Bonding Notes - Atomic Structure & Bonding (copy)
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
National 4/5 Chemistry - Unit 1 : Section 3.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Why do Atoms Form Bonds?
A full outer energy level is a very stable arrangement of atoms. Atoms form bonds to achieve a full outer energy level.
Forming Covalent Bonds.
Covalent bonds are formed between non-metal elements. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons. A covalent bond is a pair of shared electrons.
Formulae for Covalent compounds.
The valency of an atom is equal to the number of unpaired electrons in the atom.
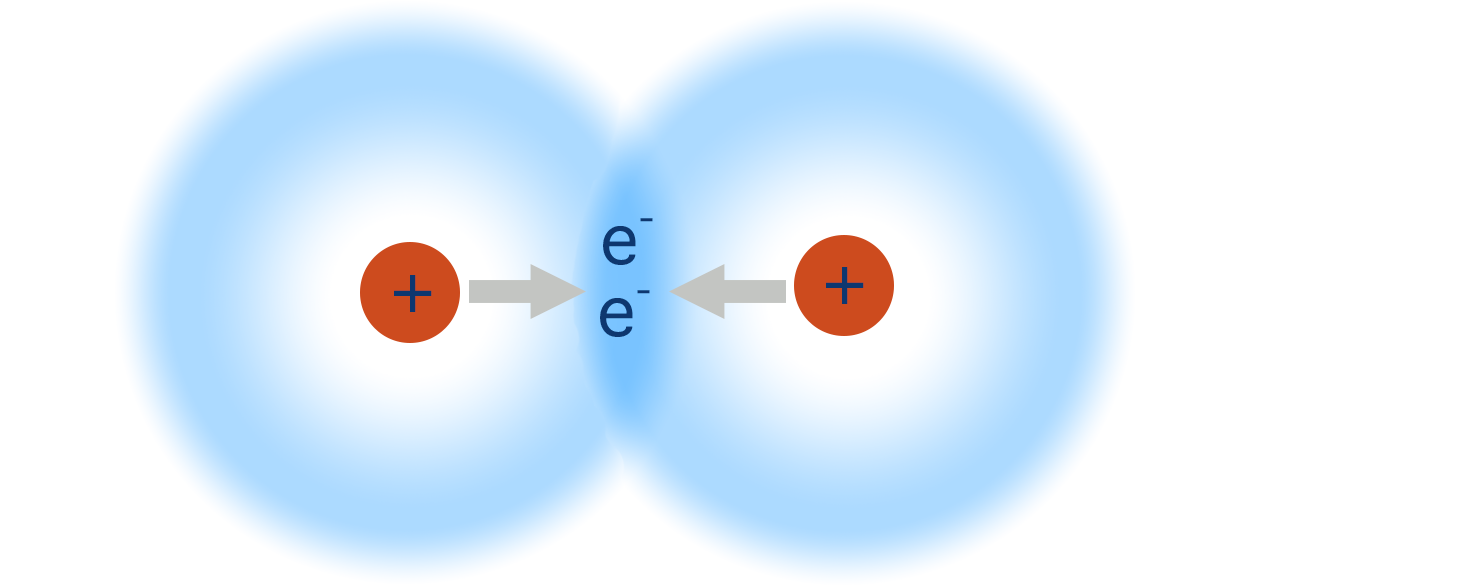
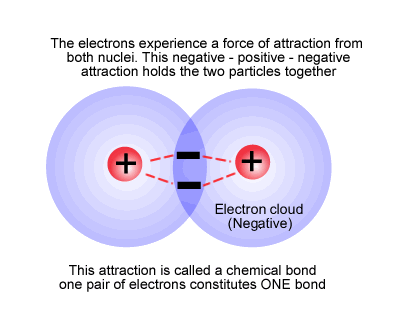
How do Covalent Bonds Hold Atoms Together?
When two atoms bond, the shared pair of electrons is attracted to the nucleus of both atoms.
Covalent Molecules
Only covalent compounds are made up of molecules. Covalent Molecules are groups of atoms held together by covalent bonds.
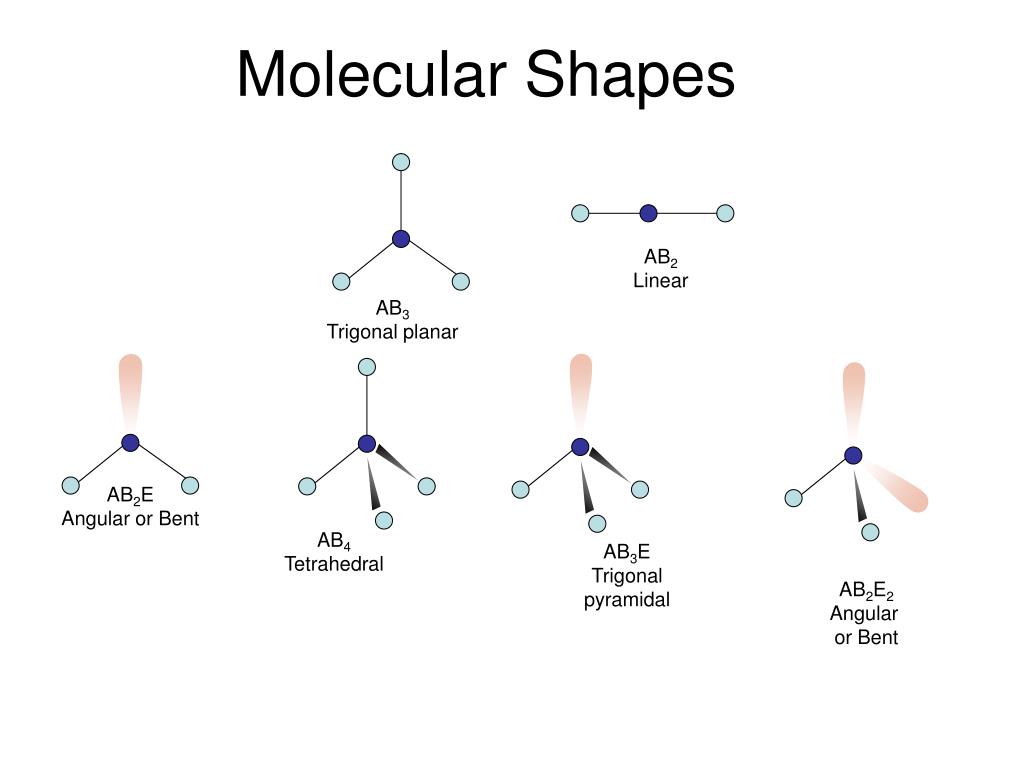
Shapes of Molecules.
Linear, Angular, Pyramidal, Tetrahedral
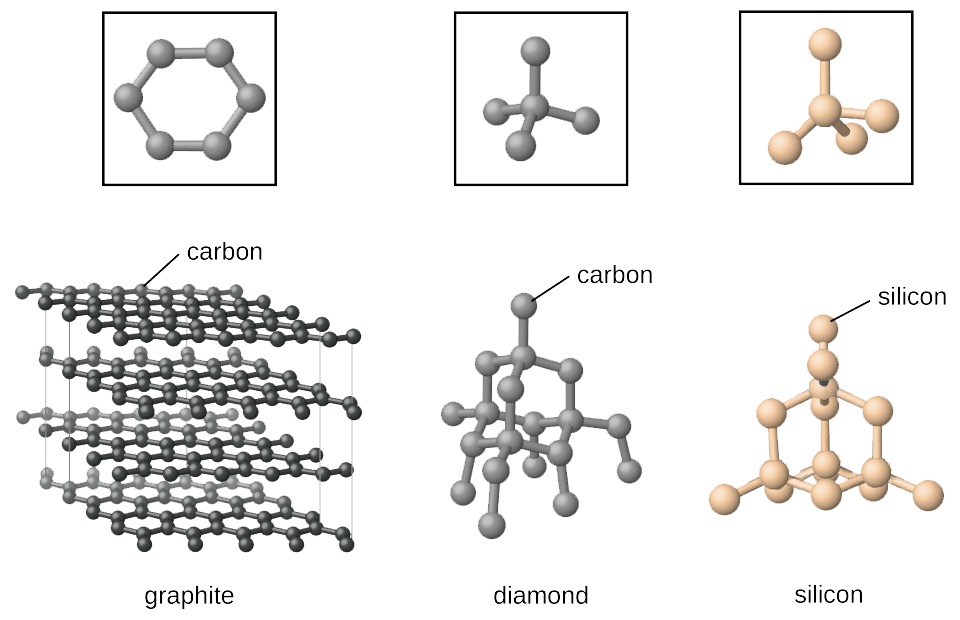
Covalent Networks.
When covalent bonding occurs between a very large number of atoms a giant covalent network structure is formed.
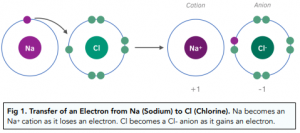
Formation of Ions.
Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal. Ionic bonding involves a transfer of electrons.
When an atom gains or looses electrons it becomes an ion. An ion is a charged particle.
-Metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions.
-Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negative ions.
The size of the charge on the ion is equal to the valency of the element, i.e. the number of unpaired electrons.
What Holds Ionic Substances Together?
An ionic bond is the attraction between ions of an opposite charge.
An Ionic Lattice.
An ionic lattice is a large 3-dimensional network of oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic forces.

State at Room Temperature.
Ionic compounds have very high melting and boiling points and are solids at room temperature. Covalent substances can be separated into:
a ) Discrete Molecules : These have lower melting and boiling points and are gases, liquids or low melting point solids at room temperature. Covalent bonds are not broken when covalent molecular substances melt or boil. Only the weak attractions between molecules are broken.
b ) Covalent Networks : These have very high melting and boiling points and are solid at room temperature.
Conductivity.
- Covalent substances do not conduct electricity in any state because they are made up of molecules and do not contain charged particles.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity as solids because they are held tightly together in the lattice and are not free to move.
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in solution because the lattice is broken up and the ions are free to move.
Solubility.
Ionic substances tend to dissolve in water and not in non-aqueous solvents.
Covalent substances tend to dissolve in non-aqueous solvents and not in water.
Conductivity of Elements.
Note : Although metals, ionic melts and ionic solutions all conduct electricity, there is a difference
• In metals it is electrons which carry the current.
• In ionic melts and solutions, it is ions which carry the current. The ions are chemically changed by the current. ( see part 2e )
Electrons cannot flow through solutions and ions cannot flow through metals.
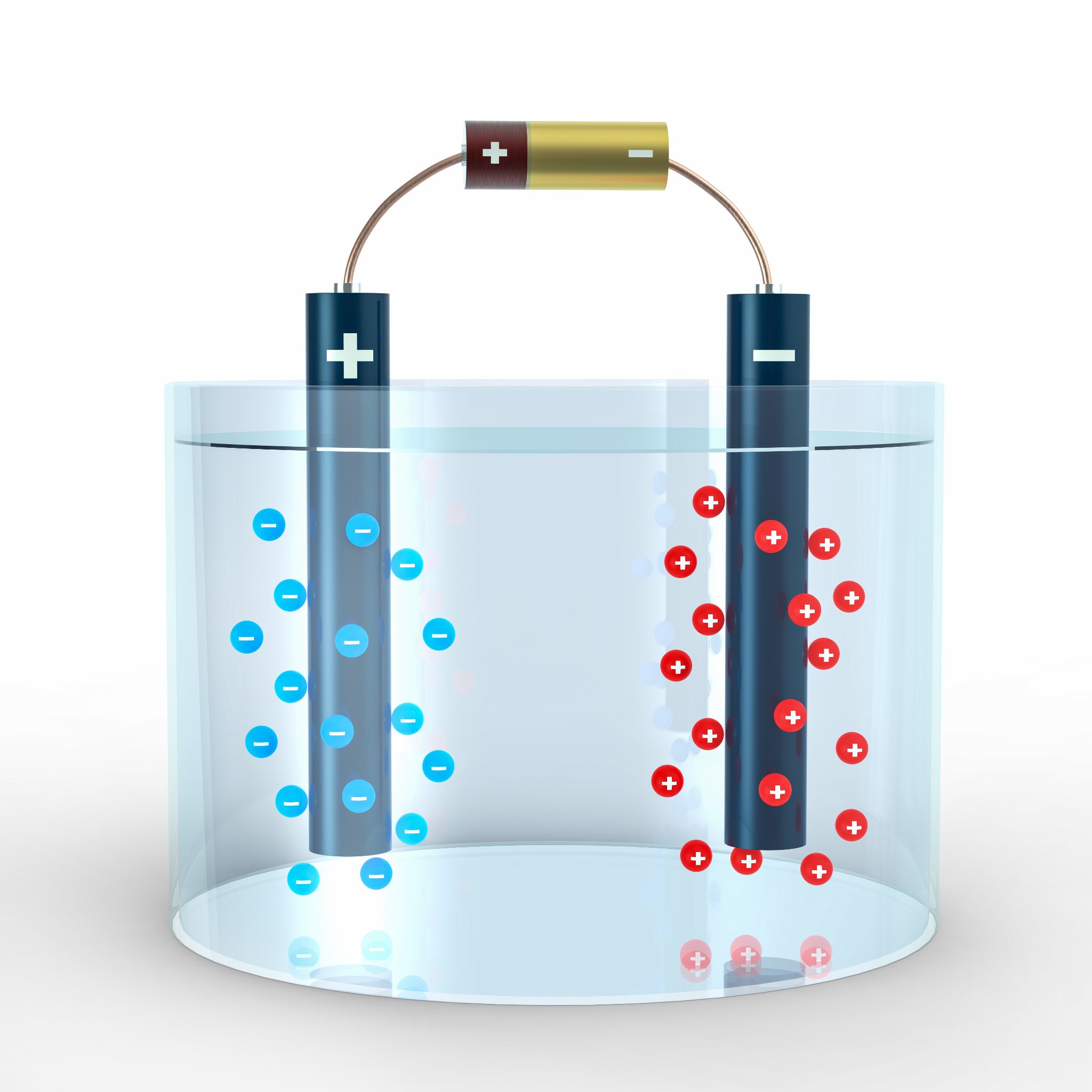
What is Electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the decomposition of an ionic compound into its elements using electricity.
What Type of Compounds Undergo Electrolysis?
A solution or melt which conducts electricity is called an electrolyte.
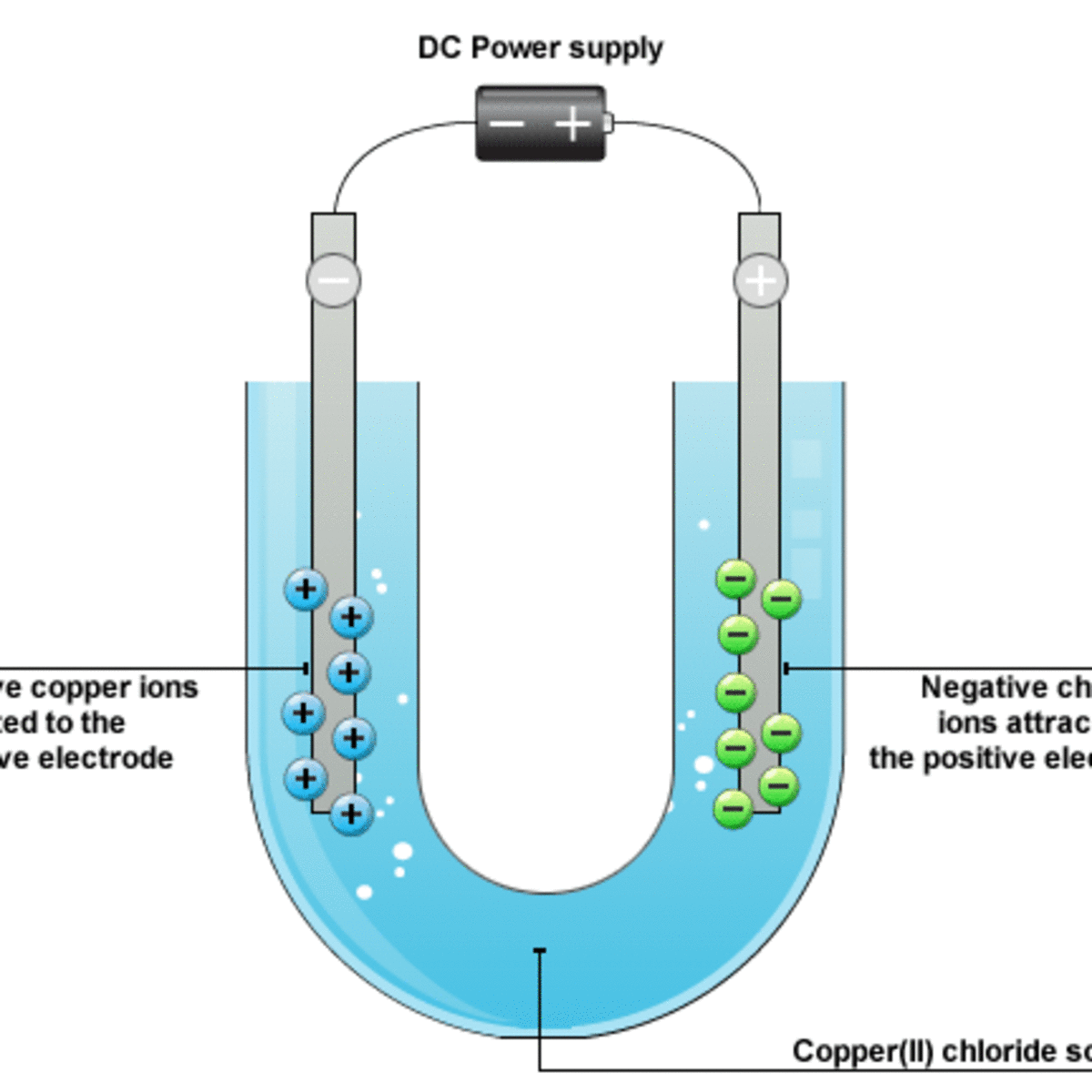
What is Happening at the Electrodes.
Non-metal negative ions are attached to the positive electrode where they loose electrons.
Metal, positive ions are attached to the negative electrode where they gain electrons.
During electrolysis a D.C. ( Direct Current ) supply is used to provide unchanging positive and negative terminals, which allows the products to be separated and identified.
Oxidation and Reduction.
The loss of electrons which occurs at the positive electrode is called oxidation. The gain of electrons which occurs at the negative electrode is called reduction.
• Oxidation is the loss of electrons.
• Reduction is the gain of electrons.
OIL RIG