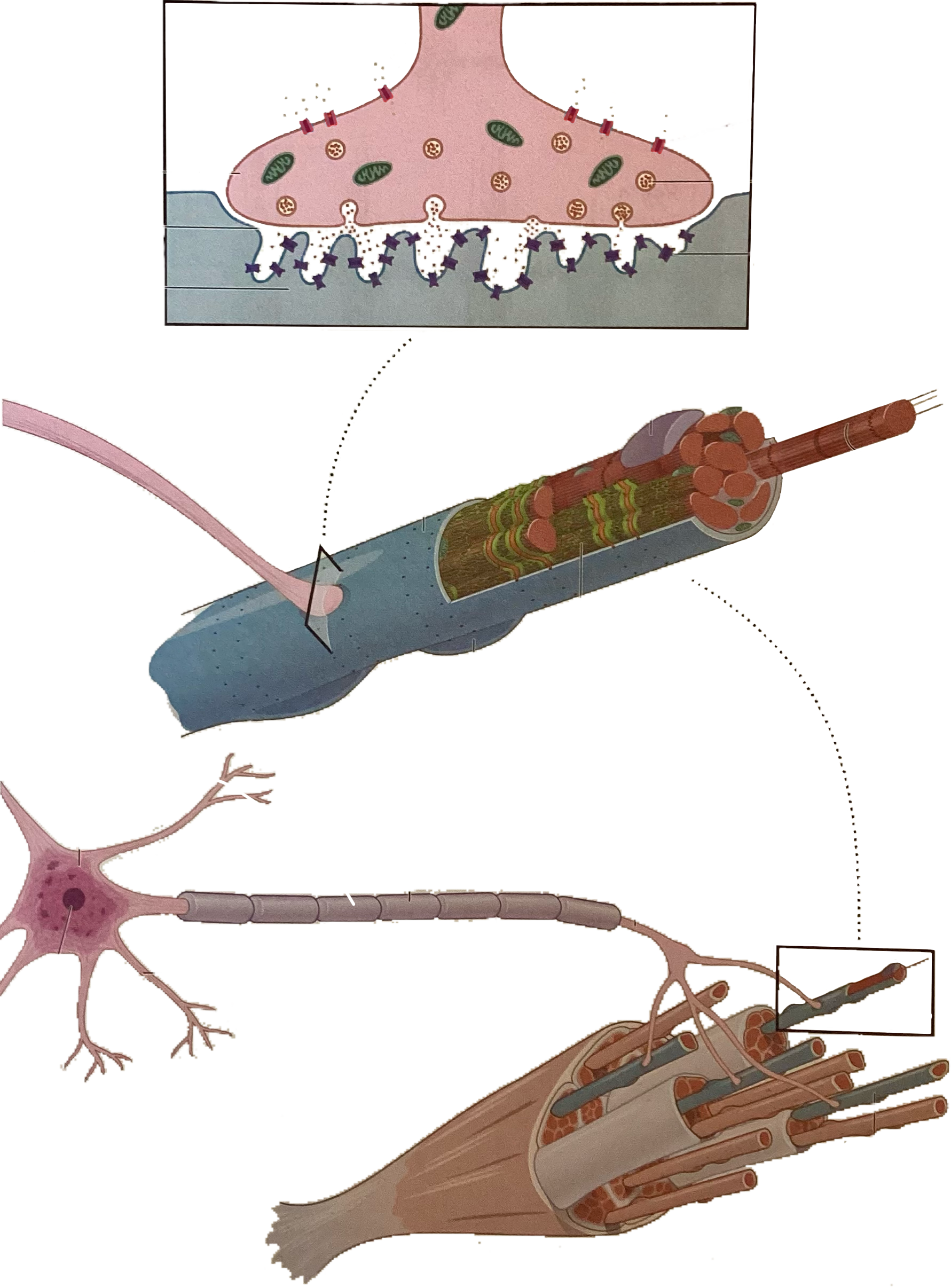
What is this?
Voltage gated calcium channels
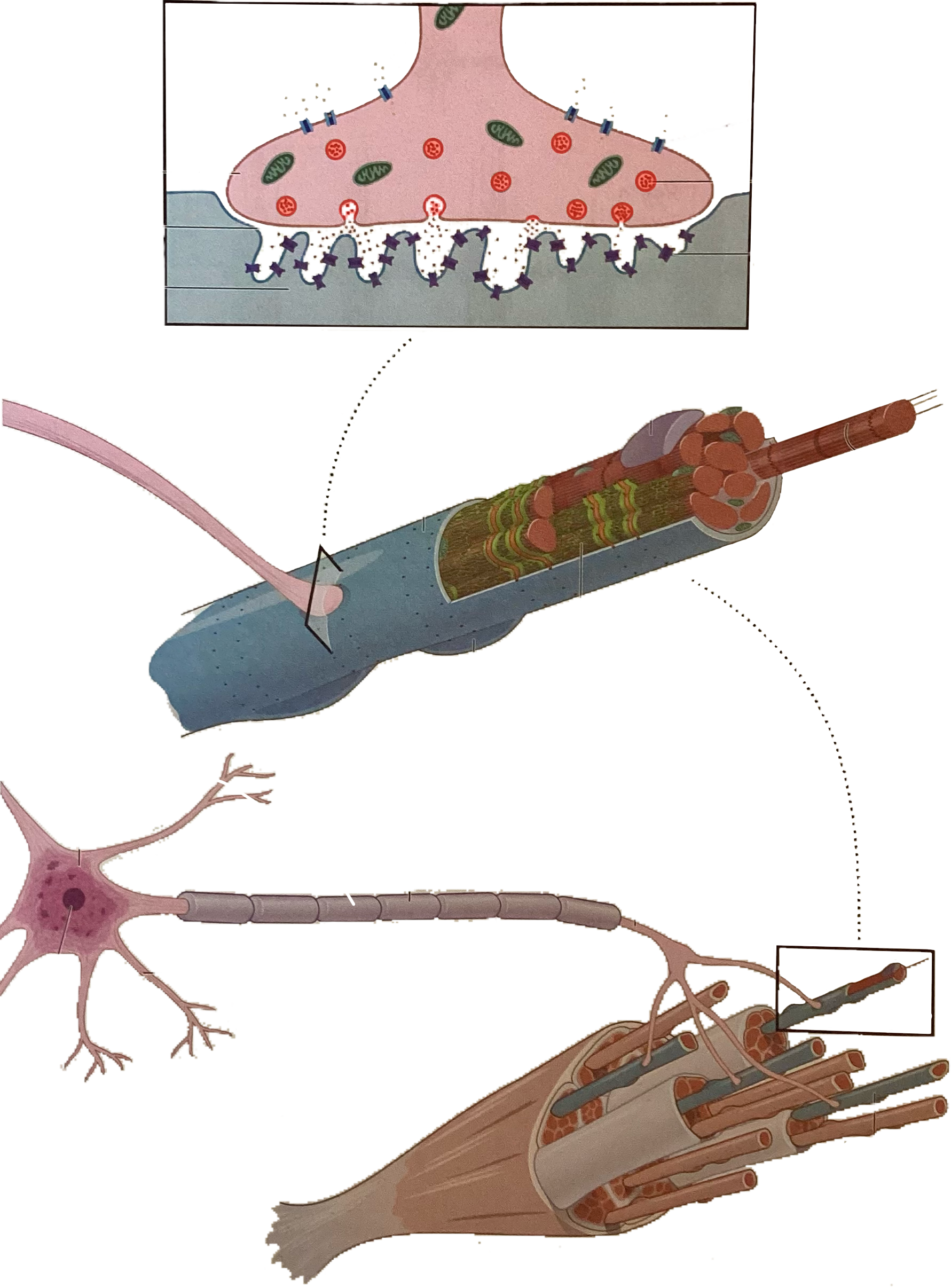
What is this?
Vesicle containing acetylcholine
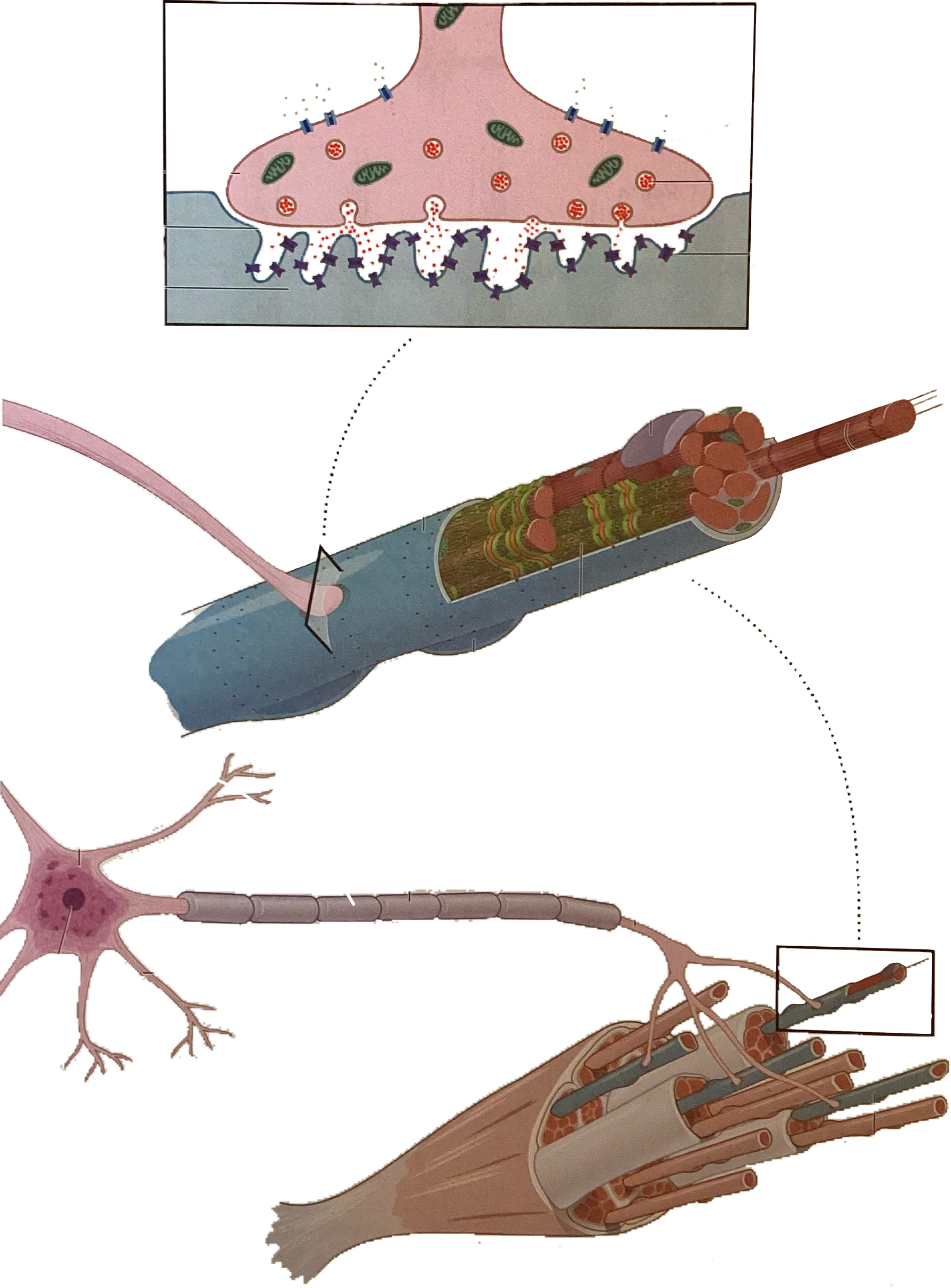
What is this?
Acetylcholine
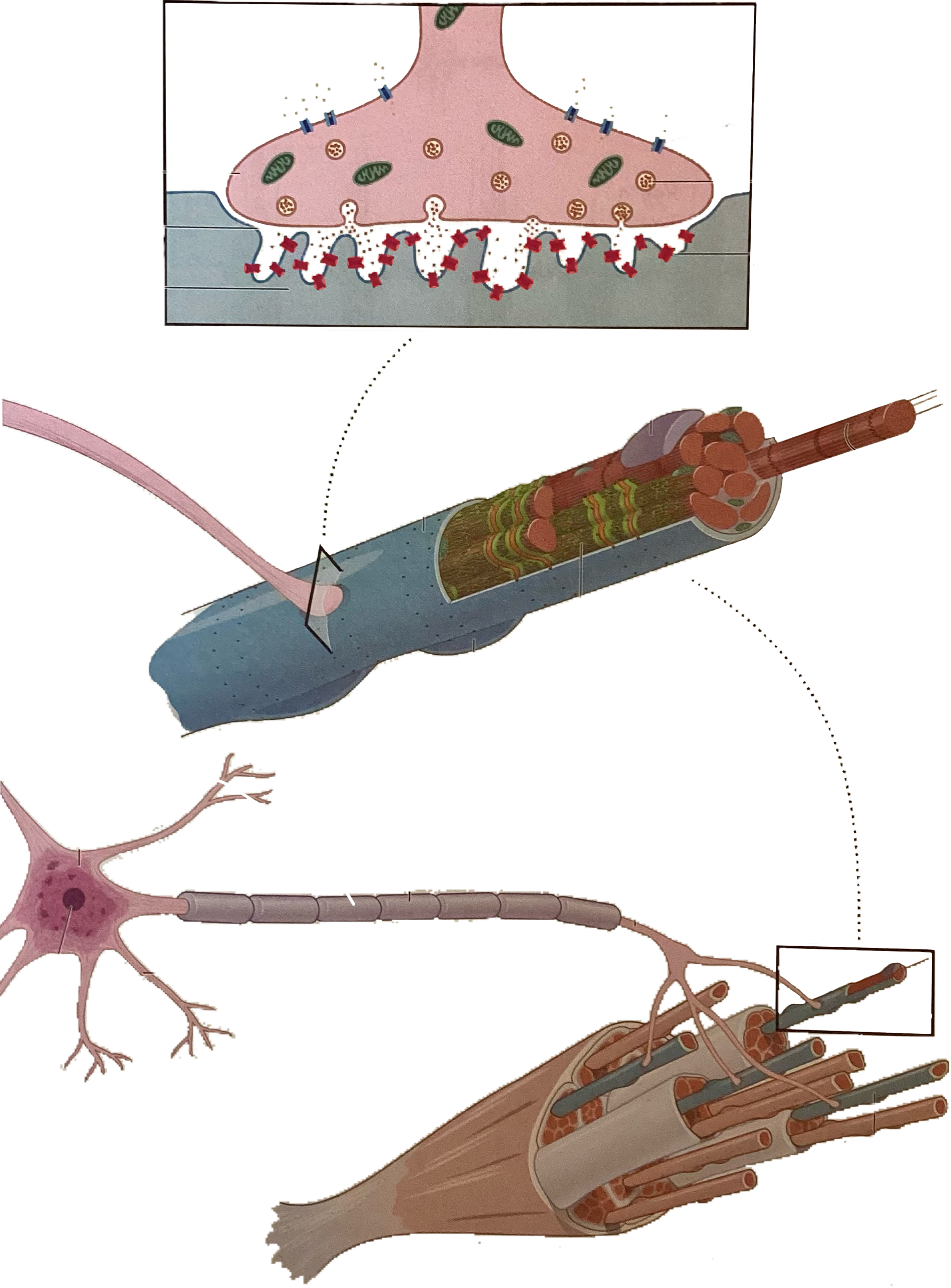
What is this?
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
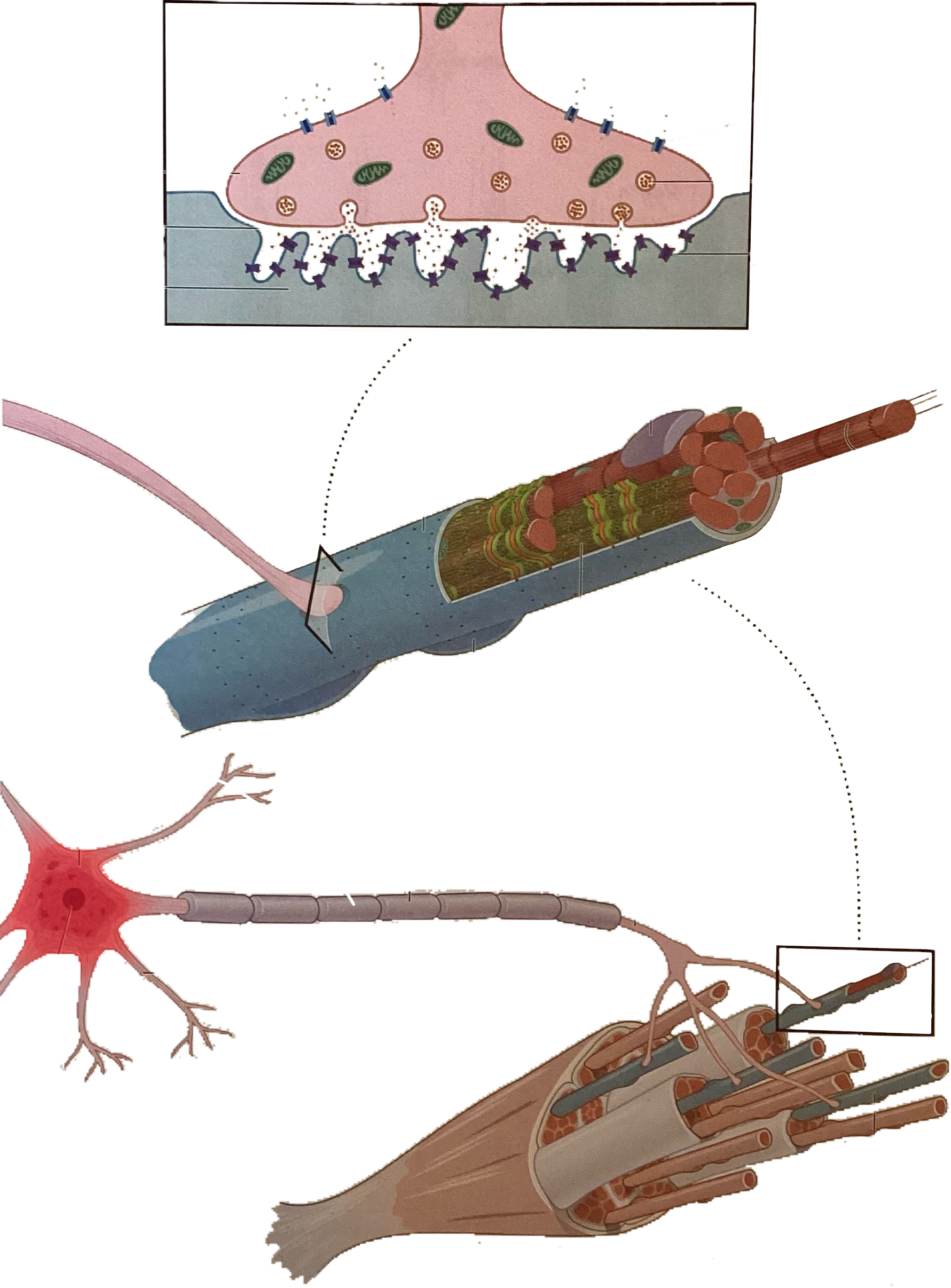
What is this?
Cell body
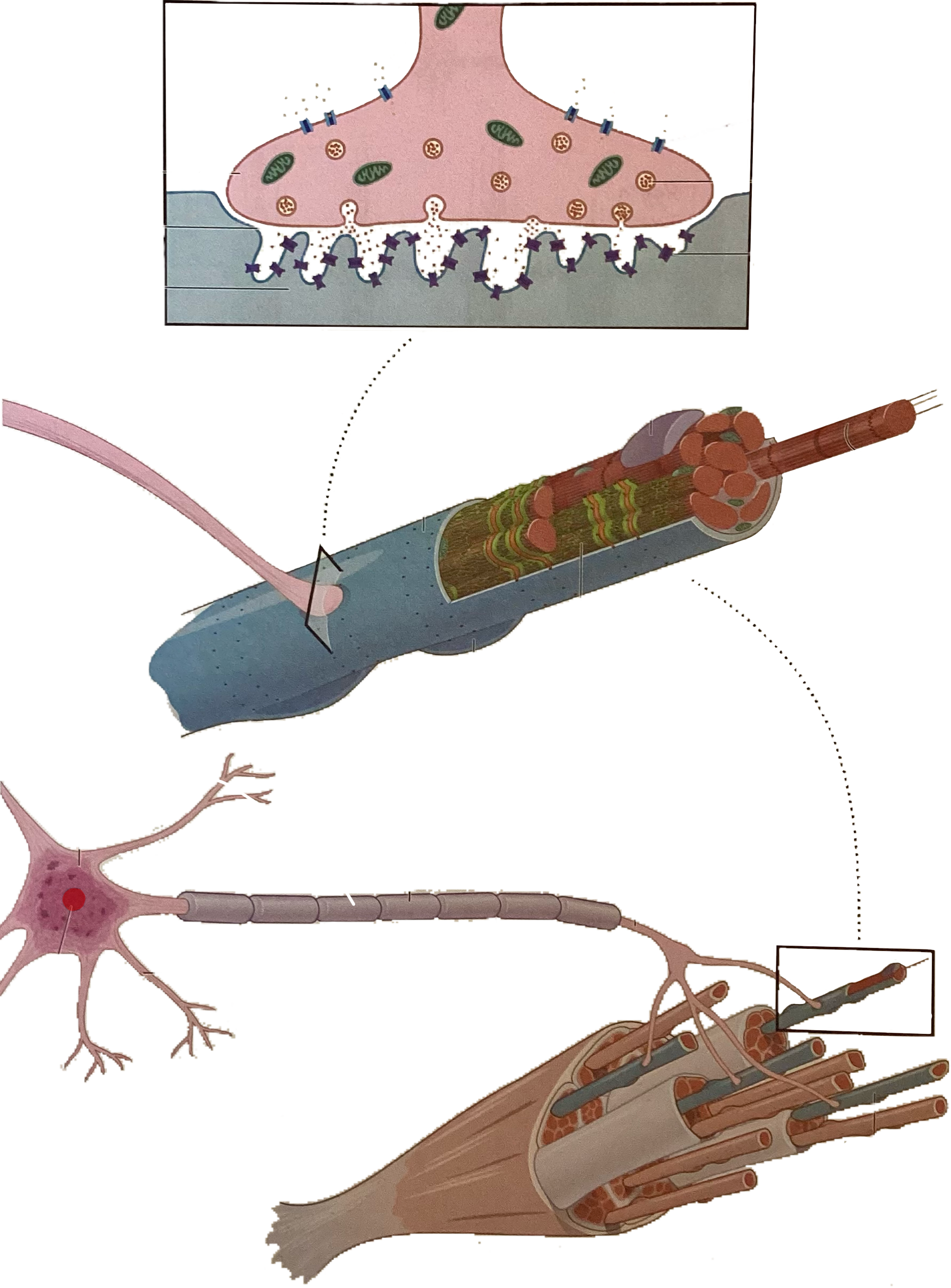
What is this?
Nucleus
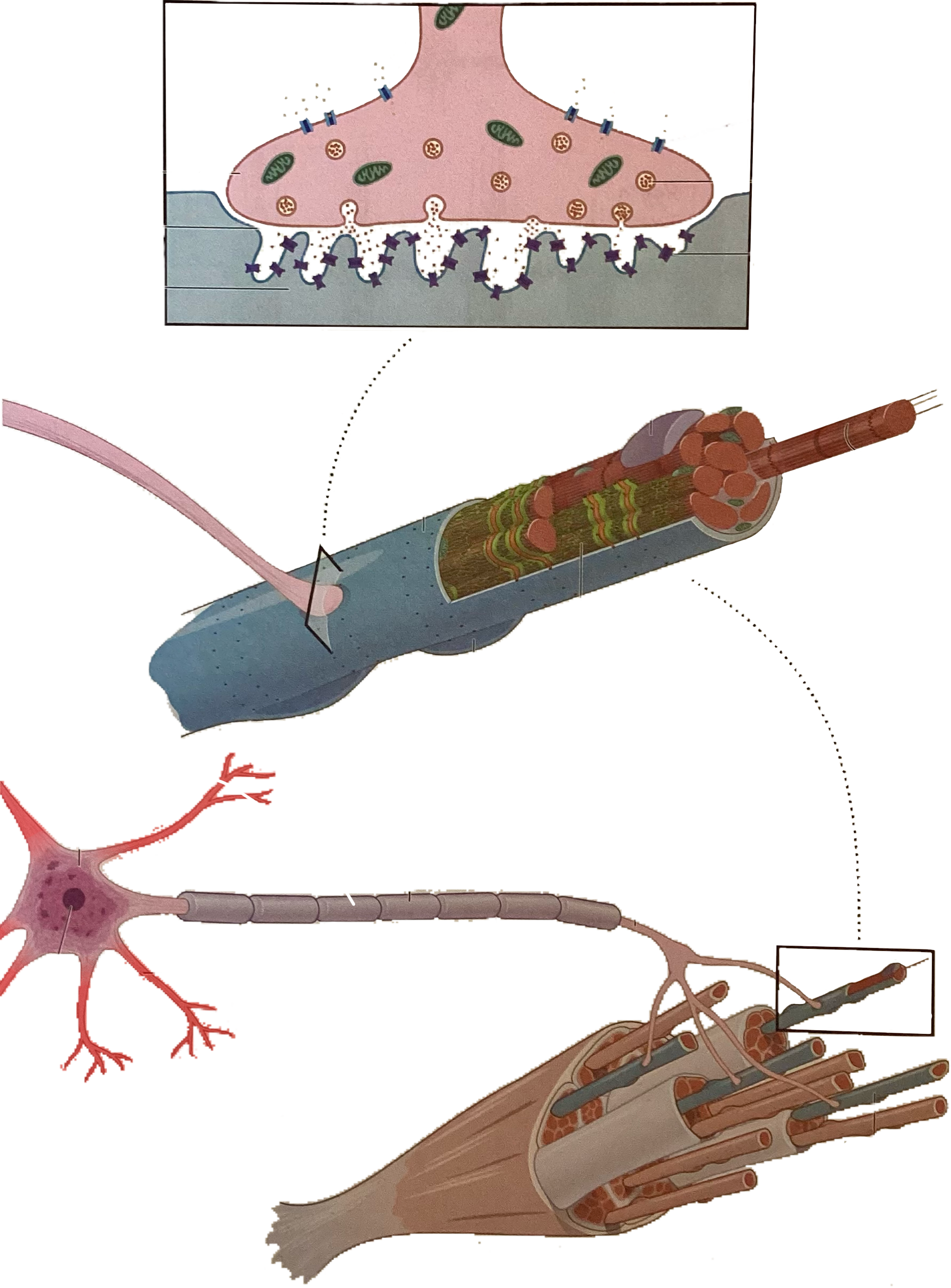
What is this?
Dendrites
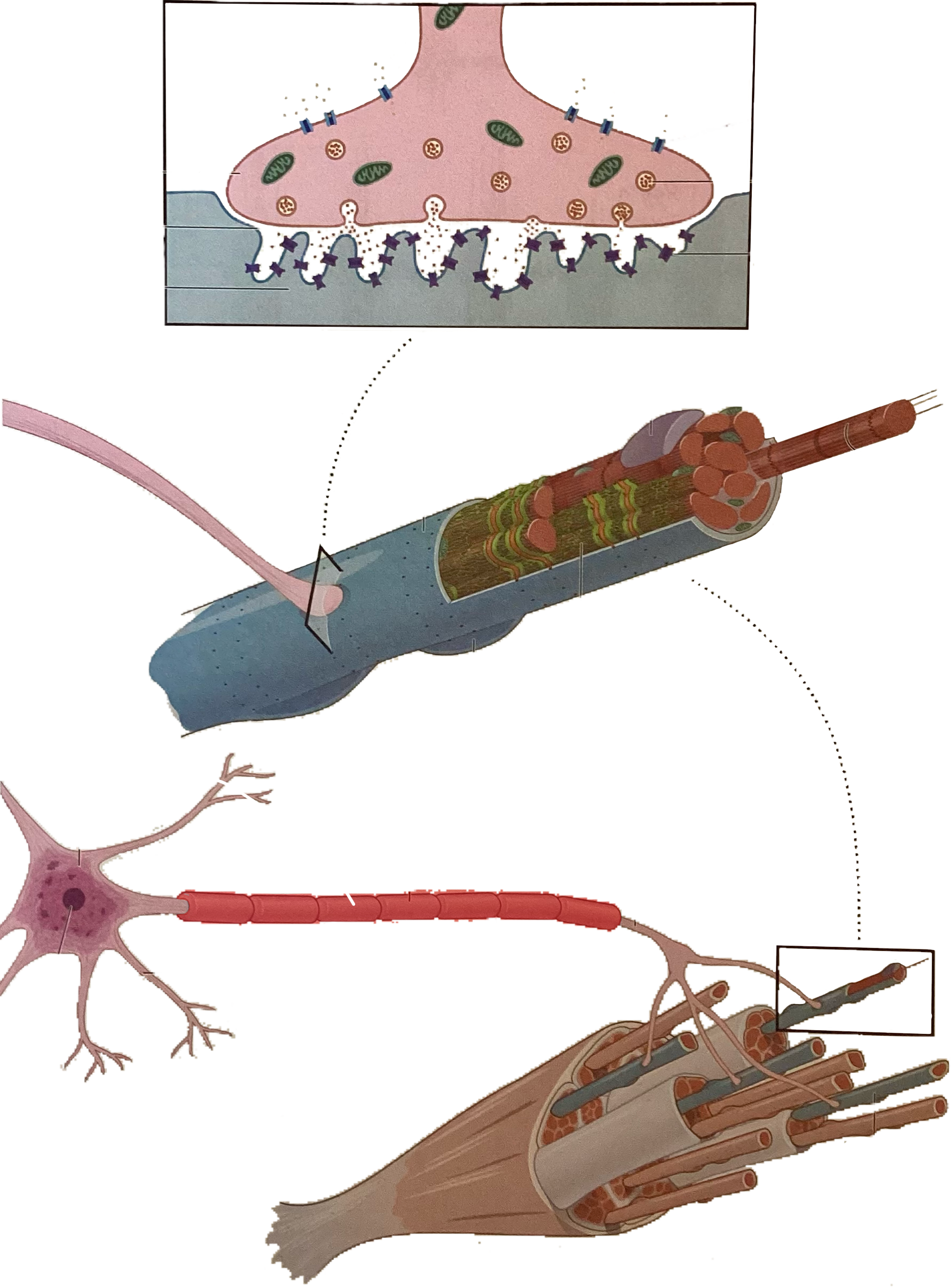
What is this?
Myelin sheath
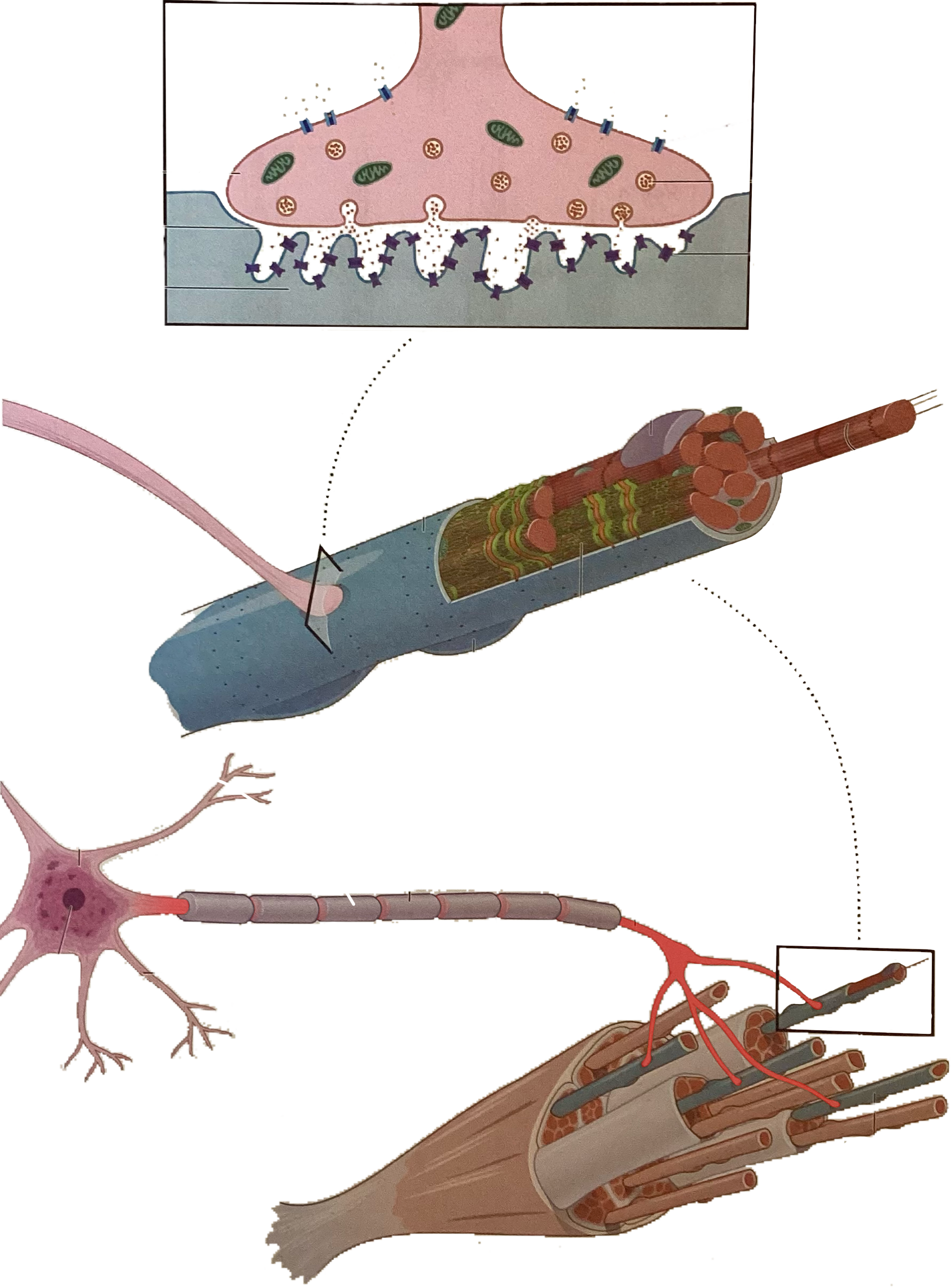
What is this?
Axon
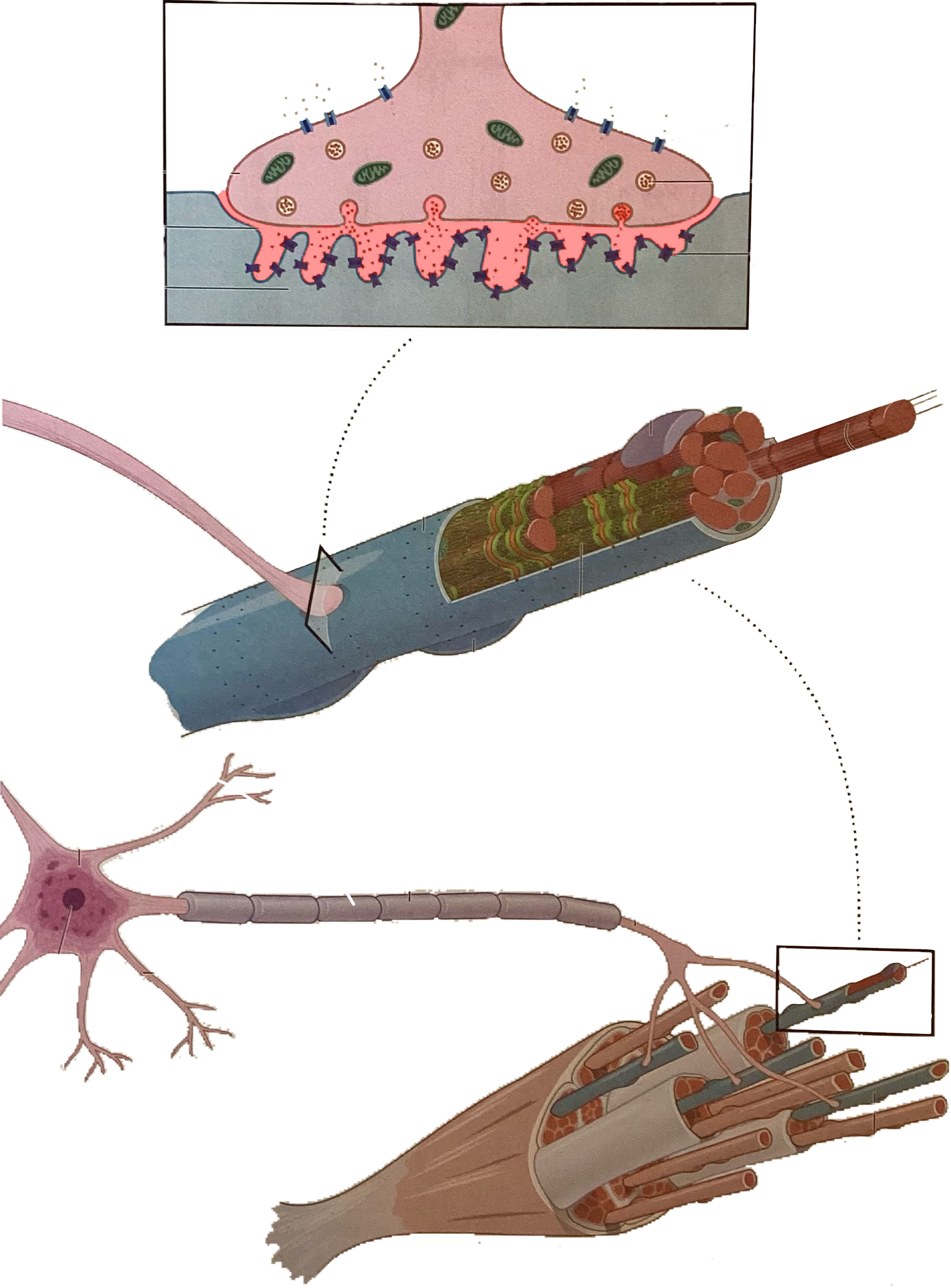
What is this?
Synaptic cleft
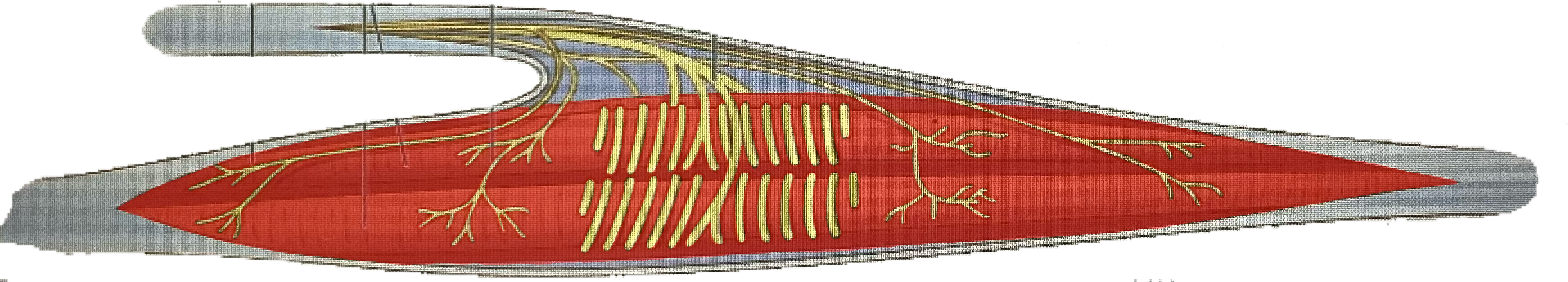
What is this?
Extrafusal fibers
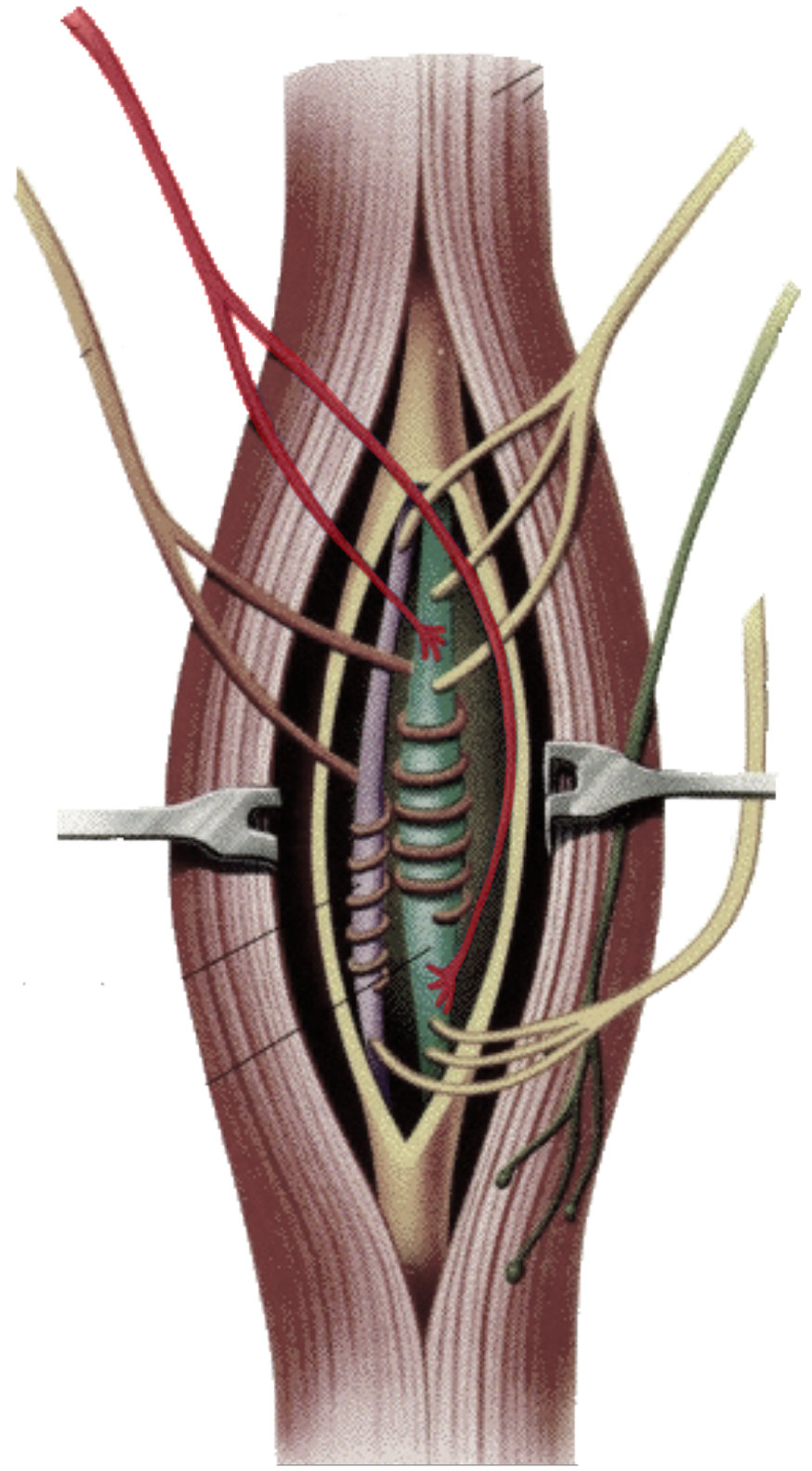
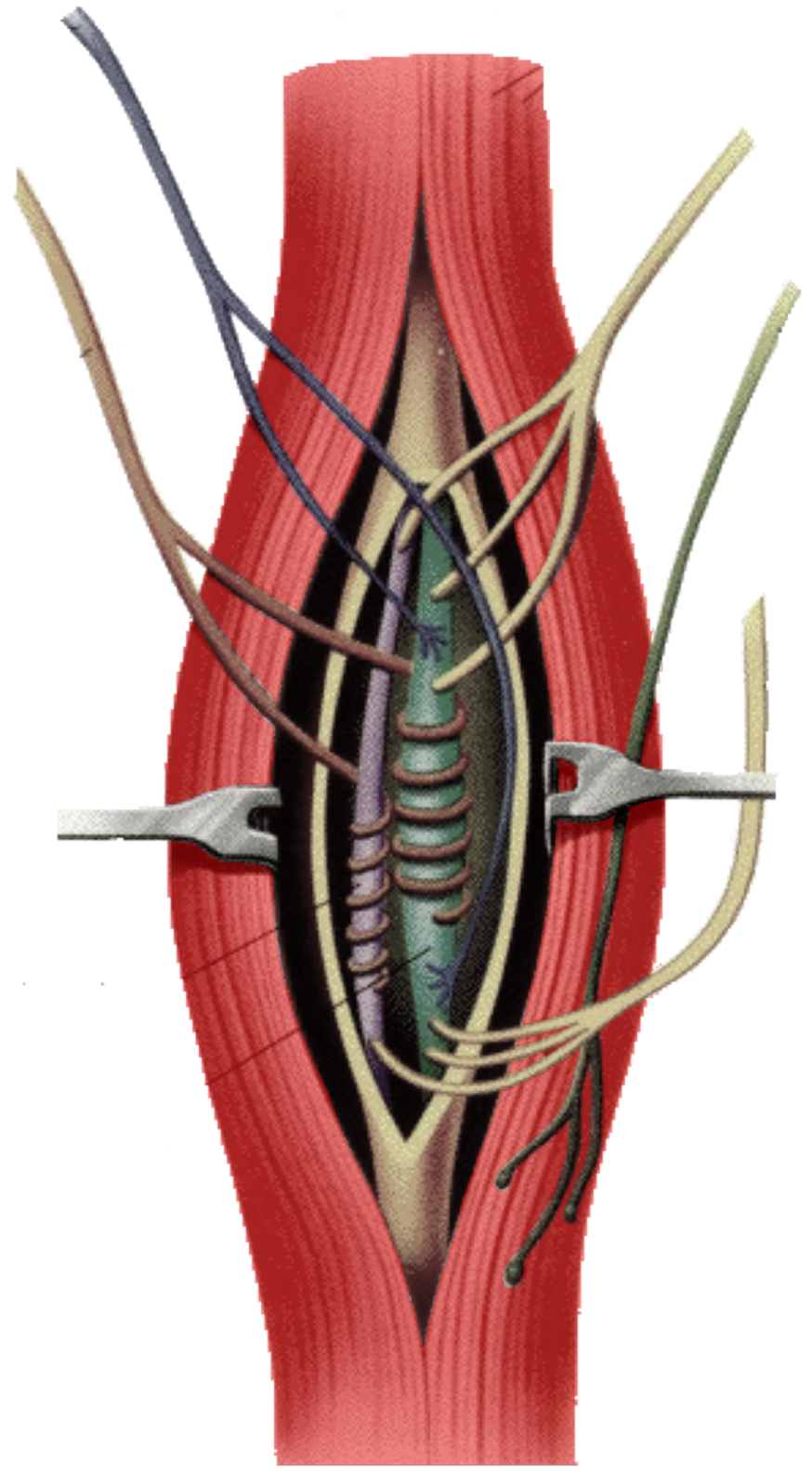
What is this?
Flower spray endings
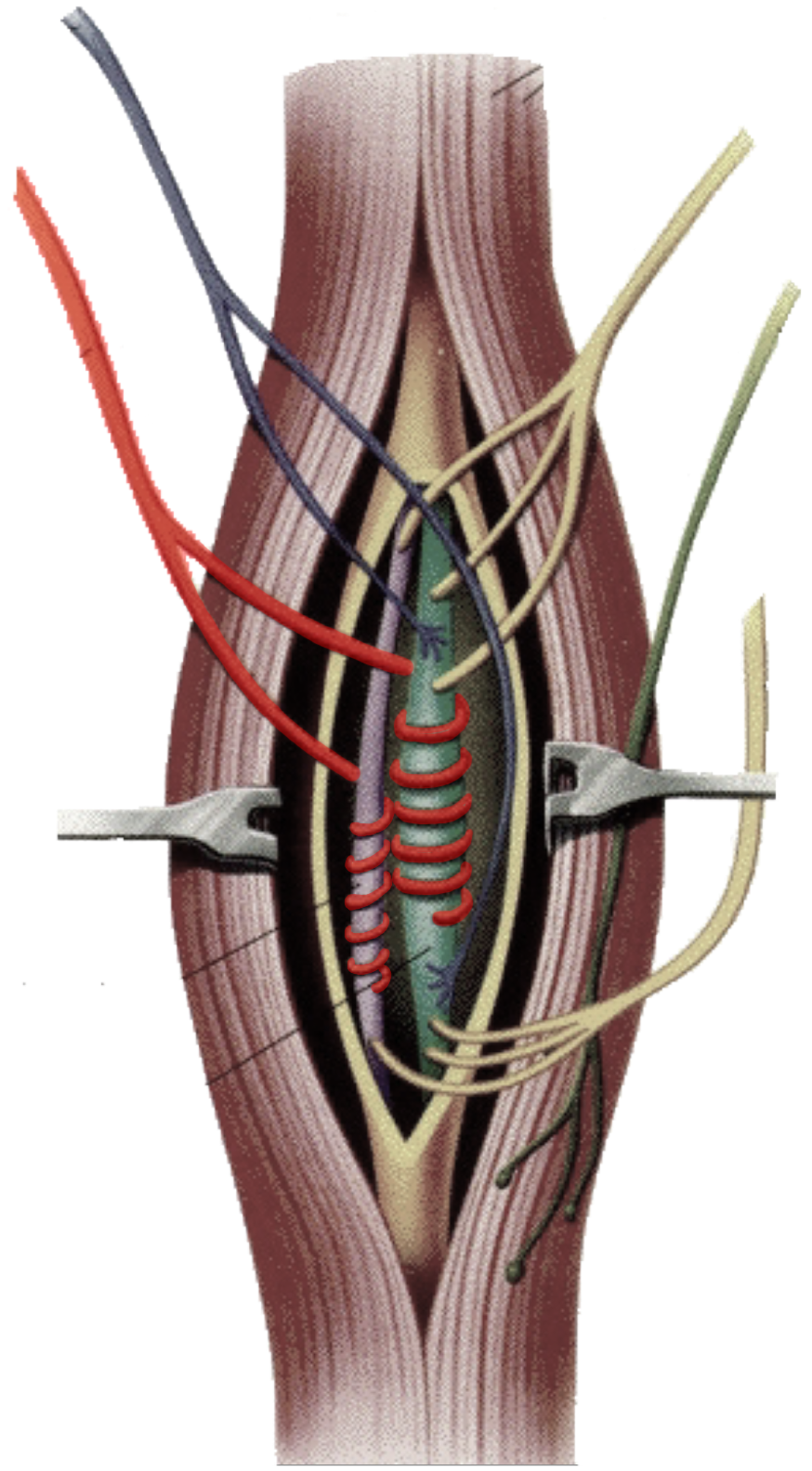
What is this?
Annulospiral endings
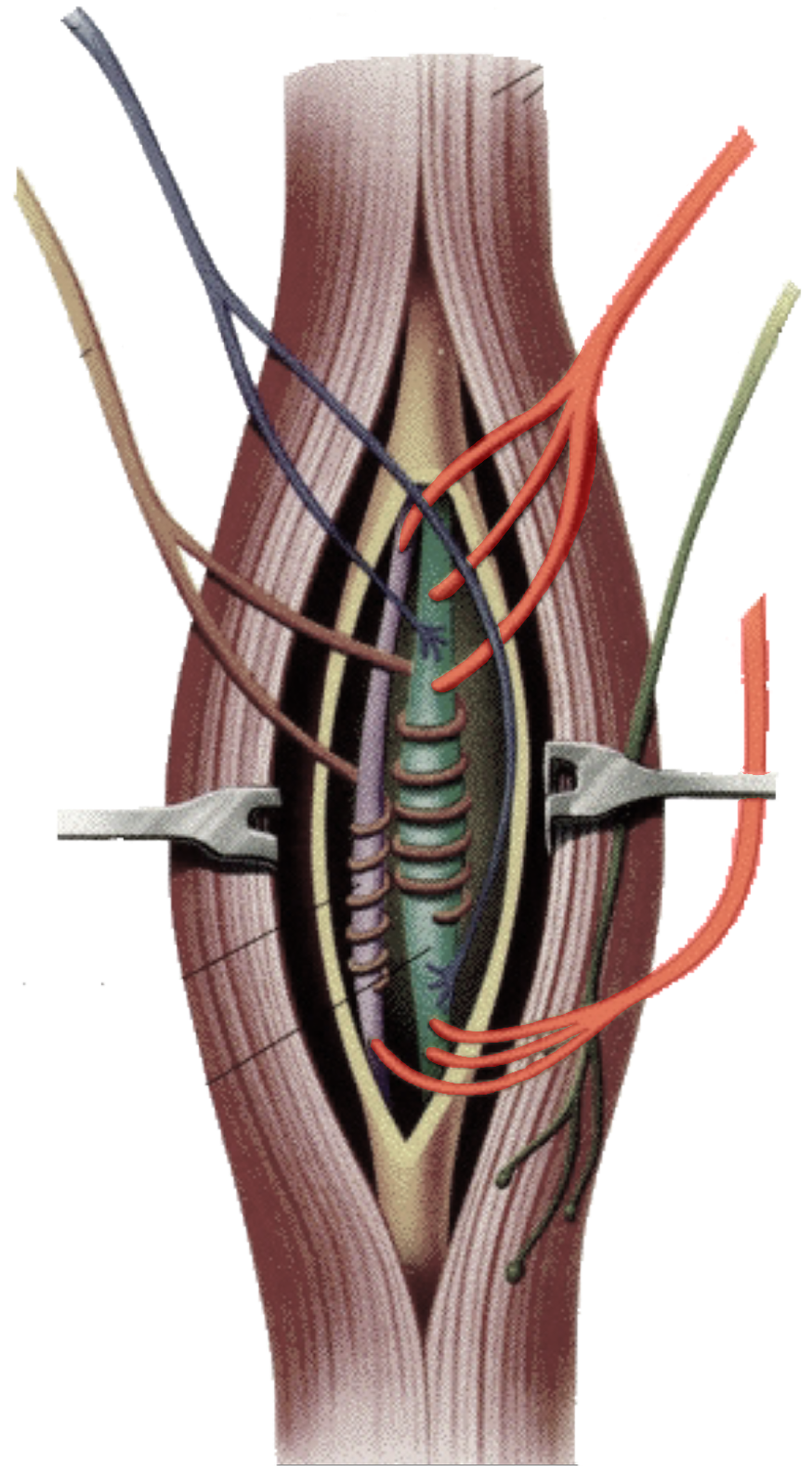
What is this?
Gamma efferent fibers
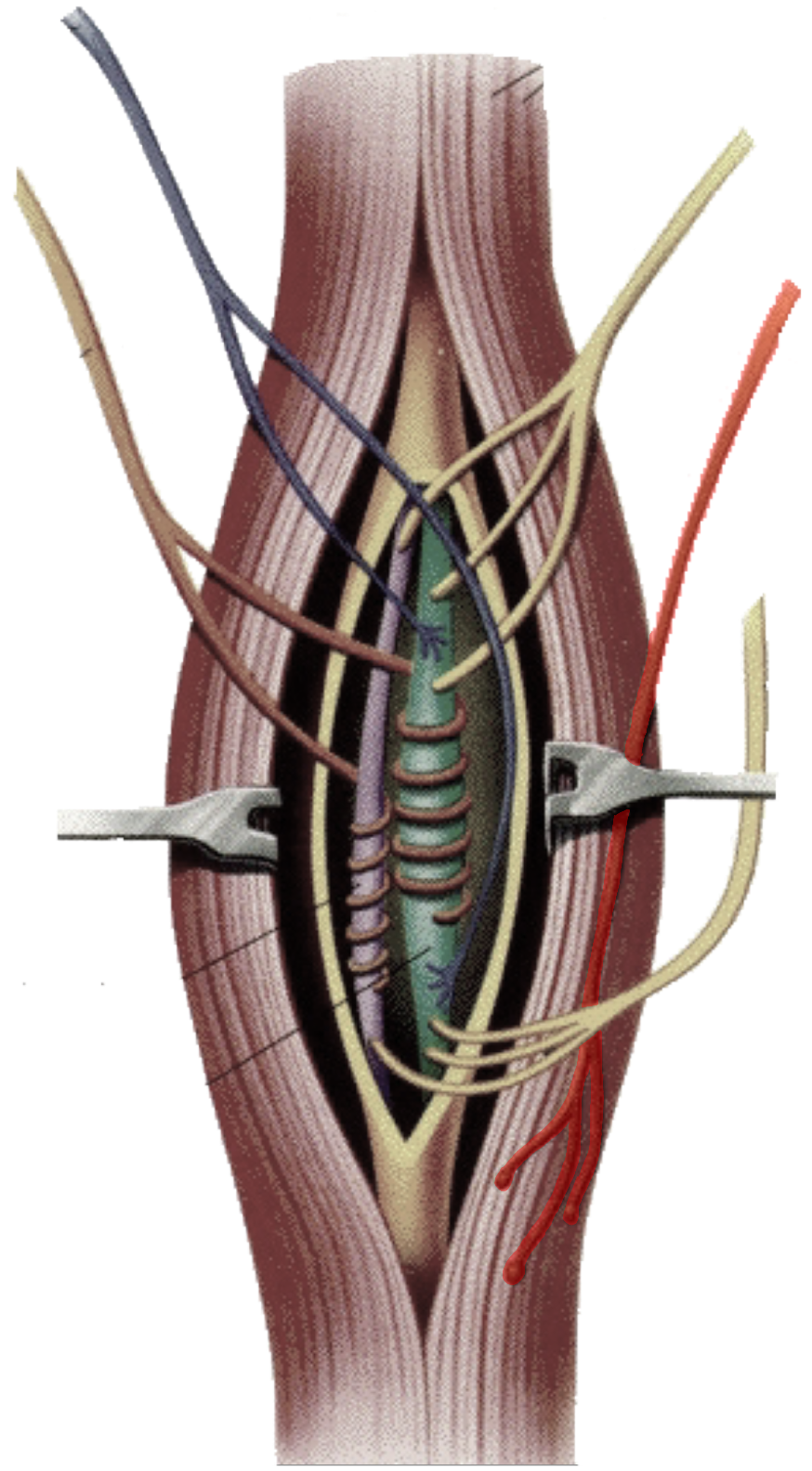
What is this?
Alpha efferent fibers
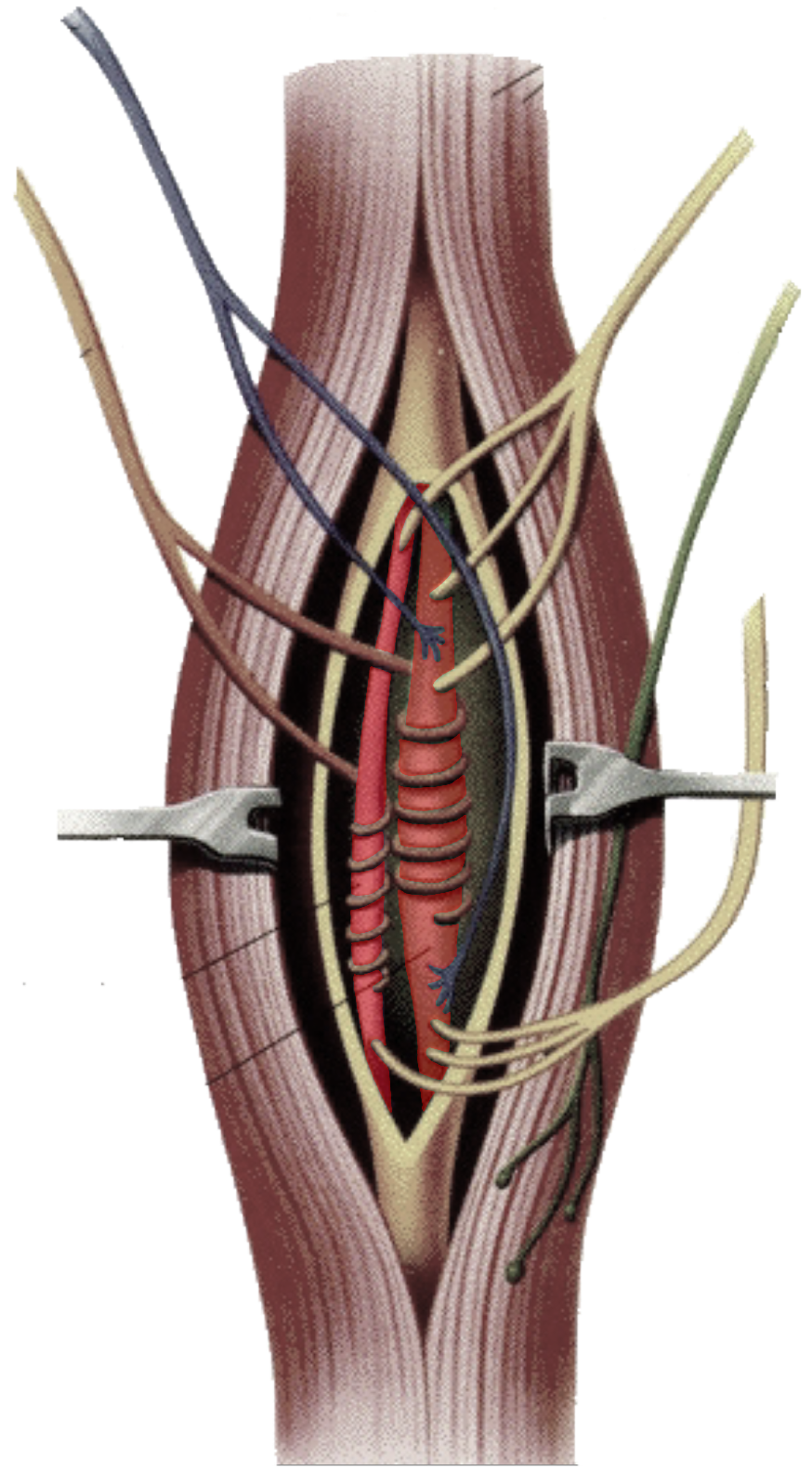
What is this?
Intrafusal fibers
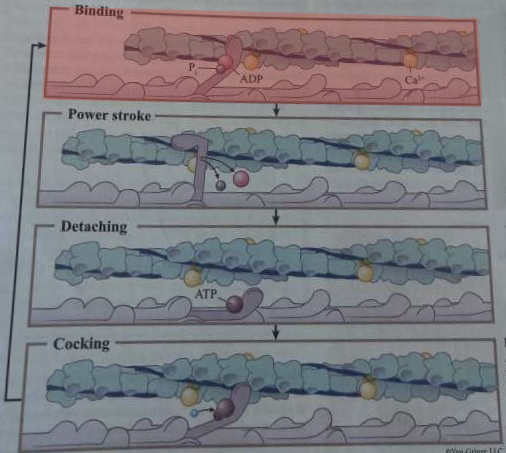
What happens during this step of cross-bridge formation?
A myosin head in high-energy configuration binds to an exposed myosin-binding site on actin
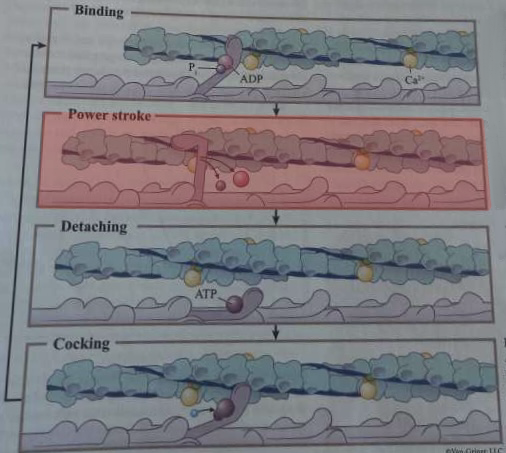
What happens during this step of cross-bridge formation?
ADP and inorganic phosphate are released from myosin head, returning it to its low-energy state, resulting in a power stroke
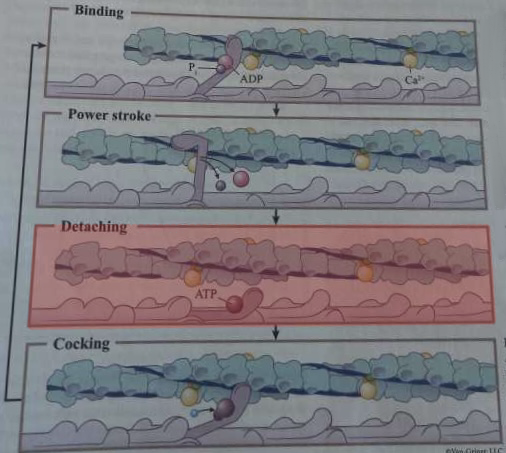
What happens during this step of cross-bridge formation?
ATP binds to myosin head, causing detachment
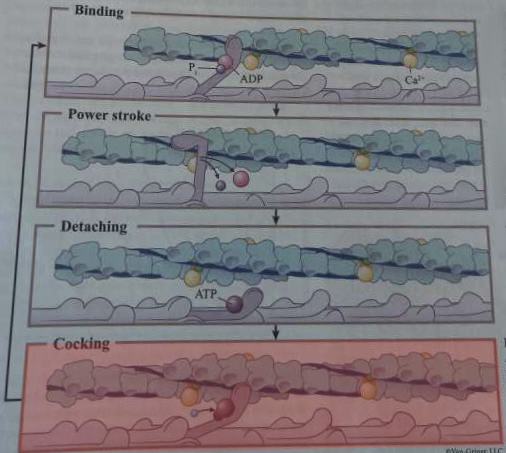
What happens during this step of cross-bridge formation?
Hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate repositions the myosin head into its high-energy configuration
What are the steps of cross bridge formation?
binding, power stroke, detaching, and cocking
Cross bridge
globular myosin links thick and thin filaments together and swivel as motors to shorten sarcomere
Dystrophin
links thin filaments to sarcolemma, causes muscular dystrophy when not enough
How many thick filaments surround each thin filament?
3
How many thin filaments surround each thick filament?
6
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
smooth ER, surrounds myofibrils, abundant mitochondria and glycogen granules around it, controls calcium levels
Triad
a T tubule and the terminal cisterns on either side
Integral membrane proteins of T tubule
voltage sensors
Integral membrane proteins of terminal cisterns
gated channels for release of calcium
Polarization
inside of the cell has a more negative charge than outside
3 steps of an action potential
Depolarization: acetylcholine binds to receptor and opens ion channels for Na and K. Na enters cell and K leaves. Make inner surface of sarcolemma less negative
Muscle action potential: more voltage-gated Na channels open as charge increases
Repolarization: Na channels close and K channels open. Membrane becomes more negative as K leaves cell. Na and K gradient differences are restored by ATPase pump that moves Na out and K in
Refractory period
muscle cell cannot be stimulated again until sufficiently repolarized
Excitation-contraction coupling
muscle action potential travels along sarcolemma, T tubules change shape, terminal cisterns release calcium, calcium removes inhibitory action of tropomyosin, exposes myosin-binding sites on actin, cross bridge cycling starts
Motor unit
a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates, smaller unit=finer control of movement
How many neuromuscular junctions does each muscle fiber have?
1
Synaptic end bulb/axon terminal
end of an axon
Synaptic cleft
space between the axon terminal and muscle, filled with extracellular fluid with collagen and glycoproteins
Acetylcholinesterase
in synaptic cleft, breaks down acetylcholine into acetic acid and choline to terminate the signal for fine muscle control
Myasthenia gravis
deficient acetylcholine receptors due to autoimmune destruction, symptoms are difficulty talking and swallowing, drooping upper eyelids, generalized muscle weakness
Isometric contraction
contraction but muscle fibers maintain constant length, thin filaments do not move when cross bridges form, tension increases but length is constant
Isotonic contraction
muscle fibers shorten or lengthen, muscle tension is constant but length changes
Concentric isotonic contractions
muscle length decreases
Eccentric isotonic contractions
muscle length increases