Neuroanatomy & General Structure/Function
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Our nervous system is broken up into ____ and ____
Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
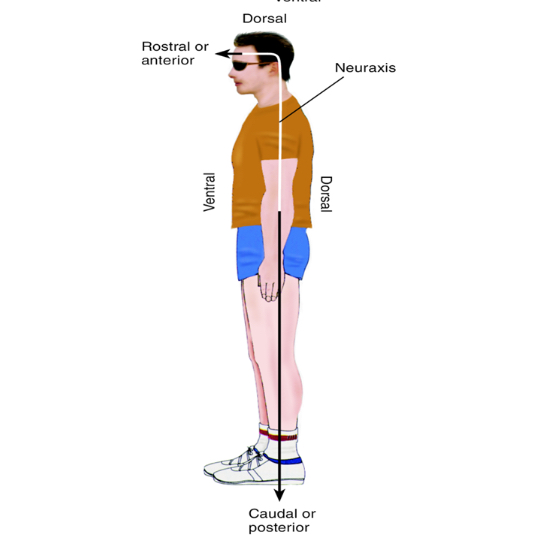
What is neuraxis?
An imaginary line that’s drawn through the CNS from the base of the spinal cord to the front of the brain.
What is frontal plane?
A slice that reveals the ventral and dorsal
What is sagittal plane?
A slice that reveals the left and right of something
What is transverse plane?
Horizontal slice of something
Within the PNS there are two systems, ____ and ___
Somatic Nervous System
Automatic Nervous System
What is the Somatic Nervous System responsible for?
Responsible for voluntary muscle movement
What is the automatic nervous system responsible for?
Responsible for automatically controlling certain organs in the body like the heart.
What part of the human head helps protect the brain?
Skull
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Meninges
Blood-brain barrier
Where is cerebrospinal fluid found in?
CSF is found in the ventricles of the brain.
How does cerebrospinal fluid protect the brain?
CSF is surrounded around the brain and helps protect the brain from sudden impact injuries.
What is hydrocephaly?
Hydrocephaly is a condition where the ventricles of the brain are clogged, resulting in CSF fluid build up in the brain and the brain and skull to grow around the obstruction, leading to an abnormal skull structure.
Pressure could build up and cause brain damage.
What is a shunt?
A shunt is a tube that surgically connects the brain to the abdomen to let CSF drain and get repurposed.
What happened as a result of the Frenchmen’s shunt not working?
His lateral ventricle produced too much CSF, causing it to eat away at the brain to compensate for the amount of fluid held, leaving little cortex left.
He still lived a normal life.
How does meninges protect the brain?
Meninges are like padding for our brain and is located around the walls of the skull.
It also keeps your brain attached to your skull, protecting it from moving during momentum movements.
What layers make up the meninges?
“PAD”
Pia mater (closest to brain)
Arachnoid membrane
Dura mater (thickest layer farthest from brain)
How does the blood-brain barrier protect the brain?
It prevents viruses, bacteria, and other harmful things from entering the brain.
What can pass the blood-brain barrier?
Oxygen, water, carbon dioxide, vitamins A, D, and drugs
What is the cortex?
The cortex is the outer surrounding layer of the brain and has grooves and bumps
What are the bumps of the brain called?
Gyrus (Gyri)
What are the grooves of the brain called?
Sucleus (suclei)
What is the occipital lobe responsible for?
helps with vision by receiving visual information
Codes visual information
What is the temporal lobe responsible for
Codes auditory information
Higher visual processing
What is the parietal lobe responsible for?
Somatosensation (sensations happening on your body)
Spatial awareness
What would happen if the parietal lobe was damaged?
You would have a difficult time figuring out where your body is
What is the frontal lobe responsible for?
motor
Planning (Emotion regulation)
Higher reasoning
What is white matter?
White matter is caused by myelin and are made up of axons. They are responsible for moving information.
What is gray matter?
Gray matter is the soma and dendrites and is located located in the superficial cortex functional area (sensory, motor, and high order functions)