Coronary Artery Disease and Valvular Disorders
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
atherosclerosis
abnormal accumulation of lipid deposits and fibrous tissue within arterial walls and lumen
what is the leading cause of MI?
CAD
CAD prevention
Control cholesterol
Dietary measures
Physical activity
Medications
Cessation of tobacco use
Manage HTN
Control diabetes
medications for CAD control
▪Statins
▪Fibrates
▪CAIs
▪PCSK9 inhibitors
statins
lower cholesterol in the blood and reduce its production in the liver by blocking the enzyme that produces it (LDL)
'-statin'
statins side effects
GI upset: nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea
Headache
Rash
Myopathy / rhabdomyolysis
Hepatotoxicity
Fibrates
activate PPAR-α → ↑ LPL → ↓ triglycerides and ↑ HDL
gemfibrozil
fenofibrate
cholesterol absorption inhibitors
Ezetimibe
Lowers cholesterol by inhibiting absorption in small intestine
Side effects: hepatotoxicity and muscle pain
Monitor liver function and CK levels
PCSK9 inhibitors moa
Inactivation of LDL-receptor degradation, increasing amount of LDL removed from bloodstream
Alirocumab (Praluent)
Evolocumab (Repatha)
acute coronary syndrome
umbrella term characterized by an acute onset of myocardial ischemia that results in myocardial death (i.e., MI) if definitive interventions do not occur promptly
can turn into infarction
myocardial infarction
the occlusion of one or more coronary arteries caused by plaque buildup (heart attack)
STEMI
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
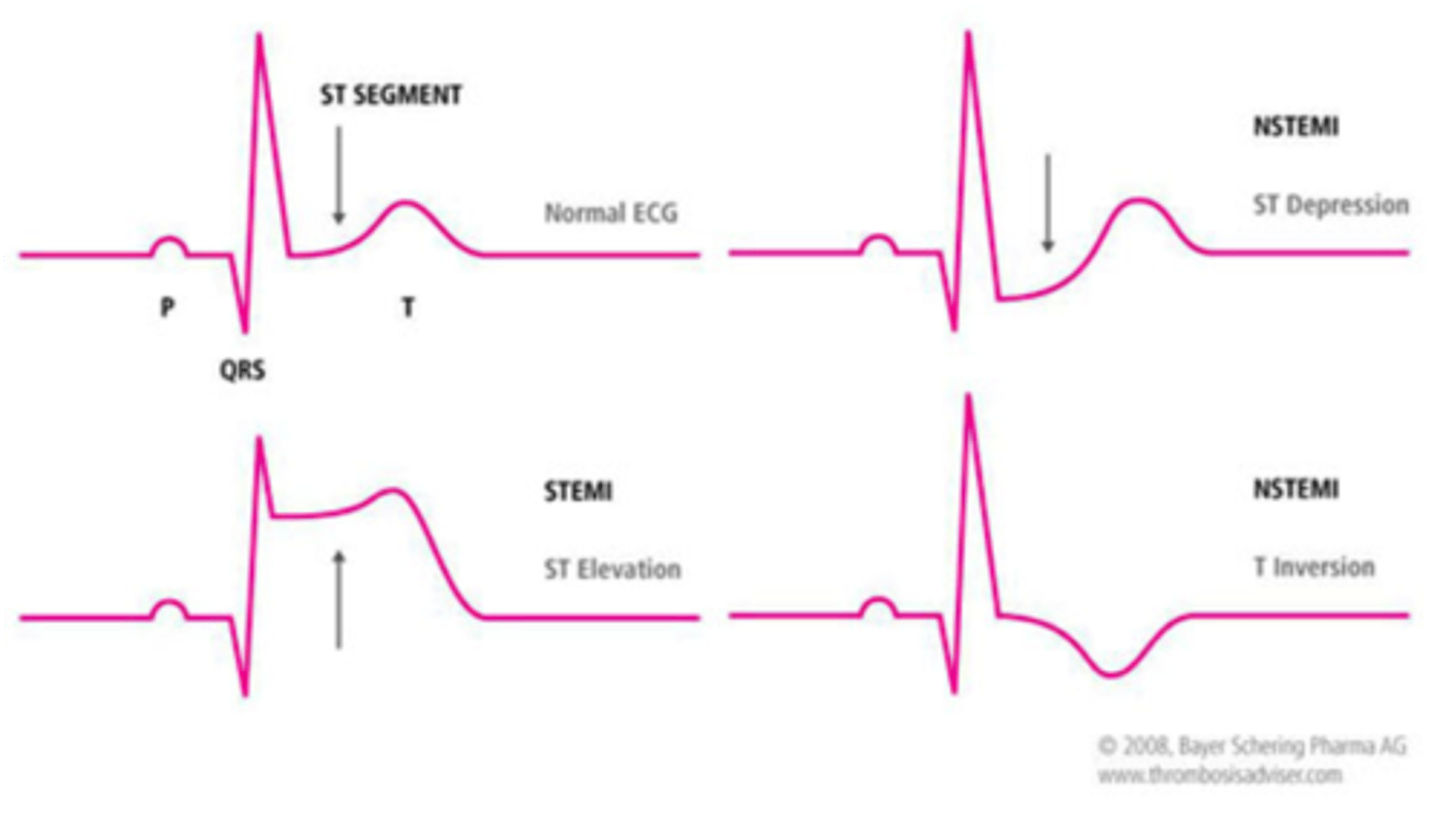
NSTEMI
Non ST segment elevation MI; a heart attack that is not diagnosed on the EKG but is diagnosed by an elevated troponin on blood test
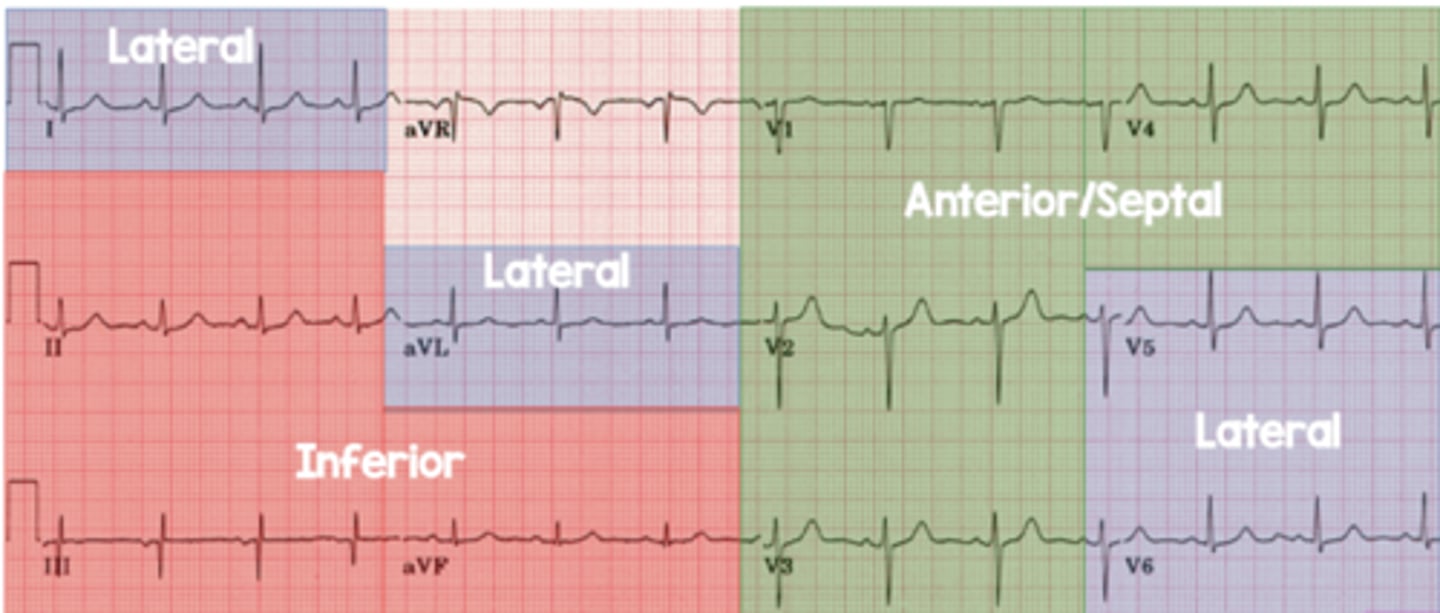
lateral leads
I, aVL, V5, V6
left circumflex or diagonal of LAD
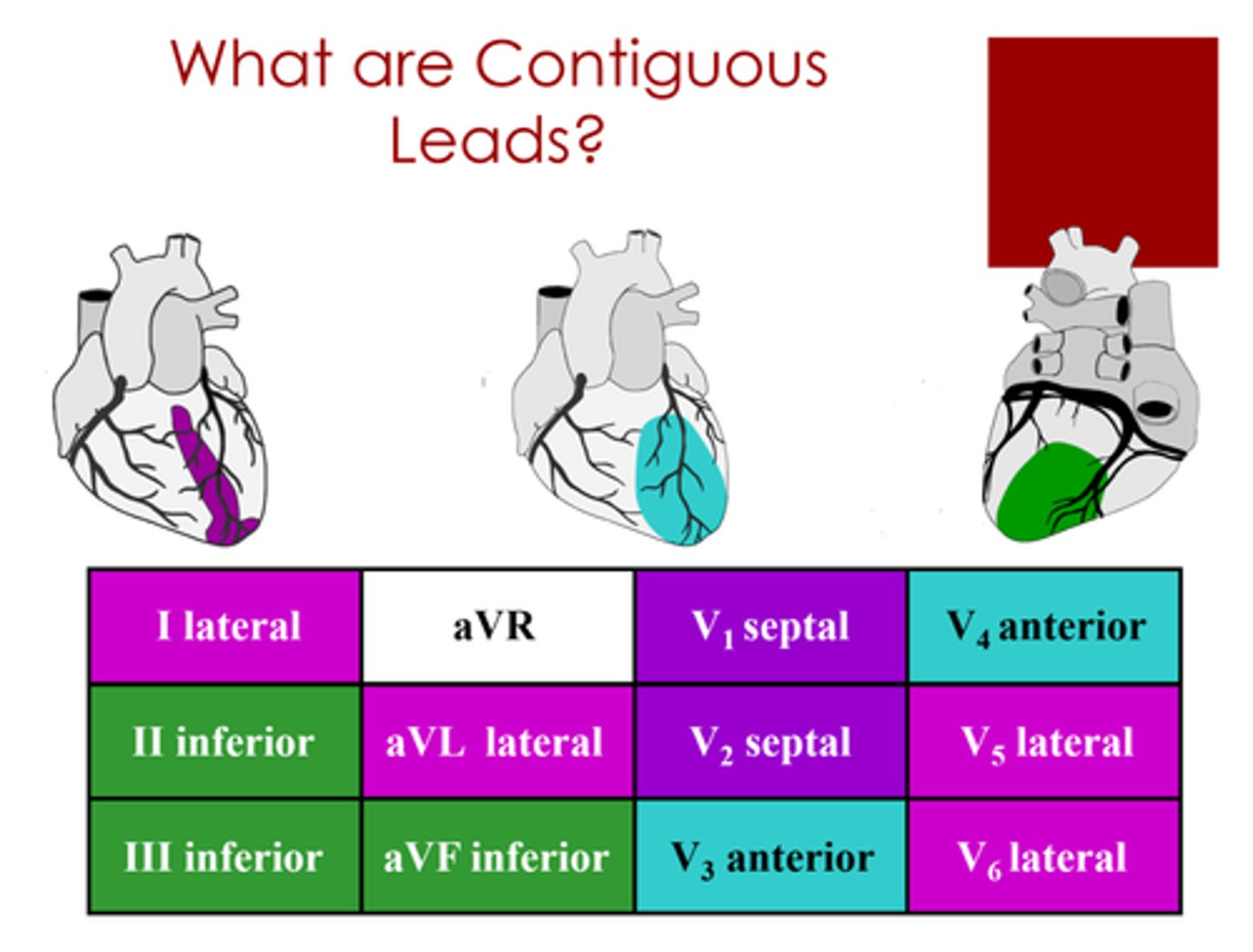
inferior leads
II, III, aVF
Right coronary and/or left circumflex artery
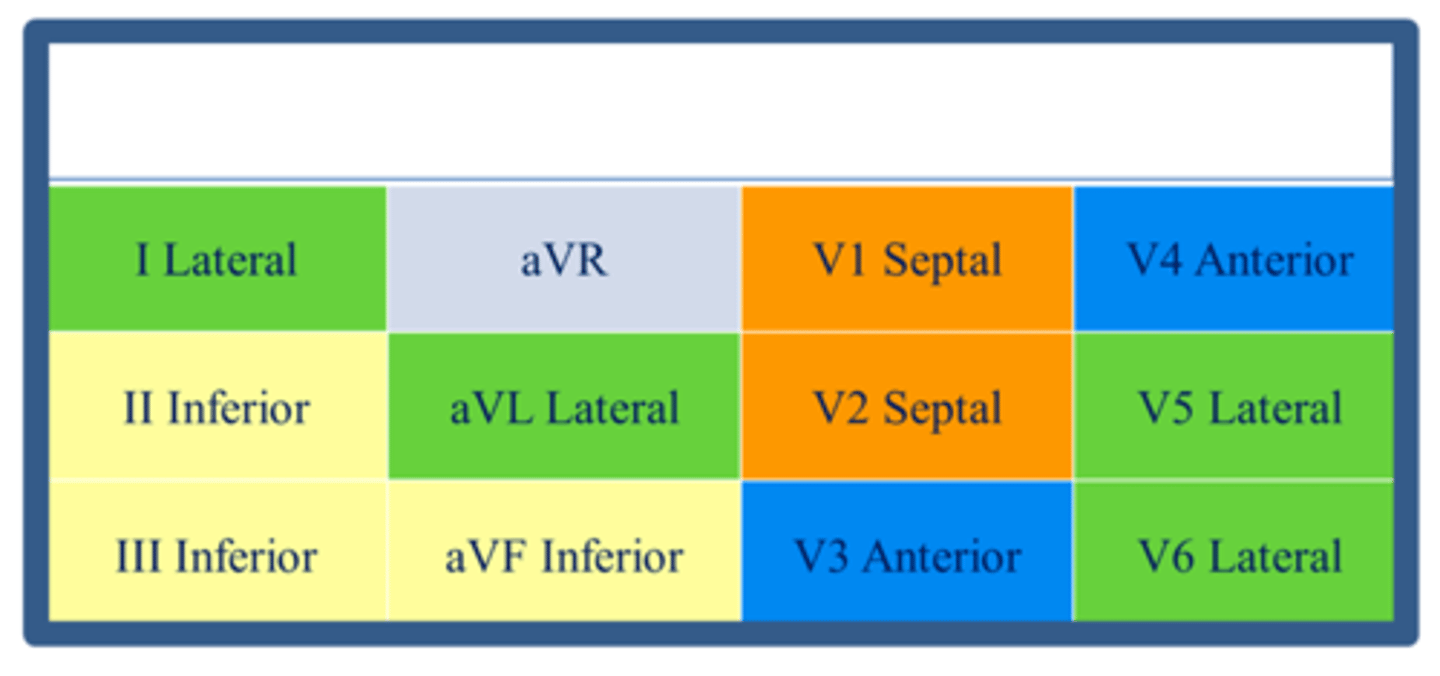
anterior/septal leads
V1, V2, V3, V4
Left anterior descending artery
s/s of ACS
radiating chest pain
dyspnea
dizziness
nausea/vomiting
diaphoresis
dizziness
extreme fatigue (more common in women)
diagnostics for ACS
ECG
Cardiac biomarkers: CK-MB, troponin, high-sensitivity troponin
normal CK-MB
0-3 ng/mL
normal troponin
<0.5 for Troponin 1 and <0.1 for Troponin T
acute interventions for ACS
ASA: reduces platelet aggregation; 160-325mg
Morphine: pain reducer and reduces vasospasms
O2: non-rebreather
Nitroglycerin: vasodilator
Heparin: blood thinner; reduces oxygen demand of the heart (high dose IV drip protocol)
invasive interventions for ACS
▪PCI / Heart Catheterization (door to balloon time of 90 minutes is optimal)
▪PTCA
▪PTCA With Stenting
▪Thrombolytic (Firbinolytic) Therapy (Activase, TPA)
▪CABG
thrombolytic therapy for ACS
high risk for bleeding
can be used if pt has multiple areas of infarction
chest pain assessment
P-precipitating events
Q-quality
R-radiation
S-severity (0-10)
T-timing
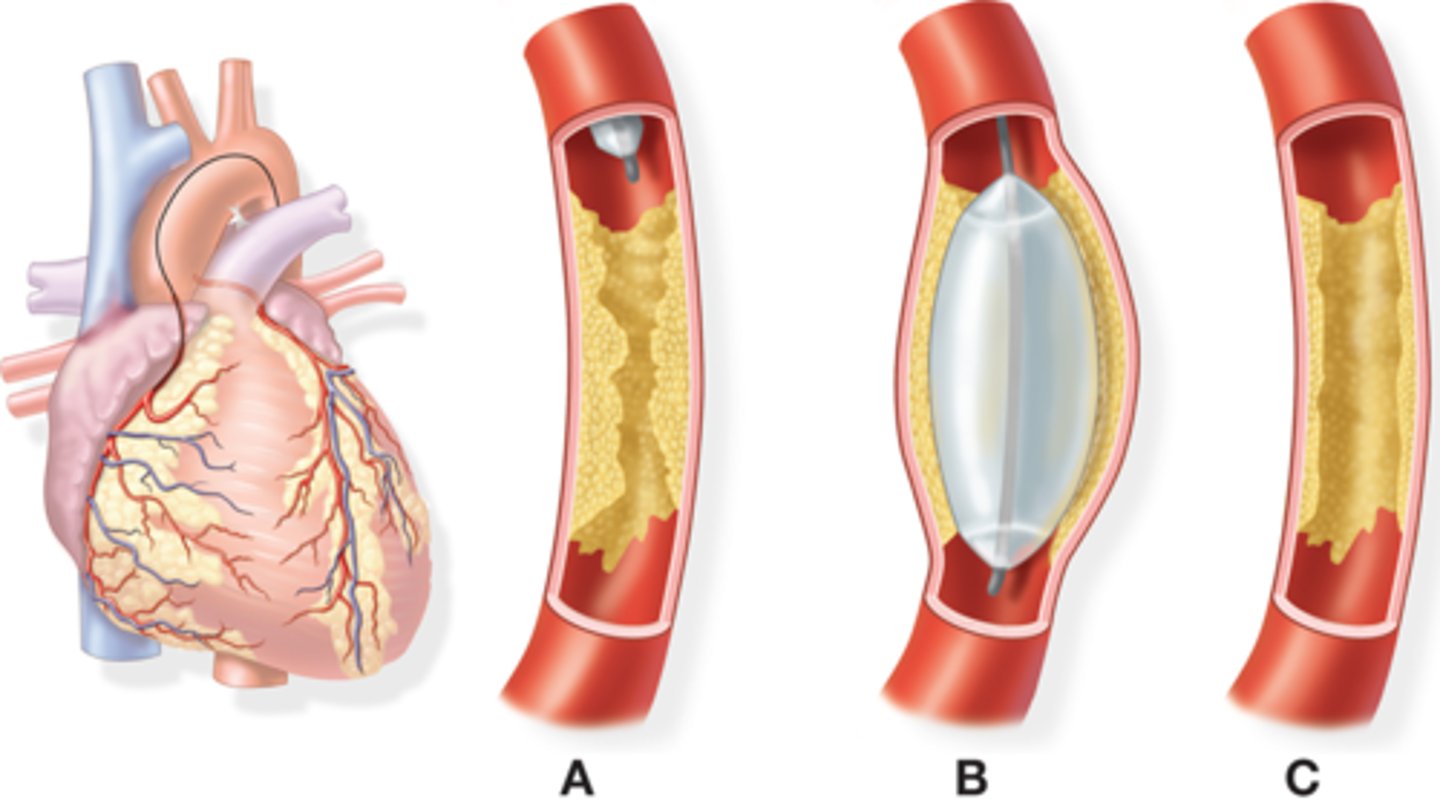
PTCA
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
can be done with or without stenting
commonly inserted through femoral artery or vein
right PCTA
right side of the heart; venous access from vena cava; mostly used for assessment using contrast agents
left PTCA
left side of the heart; interventional; through aorta and into the left side
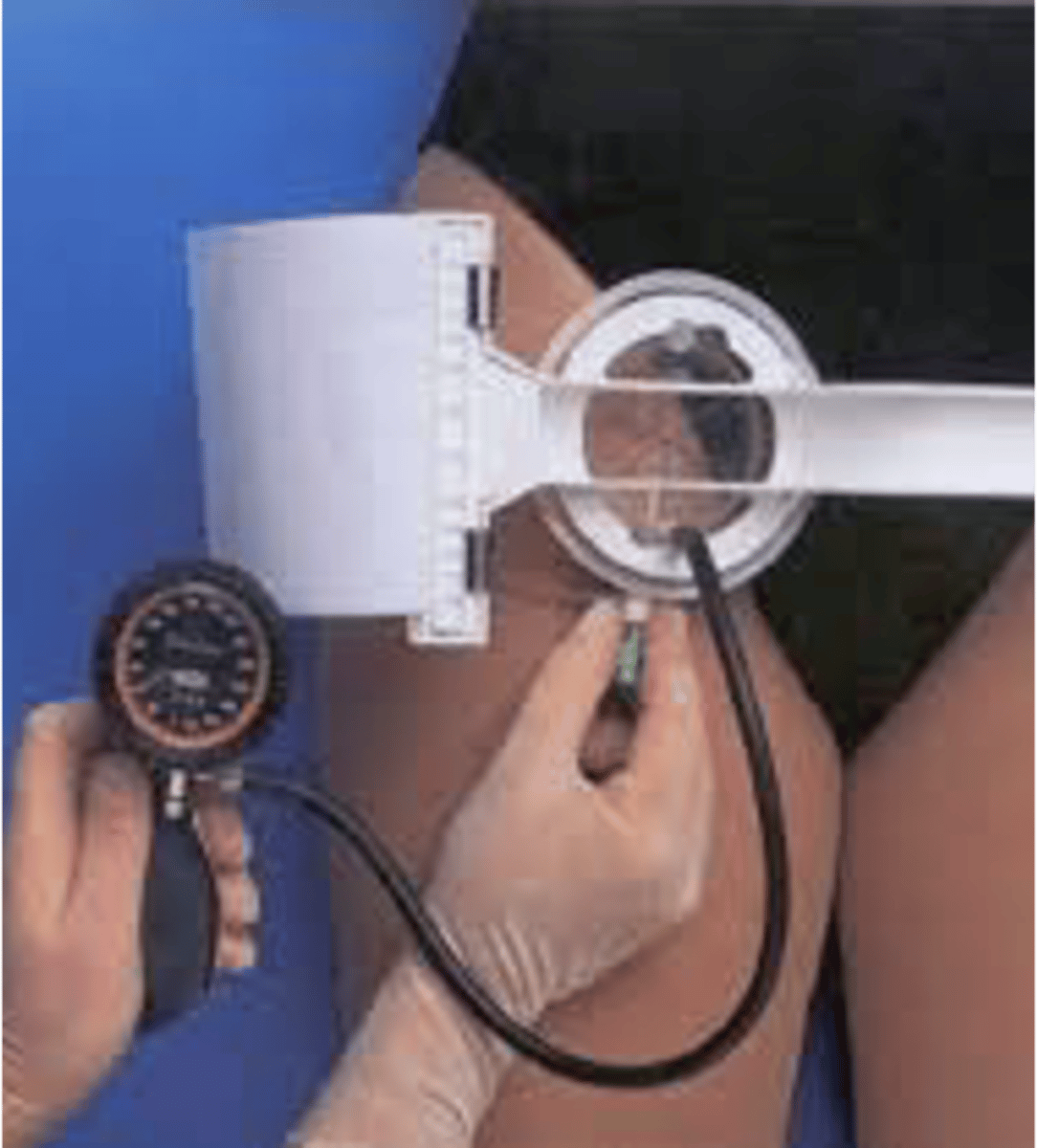
fem stop
puts pressure on femoral artery to help clot to form
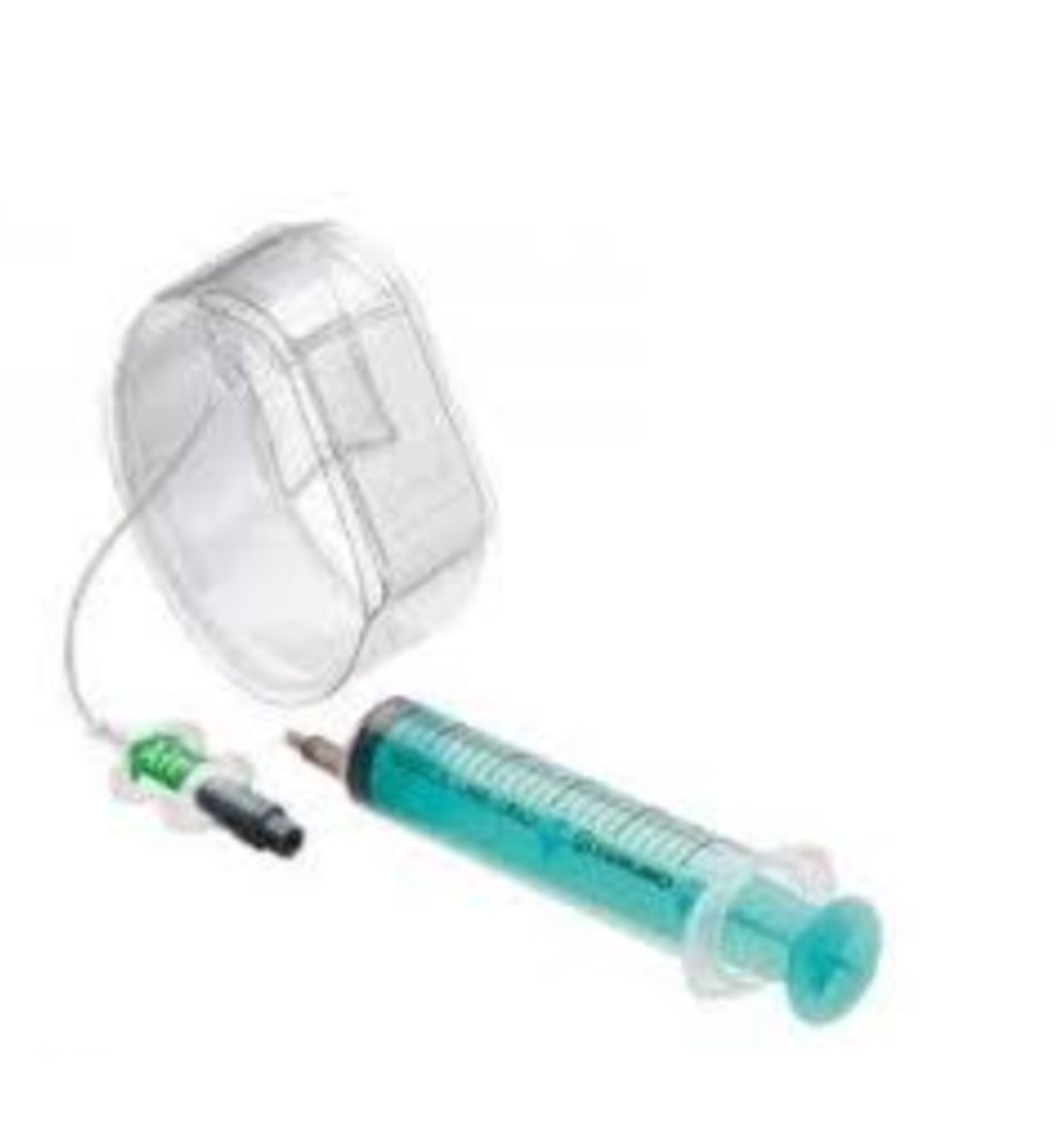
TR band
Compression device to assist hemostasis of the radial artery after transradial procedure
Patient can get up right after procedure
Left on patient for 24 hours without air
PCI considerations
▪Allergies: shellfish/iodine (pre medication with solucortef/solumedrol; corticosteroid and diphenhydramine antihistamine)
▪Medications
▪Comorbidities: renal conditions (contrast is hard on kidneys)
▪Post-Care: watching site for bleeding, bedrest, checking pulses on extremities, draw blood for activated clotting time
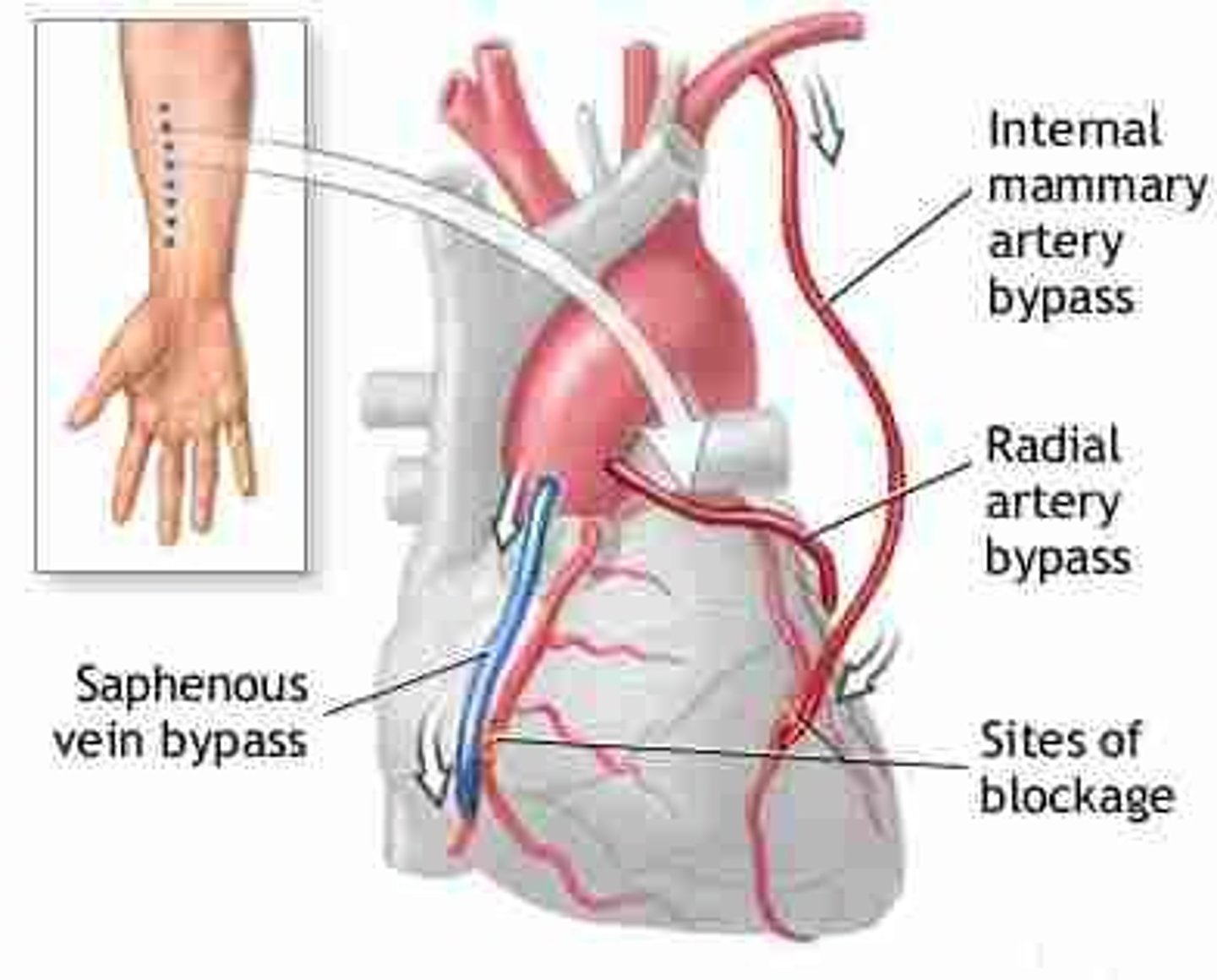
CABG
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft, "Open heart surgery"
used only when PCTA cannot be used: significant occlusions in multiple areas
can be a single or multiple bypass
off pump CABG
chest is opened
mechanical device used to steady heart
aka beating heart bypass grafting
slightly lower risk of complications
On-pump CABG
uses extracorporeal circulation
▪Allows artificial pumping/oxygenation in order to MD to perform operation
CABG post op care
Airway: intubated and sedated
Central line: for medications and CVP (right atrial pressure)
Medications: epi/norepi, fluids, insulin, antibiotics, blood
Swan-ganz catheter: right ventricular and pulmonary artery pressure
Art line: for ABGs and vital signs
Continuous ekg: common to use 12 leads
Pacing wires: may have to increase HR
Chest tubes: check often
SCDs: even if lower extremety graft was taken
Urinary catheter: strict Is/Os
nursing care of chest tubes
-mark level of drainage
-observe integrity
-check air vent
-coil tubing
-secure system upright position
avoid lifting system above pts chest
-encourage ambulation and position change
-cough and deep breathing
-sit up right
-assess dressing
-assess drainage system
common graft sites for CABG
internal mammary artery: best due to proximity to the heart
greater saphenous vein: in lower leg
CVP monitoring
∙ Measures the pressure in the vena cava and right atrium
∙ Normal CVP (post open heart) = wide variations, but somewhere between 2 - 10 mmHg
•This # varies based on fluid volume status.
∙ Elevated CVP indicates increased right ventricular preload; most often secondary to hypervolemia
∙ Decreased CVP indicates reduced right ventricular preload; most often secondary to hypovolemia
pulmonary artery pressure monitoring
∙ Measures right ventricular function
∙ Normal Pulmonary Artery Pressure
Systolic = 18 – 25 mmHg (MAP around 15)
Diastolic = around 10 mmHg
∙ Elevated PAP indicates Pulmonary HTN, sometimes pulmonary embolism
∙ Catheter (Swan Ganz) is inserted through sterile procedure by a trained provider and covered with sterile dressing
CABG complications
▪Bleeding
▪Arrhythmias
▪Clots
▪Hypotension
▪Dehydration
▪Pain
valve regurgitation
back up of blood flow due to valves not closing completely
valvular stenosis
reduction of blood flow through valves due to narrowing causing incomplete opening of the valve
valve prolapse
one or more cusps will protrude in the wrong direction resulting in backflow
Semilunar and tricuspid: have three leaflets
Mitral: only bicuspid
mitral valve prolapse
Part of one or both mitral valve leaflets slide back into the atrium during systole causing blood to regurgitate from the left ventricle into the left atrium; usually both leaflets
Can be hereditary; increases risk for infective endocarditis
treatment of mitral valve prolapse
none for mild cases, medication to treat symptoms, surgery to repair
mitral valve regurgitation
During systole, blood "backflows" from left ventricle to left atrium during systole
Leads to increased systolic pressure in the left atrium; can lead to left atrial enlargement due to the atria working harder to pump into the ventricle
s/s of mitral valve regurgitation
Asymptomatic for years. Fatigue, dyspnea, orthopnea, murmurs (grade 3 or higher) and occasional palpitations
treatment of mitral valve regurgitation
Ace/ARB: vasodilation
BB: lower heart contractility
Surgery (valvuloplasty or valve replacement if severe enough)
aortic regurgitation
flow of blood backward from the aorta into the heart; caused by a weak heart valve
usually secondary to to endocarditis, congenital defect, syphilis, aortic abnormalities
complications of aortic regurgitation
hypertrophy of the left ventricle, systolic HF
ACE inhibitors
"PRIL" Captopril, Enalapril, Afosiopril
Antihypertensive. Blocks ACE in lungs from converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II (powerful vasoconstrictor). Decreases BP, Decreased Aldosterone secretions, Sodium and fluid loss.
Check BP before giving (hypotension)
*Orthostatic Hypotension
ARBs
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
'-sartan'
Treatment of aortic regurgitation
valve replacement once LV dysfunction develops
ACE inhibitors, BB, lifestyle modification, and stress reduction
aortic stenosis
- Narrowing/hardening of aortic valve (calcification); does not close or open properly
causes of aortic stenosis
-congenital defect
-degenerative changes (CAD, HTN, cardiomyophathy)
-rheumatic endocarditis
treatment of aortic stenosis
valve replacement after onset of complications
BB, ARBs, ACE
valvuloplasty
surgical repair of a valve
* Commissurotomy - repair of the commissure (area where the leaflets connect)
* Annuloplasty - repair of the annulus
* Leaflet Repair - repair of the leaflets
* Chordoplasty - repair of the chordae tendineae
types of valve replacements
* Open (sternotomy)
* Secondary Approach: more common
- TAVI (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation)
- TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement)
types of artificial valves
* Mechanical: more prone to blood clotting
* Tissue:
- Bioprostheses: pig or cow
- Homograft: from a cadaver
- Autograft: a leaflet from another valve of the same person
post valve replacement care
* Anticoagulation therapy
* Warfarin - lab maintenance and dietary restrictions
* Prevention of infective endocarditis
* Antibiotic prophylaxis prior to dental procedures or surgery
* Follow up
* Cardiologist
* CT surgeon
* Cardiac rehab
* Repeat echocardiograms