Material Science OSU Quizzes 1-3 for midterm 1
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 1-4 from the honors course w Dr. Santala
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are elements to consider with regard to the design, production, and utilization of materials?
In-service conditions,deterioration during operation, and cost
Processing, structure, properties, and performance
Processing and performance
Structure, deterioration during operation, and cost
Processing, structure, properties, and performance
Classify the material as to whether it is a metal, ceramic, or polymer.
Silicon dioxide or silica (SiO2) Ceramic
Ceramic
Compute the percent ionic character of the interatomic bonds in the compound MgCl2. The electronegativity of Mg and Cl is 1.3 and 2.9, respectively.
39%
47%
68%
53%
47%
Which of the materials below would have delocalized electrons (i.e., electrons not bound to ion cores)?
FeCr
SiO2
None of these
CsF
FeCr
The potential energy curve of two atoms bonding has a minimum. Why?
Repulsive forces are negligible.
The force is zero when the attractive and repulsive forces cancel out.
Interactions forces are negligible.
Attractive forces are at their maximum.
Forces are moderate because the atoms are attracted to each other.
The force is zero when the attractive and repulsive forces cancel out.
Why are materials with metallic bonds good conductors of heat and electricity?
The electrons freely move between ion cores
The atoms vibrate more for metals than other materials
Bonds are easily broken for metals
The electrons are tightly bound to the ion cores
The electrons freely move between ion cores
Ionic bonds are formed between:
Atoms with large differences in their electronegativities
Noble gas atoms
Polymer chains
Atoms with very similar electronegativities
Atoms with large differences in their electronegativities
Electronegative elements: multiple choices correct
Give up electrons
Tend to reside in the top right side of the periodic table
Accept electrons
Do not participate in electron exchange
end to reside in the top right side of the periodic table
Accept electrons
How many electrons can occupy the p subshell (e.g., 3p)?
2
6
14
10
6
Which of the following atoms has 3 valence electrons?
He
Li
I
Bi
Al
Al
Which of the following compounds would most likely exhibit covalent bonding?
MgO
NaCl
SiC
LiBr
SiC

atom 2
atom 5
atom 7
atom 13
(1,0,0)
(.5,.5,0)
(1,.5,.5)
(0,1,1)
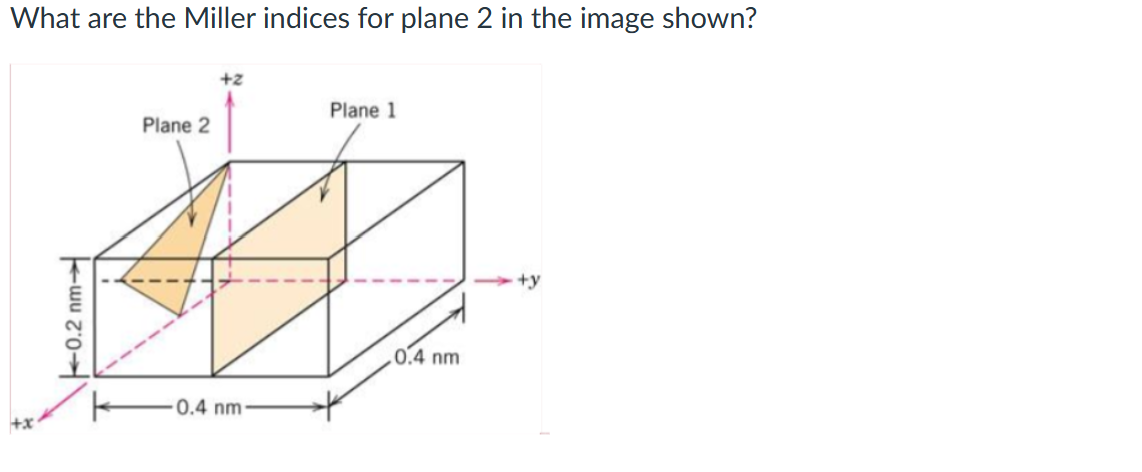
(3 2̅ 4)
(2 2 1)
(0 2 0)
(2 2̅ 1)
(2 2̅ 1)
Consider nickel (Ni) metal with an atomic radius of 0.12 nm. Ni has the FCC crystal structure. Calculate the lattice parameter in nm.
0.34
0.64
0.45
0.54
.34
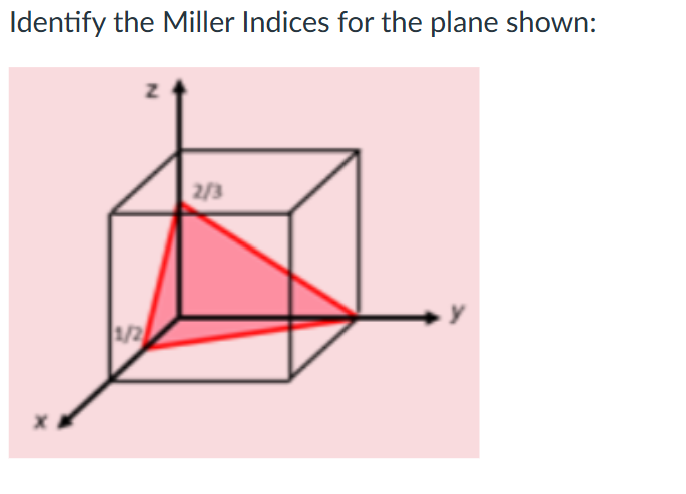
(4 2 3)
(4 1 3)
(4 3 2)
(3 1 4)
(2 1 3)
(4 2 3)

(1 0 0)
(1 0 1)
(1 1 1)
(-1-1 0)
(1 1 0)
(1 1 0)
White tin (Sn) is known to crystallize into a body-centered tetragonal cell shown below. In this cell, a= b= 0.37 nm and c= 0.34 nm (c is the dimension along the z-axis). The atomic radius R=0.15 nm. The interaxial angles are all 90°. Calculate the Atomic Packing Factor.
0.49
0.61
0.71
0.55
0.61
In the BCC crystal structure atoms touch along which direction?
(100)
(110)
[100]
[110]
[111]
[111]
White tin (Sn) is known to crystallize into a body-centered tetragonal cell shown below. How many atoms per unit cell are there?
1
2
4
6
2
For an FCC single crystal, which crystallographic plane is close packed?
(100)
(111)
(110)
[001]
[110]
(111)
The coordination number of an atom in the BCC crystal structure is:
8
6
2
4
12
8
If you would like to study dislocations with a microscopy you would most likely use:
Scanning probe microscopy
Optical microcopy
Scanning electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy
The equilibrium number of vacancies in a crystal structure:
Decreases with temperature
Is unpredictable with changing temperature
Stays constant with temperature
Increases with temperature
increases with temperature
An example of a three-dimensional volume defect is a:
Grain boundary
Crack
Screw dislocation
Vacancy
crack
An example of a two-dimensional interfacial defect is a:
Grain boundary
Void
Vacancy
Screw dislocation
grain boundary
An example of a one-dimensional or linear defect is:
A vacancy
A self-interstitial
A screw dislocation
An external surface
A screw dislocation
Annealing twin boundaries are usually observed in which types of metals?
FCC crystal structure
HCP crystal structure
BCC crystal structure
FCC crystal structure
Which of the following are point defects? Choose all that apply.
Vacancy
Impurity atom
Dislocation
Interstitial
Vacancy
Impurity atom
Interstitial
Which of the following is NOT one of the Hume-Rothery rules?
The atomic radii between the two atoms types shouldbe less than 15% different.
Both atom types should have similar electronegativity.
Both atom types must be in the same column on the periodic table.
The crystal structure of the two atom types should be the same.
Both atom types must be in the same column on the periodic table.
When the orientation between grains is slightly misaligned we call it:
Slip boundary
High angle grain boundary
Low angle grain boundary
Twin boundary
Low angle grain boundary