Microbiology quiz 2 (biological molecules)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I'm cooked pt. 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Covalent Bonding
Electrons are shared between 2 atoms
Non-polar covalent bond (equal electron sharing)
C-C
C-H
H-H
Polar covalent bond (unequal electron sharing)
O-H
N-H
O-C
N-C
Hydrophobic molecules repel water -
Often non-polar molecules (oil)
Hydrophilic molecules like water -
Often polar molecules (sugar)
Polar molecules can form attractions called hydrogen bonds
Very polar bonds create partial positive and partial negative charges.
A partial negative charge can attract a partial positive charge of another molecule to form a hydrogen bond
A partial positive charge can have its electrons pulled away from it towards another atom
Polar molecule that is hydrophilic
(Photo)
Non-polar molecule that is hydrophobic
(photo)
Polar molecules can form -
Attractions called hydrogen bonds
Very polar bonds create -
Partial positive (δ+) and partial negative (δ) charges.
A partial negative charge can -
Attracts partial positive charge of another molecule to form a hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bonds are incredibly important in -
DNA molecules, RNA molecules, and protein and how they function
4 classifications of biological molecules
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic acids
Proteins consist of -
Catalase
Keratin
Amylase
Actin
Myosin
Carbohydrates consist of -
Fructose
Glucose
Starch
Chitin
Lipids consist of -
Fatty acids
Phospholipids
Triglycerides
Nucleic acids consist of -
ATP
DNA
RNA
Protein functions
Defense
Storage
Transport
Regulation
Enzymes
Reception
Motion
Structure
Make pigments
Carbohydrate functions
Quick energy
Energy storage
Structure
Lipid functions
Long-term energy storage
Cell membranes
Nucleic acid functions
Information storage
Transmitting information
Easy energy source (ATP)
Elements in Proteins
C
H
O
N
Sometimes S
Elements in Carbohydrates
C
H
O
1:2:1 ratio
Elements in Lipids
C
H
Little or no O
Elements in Nucleic acids
C
H
O
N
P
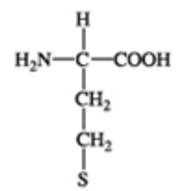
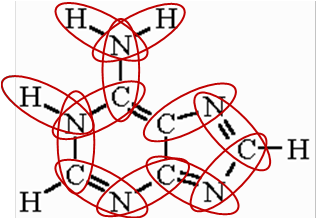
Protein
(Photo)
Lipid
(Photo)
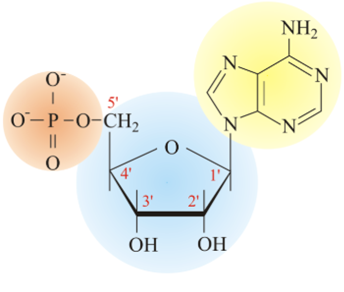
Nucleic acid
(Photo)
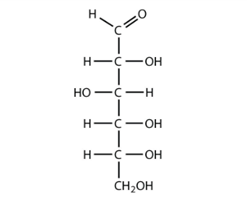
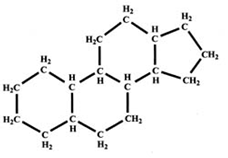
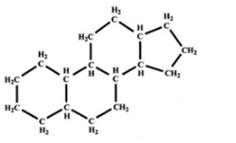
Carbohydrate
(Photo)
Monomer of Proteins
Amino acids
Monomers of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharide
Monomers of Lipids
Fatty acids
Monomers of Nucleic acids
Nucleotides
Protein classifications
Di-peptide (2)
Tri-peptide (3)
Poly-peptide (many)
Lipid classifications
Di-glyceride (2)
Tri-glyceride (3)
Carbohydrate classifications
Di-saccharide (2)
Tri-saccharide (3)
Poly-saccharide (many)
Nucleic acid classifications
Di-nucleotide (2)
Tri-nucleotide (3)
Poly-nucleotide (many)
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction where smaller molecules are joined together to form larger molecules
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction where large molecules are broken down to form smaller molecules
Monomer
A single, small molecule that can join with others to form larger molecules
Dimer
A molecule made up of two monomers bonded together
Trimer
A molecule made up of three monomers bonded together
Oligomer
A short chain of monomers (usually a few, 4-10) linked together
Polymer
A large molecule made up of many repeating monomers, often hundreds or thousands in length