[ Gen Bio ] Lesson 2: Major Parts of the Cell
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Cell membrane or plasma membrane
is the cell's primary barrier.
Cell membrane or plasma membrane
separates the cytoplasm from the external environment.
phospholipids
cholesterol
membrane proteins
glycolipids
glycoproteins
Cell membrane or plasma membrane comprises the (5):
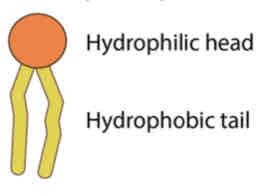
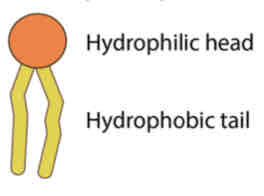
Head region / Hydrophilic Head Tail region / Hydrophilic Tail
phospholipids consists of 2 regions:
• phosphate group • hydrophilic
Head Region (2):
• two fatty acid chains • hydrophobic
Tail Region (2):
Hydrophilic
having a tendency to mix with, dissolve in, or be wetted by water.
(Heads up: know the Differences between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic)
Hydrophobic
Water fearing; a property of molecules that do not mix with water
(Heads up: know the Differences between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic)
Phospolipids
Consists of Hydrophilic head and Hydrophobic tail
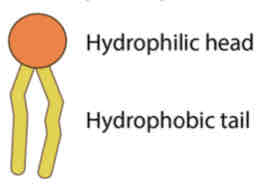
Phospolipids
make up the phospholipid bilayer.
Phosphate heads Fatty acid tails
two phospholipid layers
Phosphate heads
face the cytoplasm and the cell's exterior.
Fatty acid tails
are sandwiched.
fluid mosaic model
describes the membrane structure.
Mosaic
different molecules such as proteins, sugars, and cholesterol
Fluidity
due to its natural viscosity
Kinks Cholesterol
Membrane fluidity is determined by: (2)
Kinks
in the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids
Cholesterol
molecules which act as regulators of fluidity
Selective permeability
is an important property of the "lipid bilayer", in which it only allows certain molecules to move into and out of the cell.
Permeable
Liquids, Alcohol, Small molecules (oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water)
Impermeable
Polar molecules, Large molecules (glucose, amino acids, nucleic acids, proteins)
Channel Proteins Carrier Proteins Cell Recognition Proteins Receptor Proteins
Kinds of Membrane Proteins (4):
Channel Proteins
passageway of certain molecules
Carrier Proteins
change conformation to transport molecules
Cell Recognition Proteins
detect invading pathogens
Receptor Proteins
binding of molecules to trigger responses
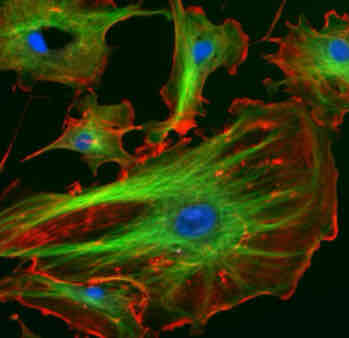
Cytoskeleton
This consists of a network of protein fibers that gives the cell its structural framework.
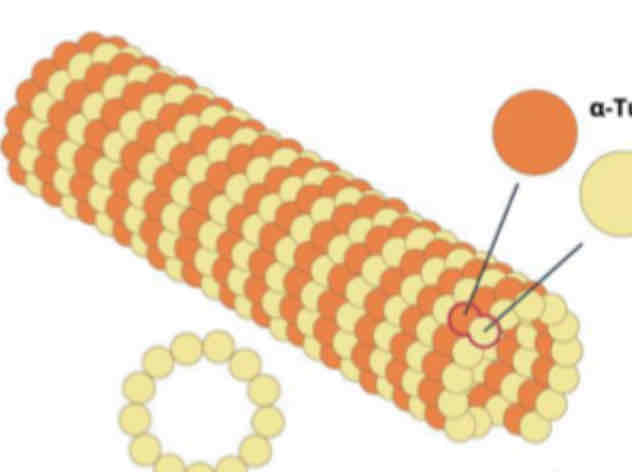
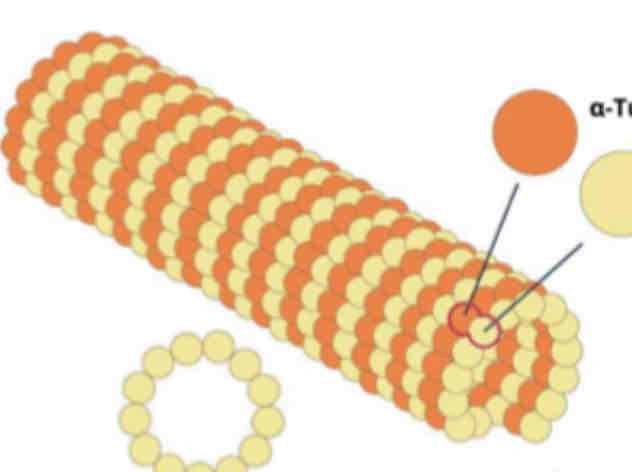
Microtubules
These consist of helically arranged globular proteins called "tubulin."
Microtubules
It radiate from the "centrosomes"
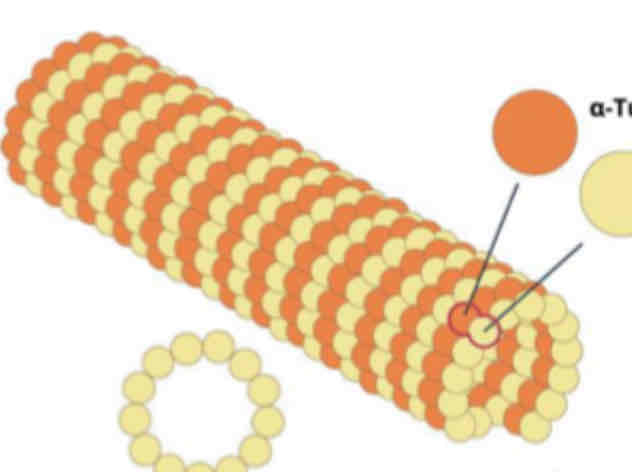
Microtubules
Form spindle fibers that move chromosomes
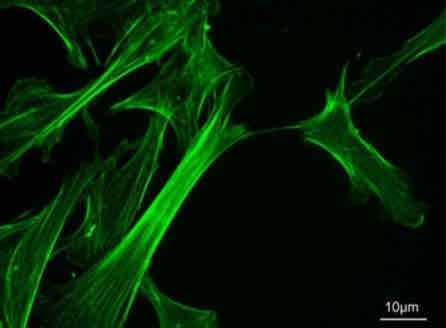
Microfilaments
They consist of long fibers of "actin" protein, making them the thinnest cytoskeleton.
microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
Cytoskeleton consists of (3):
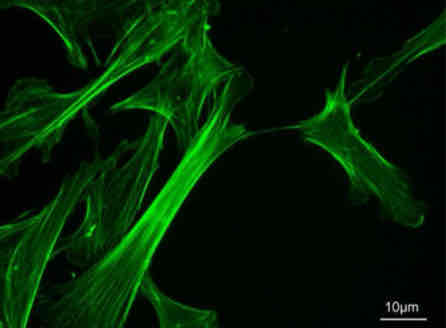
Microfilaments
They help facilitate cell and organelle movement.
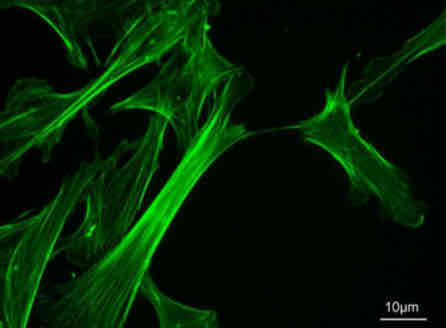
Microfilaments
They can help change the shape of the cell.
Intermediate Filaments
Helps maintain cell shape; Anchors the nucleus
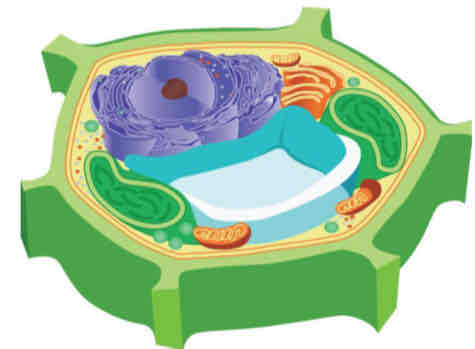
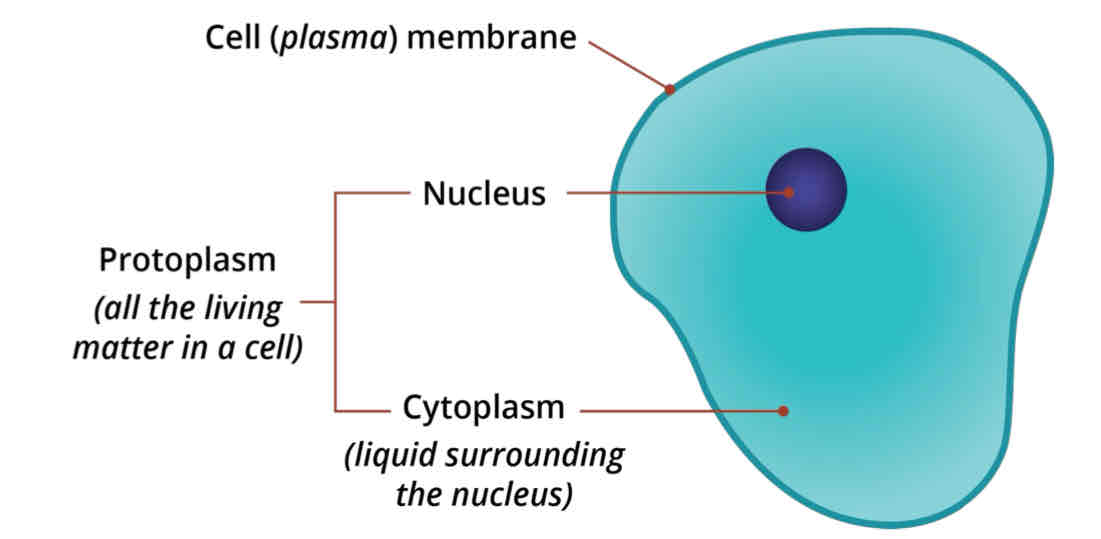
Cytoplasm
This is where all different subcellular structures are suspended.
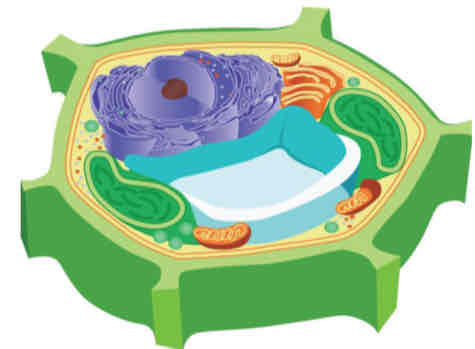
Cytoplasm
It is composed of the "cytosol."
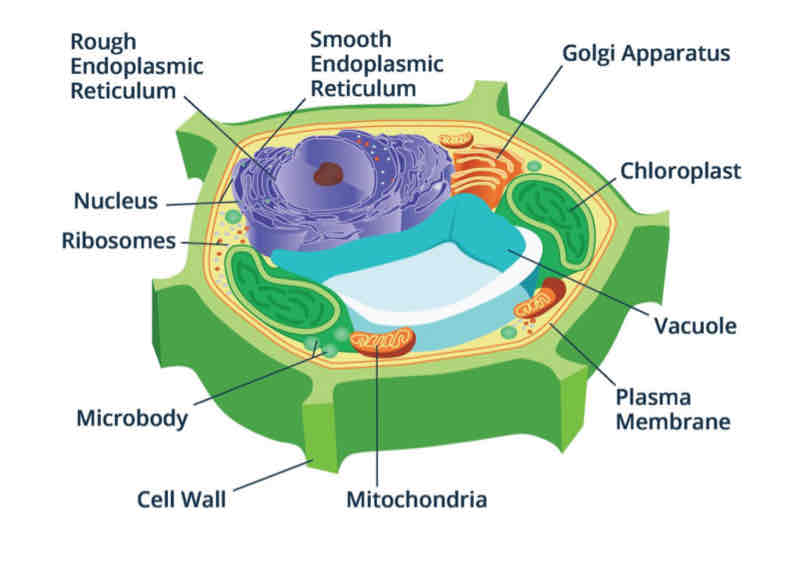
Cell Wall
is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane.
Cell Wall
It helps maintain the shape of cells and prevent them from bursting.
Peptidoglycan
Most bacteria have cell wall made up of _______.
Chitin
The cell wall in some fungi consists of _____.
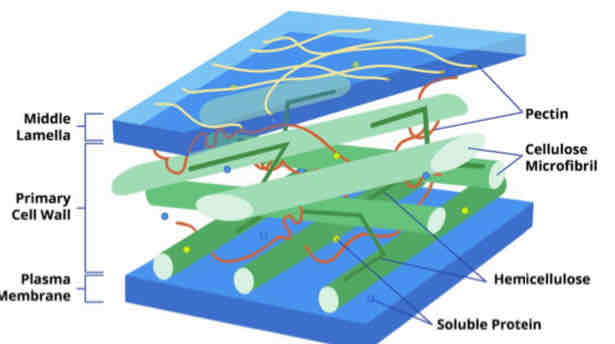
Cellulose Fibers
In plant cells, the cell wall consists of mesh-like ________.
Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Cell Wall
4 Major Parts of the Cell