Forensic Anthropology 175 Exam #1
1/392
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
393 Terms
Proximal
Towards body/head
Distal
Away from body/head
Dorsal
Back side
Ventral
Belly side
Cranial
Towards the head
Caudal
Towards tail
Saggital
Divides body into left and right halves
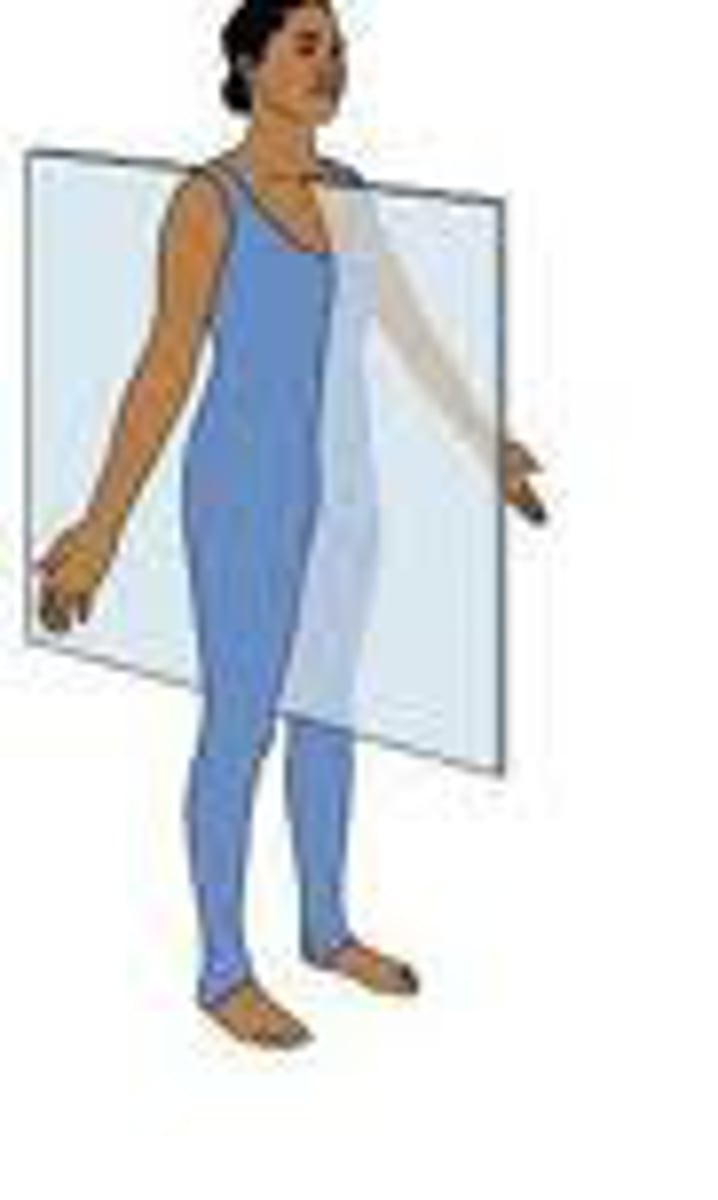
Coronal (frontal)
divides body into anterior and posterior parts
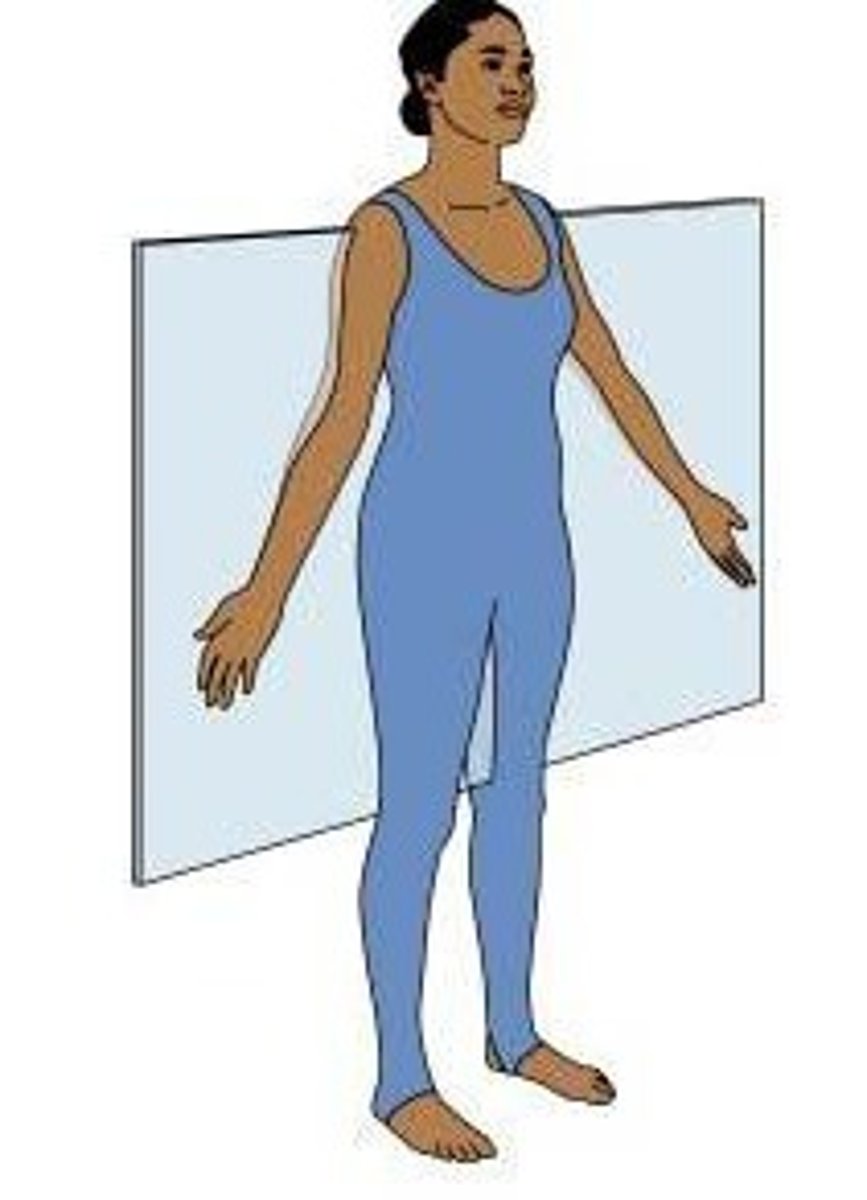
Transverse
Divides body into superior and inferior parts
Oblique
anything not perpendicular to the other planes
Skeletal system includes:
Bones
Cartilage
Tendon
Ligaments
Teeth
Bones in adult skeleton
206
Axial
head and tunk
Appendicular
limbs
Cranial
head
Postcranial
everything other than the head
Composite bone
Collagen fibers and Hydroxyapetite
Organic function
mechanical toughness
Inorganic function
mechanical hardness
Types of bones
Compart/cortical, spongy/Trabecular, articular/subchondral
Compact is
dense
Trabecular
bone that is porous, flexible, low mineral content; usually on the inside of bones
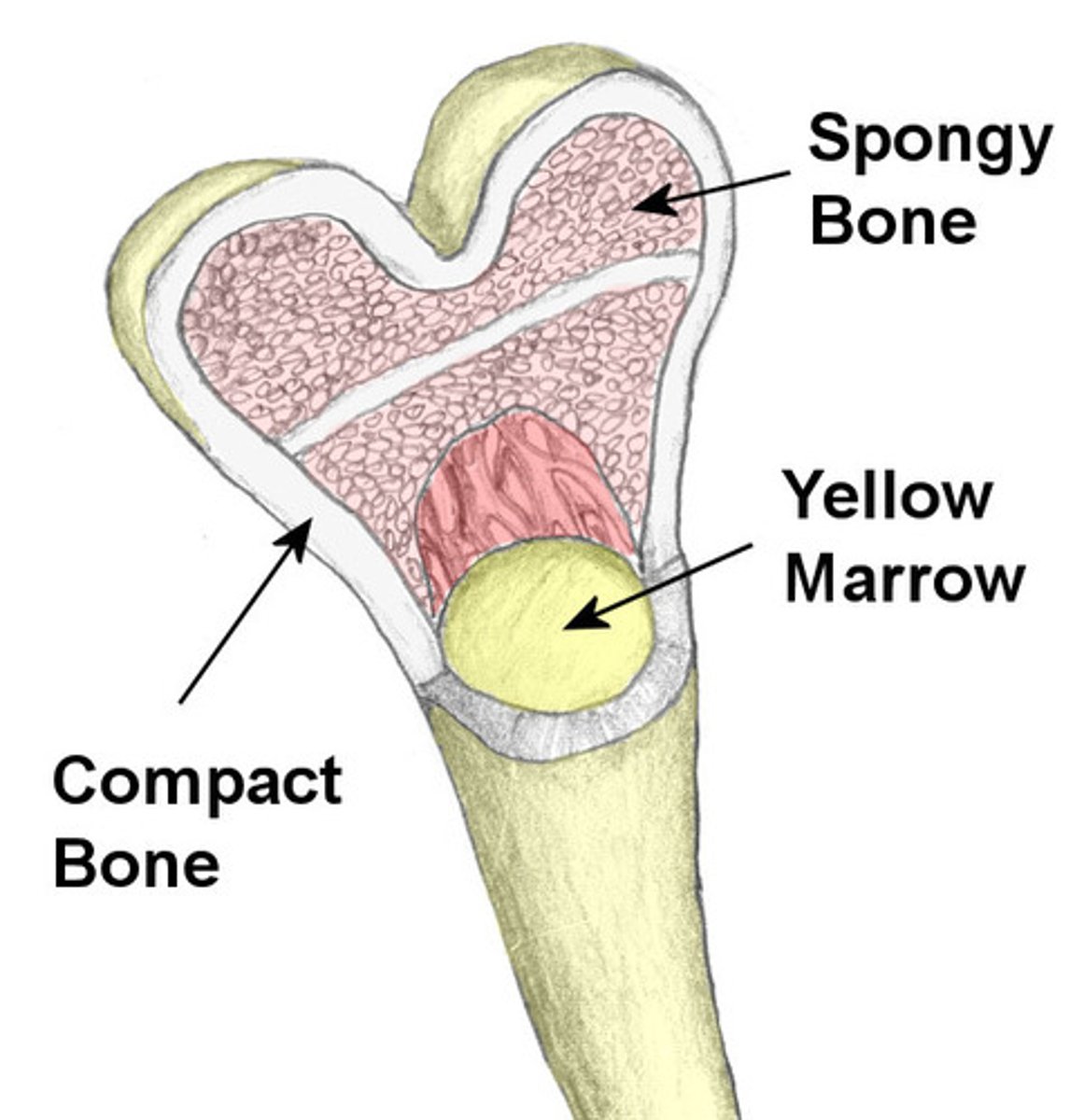
Subchondral
joint surfaces
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
Diaphysis contains
red and yellow marrow
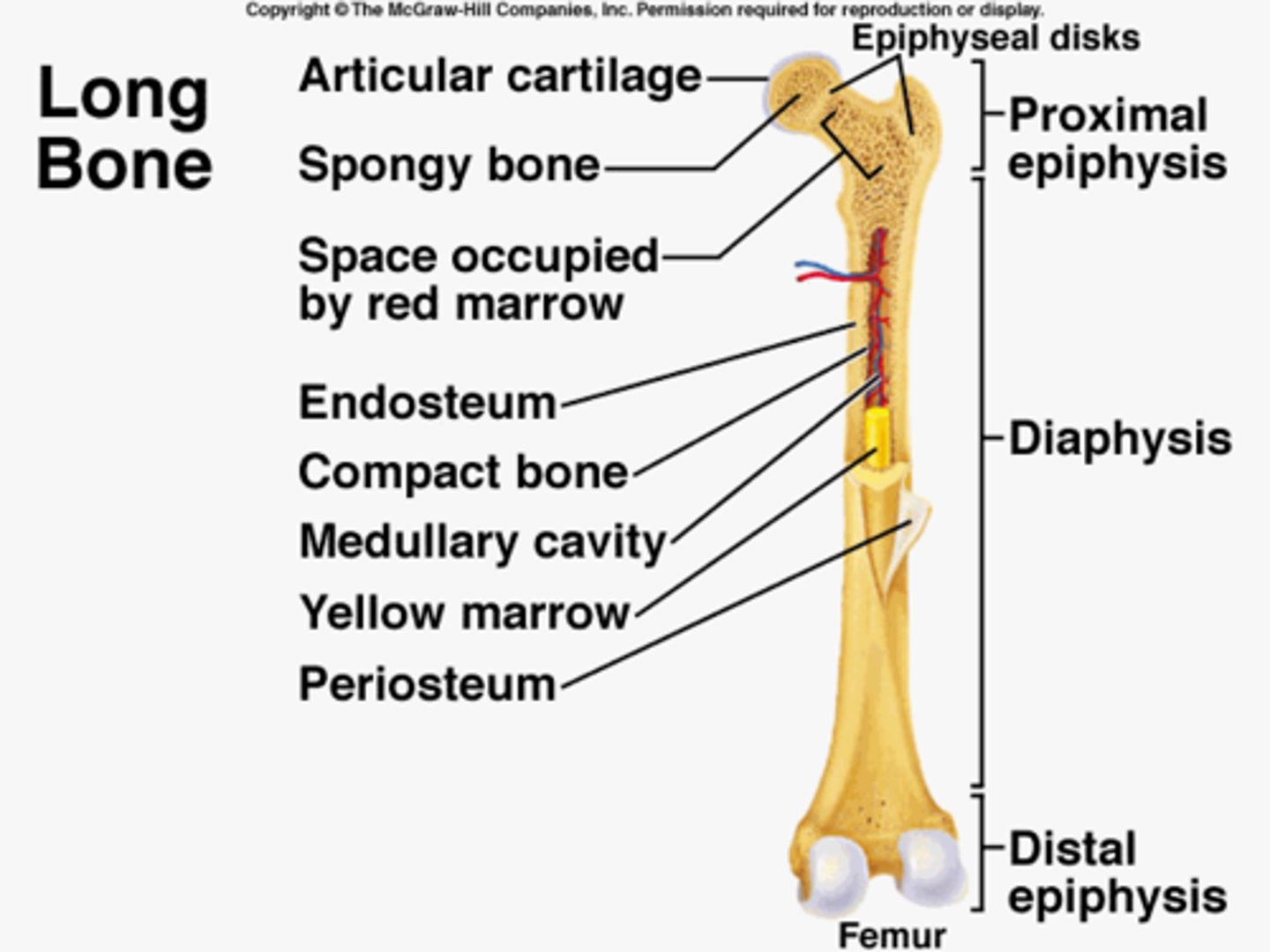
What is Hematopoiesis in the epophysis?
The production of blood cells
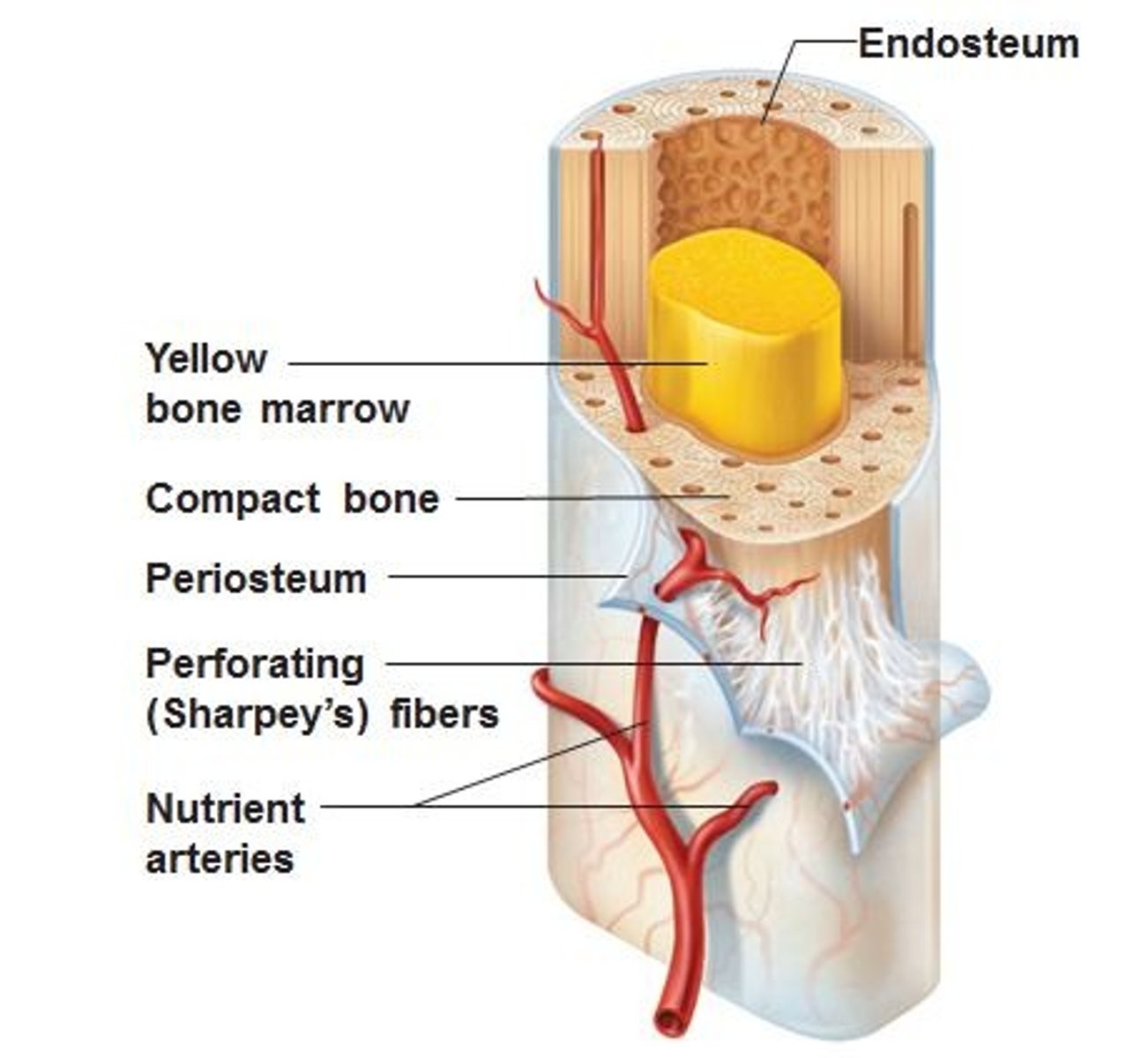
Periosteum
covers outer surface of bone
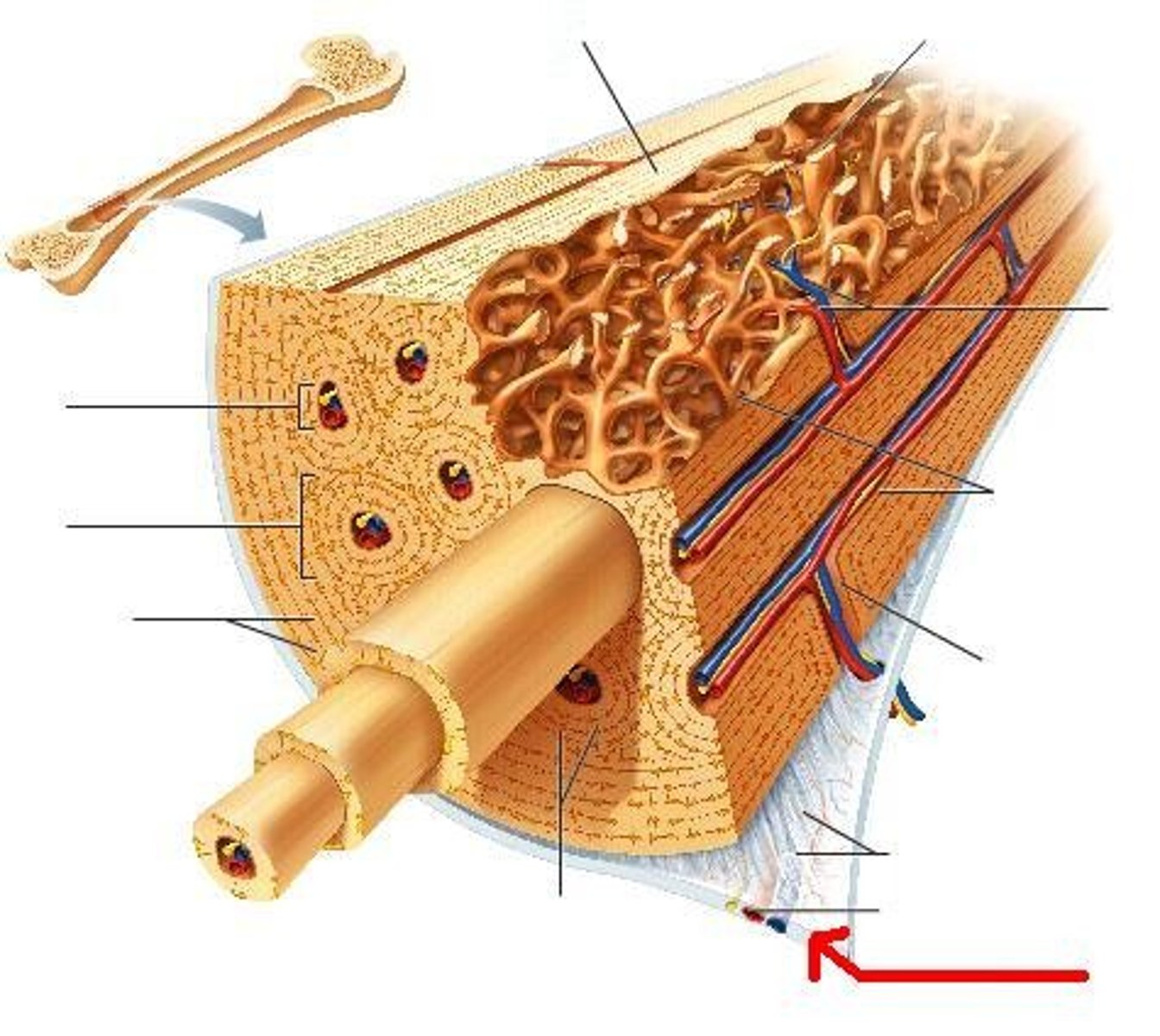
Endosteum
covers inside portion of compact bone
Articular cartilage
replaces periosteum where bone meets
Long bones are
compact bone with two ends
Short bones are
cube-like and spongy
Flat bones are
usually curved bones with sandwiched spongy layer
Irregular bones
Vertebrae, skull, hips
Sesamoid
small and round
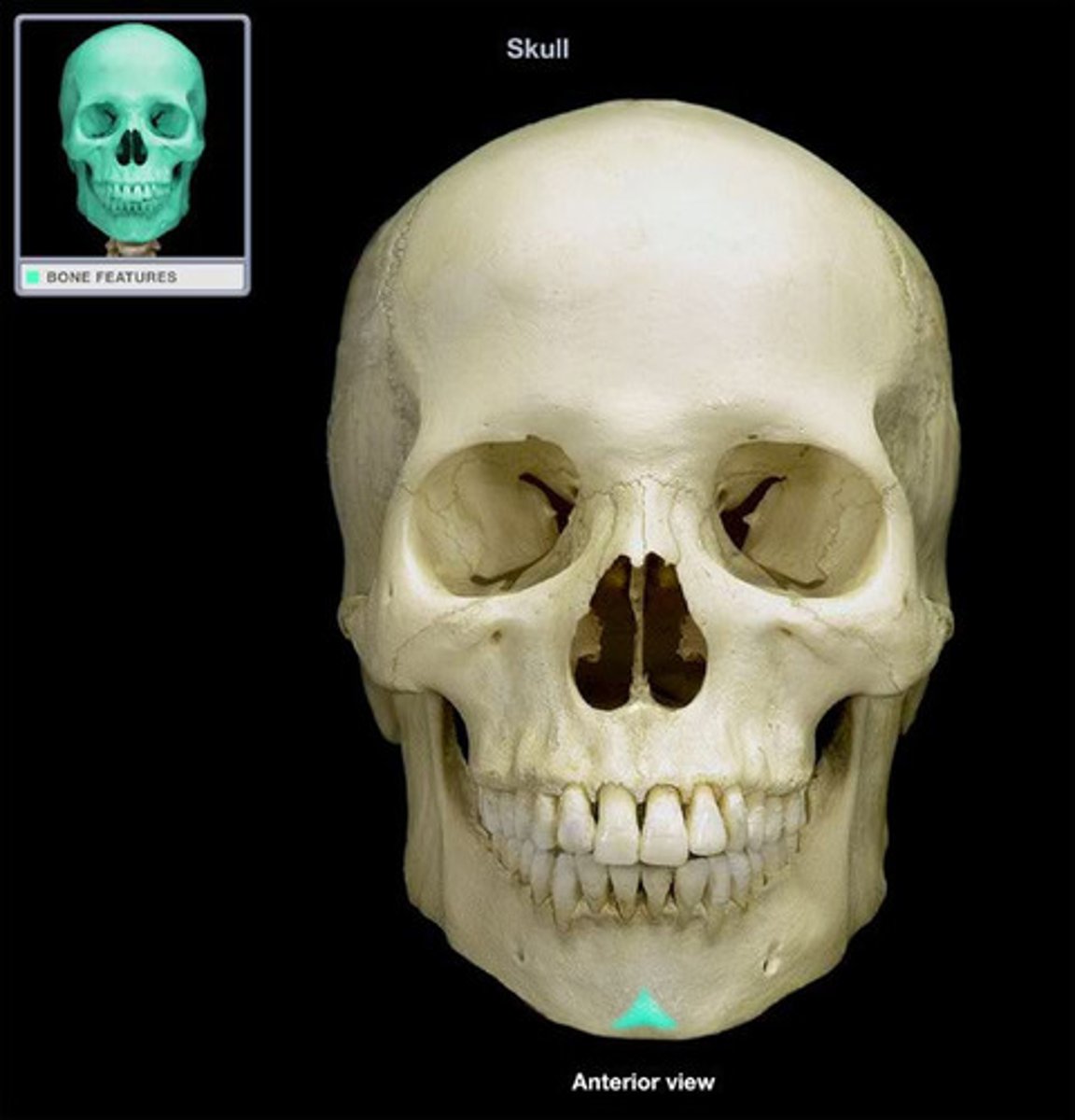
Skull
cranium and mandible
Features of the skill
orbits, anterior nasal aperture, zygomatic arch
How many bones are in the skill?
22
Neurocranium includes
frontal, parietal, temporal w/ 6 ear ossicles, occipital, sphenoid and ethmoid
Sagittal suture
midline between two parietal bones
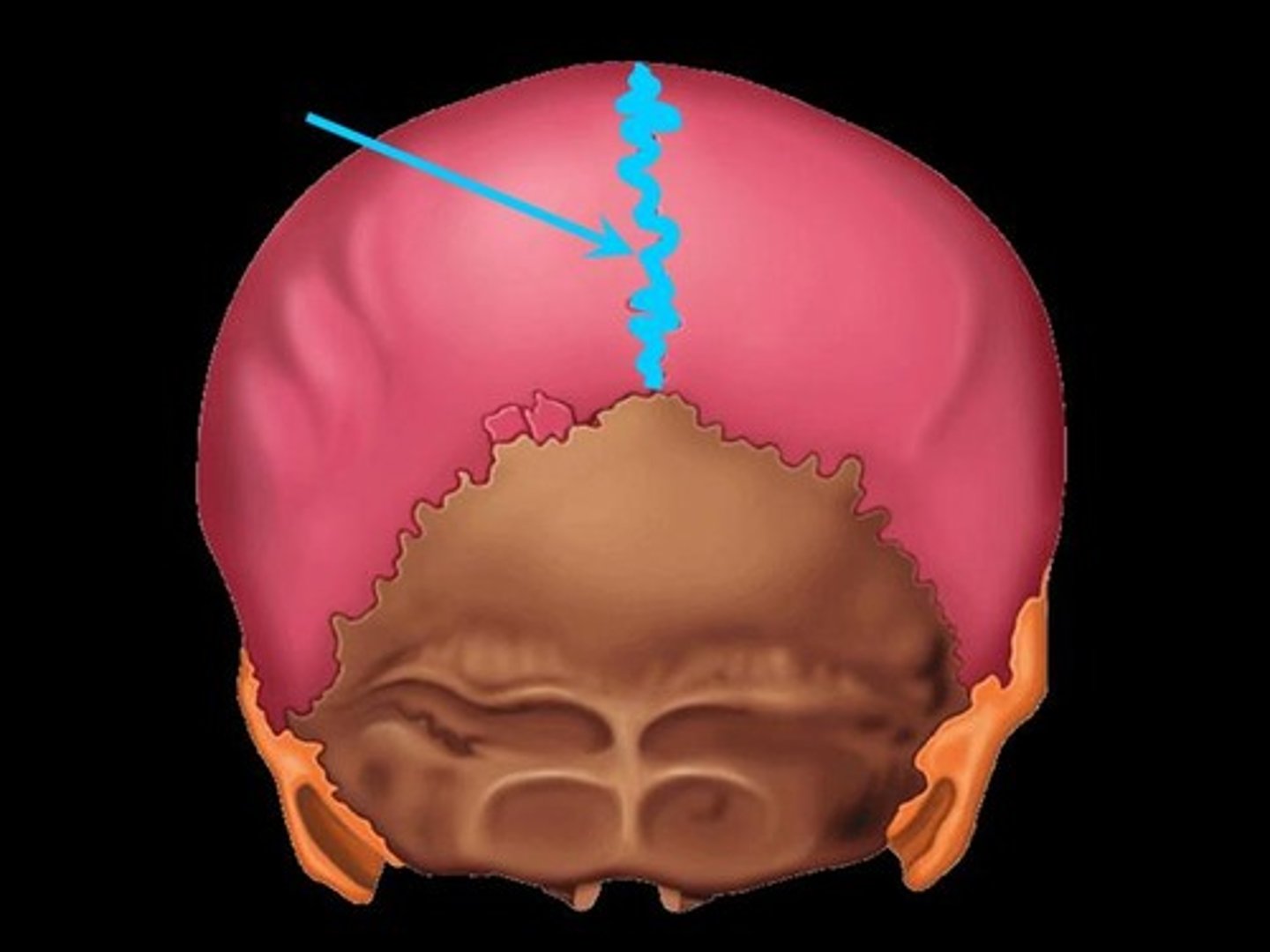
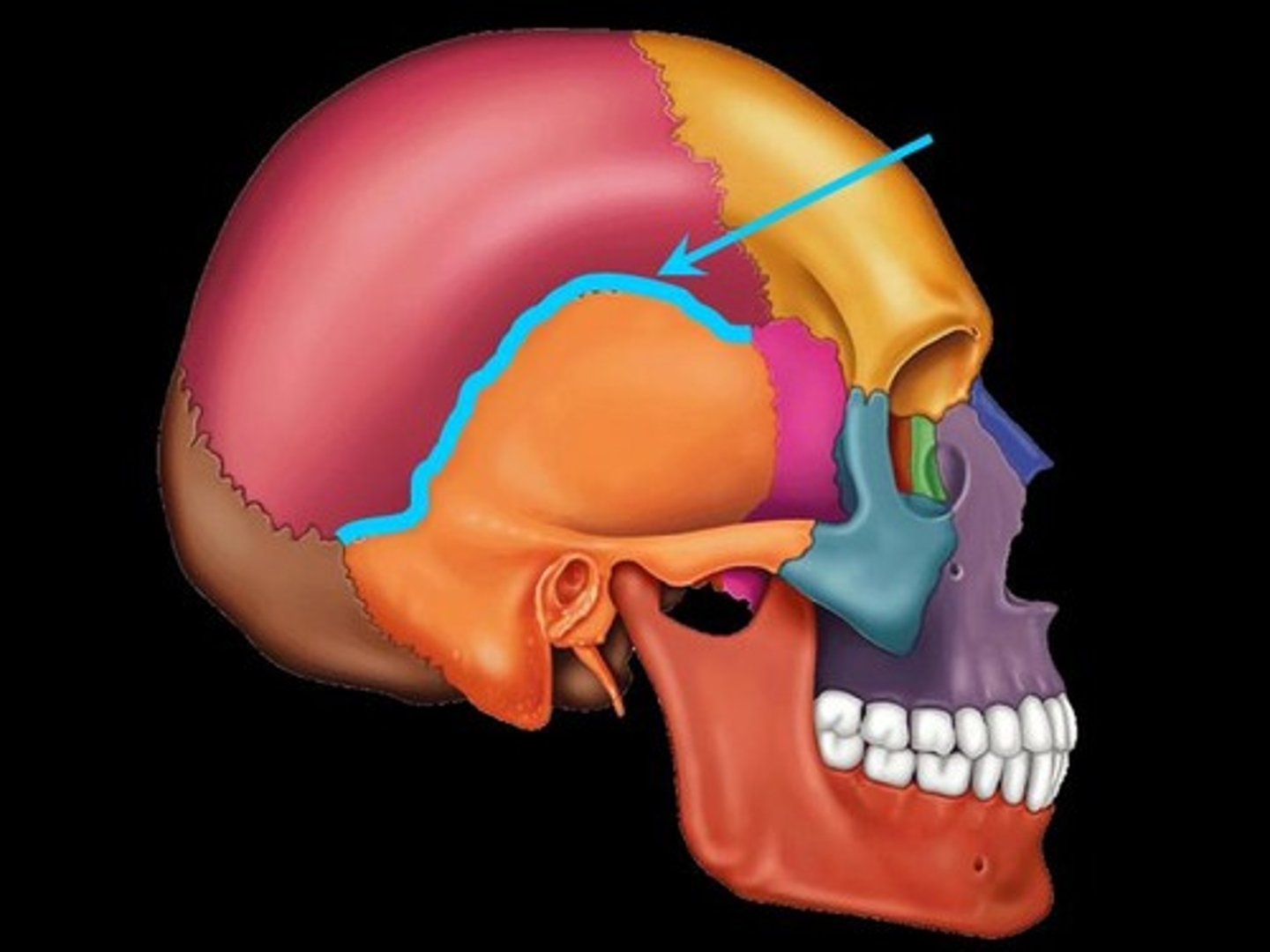
Coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
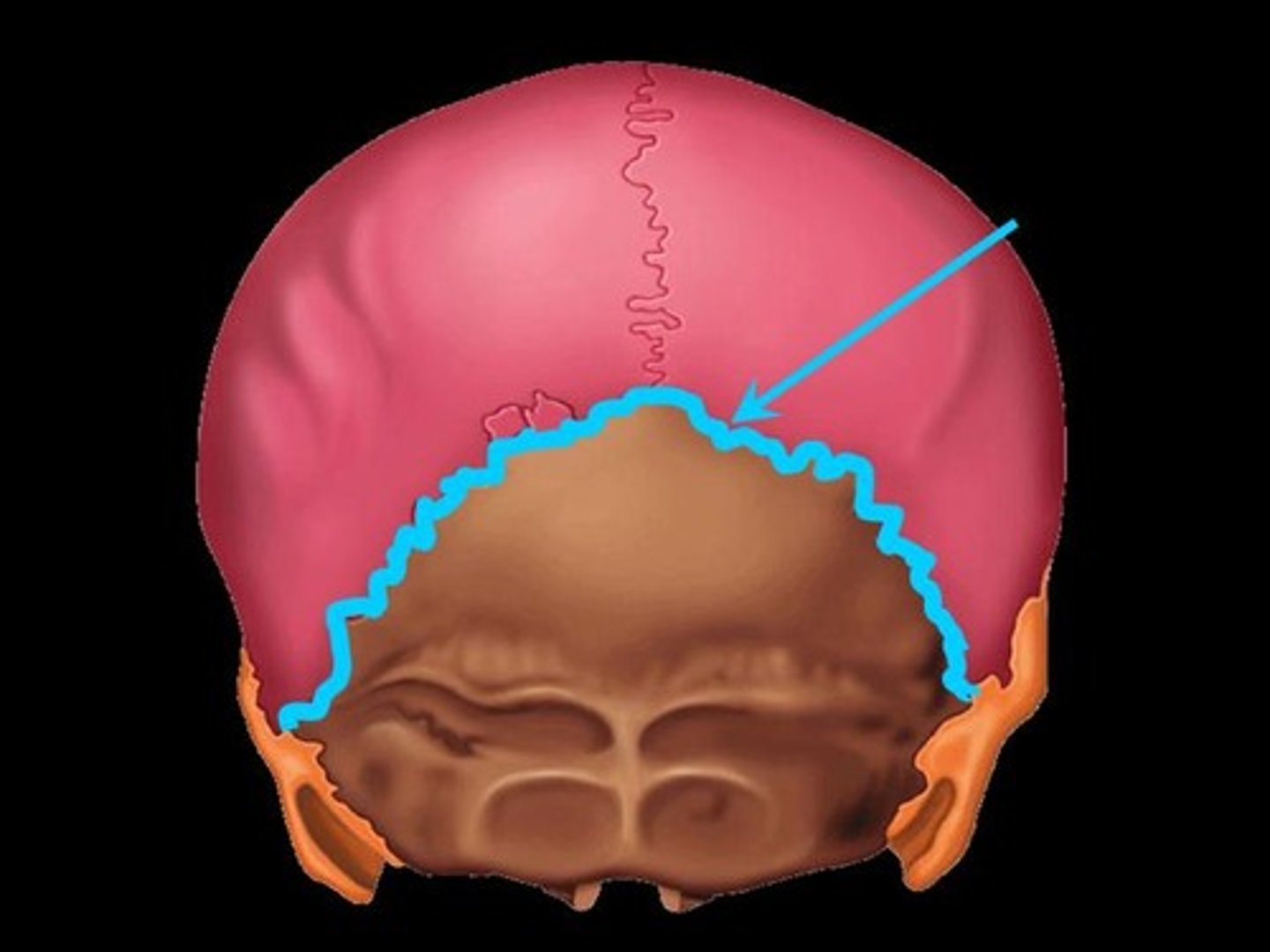
Lambdoidal suture
between occipital and parietal bones
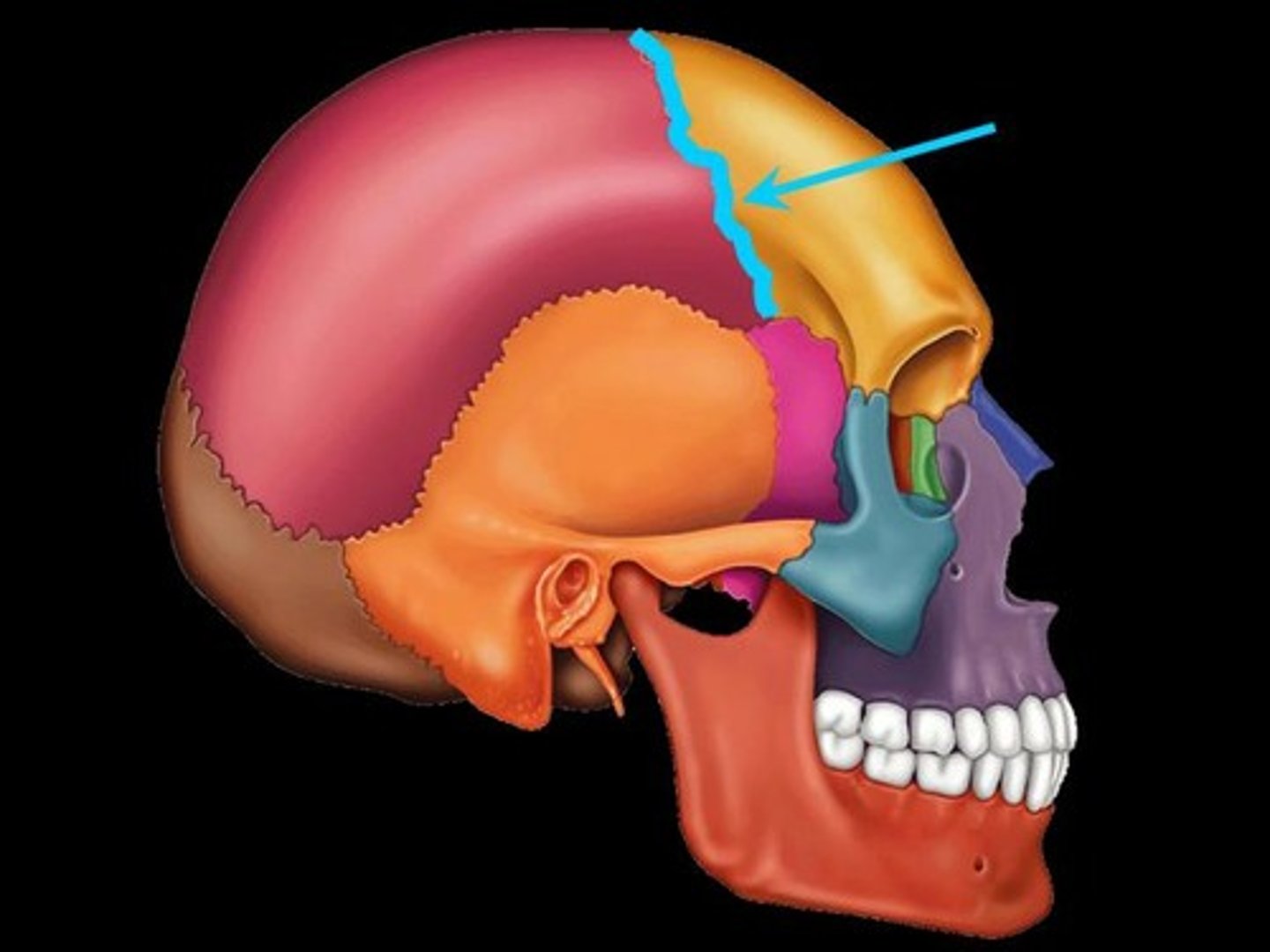
Squamosal suture
between temporal and parietal bones
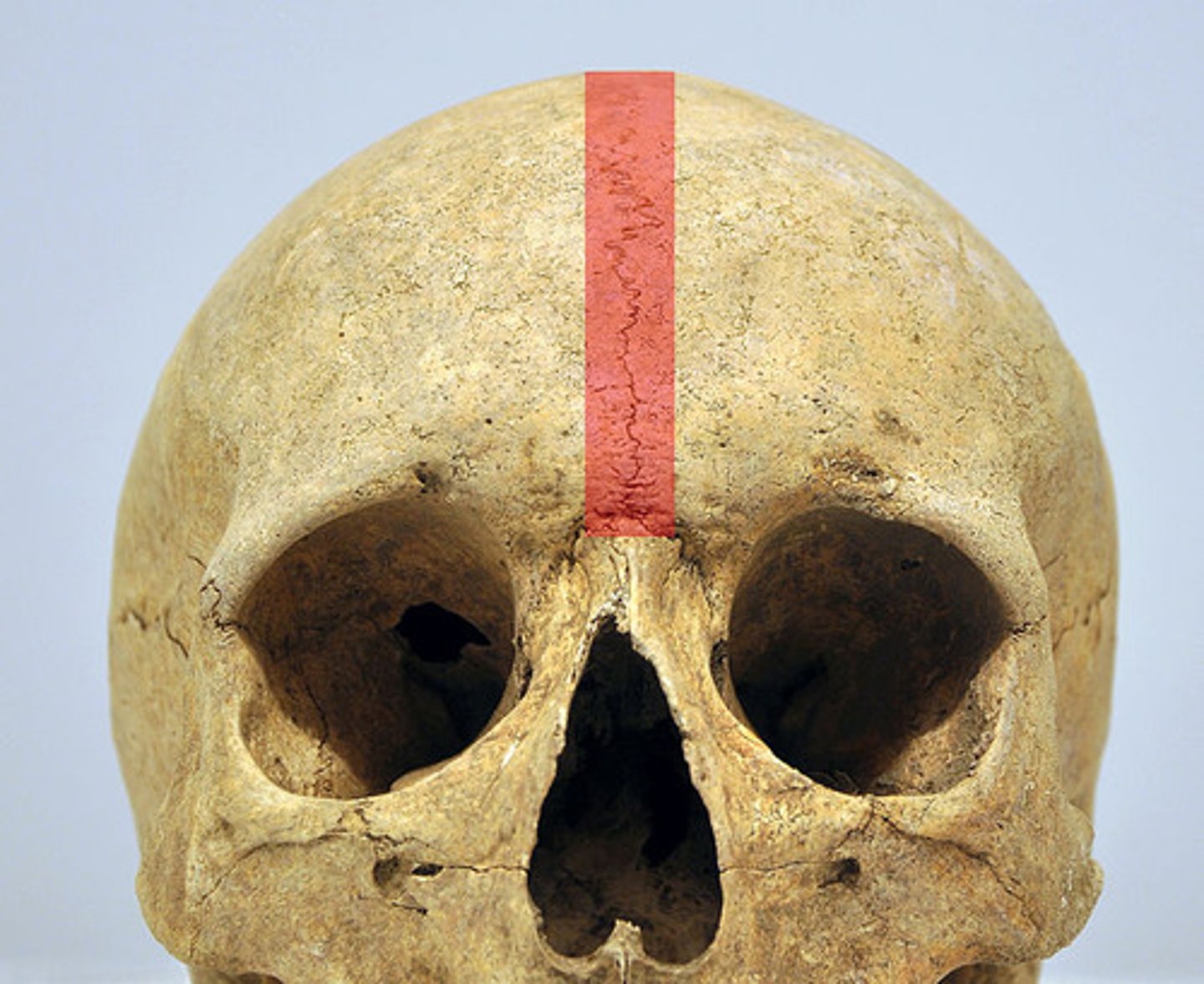
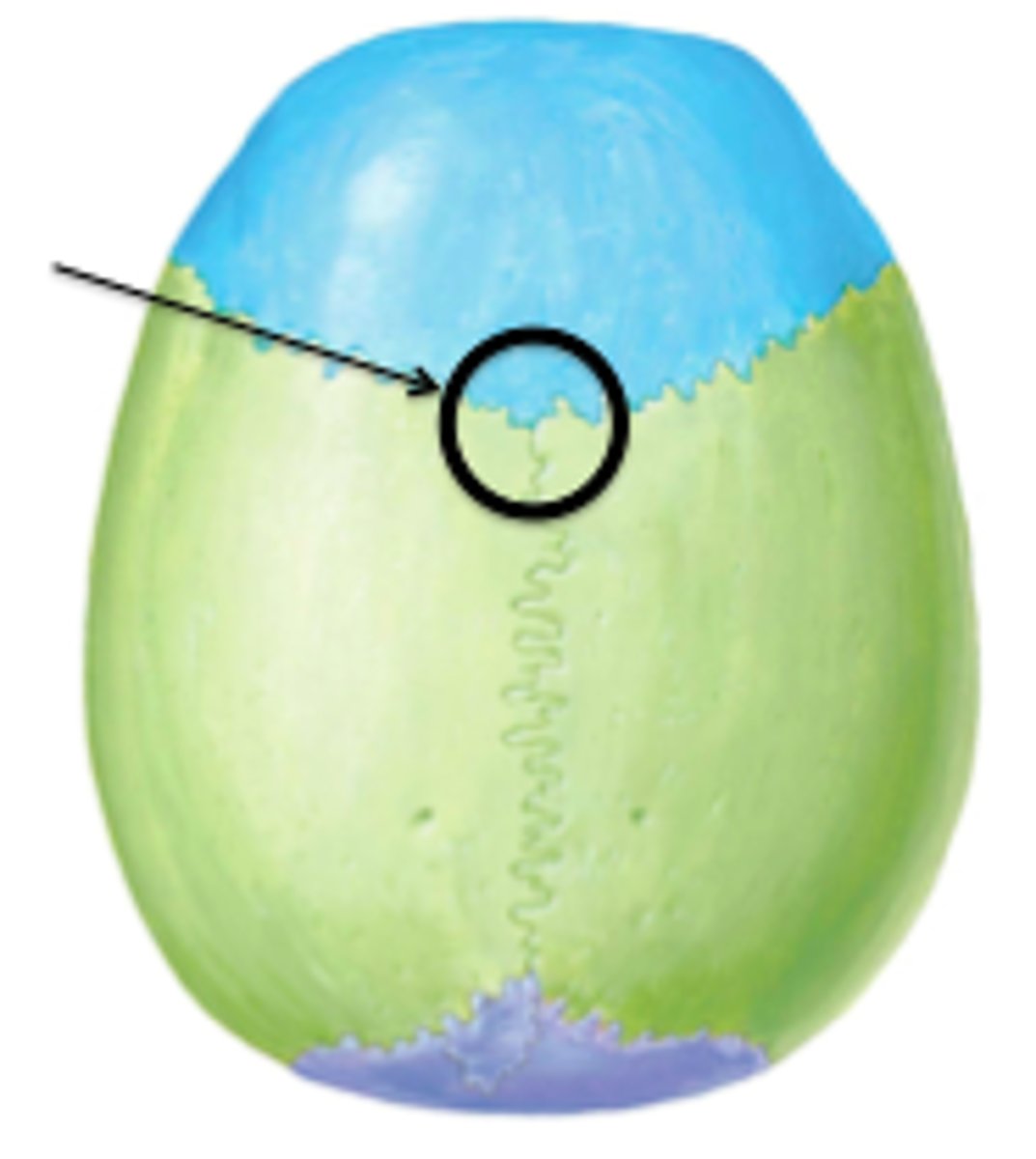
Metopic suture
-Obliterated by 7 to 8 years of age
-Approximately 8% of adults retain metopic trace
-can be mistaken as fracture on x-rays
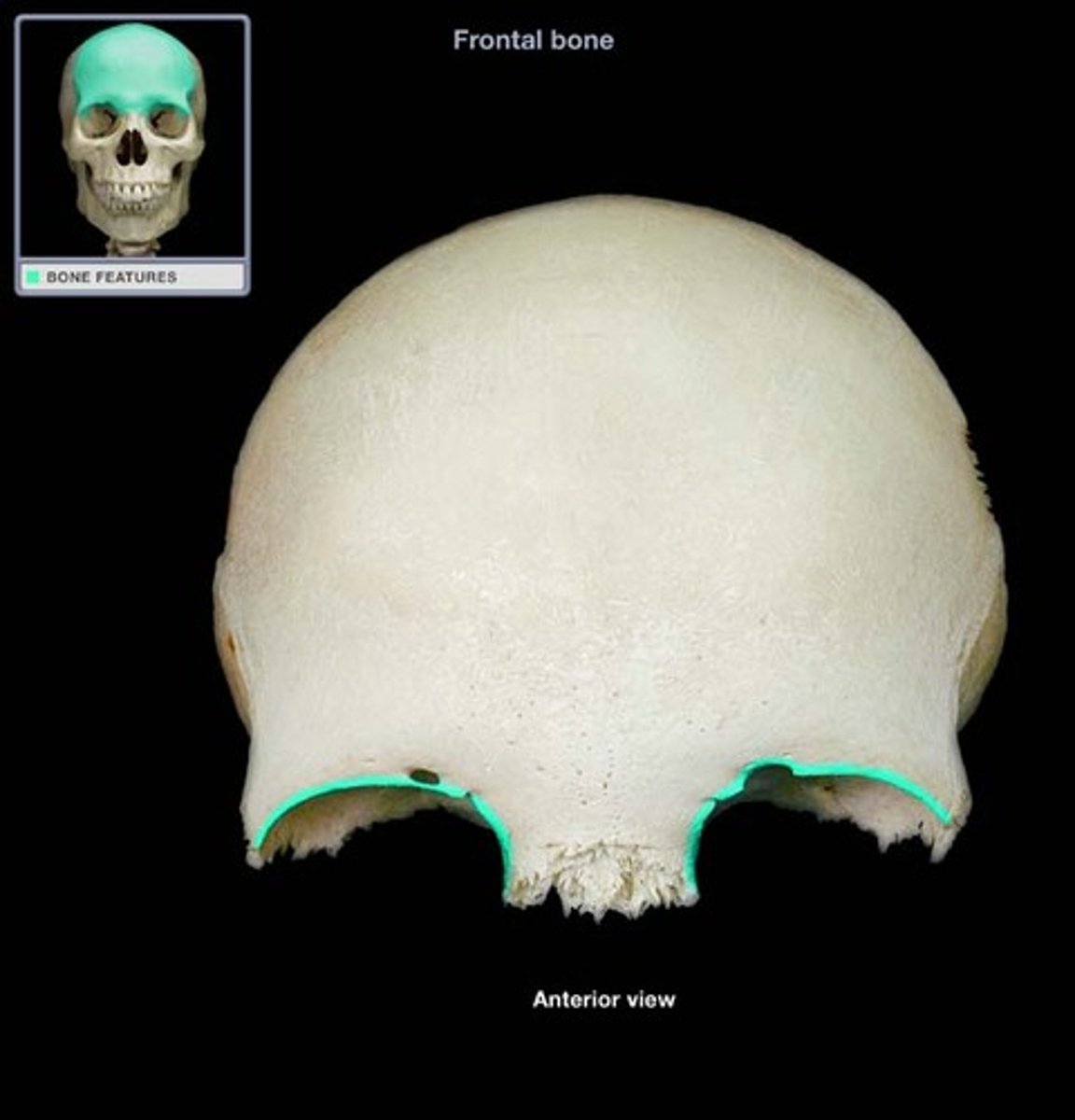
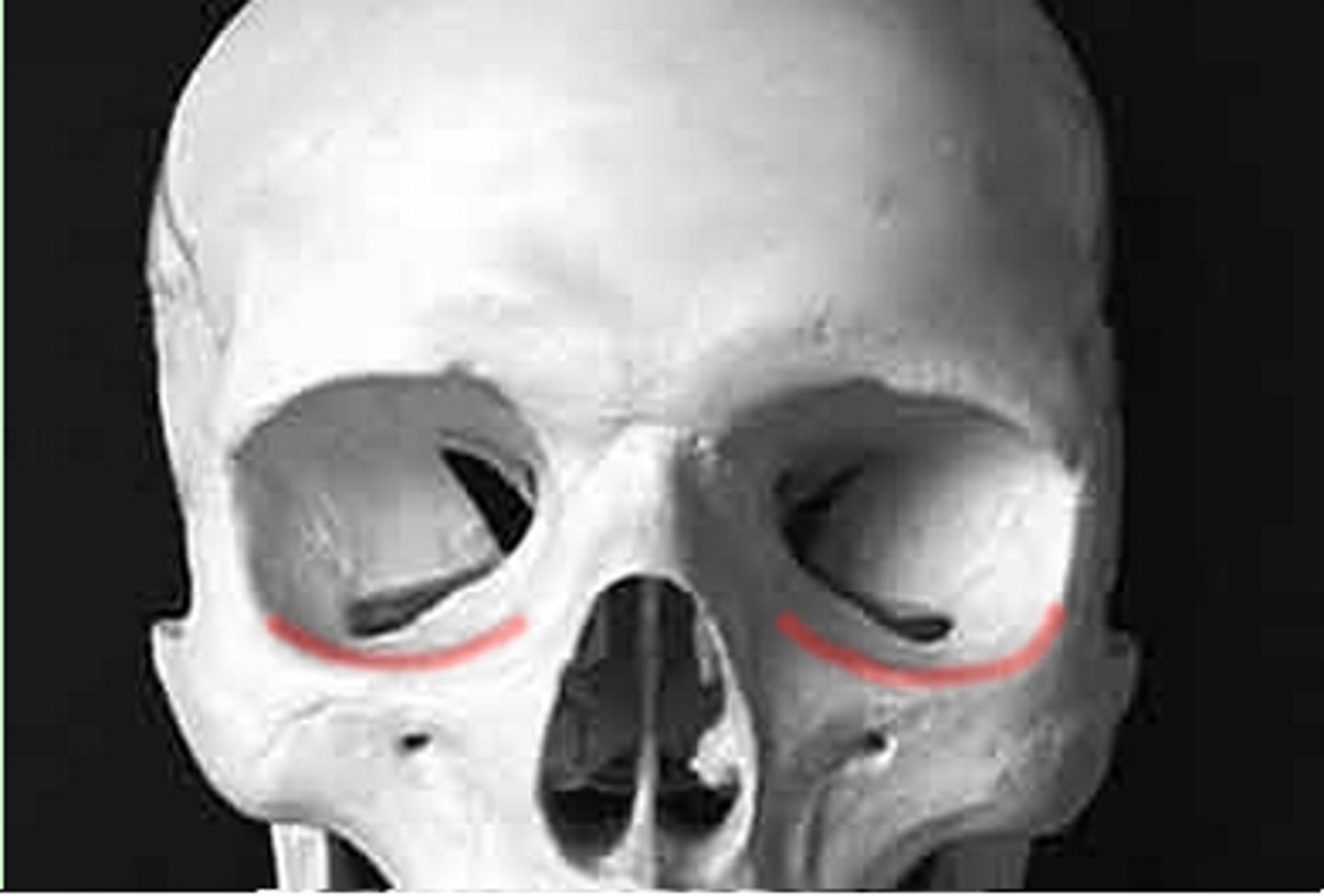
Supraorbital margin (frontal)
rim of bone that outlines upper margins of the orbits
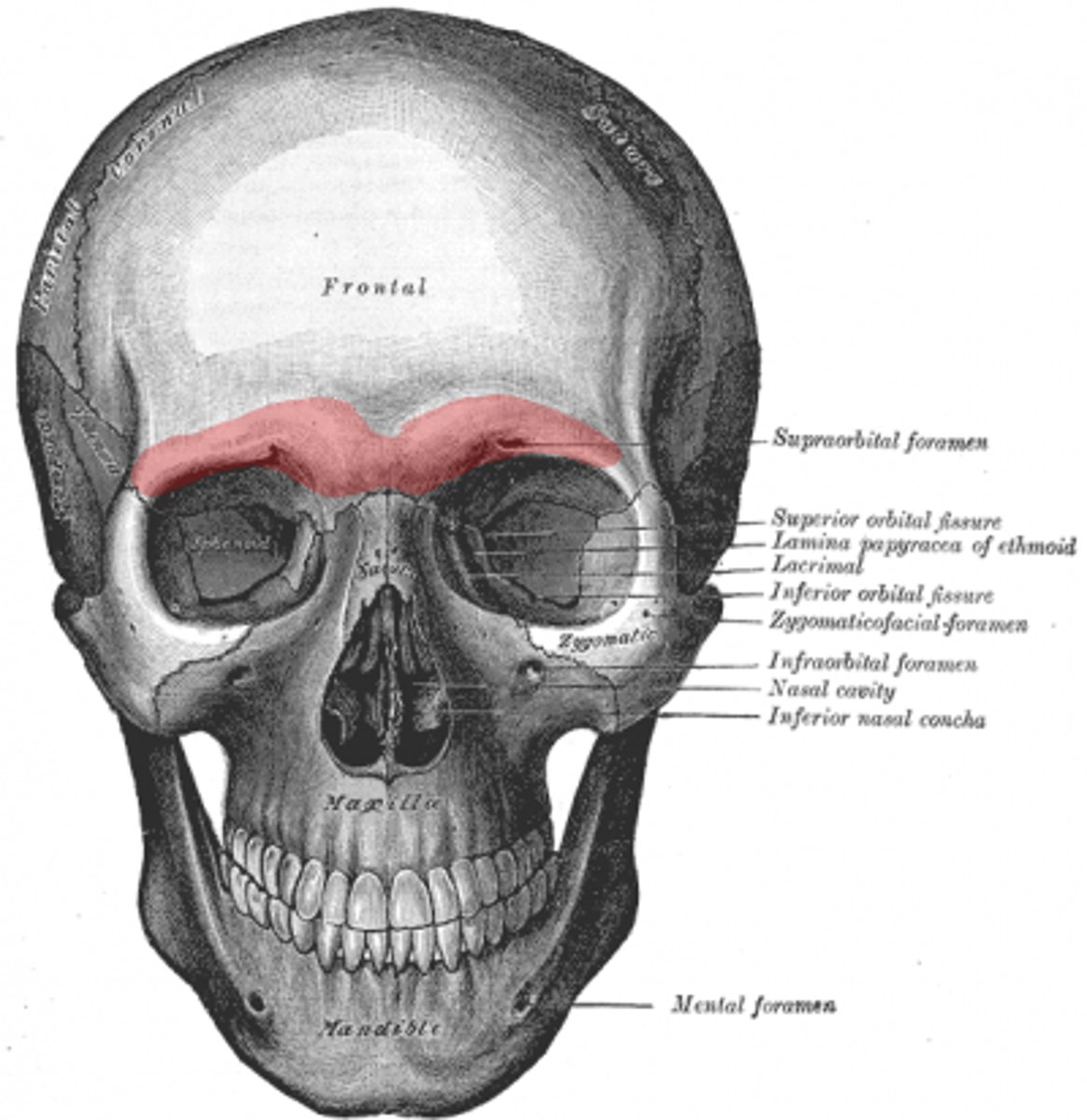
Supraorbital tori (frontal)
arch of bone above the orbits
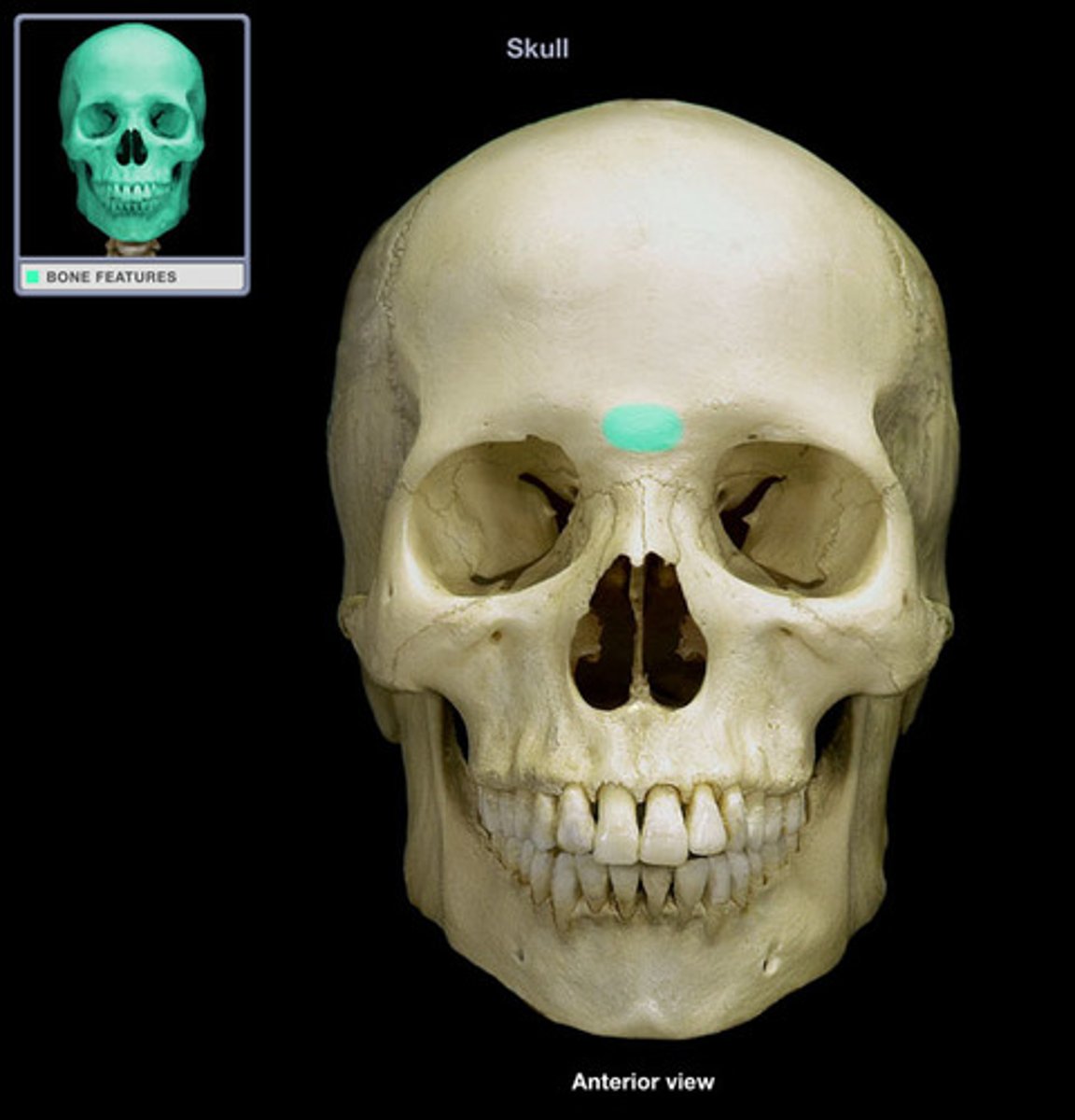
Glabella (frontal)
Smooth area between the eyes
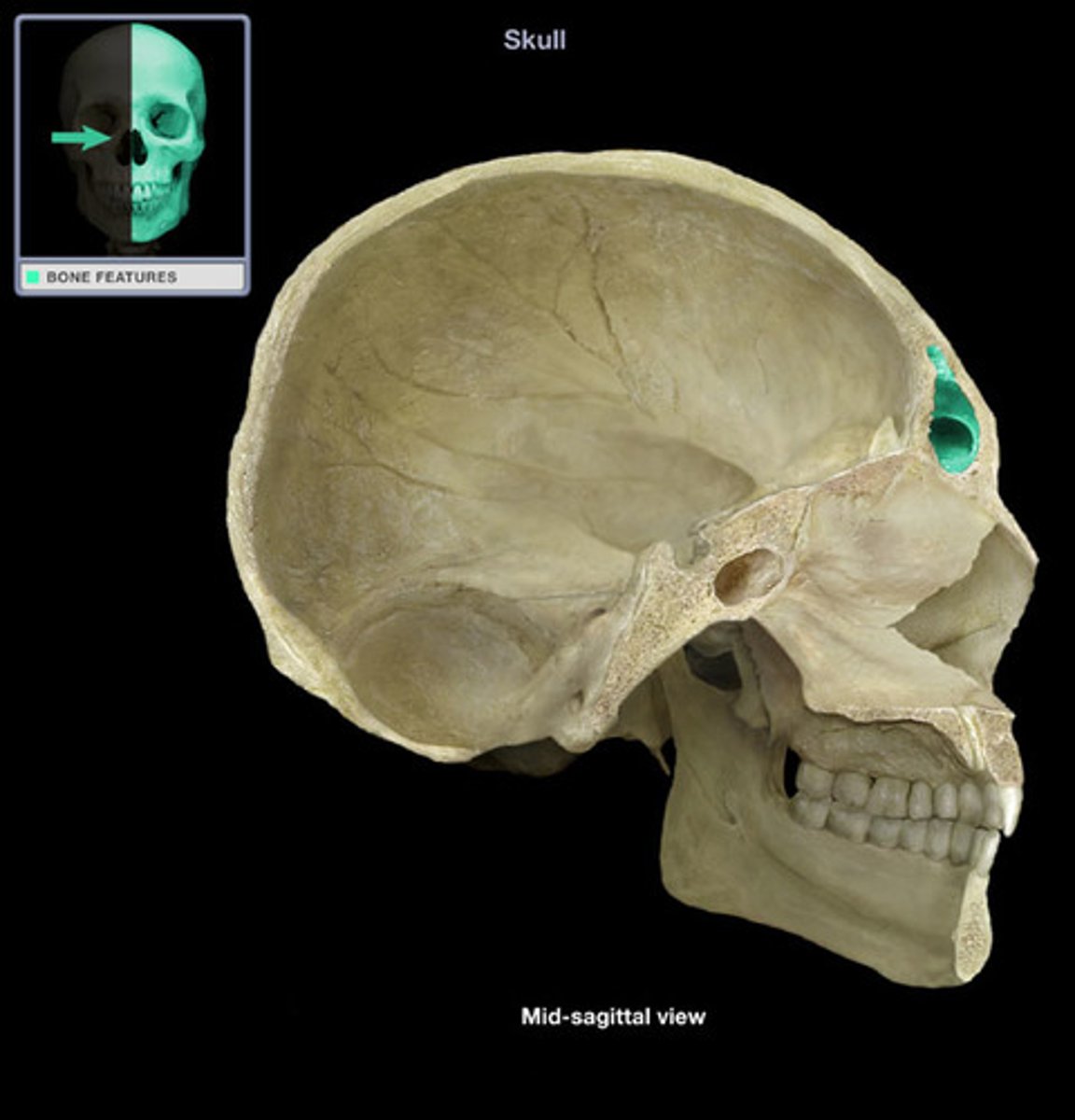
Frontal sinus
cavity within the frontal bone that allows for vocal resonance
Bregma (P)
Intersection of Coronal & Sagittal Sutures

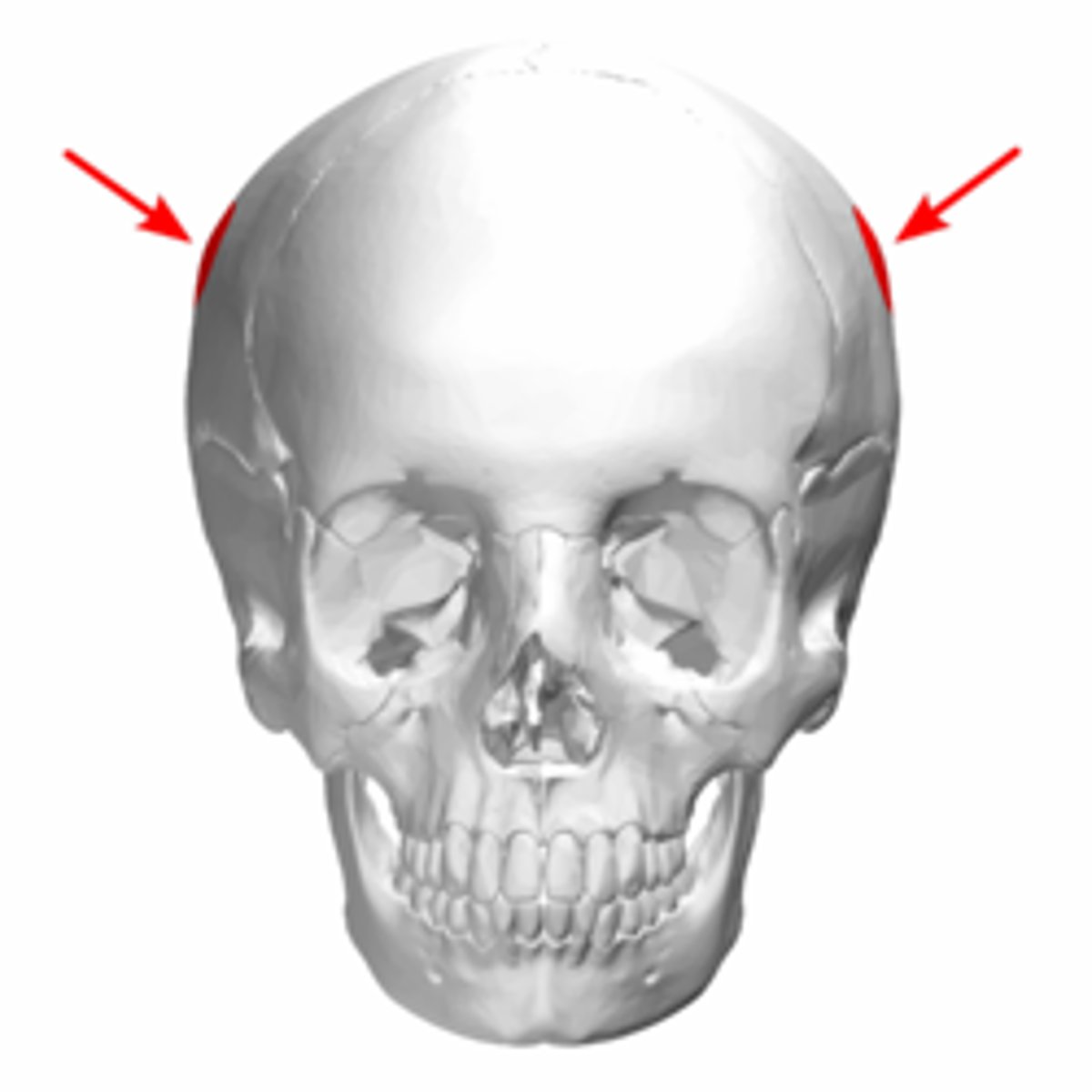
Parietal eminence
lateral "bulges" used for sex estimation
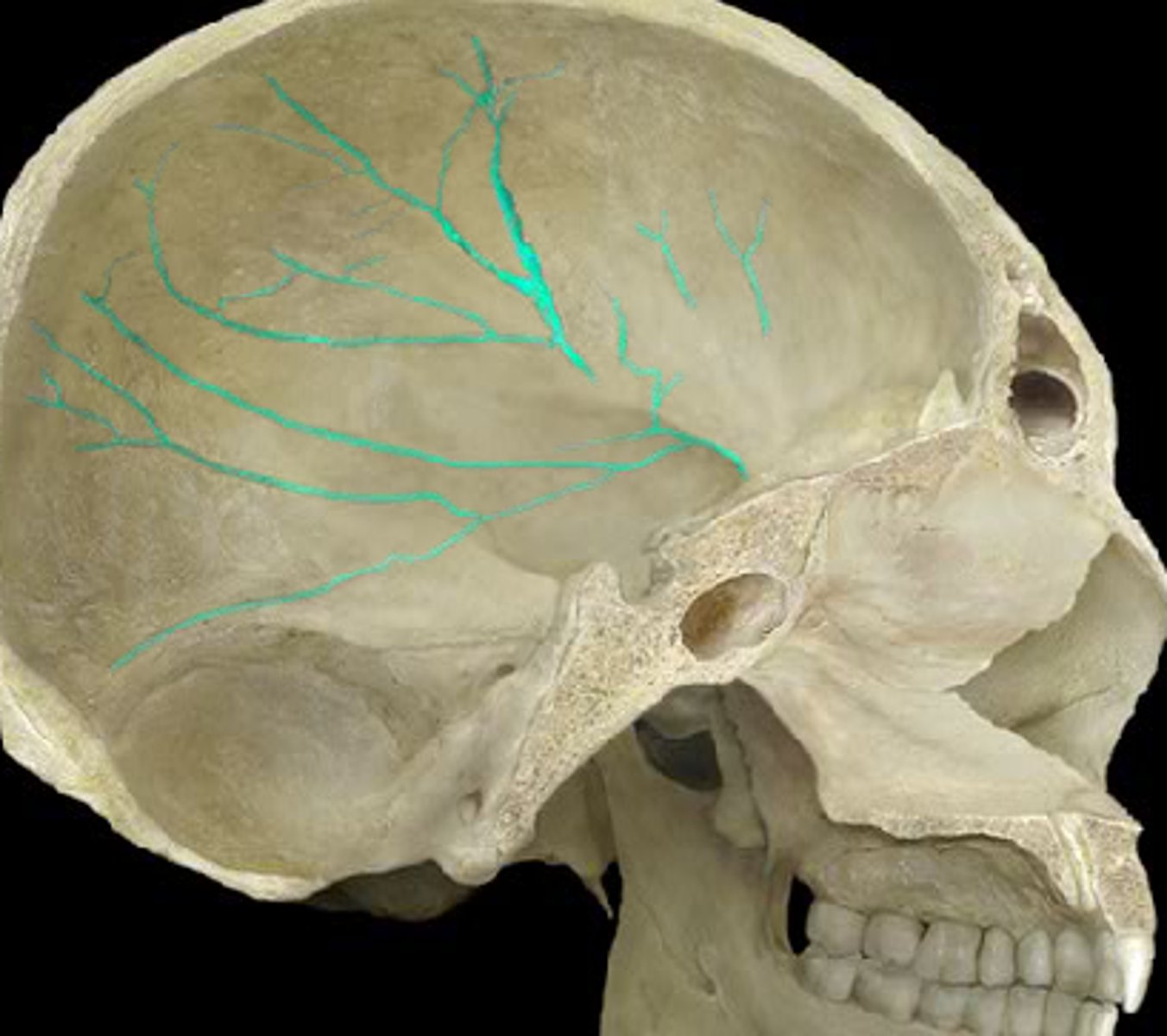
Meningeal grooves (P)
impressions of middle meningeal artery, useful for siding
External auditory meatus (T)
ear canal
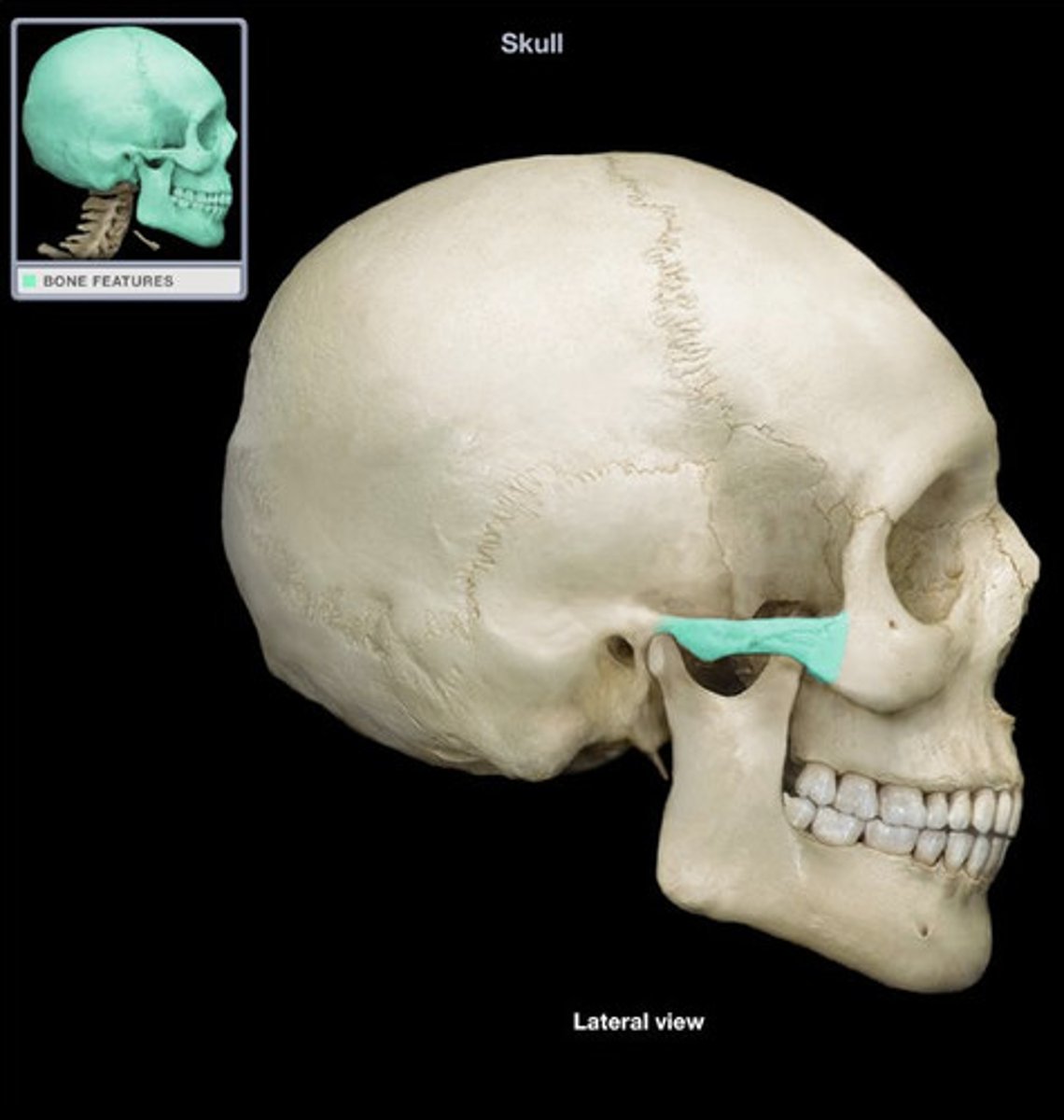
Zygomatic process (T)
a projection of the temporal bone that forms part of the zygoma
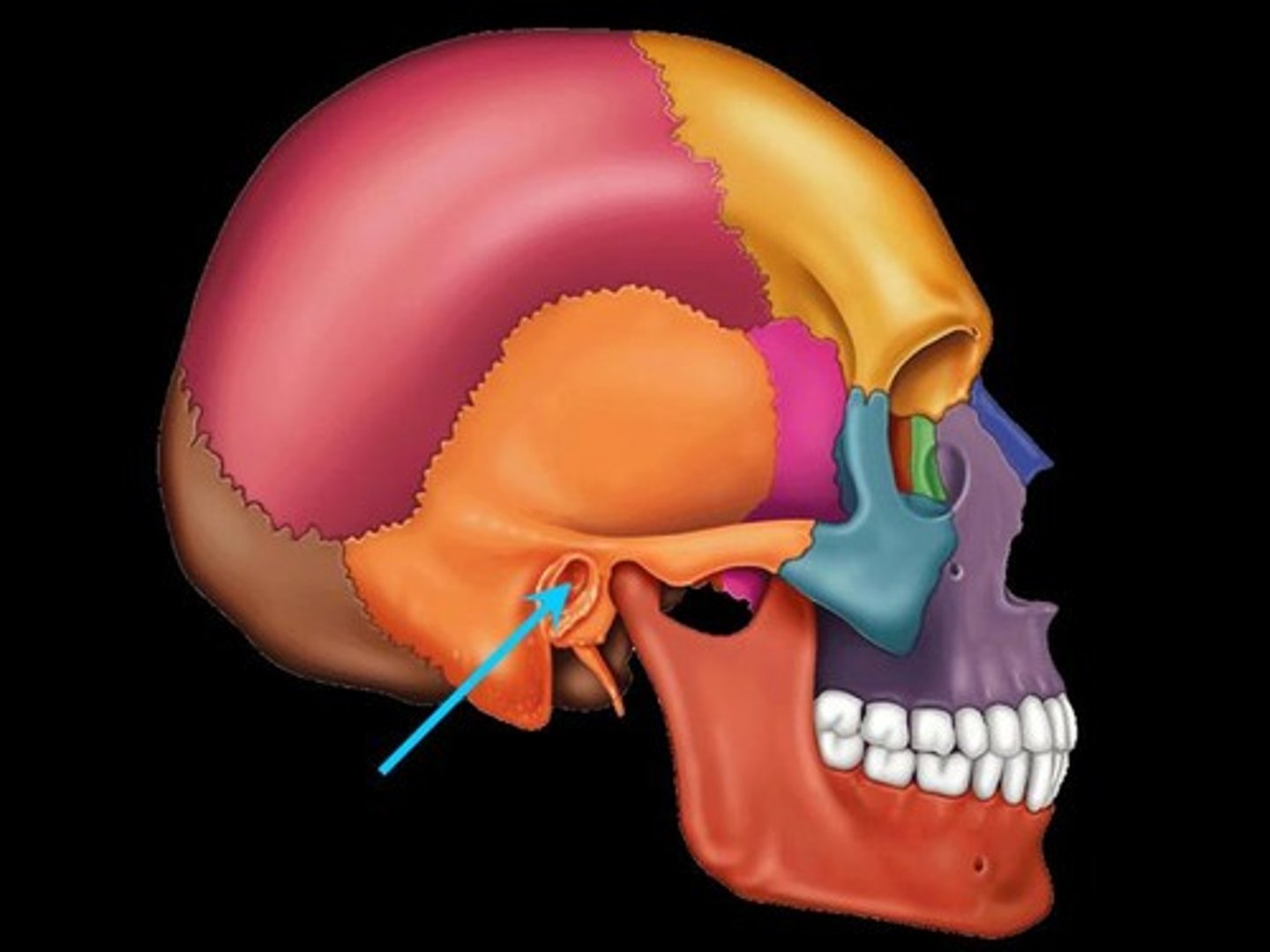
Mandibular fossa (T)
the depression in the temporal bone into which the condyle of the mandible fits
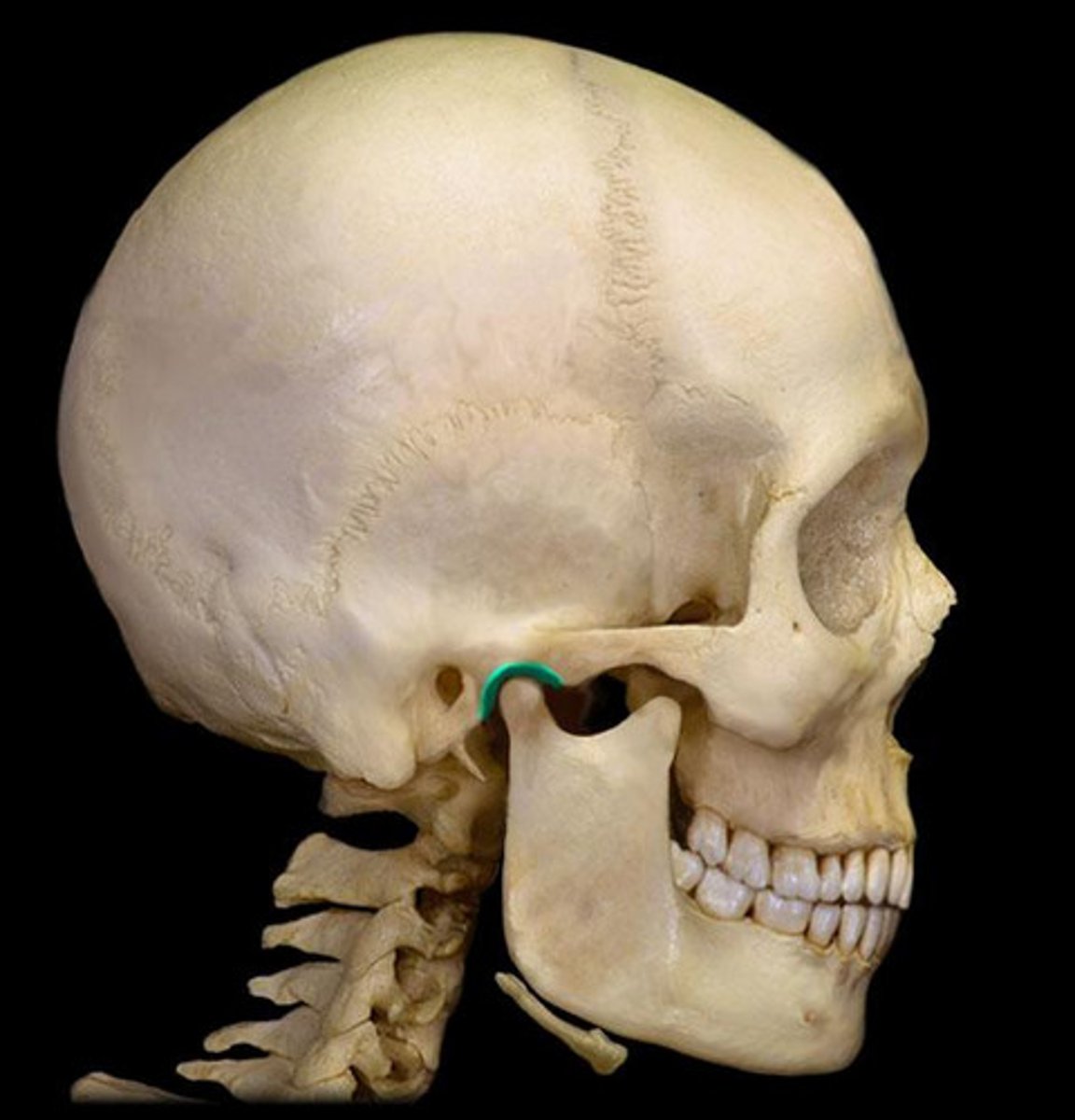
Mastoid process (T)
round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear
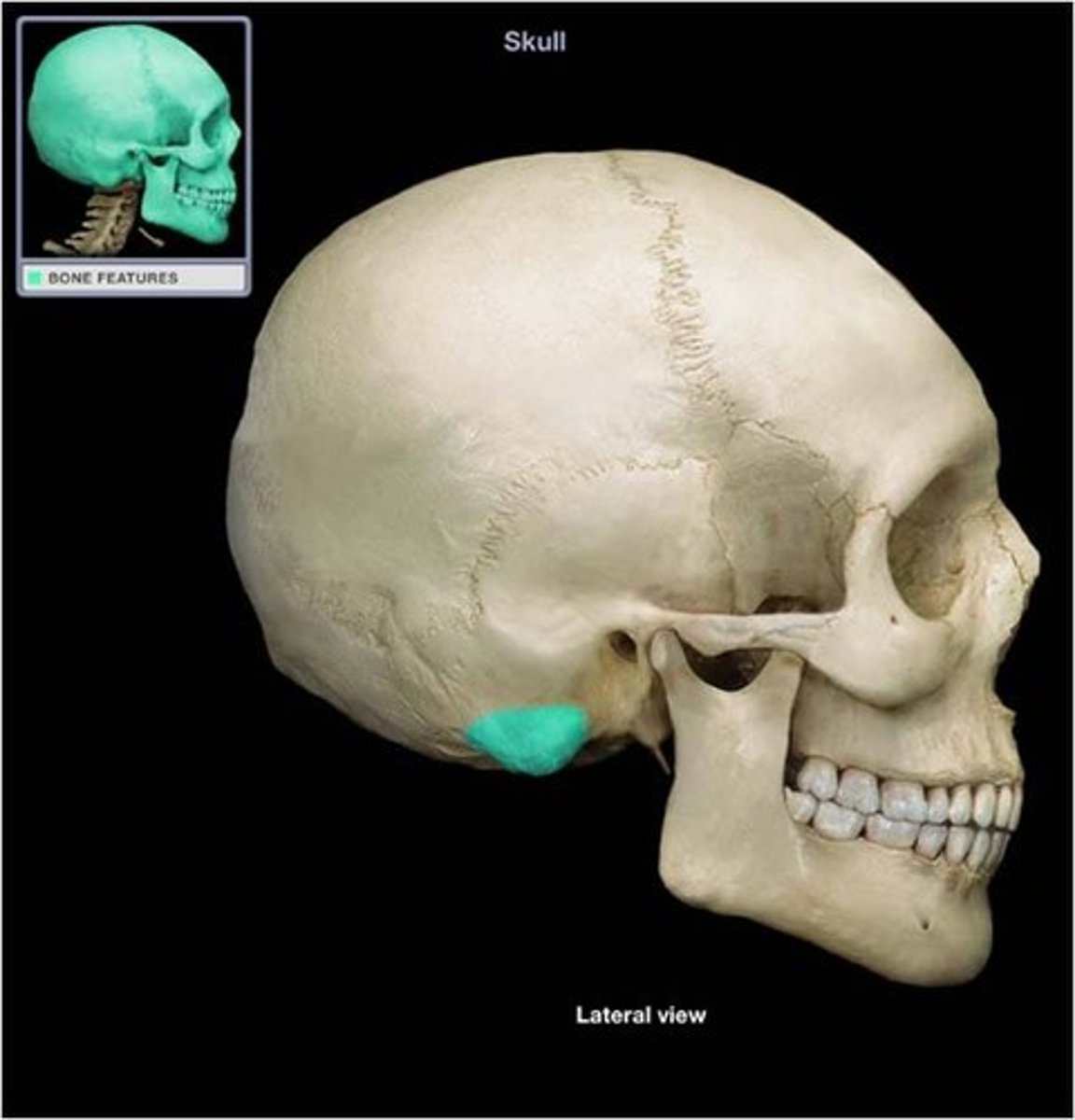
Squamous portion
flat; above ear
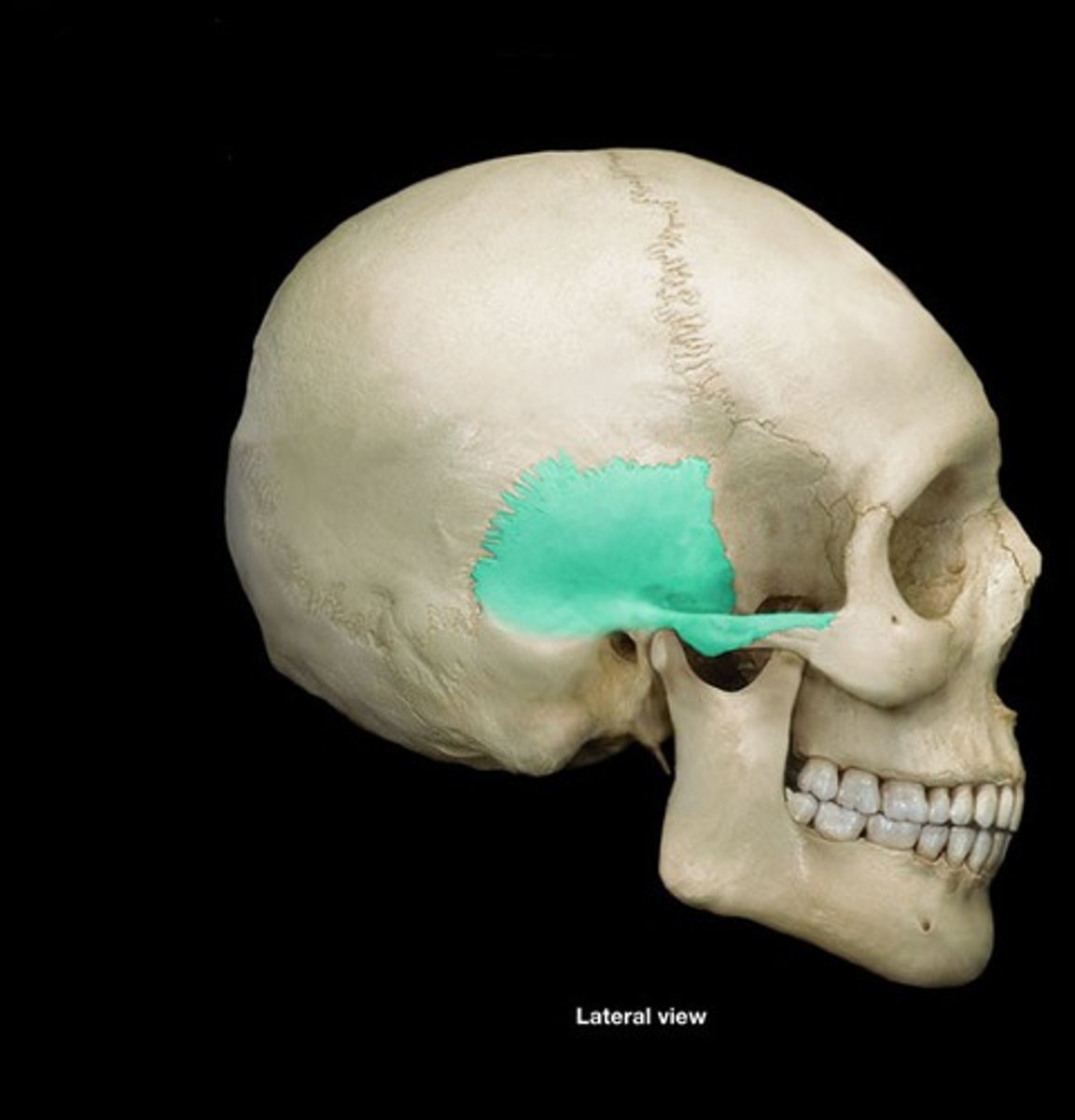
Petrous portion
raised portion on top section of skull towards bottom, contains middle ear processes
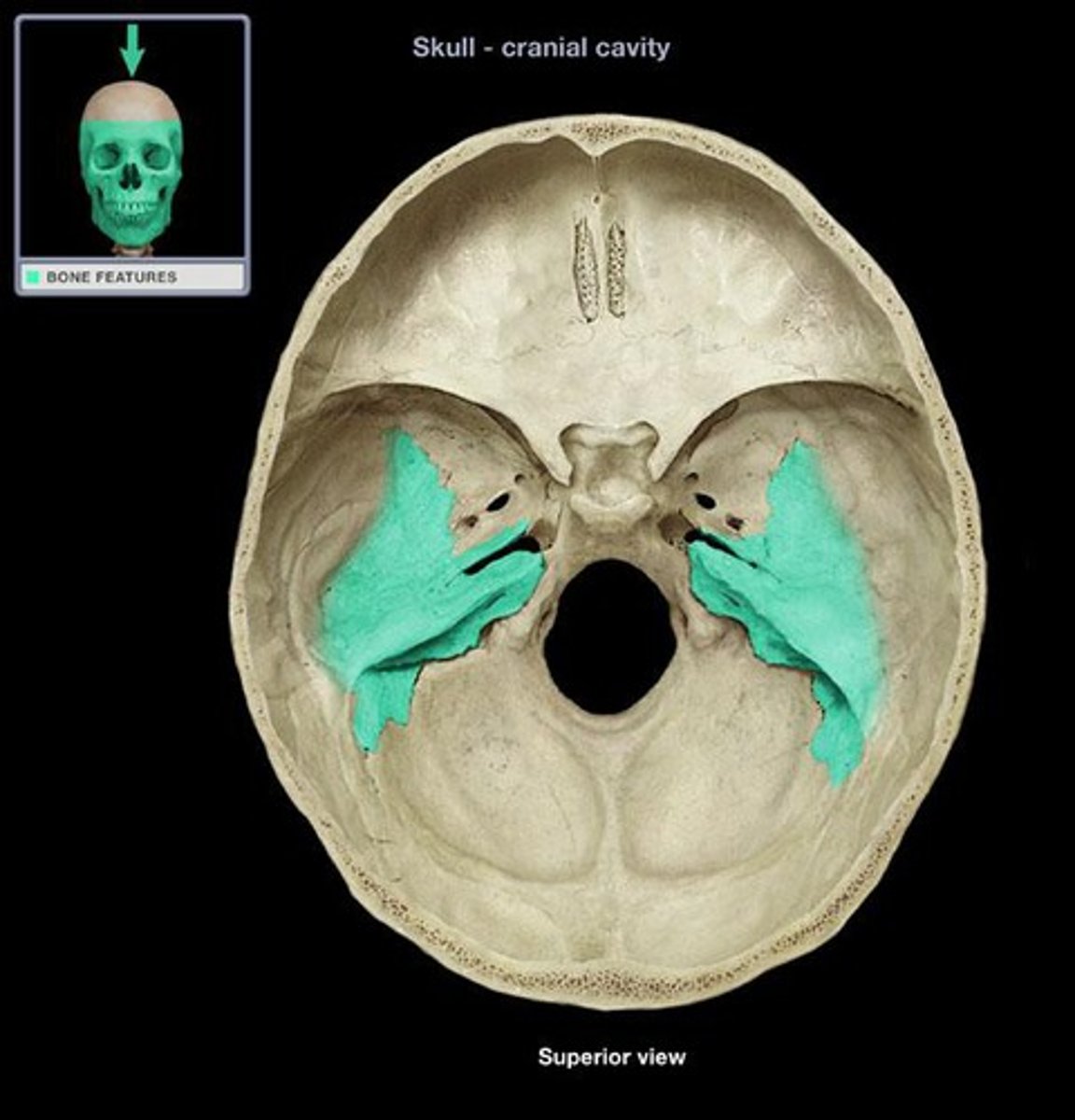
Tympanic cavity
air-filled space containing auditory ossicles
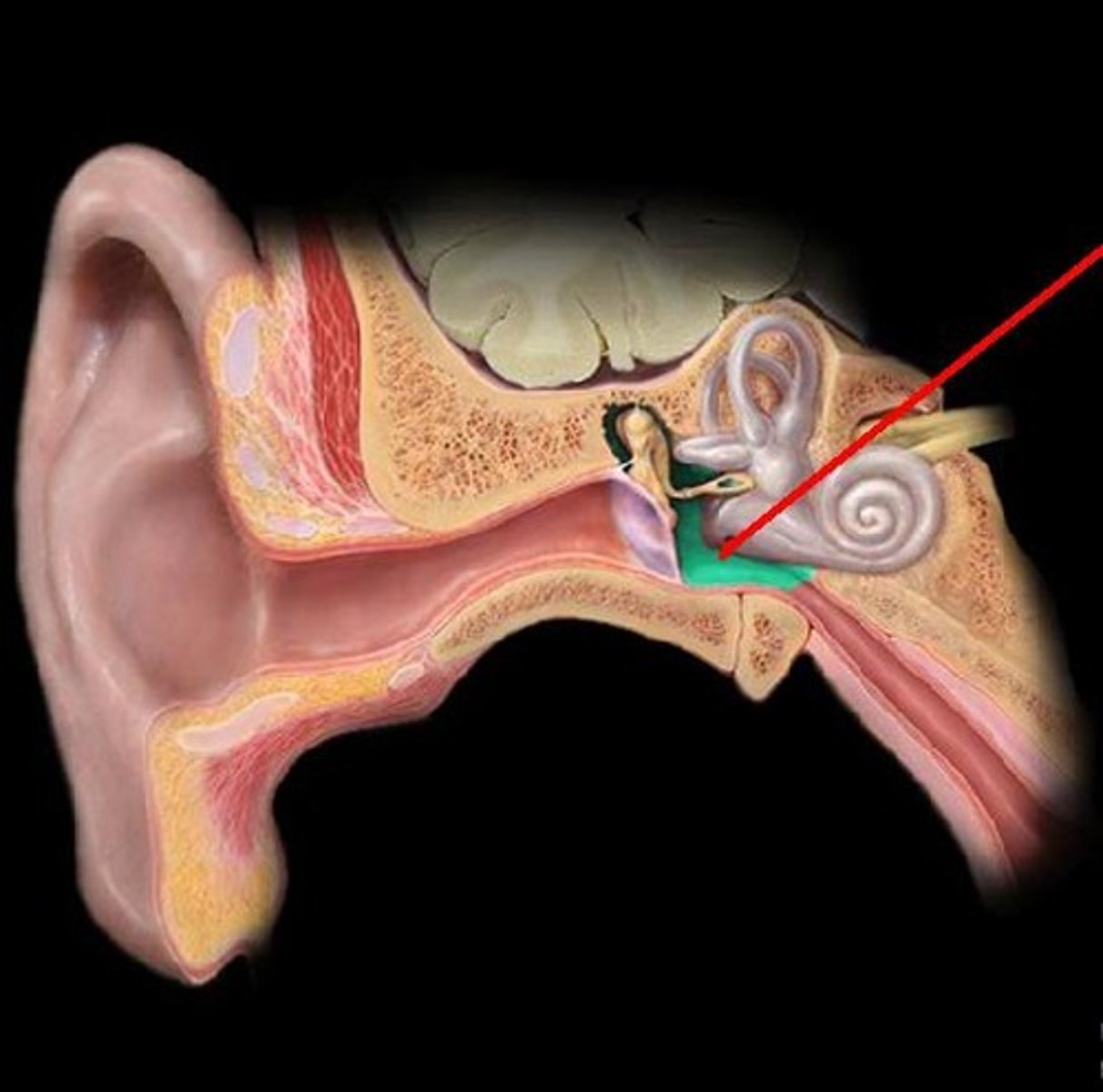
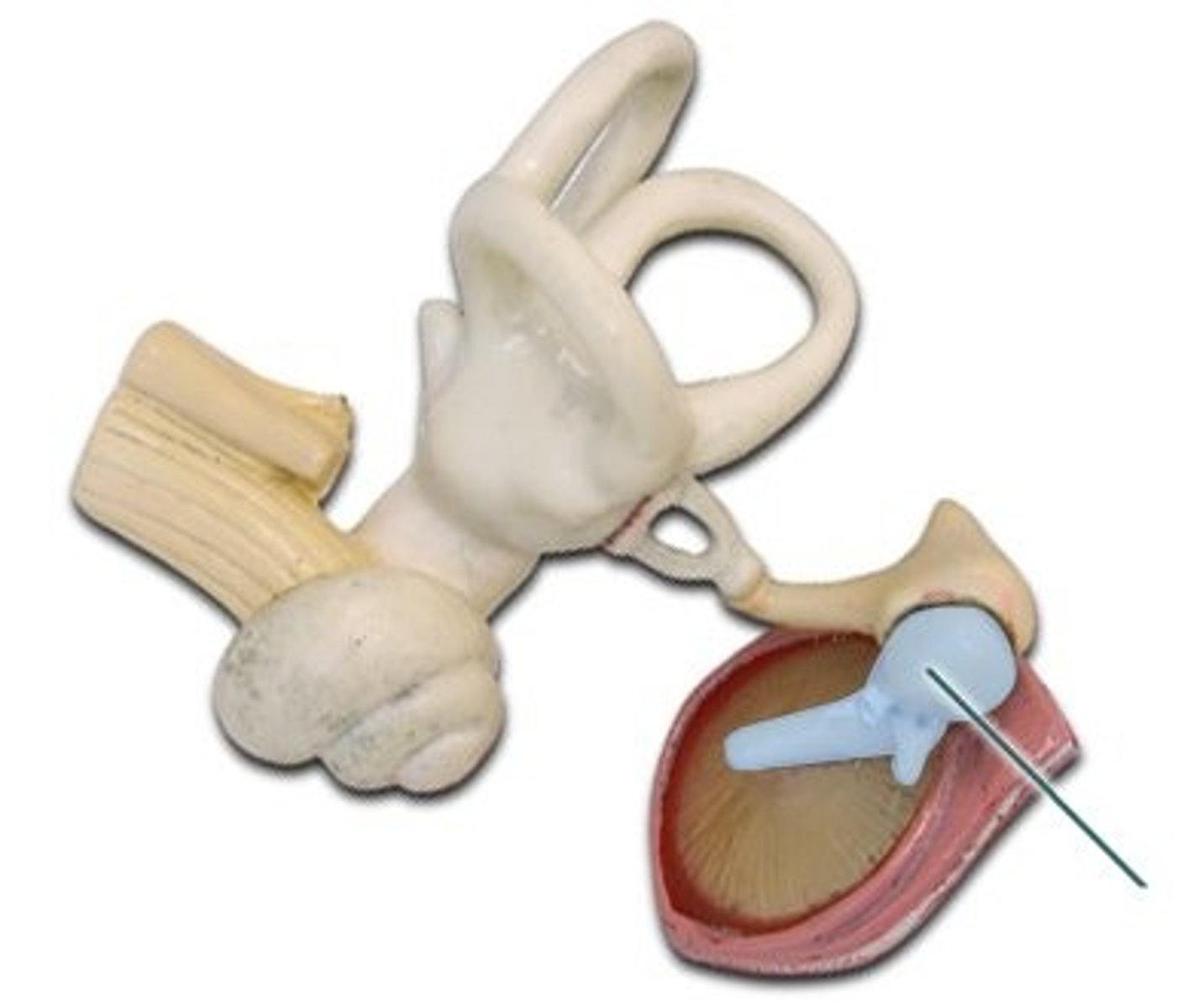
Malleus
hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
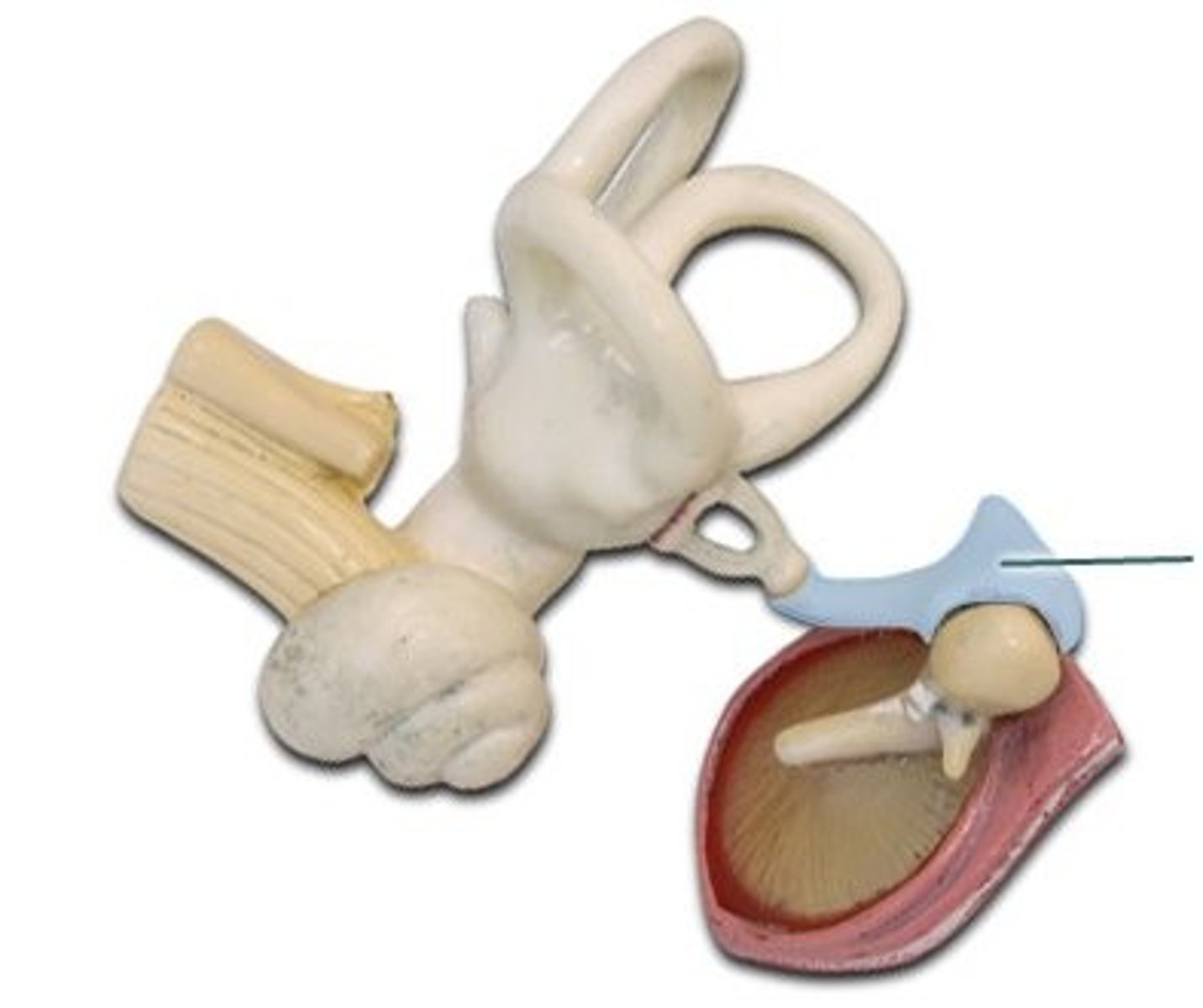
Incus
anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
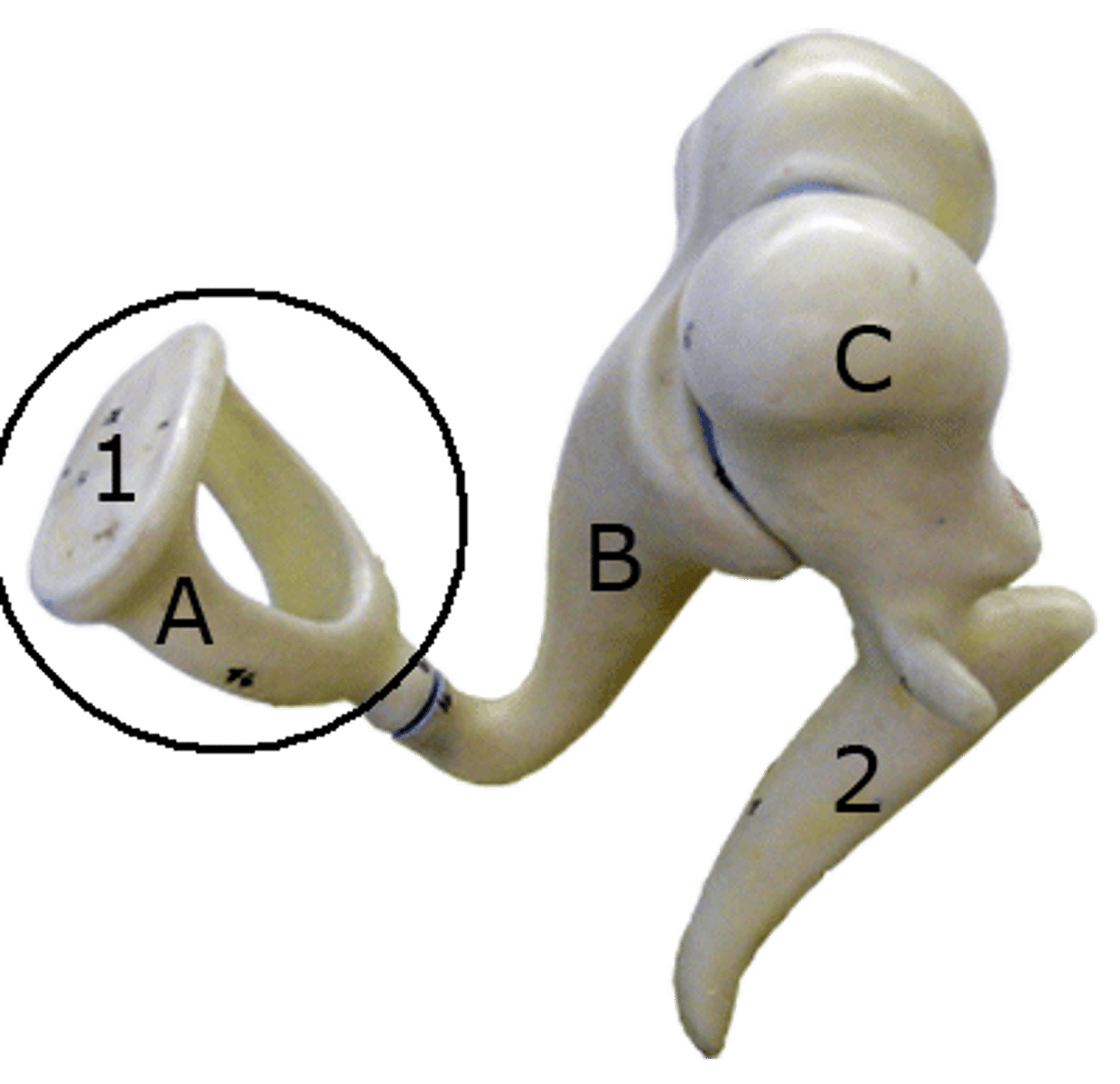
Stapes
stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
External occipital protuberance
bump on back of head
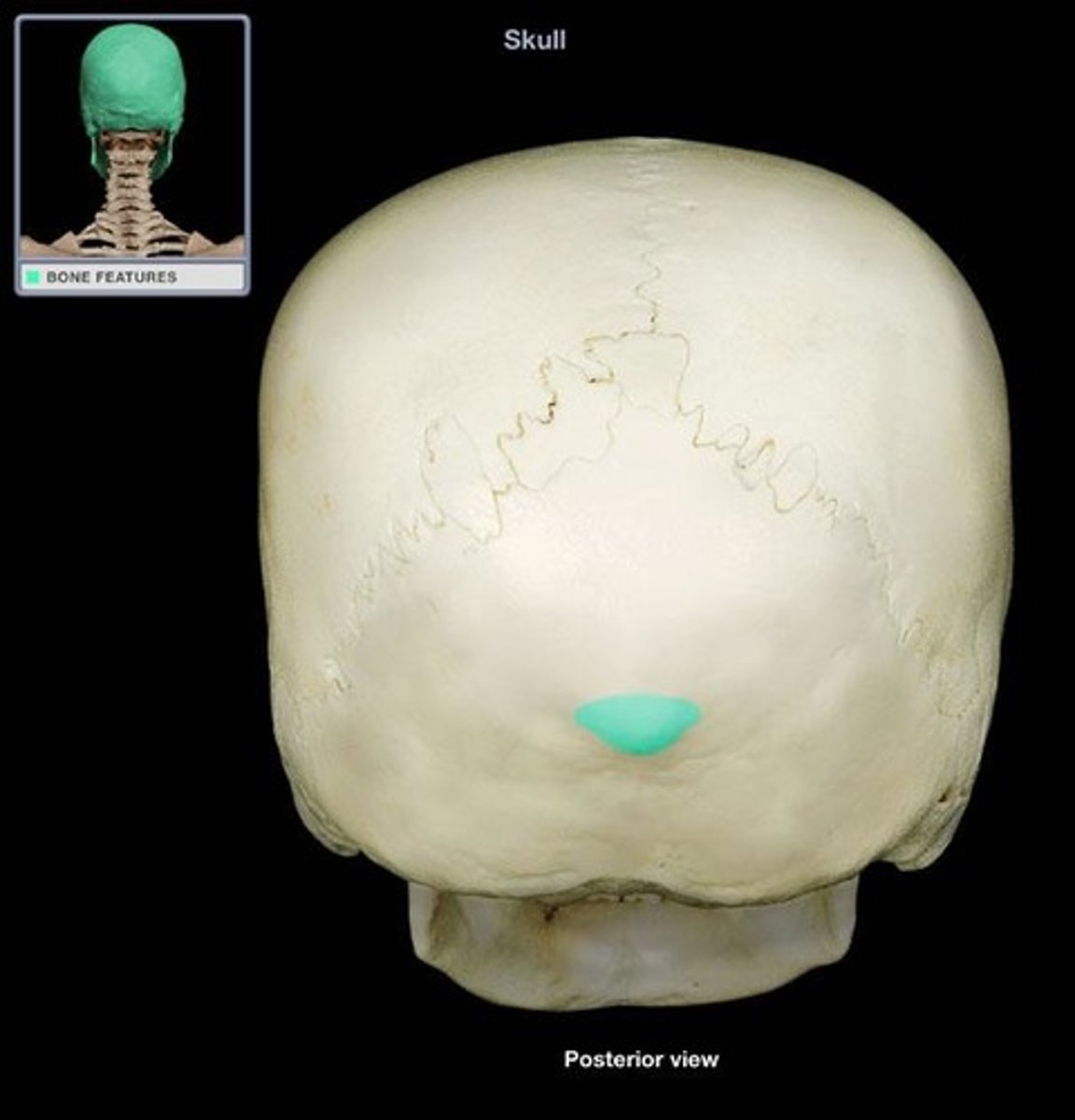
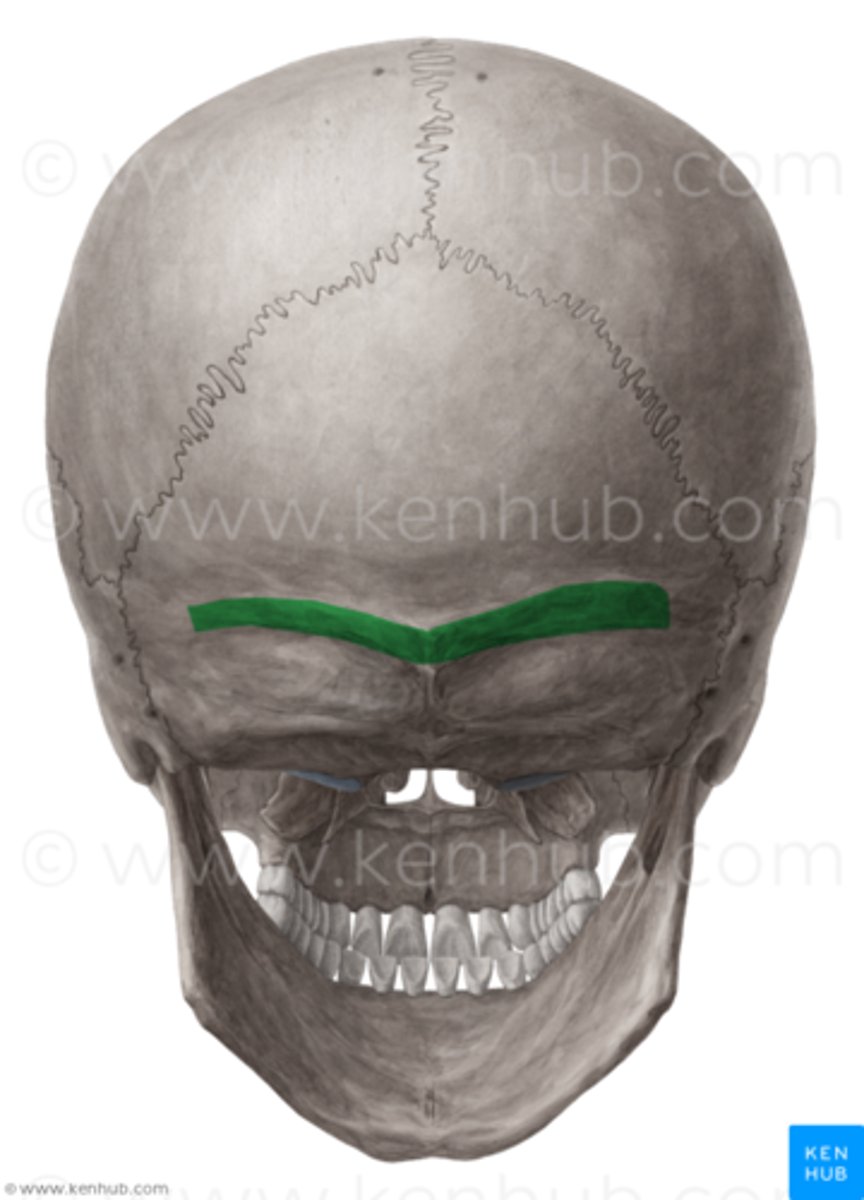
Nuchal lines (O)
neck muscle attachment points
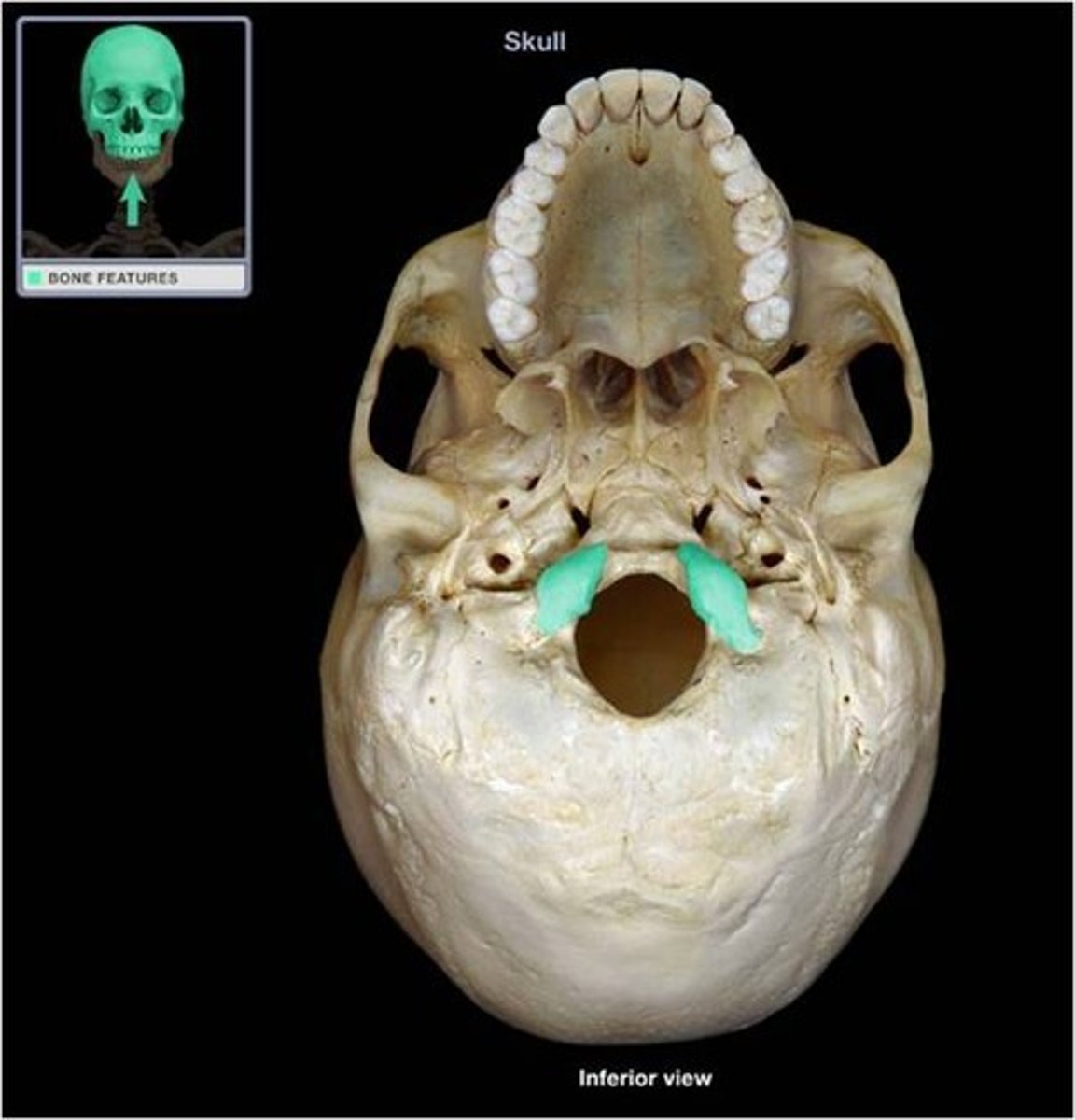
Occipital condyles
articulate with first cervical vertebra
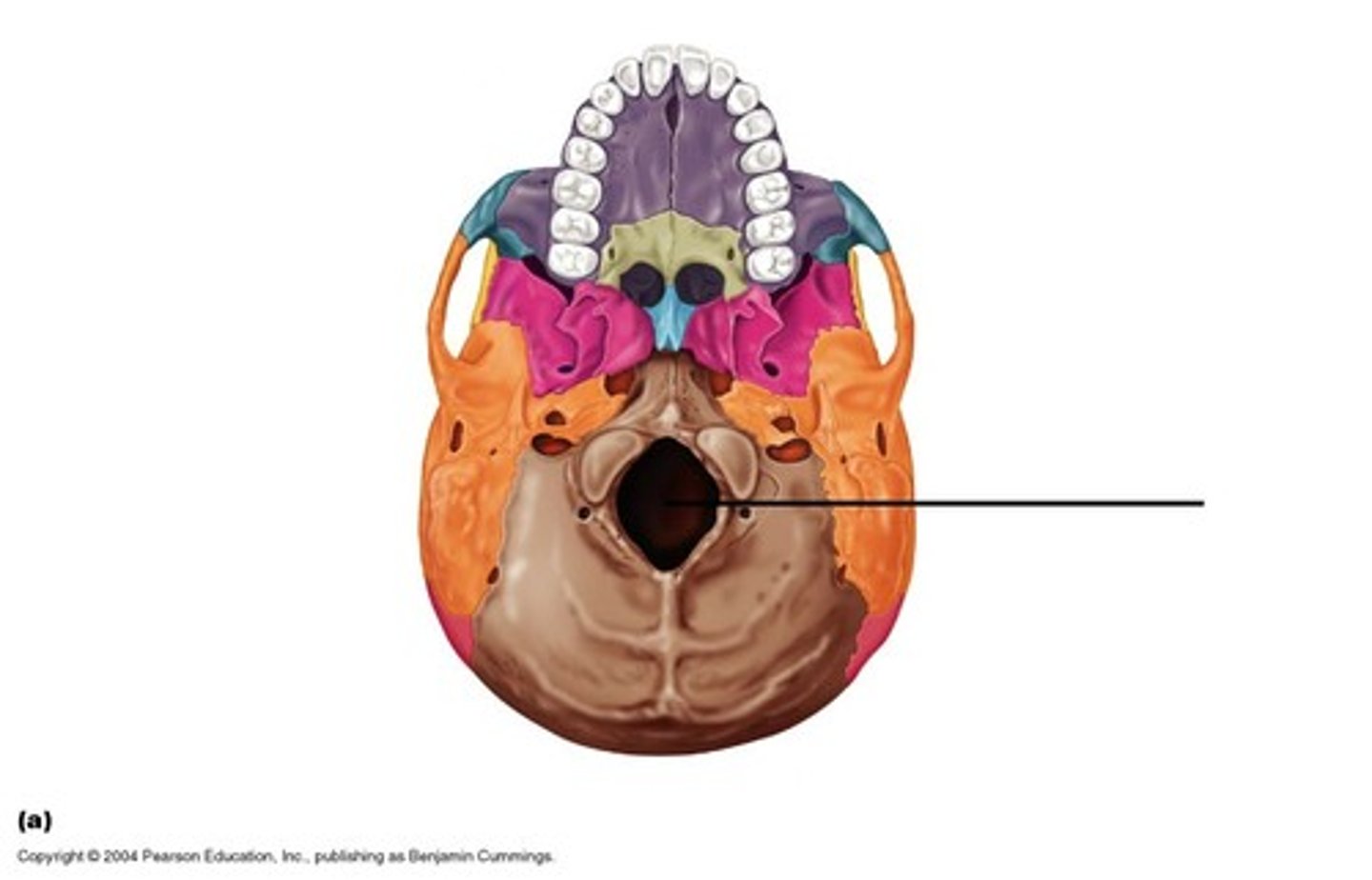
Foramen magnum (O)
the hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes.
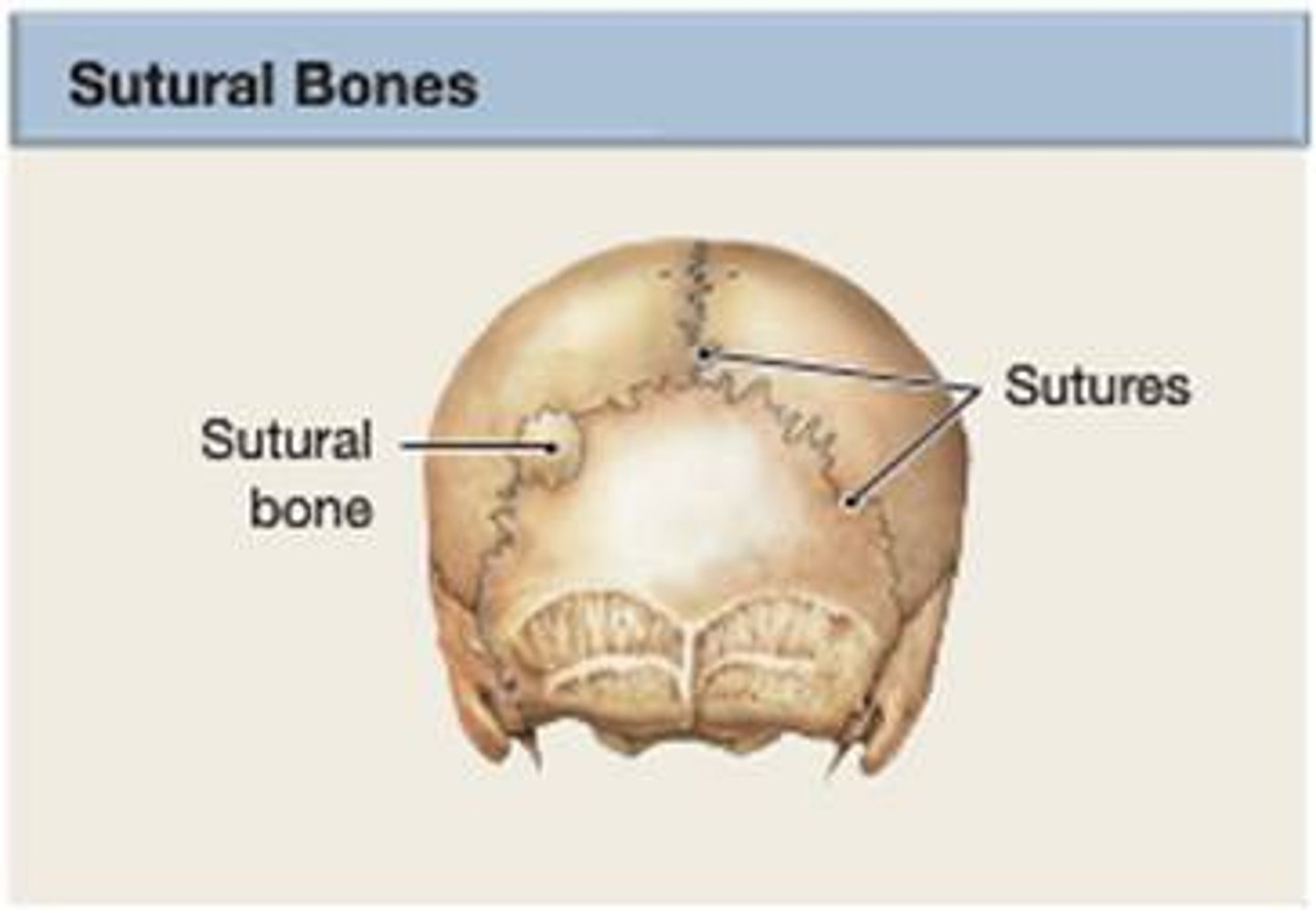
sutural (wormian) bones
extra bones that develop in skull suture lines
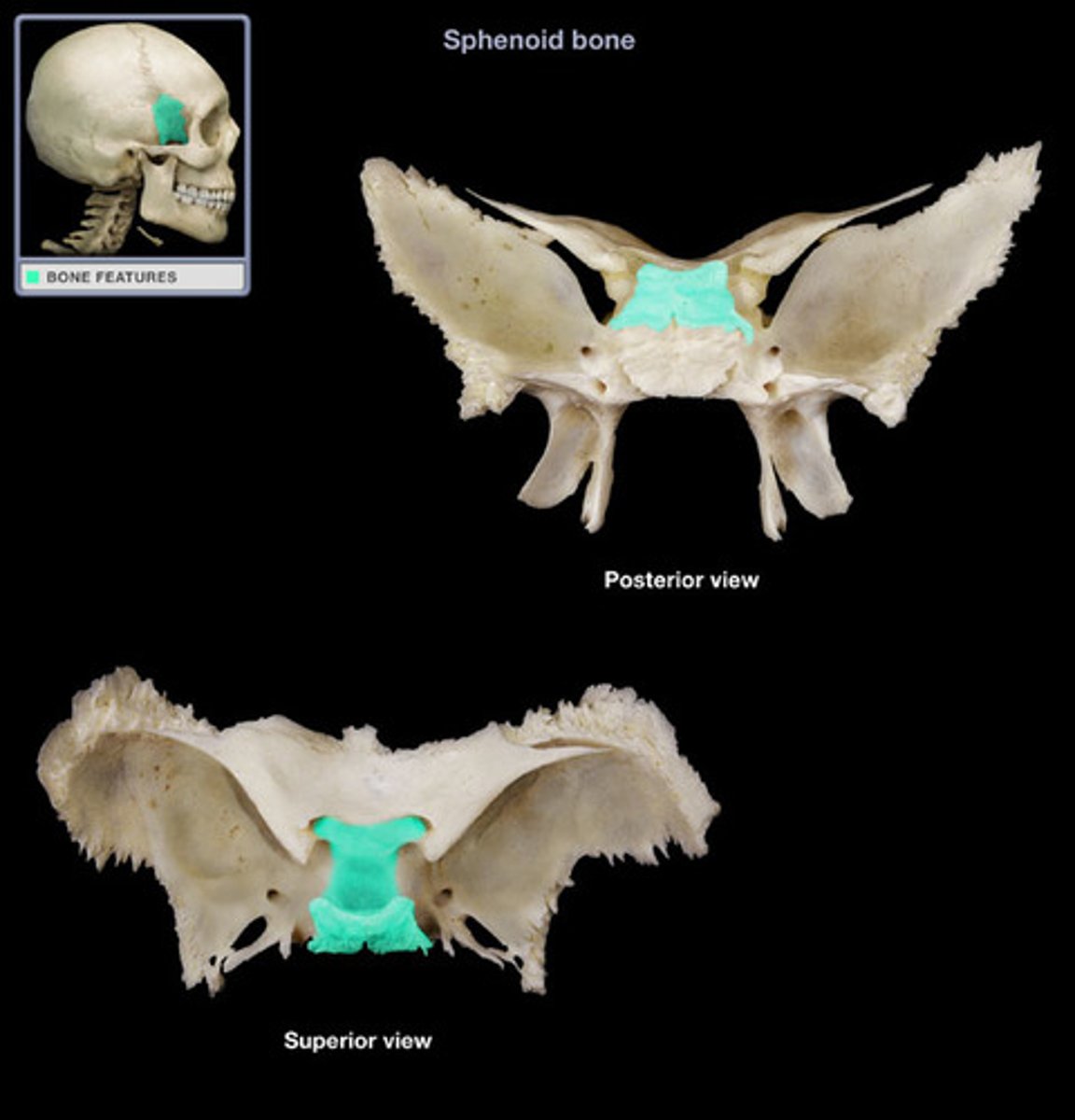
Sphenoid
single, irregular, bat-shaped bone, forming part of the cranial floor
Sella turcica
Sphenoid bone feature
Greater wing
Sphenoid bone feature
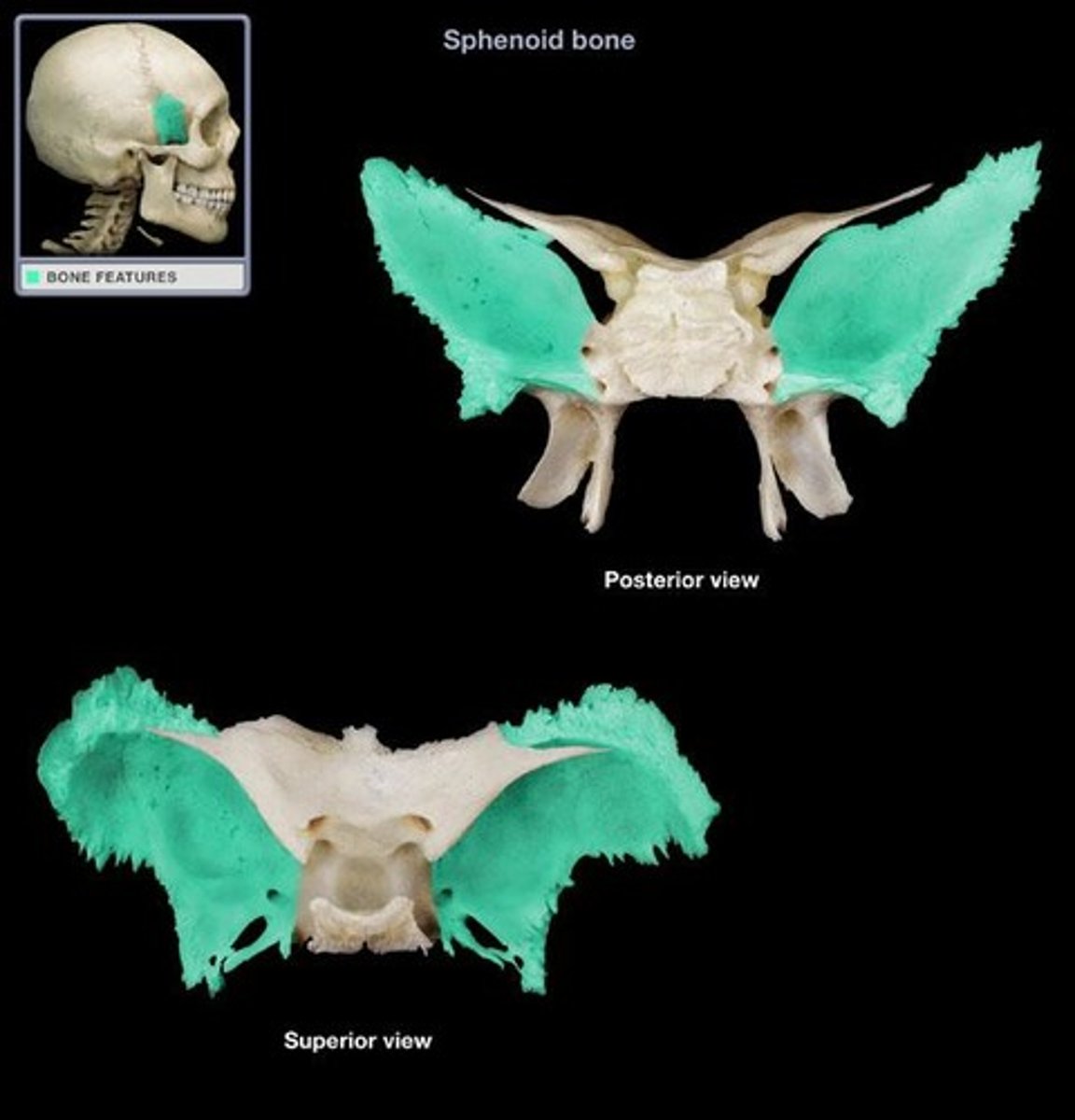
Lesser wing
Sphenoid bone feature
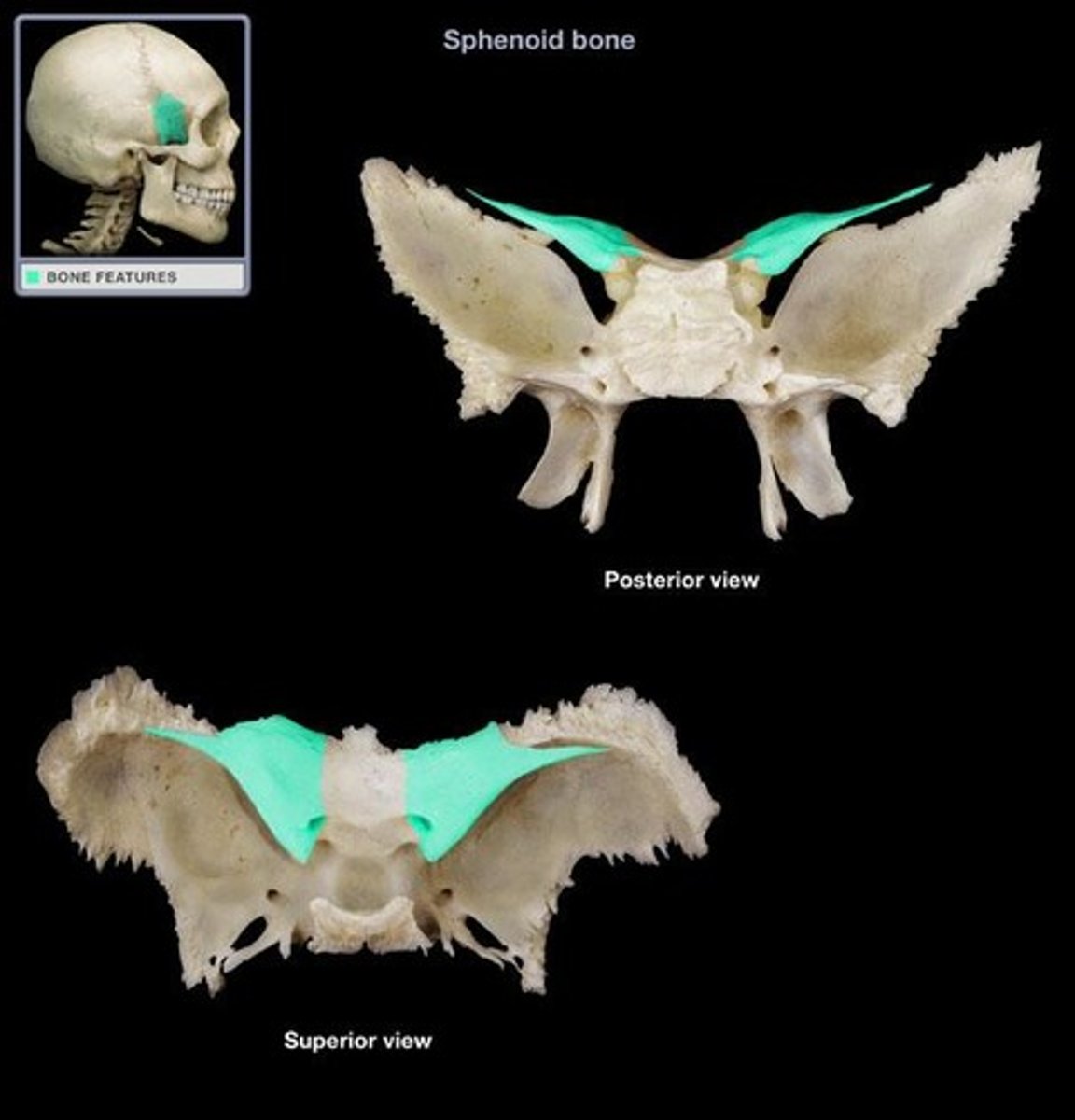
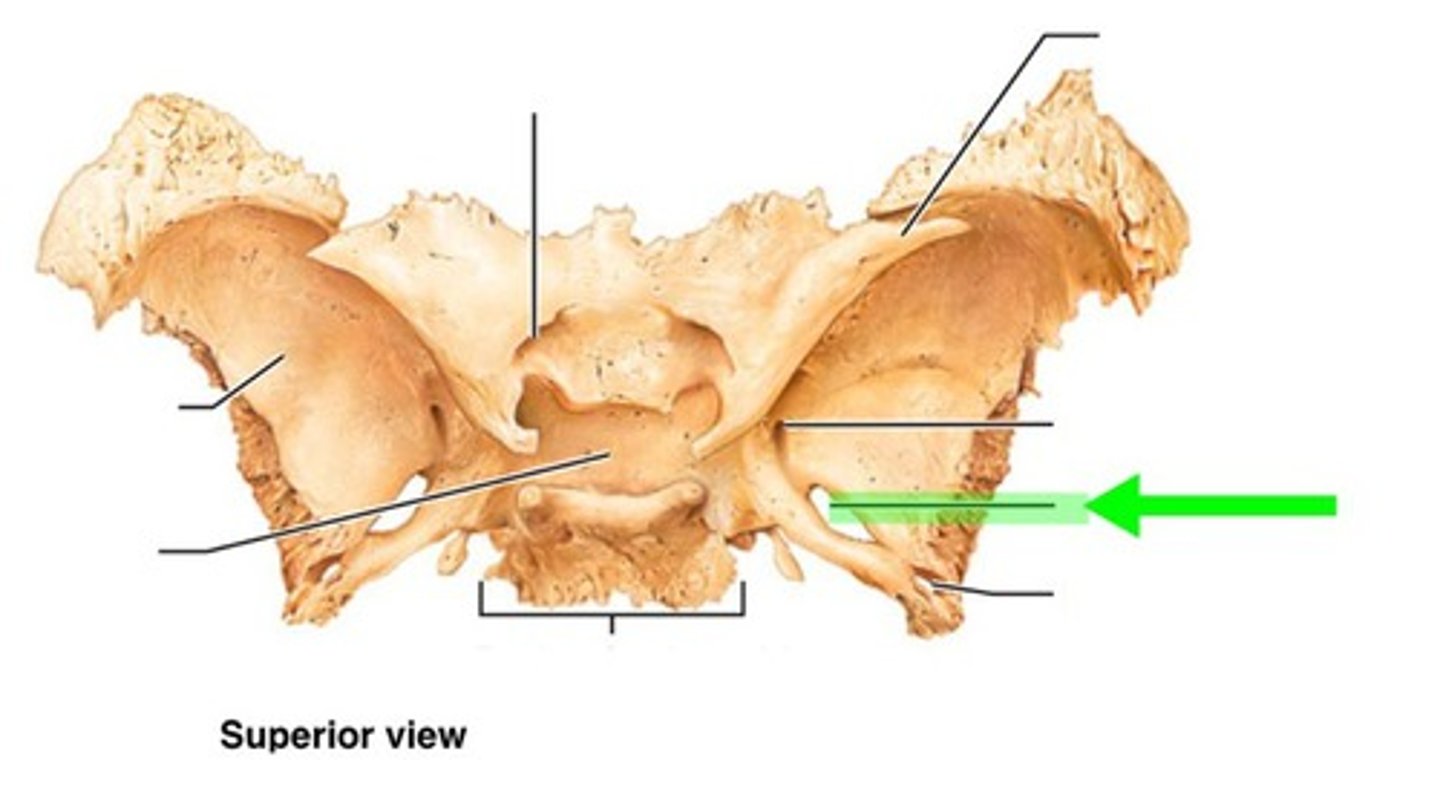
Superior orbital fissure
Sphenoid bone feature
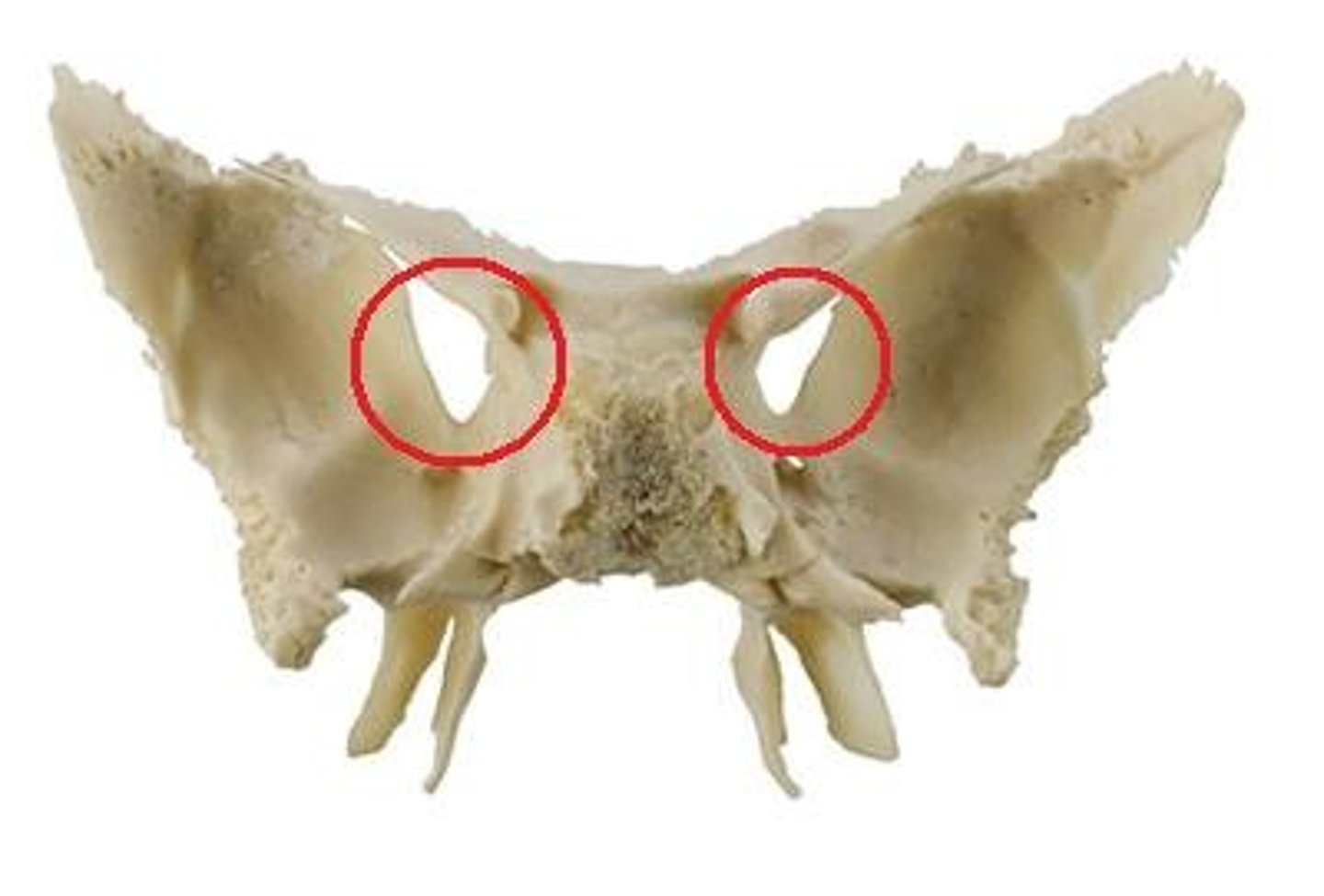
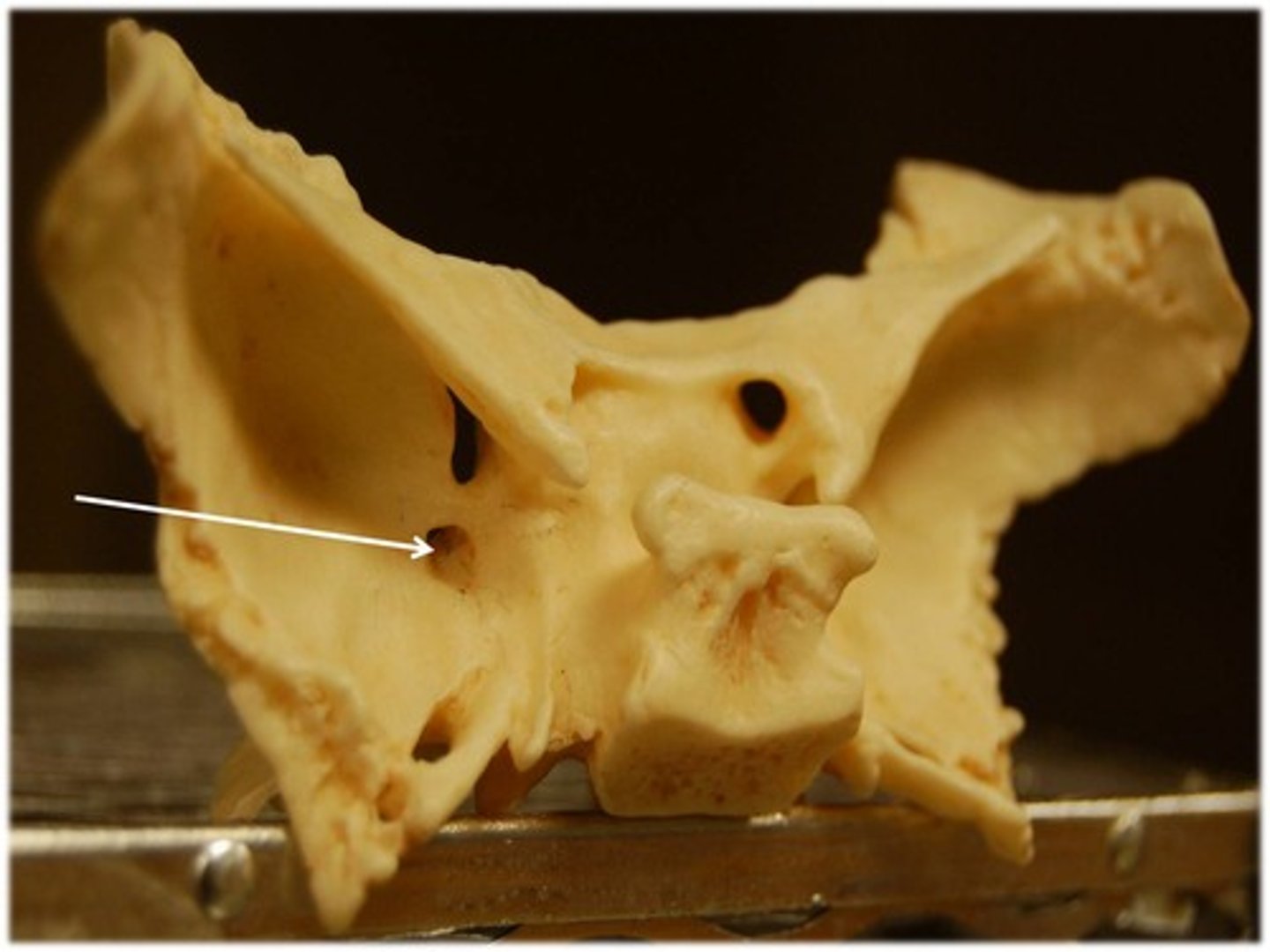
Foramen ovale
Sphenoid bone feature
Foramen rotundum
Sphenoid bone feature
Optic canal
Sphenoid bone feature
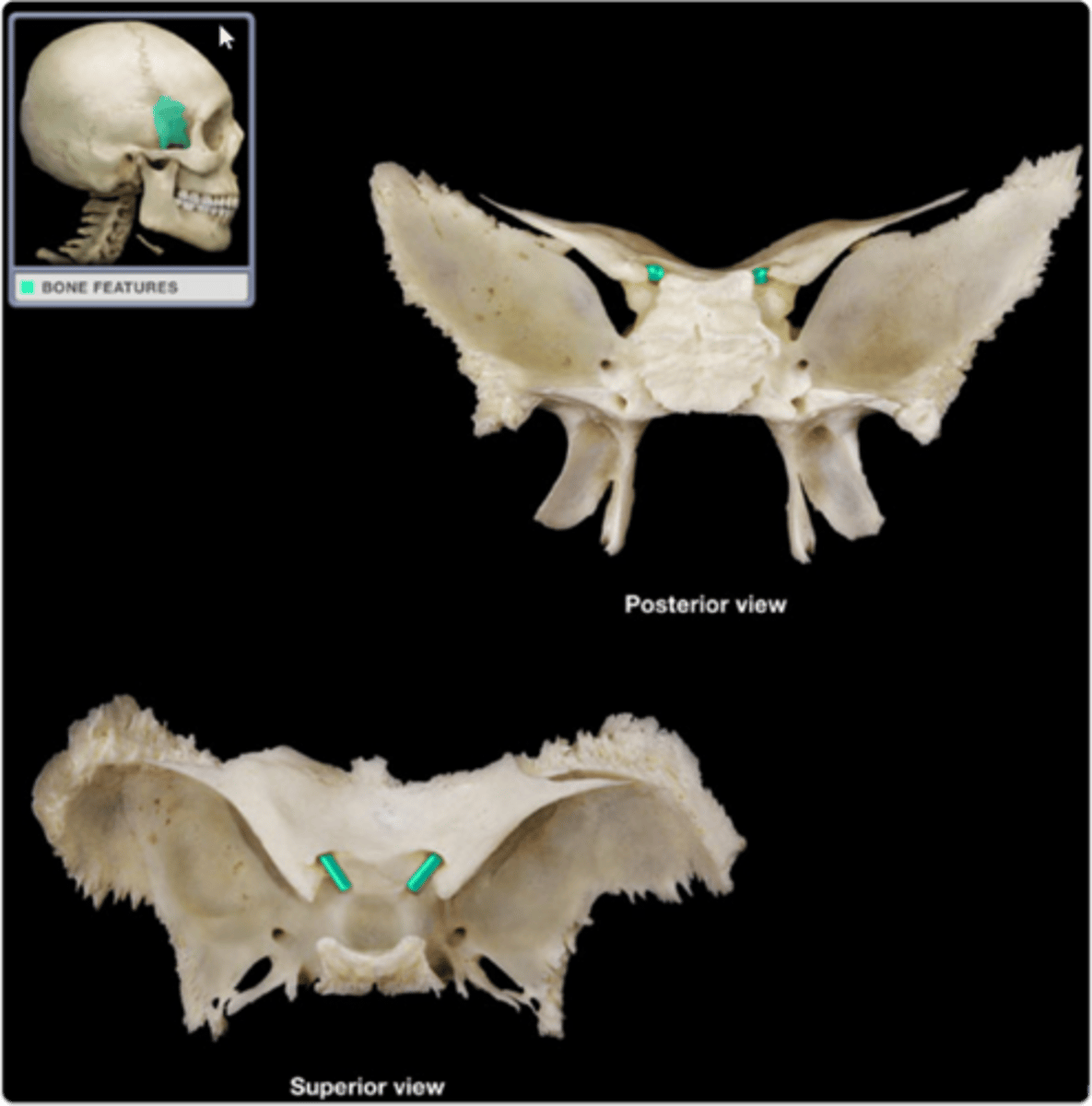
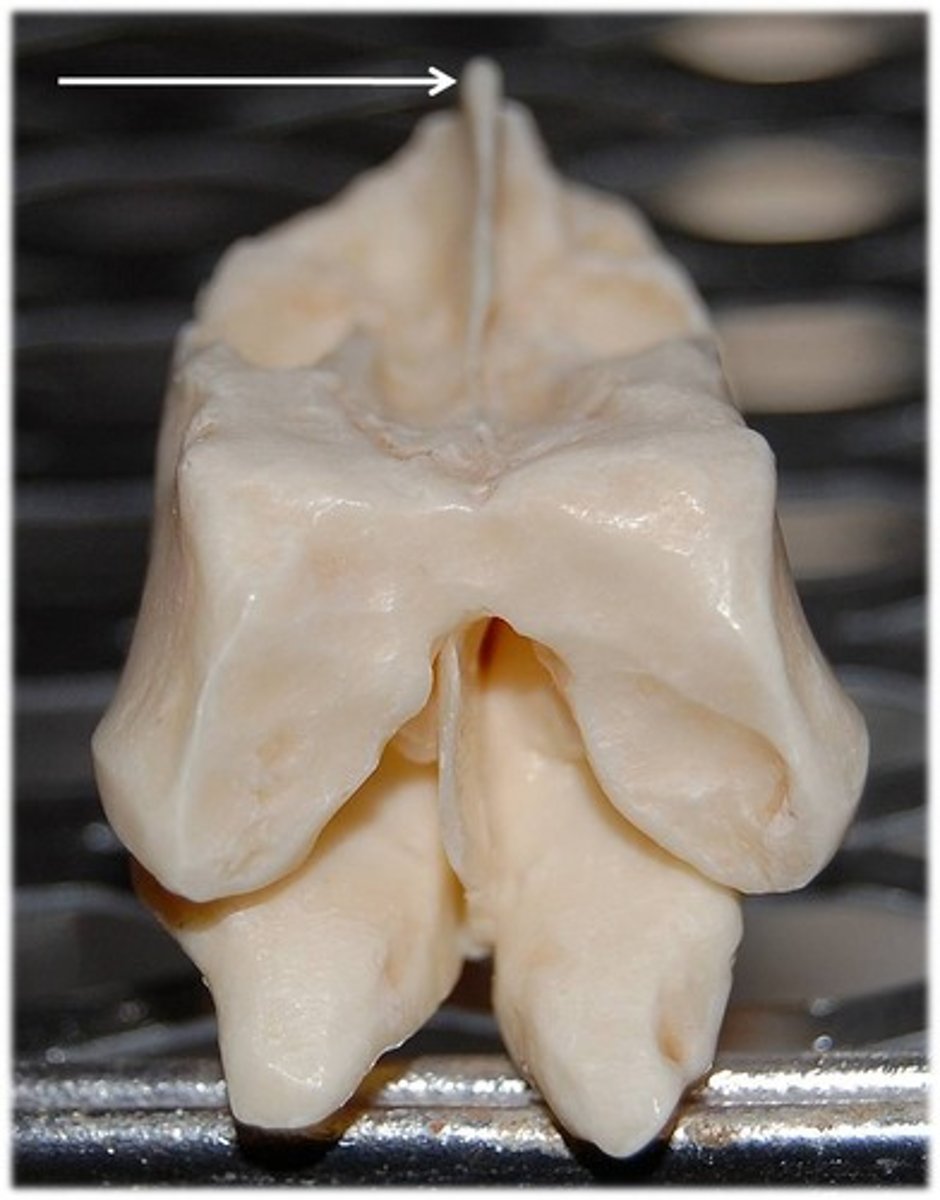
Ethmoid
helps to connect neurocranium with splanchnocranium
Crista galli
ethmoid bone feature
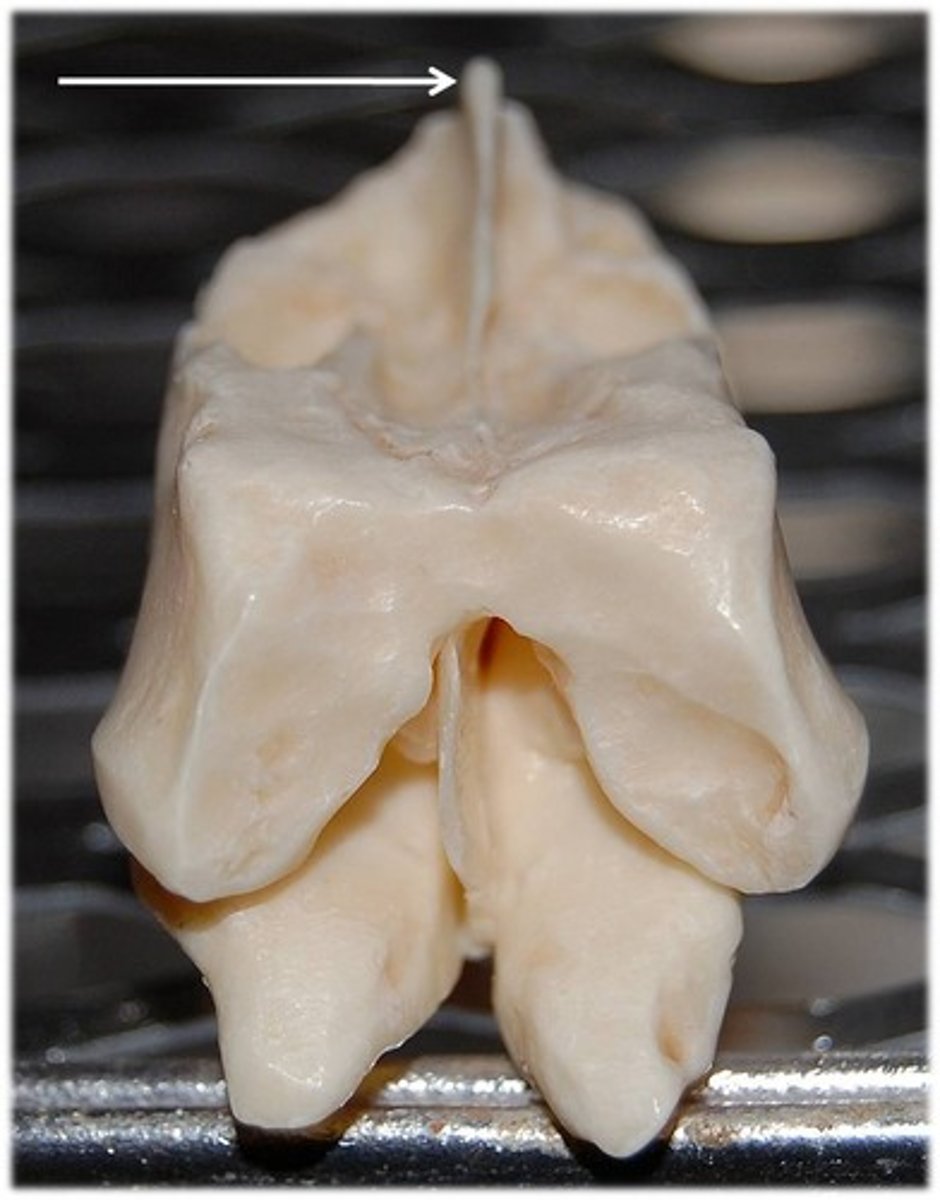
Perpendicular plate
Ethmoid bone feature
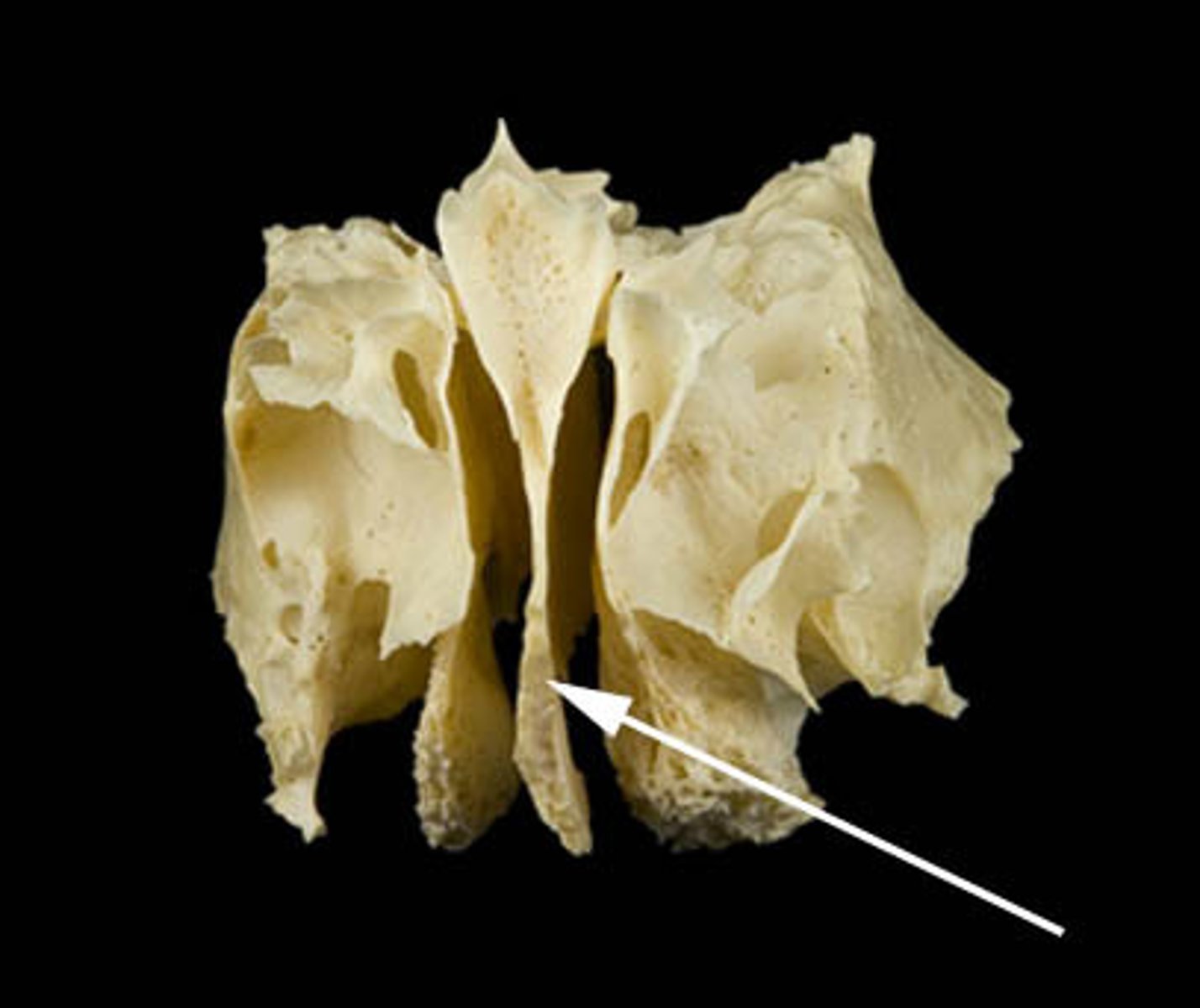
Middle nasal concha
ethmoid bone feature
Superior nasal concha
Ethmoid bone feature
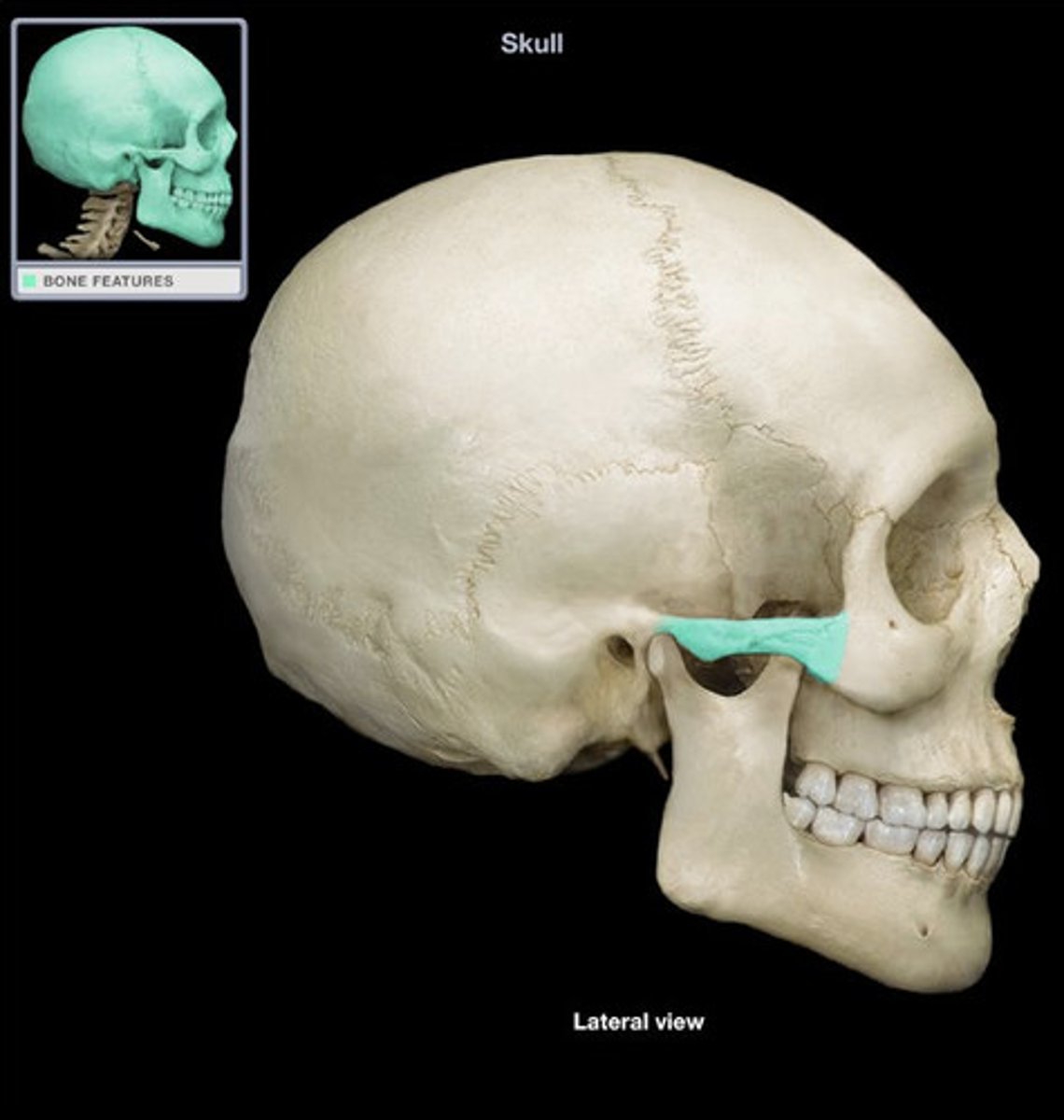
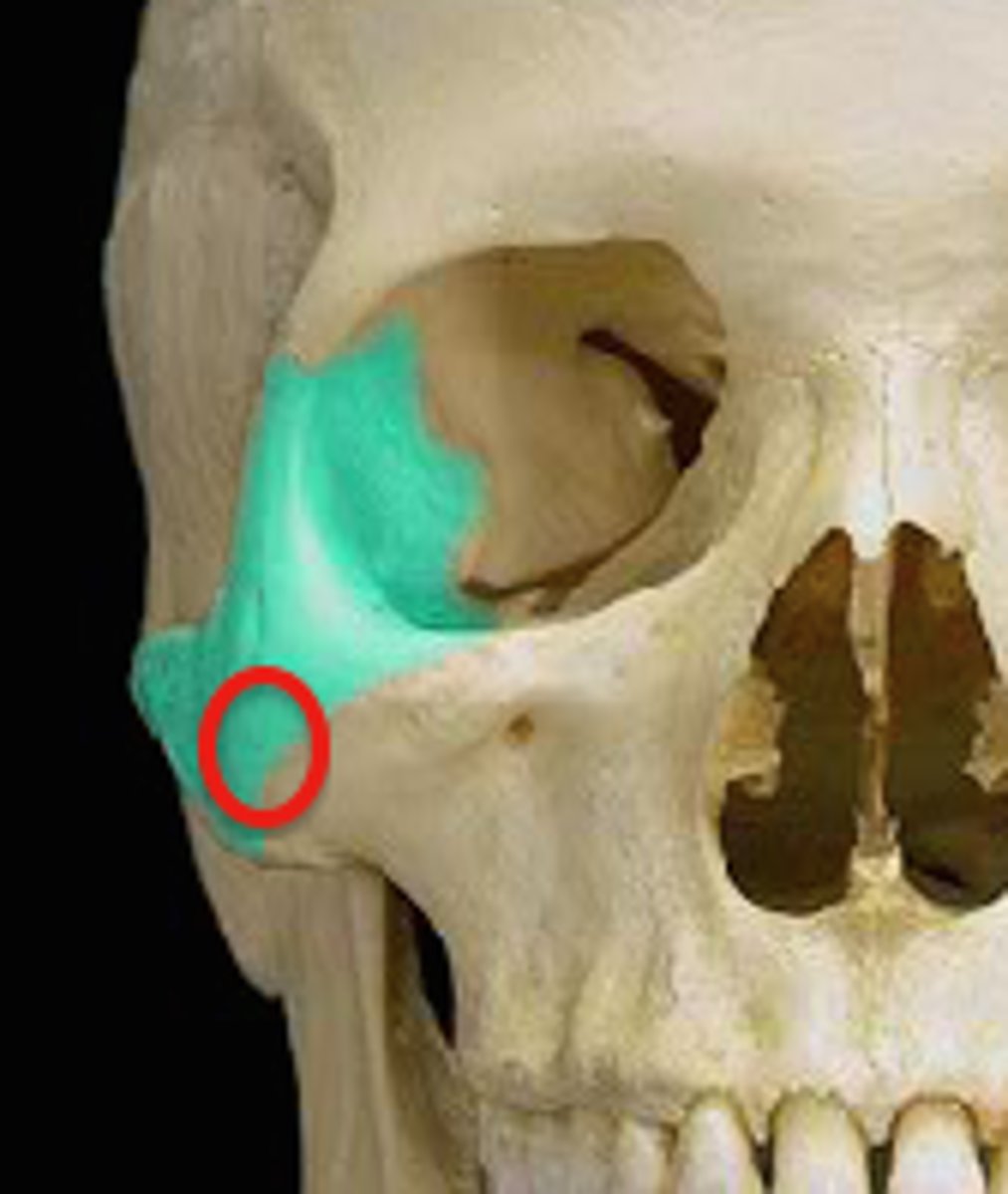
Zygomatic bone
the arch of bone beneath the eye that forms the prominence of the cheek
Frontal process
Zygomatic feature
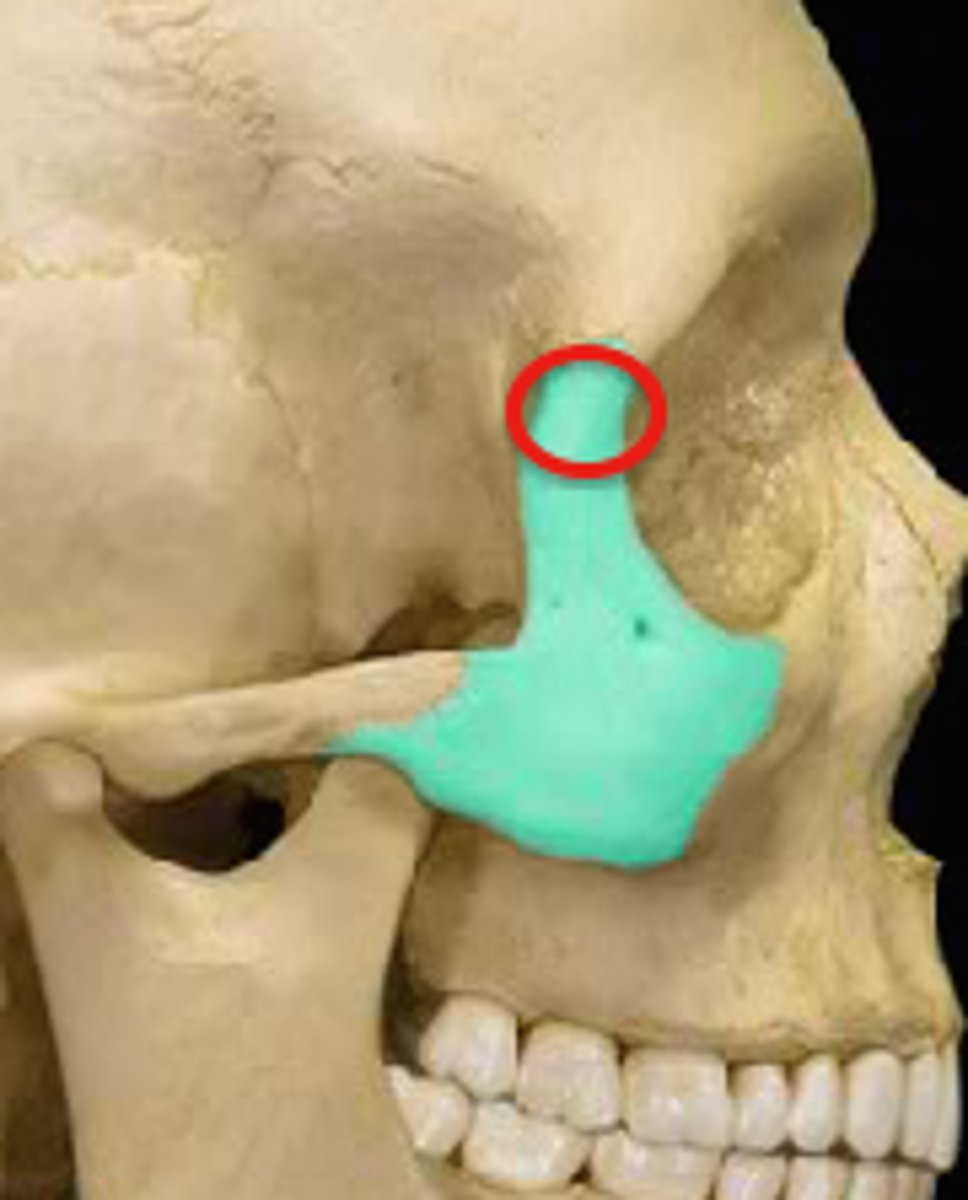
Temporal process
zygomatic bone, where it connects to temporal bone
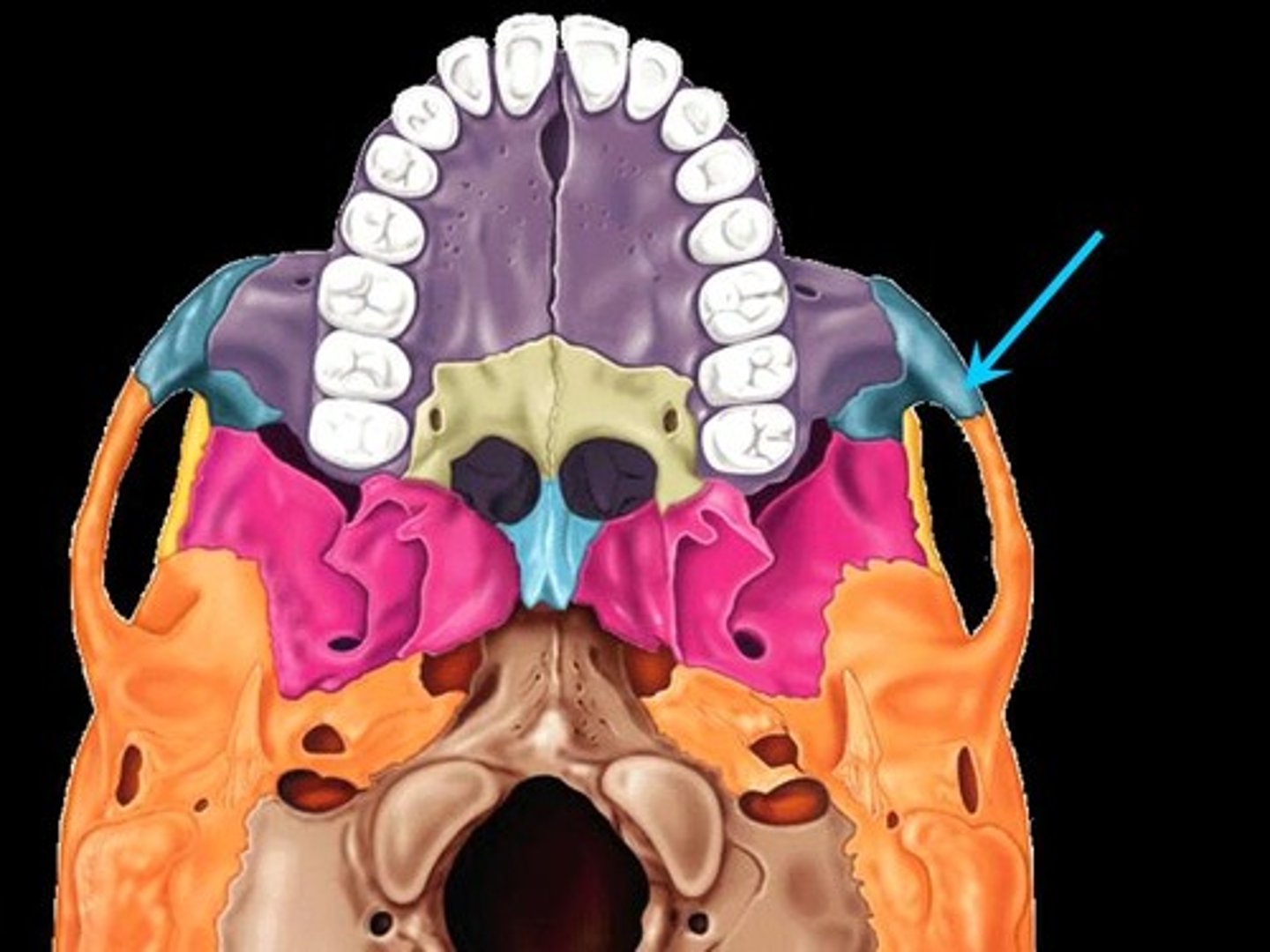
Maxillary process
zygomatic feature
inferior/lateral orbital margin
zygomatic feature
Maxilla
upper jaw bone
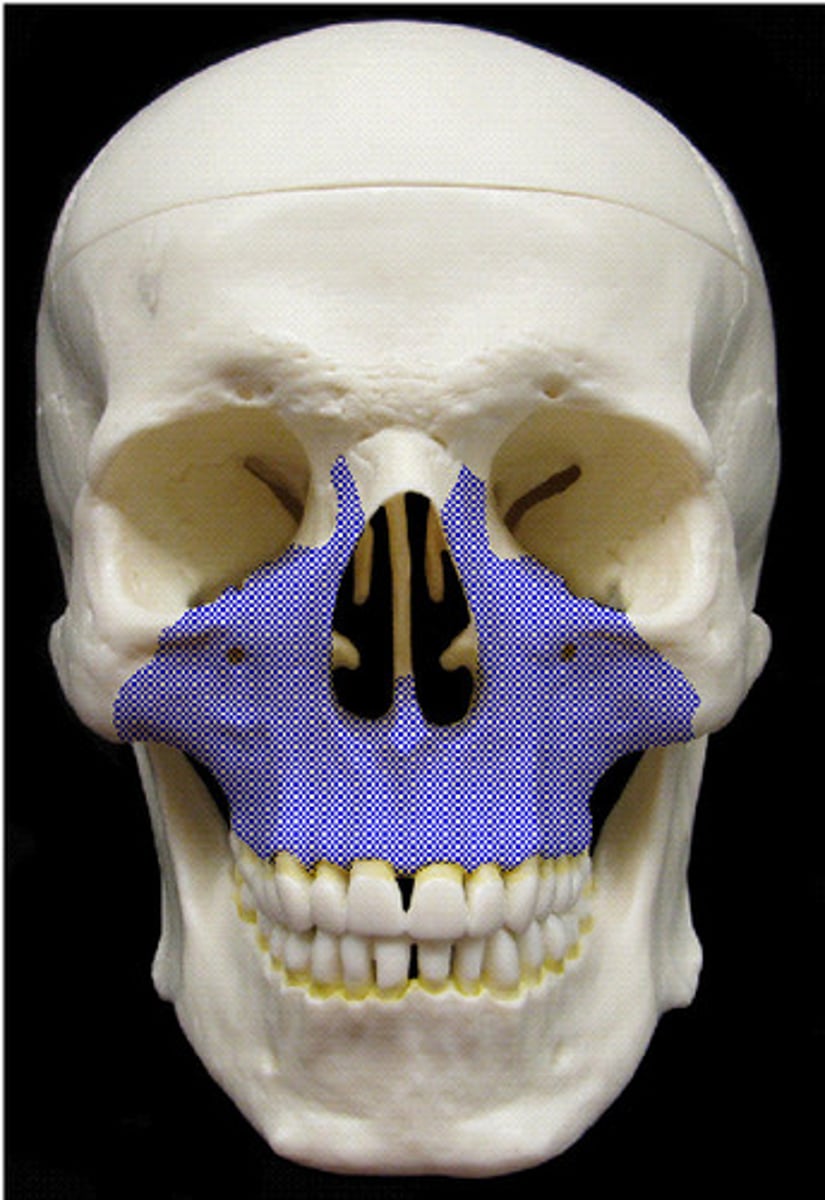
alveolar process(M)
tooth bearing bone
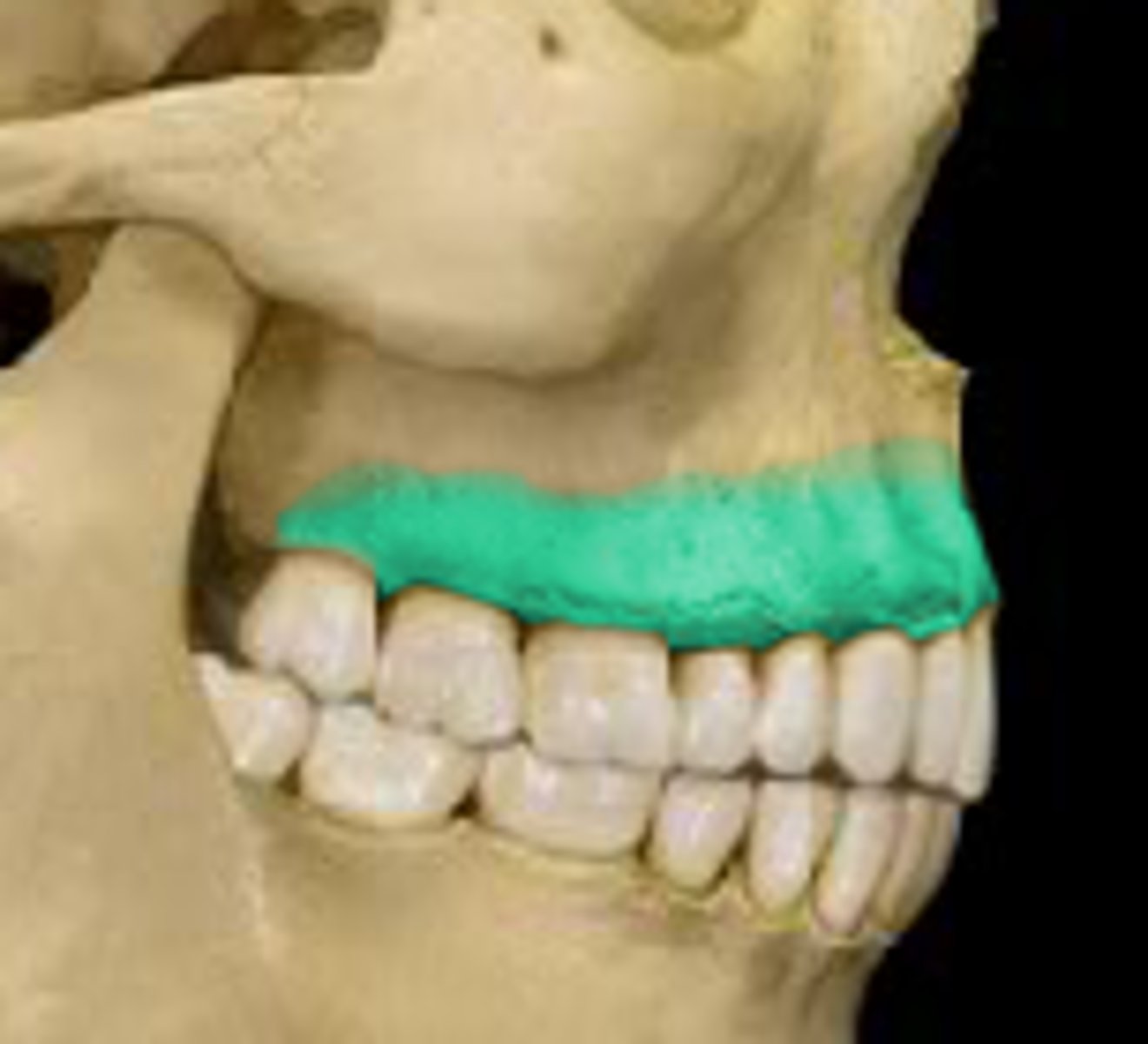
Anterior nasal spine (M)
a sharp projection of the maxilla located at the anterior and inferior portion of the nasal cavity
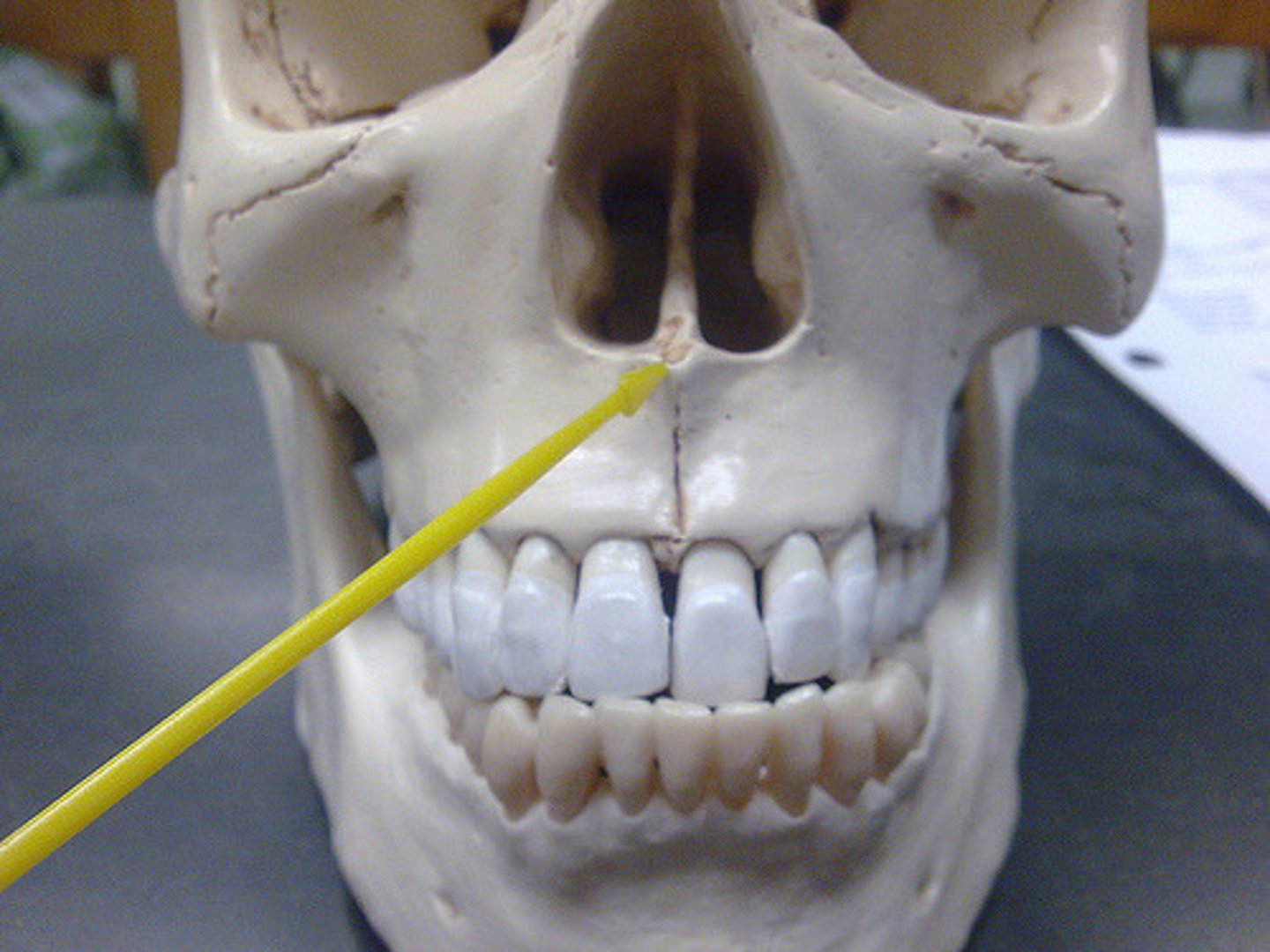
frontal process (infraorbital foramen)
Little holes
Palatine process (M)
forms the anterior portion of the hard palate (roof) of the mouth also forms parts of the nasal cavity and eye orbits
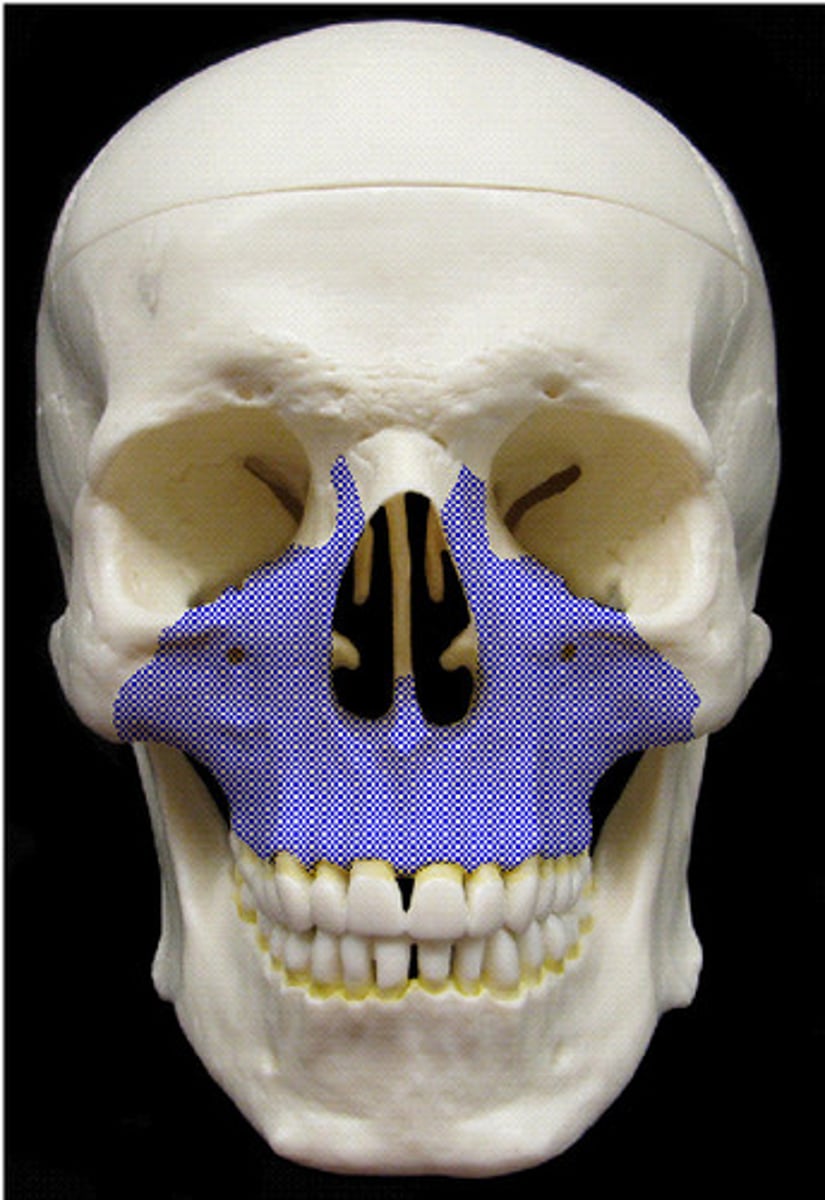
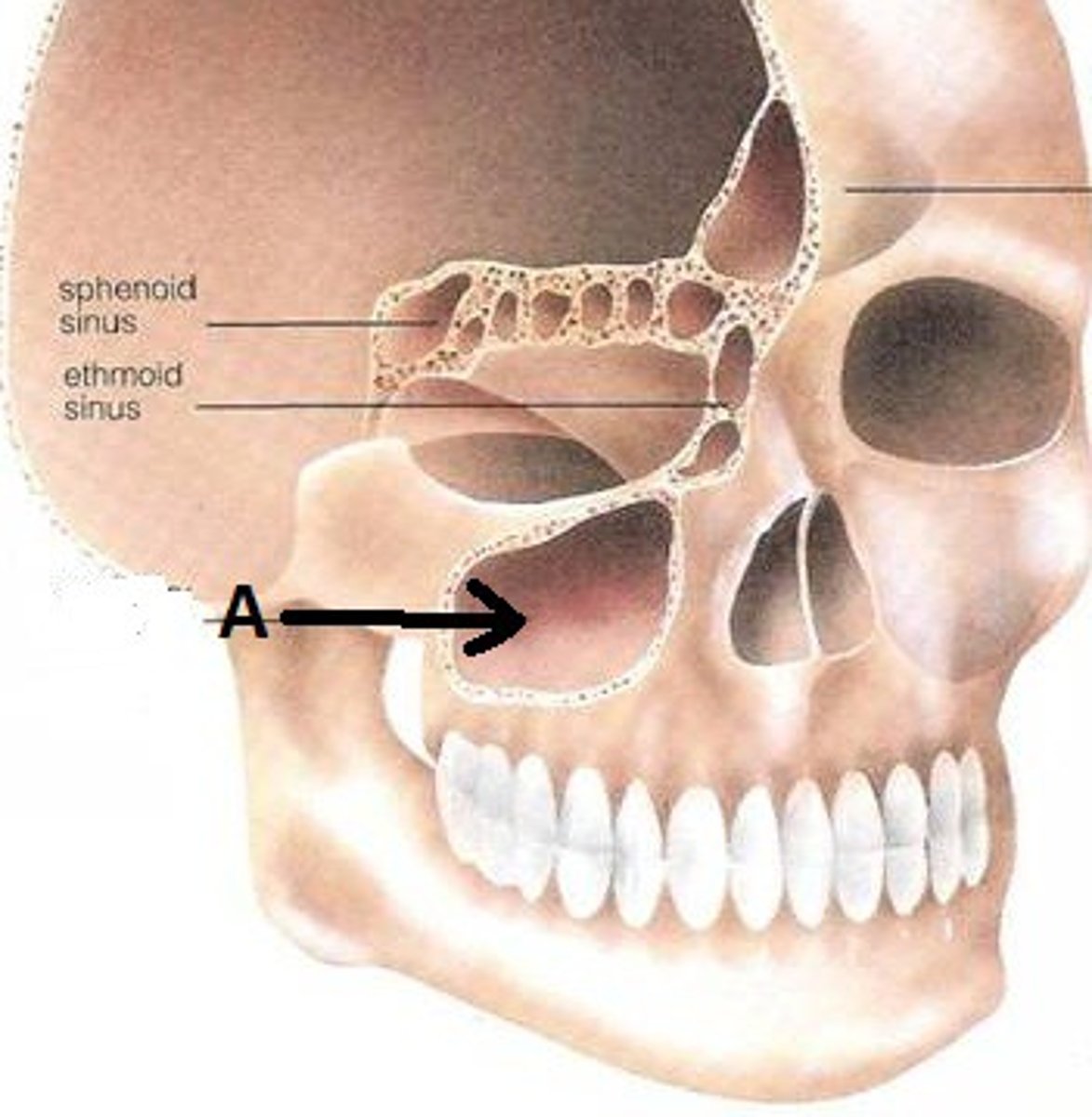
Maxillary sinus
largest paranasal sinus; pyramidal; on cheek bone lateral to nasal bone
Nasals
bridge of nose
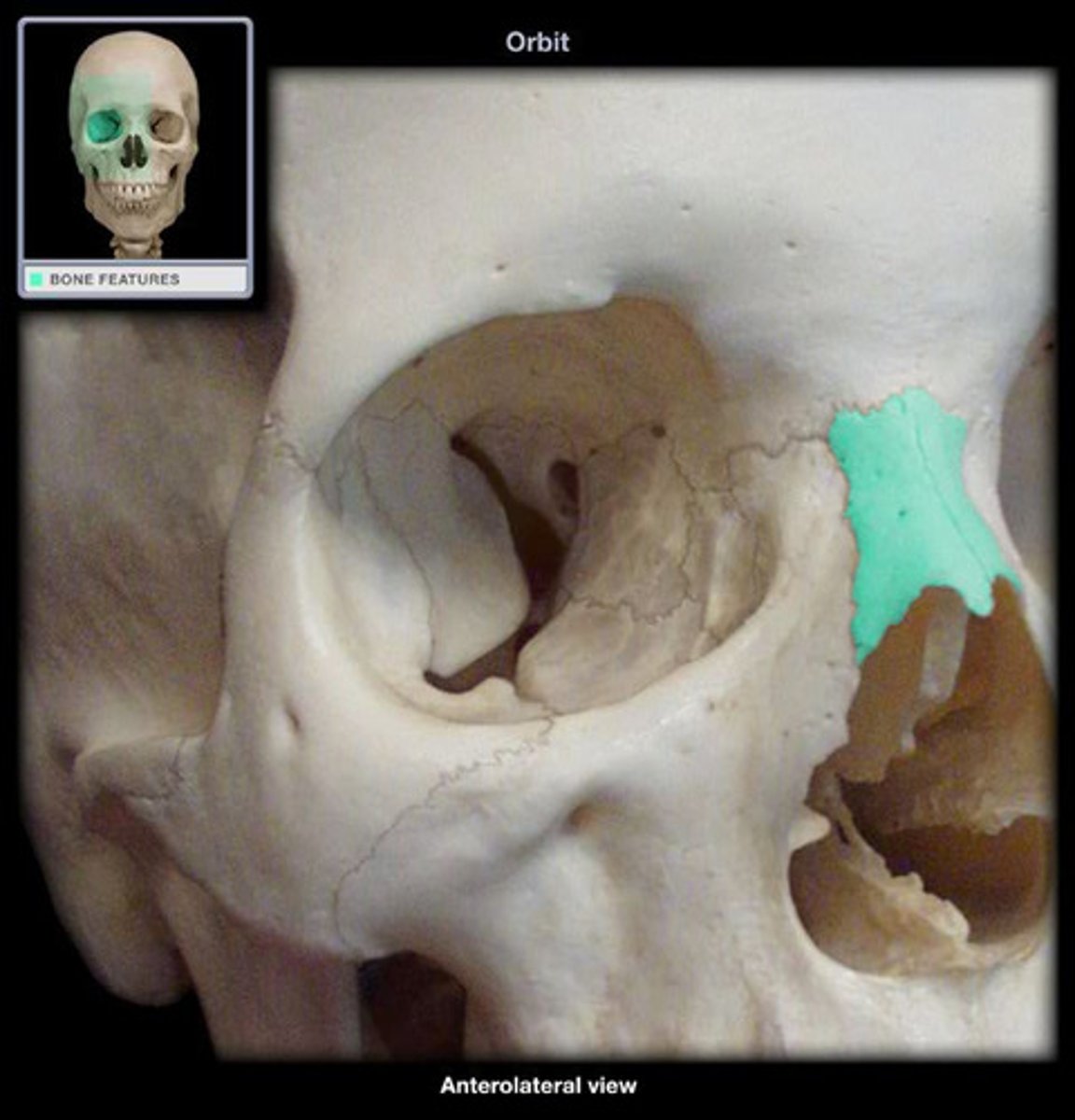
Lacrimal
smallest bone, forms medial orbital wall
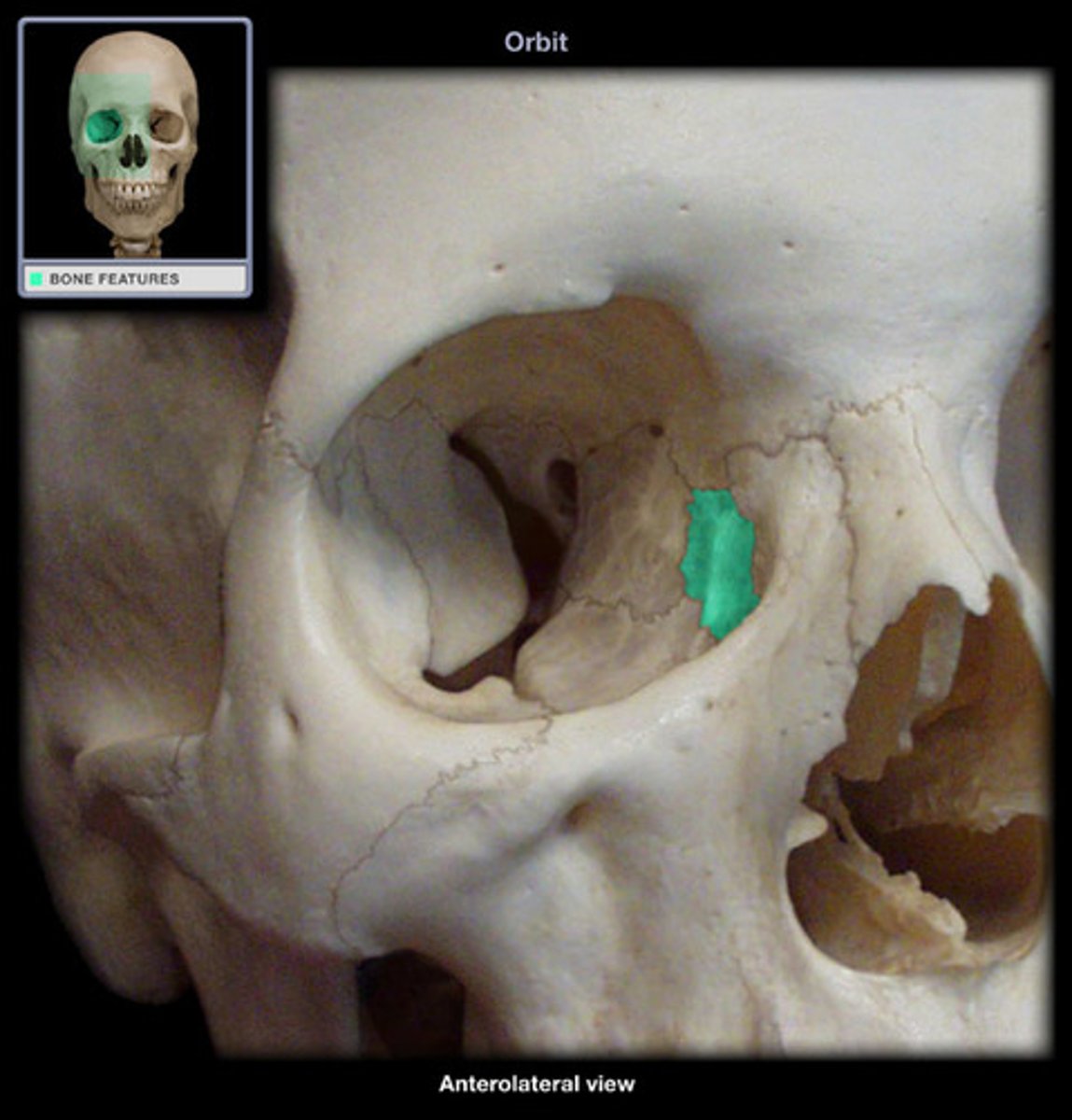
Inferior nasal conchae
The lowermost scroll-shaped bones on the sidewalls of the nasal cavity.
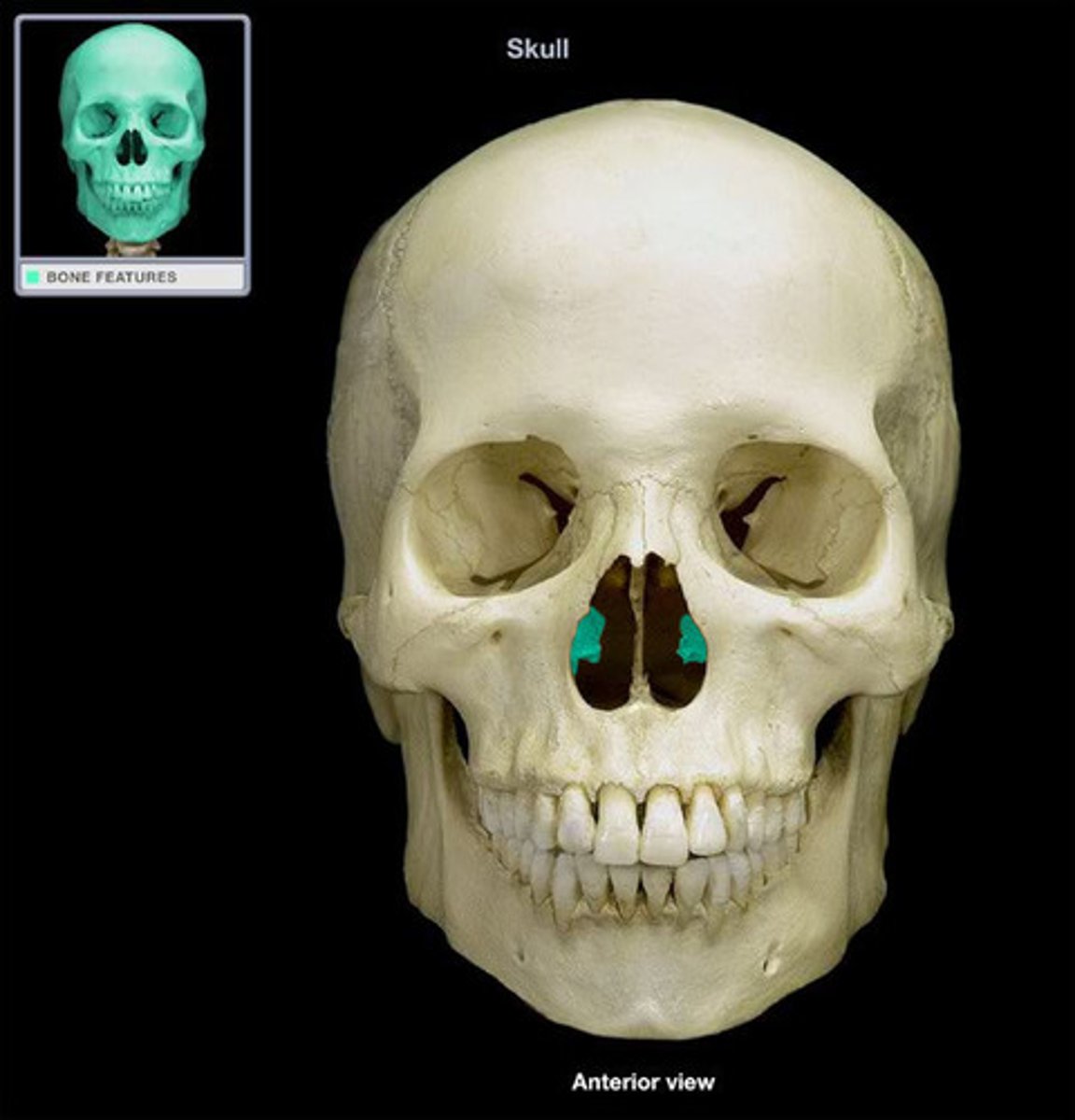
Vomer
forms the inferior portion of the nasal septum and divides nasal cavity
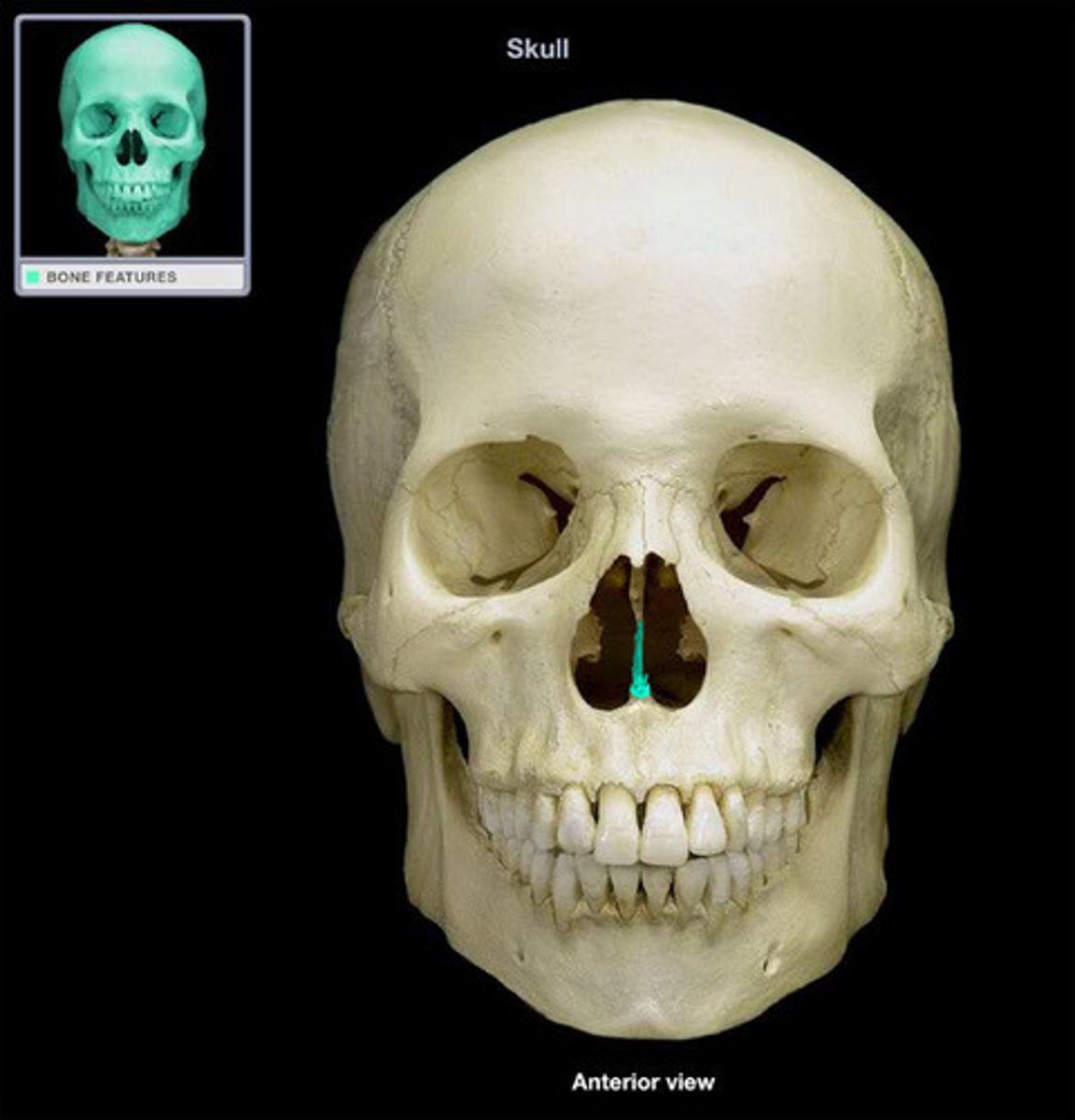
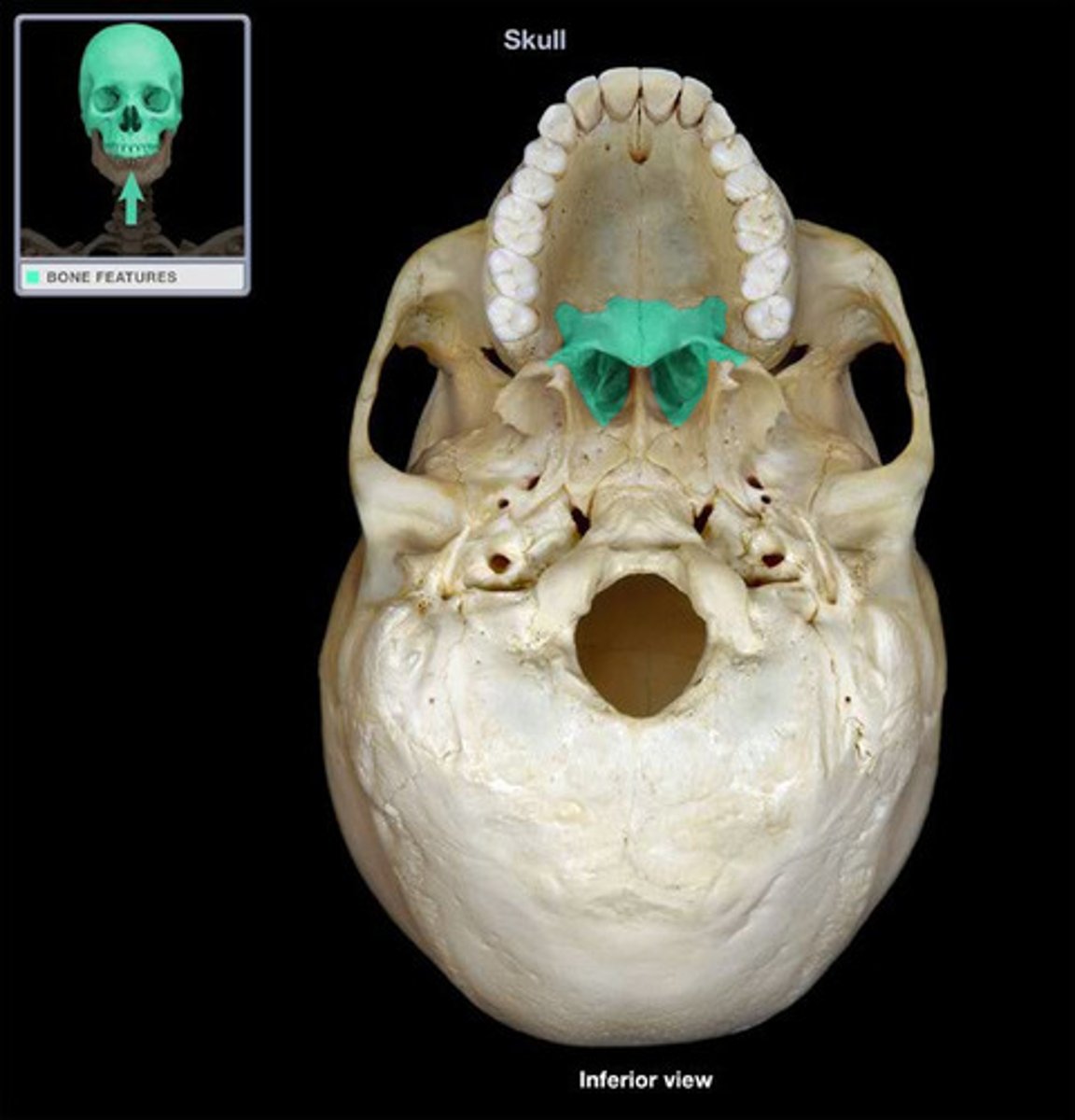
Palatine
the other 1/3 of the palate, part of nasal cavity
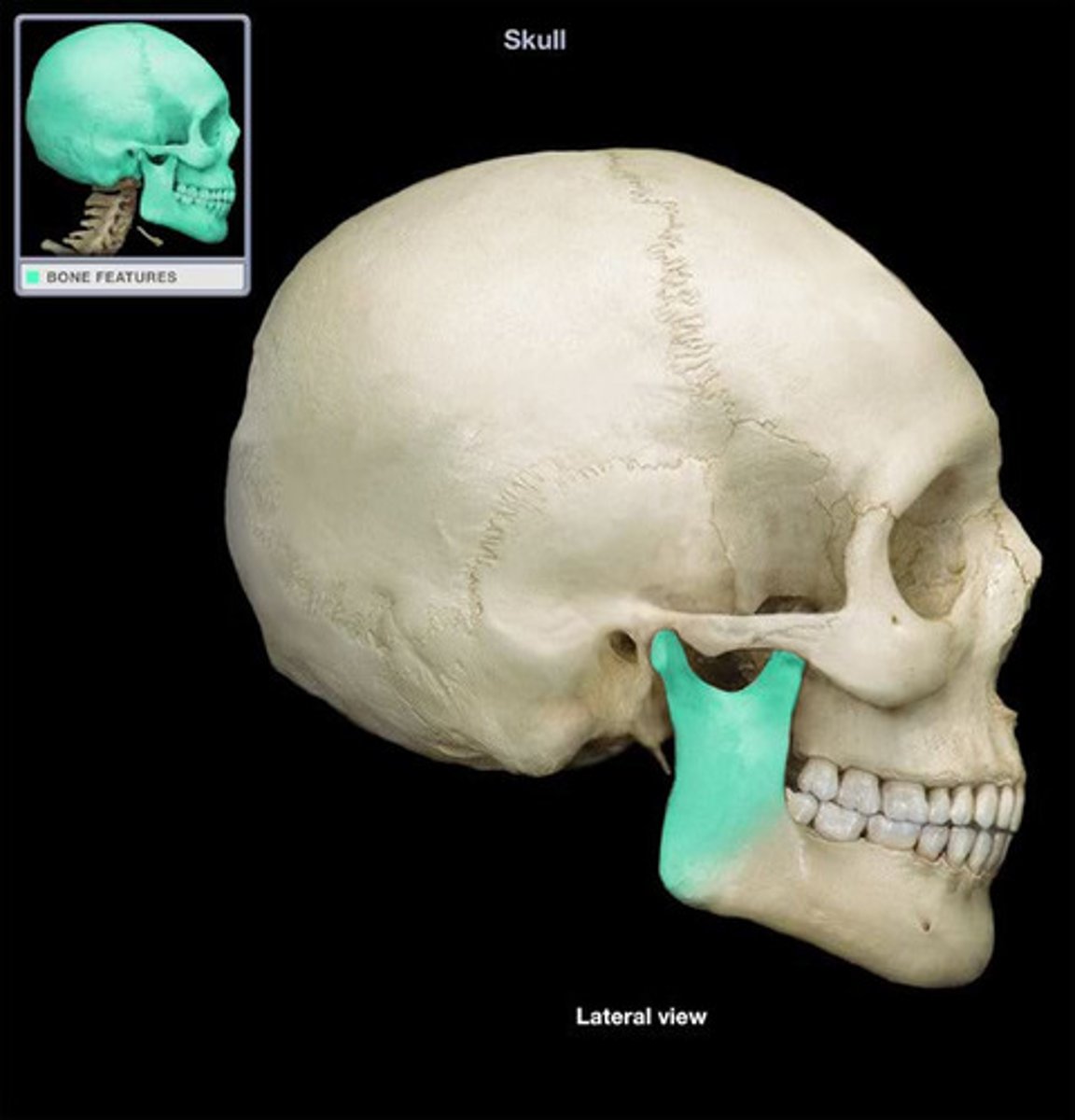
Mandible
lower jaw
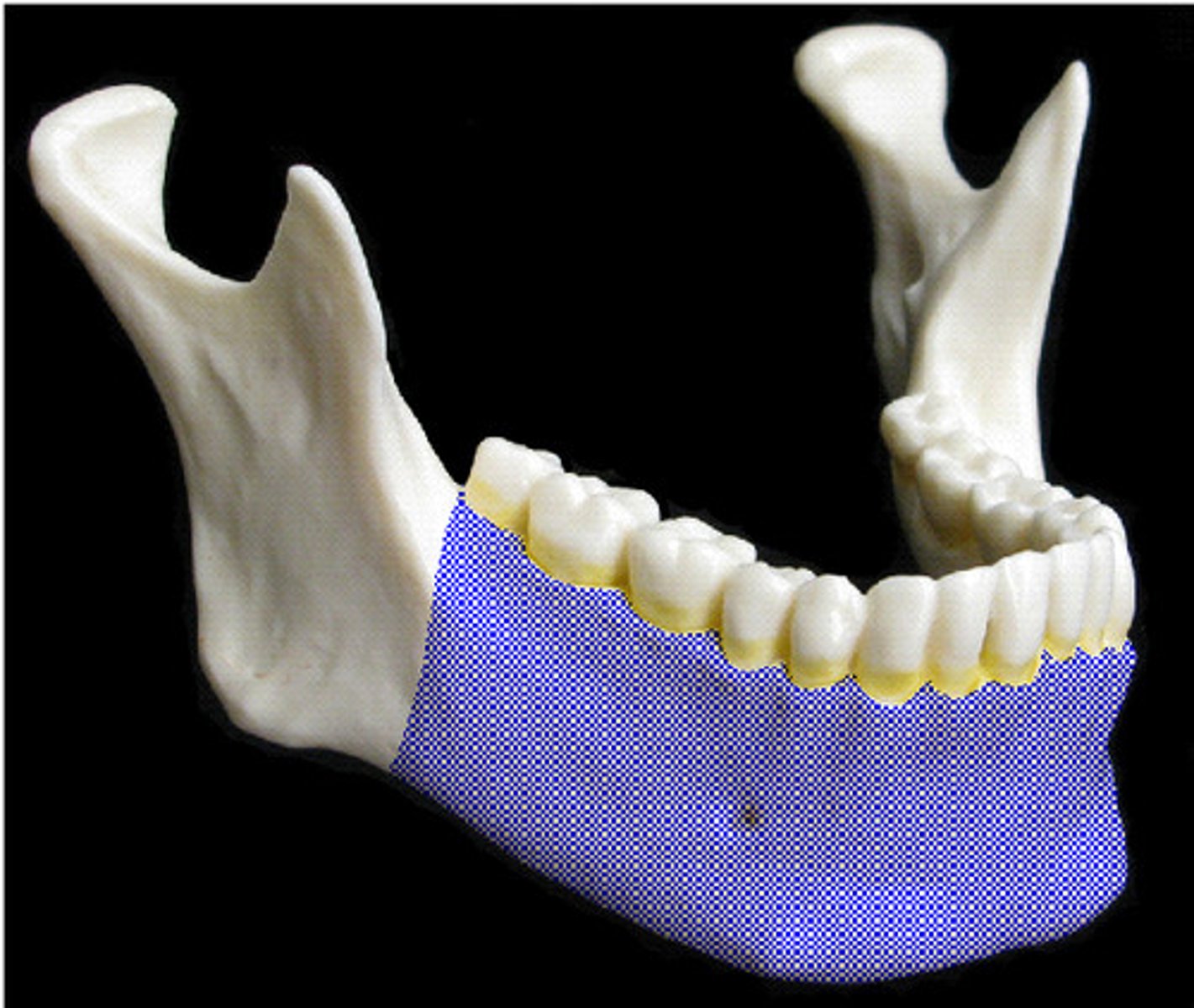
Ramus
An extension of a bone making an angle with the rest of the structure
Horizontal ramus (corpus)
horizontal part of the mandible
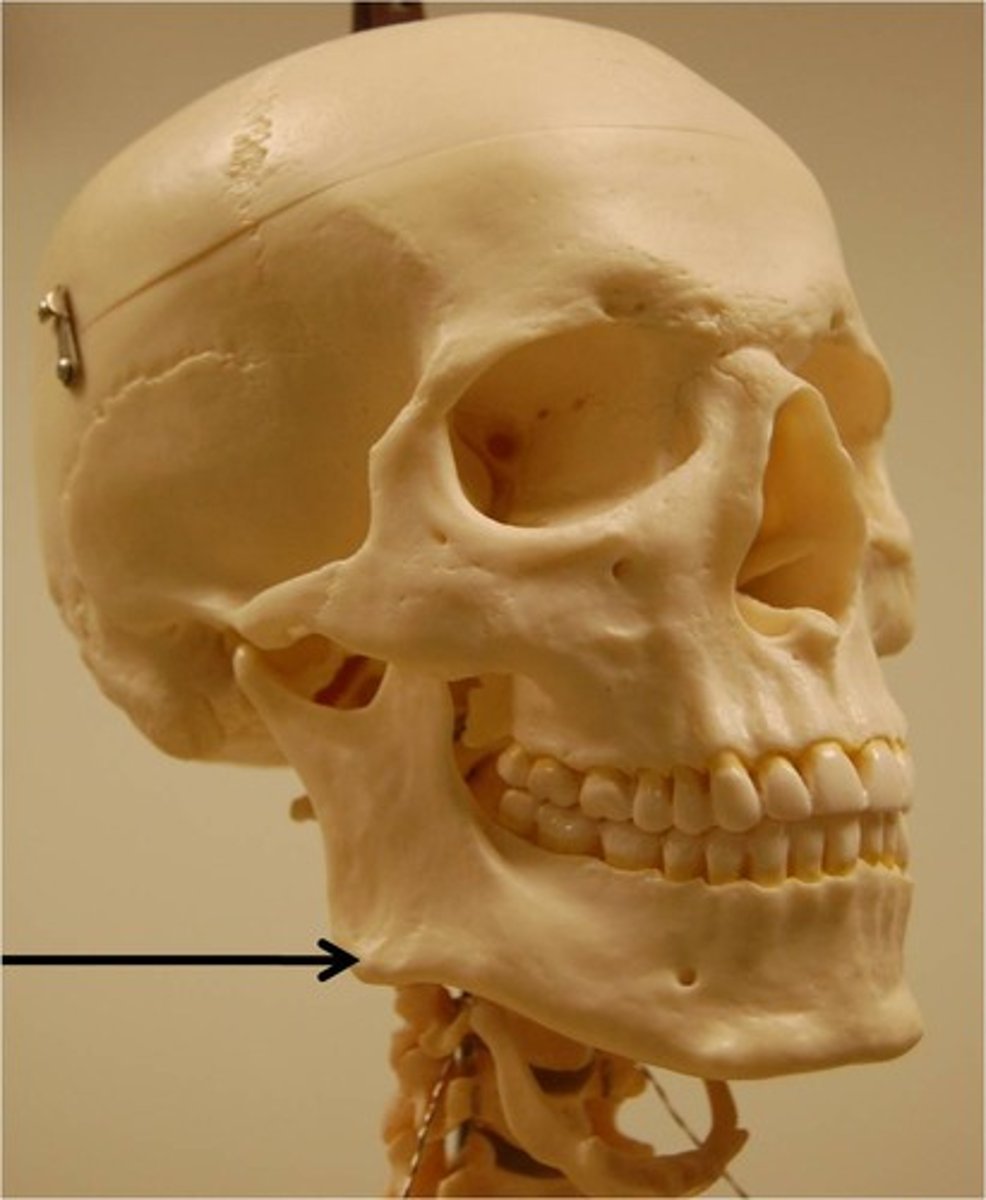
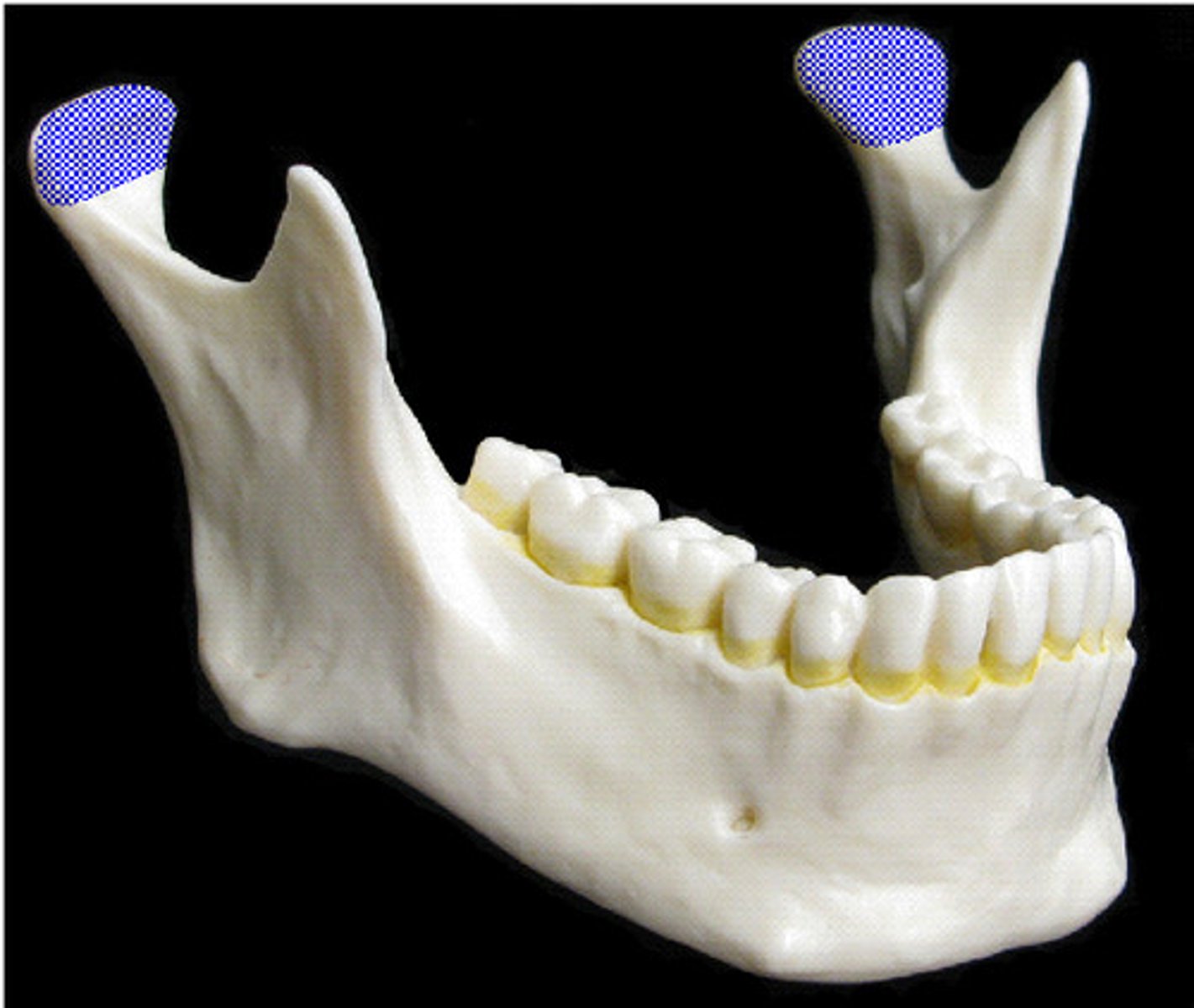
Mandibular condyle
Articulation point of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
Mental eminence
a triangular projection on the inferior portion of the anterior mandible