LAM Final Exam
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Pemphigus foliaceus
Et: Immune mediated
destroys intercellular attachments
Cs: Small Vesicles, blisters, erosions, scaling, crusting, alopecia, pyrexia, urticaria, limb edema, coronitis
starts locally (head/limbs) → generalized
Dt: Biopsy!!
Acantholysis, intraepidermal clefts, neutrophilic exudate, IF IgG staining!!
Tx: Steroids! (Dex) → remission
Immunosuppressive therapy → aggressive treatment!! until complete remission!
Px: good if young, life long if old
Alopecia areata
Et: Immune Mediated
antibodies to hair follicles
Cs: Discrete hair loss w/ normal skin
hair loss on face, mane, tail
Dt: Biopsy
Tx: Steroids help
Px: most resolve in 1-3 yrs benign neglect
Urticaria (hives)
Et: Type I hypersensitivity - IgE
insects, inhaled allergens, molds, drugs, topicals
Cs: hives/wheals/plaques, Localized dermal edema
face, neck, withers, thorax, generalized
Insect bites, drugs, atopic dermatitis, topicals, allergies
Dt: Allergy skin testing
GOAL: determine specific cause
Tx: Antihistamines, steroids, hyposensitization(long term)
Px: recede once trigger removed!
Contact dermatitis
Et: Irritant exposure
new/used tack, new bedding, sprays, soaps
Cs: edema, erythema, vesicles, erosions, crusts
localized and caused by contact with irritant
Dt: History & distribution
Tx: Eliminate exposure
Queensland itch
Sweet itch → very common
Et: Hypersensitivity to Culicoides saliva
gnats breed near standing water
Piercing mouthparts for blood feeding
Cs: Pruritic, hives, self trauma crusting, alopecia, leads to lichenification(chronic)
Dt: Dorsal-ventral distribution, seasonality
Tx: Stable at dusk, fans/screens, pyrethrin sprays, steroids(significant itch)
Aka→ vector control
Ventral dermatitis
Et: Culicoides, Onchocerca, horn flies, Habronema
Aka→ Bugs
Cs: papules, crusts, alopecia, ulcers, excoriation, leukoderma, can become chronic
Ventral abdomen, midline distribution (KEY)
Tx: Insect control, steroids
Mites (mange)
Et: Psoroptes, Sarcoptes, Demodex (rare); Trombiculidiasis (chiggers); Chorioptes in drafts(foot manage)
Sig: drafts
Cs: Pruritus, scaling, crusts, alopecia
pastern/fetlock of drafts(Choriopte)
Dt: Skin scraping - visualize
Tx: Ivermectin, lime sulfur, organophosphates
Pediculosis (lice)
Et: Damalinia (chewing), Haematopinus (sucking)
Cold weather/crowding
Cs: VERY Pruritus, scaly coat, alopecia
mane, tailhead, topline
Dt: Identify lice/nits(eggs)
Tx: Pyrethrins
KEY: Repeat 2–3× q 2w
kill the nits
Dermatophytosis (ringworm)
Et: Trichophyton & Microsporum
spread via direct contact or equipment!
Infects hair shafts
Cs: Crusting, alopecia, pruritic
Face, neck, shoulders
Dt: DTM, cytology, Woods lamp, histopath
Tx: Self-limiting (healthy adults), iodine, antifungals, lime sulfur, oral antifungals(rare), disinfect equipment
not in pregnancy animals
Dermatophilosis (rain scald)
Et: Dermatophilus congolensis infection after moisture exposure
Cs: Superficial infection, Crusts, matted hair, neutrophilic dermatitis
Dt: Cytology
railroad track” cocci
Dorsally distributed
DZ sheds in crusts
Tx: Remove crusts!!, iodine shampoo(best), keep dry, antibiotics
Saddle sores
Et: Focal Trauma from tack; secondary infection
Staph, Strep, Dermatophilus, Corynebacterium
Cs: Lesions at points of contact, poor grooming
Dt: History, clinical signs, culture, biopsy
Tx: hygiene, clean, antibiotics
Pastern dermatitis (scratches/grease heel)
Et: Chronic painful dermatitis of pastern/heel bulbs from mud/wetness, Staph, Dermatophilus, fungi, mites
Cs: dry/Crusting, alopecia, ulceration, swelling, pain
Dt: Clinical eval, skin scraping, biopsy
Tx: remove from mud/wetness, Soak, clip, topically with antifungals, steroids, antibiotics, ivermectins, time
Papillomatosis
Et: Equine papilloma virus
Sig: Young horses, yearlings
Cs: Small, firm, gray/white/tan masses
lips, eyelids, genitals/inguinal region
Tx: Self-resolving <12m, vax
Aural plaques
Et: related to Papilloma virus,
Cs: Depigmented hyperkeratotic plaques on inner ear
black fly irritation
Have to differentiate from sarcoid
Tx: Fly repellents, stable during fly season
Nodular necrobiosis (collagen granuloma)
Et: Collagen degeneration with eosinophilic inflammation
Cs: Firm dermal nodules on back/girth; non-pruritic, non-painful
Dt: Histology shows collagen degeneration + eosinophilic inflammation
Tx: Surgical, inject with steroids
HERDA (Hyperelastosis cutis)
Et: Hereditary collagen defect
Sig: QH, autosomal recessive
Cs: Loose, fragile skin, lesions after minor trauma
shows up over back under saddle!
Tx: No cure, debilitating
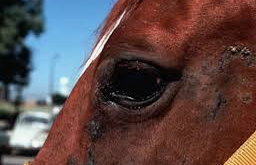
Onchocerca cervicalis
Et: Nematode infection
Adult female in ligamentum nuchae, microfilariae in SQ q 4m
Transmitted by Culicoides gnats
Sig: Adult horses
Cs: Dermatitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, blepharitis, chorioretinitis, alopecia, scaling/crusting, depigmented limbus, “bulls eye”, non-pruritic, ocular pain
Seasonal ventral midline + periocular + ocular lesions
Dt: Positive saline prep or biopsy, response to tx
Tx: Ivermectin
Not effective against adult females
Mild side effects fever and swelling → Pre-treat with NSAIDs
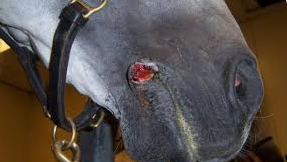
Habronemiasis (Summer sores)
Et: adult stomach worm(wall), passed in feces → fly intermediate
Larvae deposited on moist tissues → penis + medial cantus
Cs: nodules with granulation tissue & yellow “sulfur granules” necrotic center; commonly penis/urethral process, medial canthus
Dt: Histopath (eosinophils, mast cells, granulation tissue)
Tx: Ivermectin, steroids
Aka → Kill larvae/adults, control flies, reduce inflammation
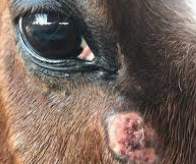

Thelazia lacrymalis
Et: Eyeworm of horses of all ages
transmitted by Muscid & fruit flies
lives in conjunctiva + nasolacrimal system
Sig: all ages
Cs: Mucoid discharge, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis, dacryocystitis, nasolacrimal duct obx!
Often asymptomatic or mild eye irritation
Dt: Adults visible on cornea/fornix or in nasolacrimal wash cytology
Tx: Manual removal, irrigate, retrograde flush, multi day fenbendazole, topical organophosphates!!!!
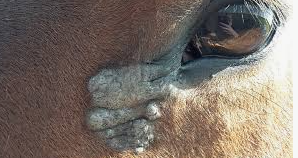
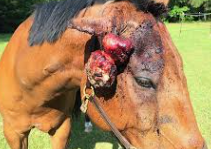
Sarcoids
Et: bovine papillomavirus + wound + genetics
#1 skin tumor!!!!
Locally invasive fibroblastic tumor
Cs: nodules → face, periocular, ears, neck, genital, distal limbs
Can compromise fxn → welfare issue
Dt: clinical presentation, excisional biopsy
Wide excision →Take everything or nothing
Tx: complete wide Sx removal/debulking, injection cisplatin or cryosurgery(adjunctive w/ sx), BCG injection (facial/ocular), benign neglect, no biopsy!
No curative therapy and high recurrence
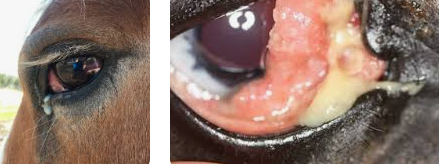
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Ocular and genitals areas most common
Et: #1 malignant tumor
Locally invasive, slow metastasis!!
Sig: Appaloosa, Paint, Clydesdale, Belgian
Colour dilution
Cs: Nodules of non-pigmented + mucocutaneous areas
eyelids, third eyelid, limbus, genitals, lips, muzzle
Tx: UV masks, wide excision (curative), enucleation, posthectomy, ± local chemo
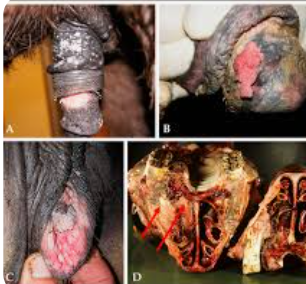
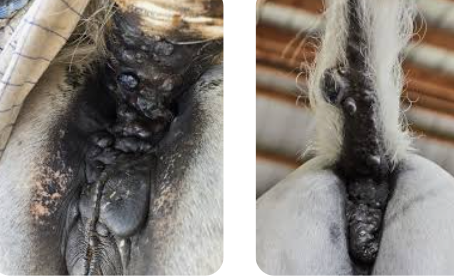
Equine Melanoma
Et: Genetic, slow growing, 2/3 mets later in life
Melanocytic nevi: small flat, superficial, benign, “birthmark”
Dermal melanomas: solitary, pigmented nodules in dermis
Dermal melanomatosis: multiple confluent nodules, gray horses
Anaplastic malignant melanoma: aggressive, non-gray horses, RARE
Sig: gray/white horses >15y
Cs: nodules on ventral tail, perianal region, parotid gland, periocular, genital
Tx: Benign neglect #1, sx excision/debulking w/cisplatin(problematic ones)
Px: Recurrence common

Cutaneous Lymphosarcoma
Genital masses
Et: B, T, or mixed cell types
Cs: subcutaneous nodules, rarely metastasize, benign
Slowly progressive; sometimes progestin responsive
Tx: sx excision ± w/ local chemo
Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis (HYPP)
Et: Na⁺ channel mutation → muscle excitability
autosomal Dominant trait
Sig: QH, Paint, Appaloosa breeds, “Impressive” bred horses
Cs: intermittent episodes muscle twitching, muscle dimpling, 3rd eyelid prolapse, weakness, recumbency, resp distress, hyperkalemia
spontaneous Episodic → triggered by stress or excitement.
Dt: Genetic test, ↑ K
Tx: (Acute)dextrose, ↑Ca, ↑ bicarb, acetazolamide, thiazide
avoid K-rich feeds and alfalfa
Sodium Deficiency
Muscle cramping
Dietary
Et: Inadequate intake, sweating loss
Sig: Performance horses
Cs: Stiffness, cramping, rhabdomyolysis
Tx: Feed loose salt, supp electrolytes
Exhausted Horse Syndrome
Et: Prolonged exercise, dehydration, electrolyte loss
Sig: Endurance/working horses → lost though sweat
Cs: Hyperthermia, ileus, metabolic alkalosis, cramping, rhabdomyolysis
Thumps → synchronous HR + diaphragmatic contractions
Dt: ↓ Ca, ↓ K, ↓Cl
Tx: fluids, electrolytes, proper conditioning, salt supp, common sense
Mild = self limiting
severe = emergency
Hypocalcemic Tetany
Muscle cramping
Clinical hypocalcemia (<8mg/dl)
Et: Lactation, transport, blister beetle toxicosis, exhaustion
Cs: Severe hindquarter crampingDt: ↓ Ca
sync diaphragm flutter: “Thumps” → diaphragm contracts in sync w/ atrial depolarization
Tx: IV Ca gluconate infusion
slowly and monitor heart rhythm
Otobius megnini
Ear tick → Muscle cramping
Et: Spinous ear tick
Larval stages infest external ear canal
Cs: Head shaking, intermittent cramping & elevated CK(rhabdo), fasciculations, recumbency
Intermittent
Tx: Local TX: Pyrethrins, piperonyl butoxide, acepromazine(acute)

Rhabdomyolysis
Muscle cramping
Et: Skeletal muscle breakdown → myoglobinuria(red urine)
Sporadic Exertional “tying up”: Poor conditioning, electrolyte imbalance, CHO excess → excessive exercise
Recurrent Chronic Exertional: Abnormal Ca regulation, high strung racehorses
Cs: Firm painful muscles, crampling, pain, anxiety, sweating, pigmenturia, stiffness, myoglobinuria
“Tying-up”
Dt: ↑ CK, ↑ myoglobin, muscle biopsy(chronic)
Watch for AKI → #1 risk
Tx: Stop exercise!!, sedate,IV fluids, NSAIDs, diet
↑ fat + ↓ low starch feed
gradual return to work→ hand walk 2-3w
** E. Influenza and EHV1 can cause muscle stiffness and rhabdo **

Polysaccharide Storage Myopathy (PSSM)
Glycogen storage disease
Type 1 → Young QH & Draft horses
Et: GYS1 mutation
Cs: recurring rhabdomyolysis, draft horse →weakness
Dt: ↑ CK, genetic test, amylase-resistant glycogen m. biopsy
Tx: ↑ fat + ↓ low starch diet, consistent exercise
Type 2 → Adult/mature warmbloods
Et: unknown
Cs: chronic stiffness, exercise intolerance, gait abnormalities, gradual muscle loss
Dt: breed & history, ↑ CK
Type 1: genetic test
Type 2: muscle biopsy→ amylase-sensitive glycogen
Tx: ↑ fat + ↓ low starch diet, consistent exercise
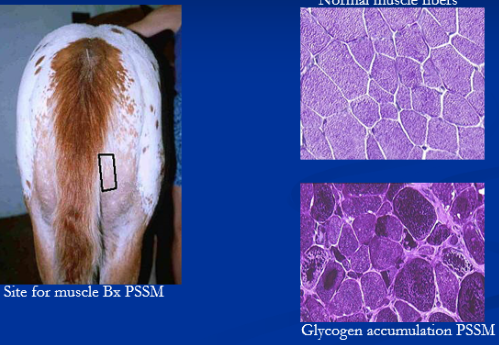
Equine Myofibrillar Myopathy (MFM)
Et: Myofibril disorganization and desmin + glycogen accumulation
Sig: Arabians, WB
Cs: Rhabdomyolysis(arabians) or muscle atrophy(WB)
previous dx RER(arabians) or PSSM2(WB) may be MFM, desmin staining
Dt: Biopsy
Tx: Supportive, consistent exercise, diet
Malignant Hyperthermia
Et: RYR1 mutation, autosomal dominant
Sig: QH
Cs: anesthesia: ↑ Temp, rigidity, acidosis, exertional rhabdomyolysis = fatal
After anesthesia and exertion → fatal rhabdomyolysis
Dt: Genetic test of blood/hair roots
Tx: cooling, avoid triggers
Post-Anesthetic Myopathy
Complication of general anesthesia
Non-exertional rhabdomyolysis
Et: Ischemia from prolonged recumbency or hypotension during surgery with inadequate padding/protection
generalized form: PSSM, Malignant hyperthermia
Cs: Muscle pain, swelling in triceps/quadriceps/gluteals
Localized into muscles contacting table
Tx: fluids, DMSO, NSAIDs, weight bearing support
Emergency treatment
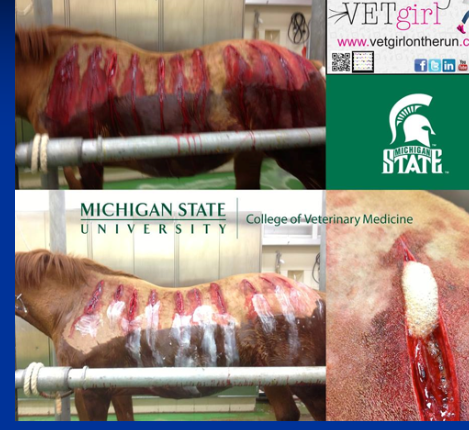
Clostridial Myonecrosis (Gas Gangrene)
Iatrogenic most often (IM injections, NSAIDS, vaccines)
Et: C.perfringens type A, anaerobic infection causing necrosis and gas production(gas gangrene)
post-injection → NSAIDs or Vax
Cs: Painful swelling, gas, toxemia
Rapid progression
Dt: Smear/culture
Tx: Fluids, fenestrate tissues, ventalate, penicillin, metronidazole
Aggressive emergency treatment
Px: Guarded
Infarctive Purpura Hemorrhagica
Et: Ab-mediated vasculitic myopathy
Post-strangles horses
Cs:severe Pain, swelling, rhabdomyolysis, recumbency, myositis
Located in large muscle
Dt: history and CS, dramatic ↑CK, ↑ M protein antibody
Tx: Steroids, fluids, antibiotics
Px: guarded to poor
Myosin Heavy Chain Myositis
Et: mutation in MYH1
Triggered by strangles or anaplasmosis or vax
Sig: QH
Cs: Rapid(days) gluteal/epaxial atrophy,
fatal non-exertional rhabdomyolysis → w/ active strangles, anaplasmosis infections
Dt: ↑CK without vasculitis, biopsy, genetic testing
Tx: Corticosteroids: responds well
Px: Guarded
Toxic Myopathies
Et: Ionophores,
Box elder seeds “seasonal pasture myopathy”
Cs: acute rhabdomyolysis, myocarditis, death
Box elder → seasonal pasture myopathy
Px: Guarded
White Muscle Disease
Et: Selenium deficiency
Sig: Foals, Se-poor soil
Cs: Skeletal stiffness, weakness, myoglobinuria, acute death
2 forms: Skeletal muscle + cardiac form
Dt: ↓ Se, ↑ CK, biopsy
Tx: Skeletal: supportive + Selenium injection
Cardiac: poor/grave prognosis
Vitamin E–Responsive Myopathy
Et: Vitamin E deficiency
Cs: Weakness, gradual muscle loss, trembling, poor performance
Dt: Biopsy sacrocaudalis dorsalis medialis muscle
Tx: Supp Vitamin E
Glycogen Branching Enzyme Deficiency
Et: GBE1 mutation
autosomal recessive
Sig: QH neonatal foals
Cs: Weakness, seizures, recumbence, fatal
Dt: Biopsy, genetic test → post mortem
Tx: Euth or death
General Principles of Emergency Management of Fractures
Gain control & calm horse
Initial exam determines
Nature of injury, Feasibility of treatment
Immobilize limb, address pain & infection
Splint, antibiotics (open wound), tetanus toxoid, Pain meds
Transportation
Hind limb fractures face forward
Forelimb fractures face backward
Splinting Techniques
Use: ↓ soft tissue damage, allows weight bearing, ↓ swelling/pain
Methods: Modified Robert Jones bandage + external support(split)
RJB = many layers of cotton + brown gauze + elastic tape
Modified RJB uses less padding; bulky bandage can impede movement and cause displacement
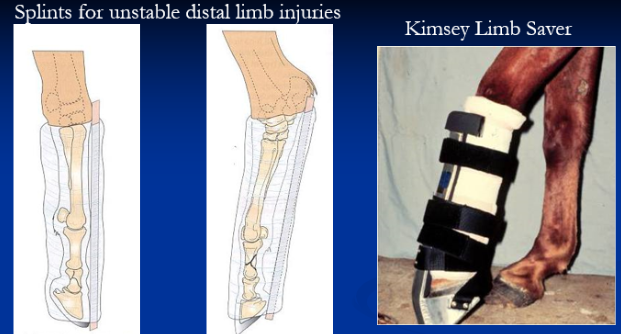
Distal Limb Splints
Et: Injuries between distal phalanx & distal cannon
Division 1 fractures: P1, P2, distal MC/MT
Luxations of fetlock & pastern
Complete Flexor tendon lacerations
Suspensory apparatus breakdown
How: fix phalanges in frontal plane with cannon bone
Mod. RJ bandage with rigid support, kimsey limb saver

Forelimb Fractures Splints
Division 2 fractures: Distal cannon & distal radius
Modified RJB + 2 splints → elbow to ground
Division 3 fractures: Mid-Radius to Elbow
RJB + two splints
Caudal splint ground to elbow
Lateral splint extends to mid scapula
Olecranon
Support carpus in extension
Humerus & scapula
Protected by muscle; no splint practical
Carpal extension bandage possible
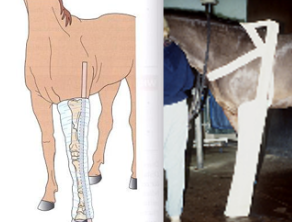

Splinting Hind Limb Fractures
Mid-cannon to hock: division 2
Extend padding above hock and lateral splints proximally
avoid excessive padding
Wooden wedge on foot helps align phalanges
Tarsus & tibia: division 3
Difficult to stabilize
Lateral splint extends to tuber coxae
Femur: division 4
No splint needed
Methods of Fracture Repair
External coaptation
Fiberglass casts: limited to below mid-radius/tibia
risk of cast sores
External fixation: foals/ponies, mandibular, metacarpal, metatarsal, radius, and tibia fractures
Internal fixation
Lag screws & plates: accurate reduction critical
Cancellous bone grafting
Nunamaker device: for comminuted phalangeal fractures
Post-operative Care
Extended convalescence
Pain management & nutrition
Physical therapy:
Controlled exercise, manipulation, hydrotherapy, electrical stimulation
Complications: GI problems(colic), support limb laminitis, repair breakdown, delayed/non-union, cast sores
Osteomyelitis
Inflammation of the bone due to infection
Open fractures, sequestrum, hematogenous
Focal traumatic - sequestrum
Et: Detached cortical fragments → infected → sequestrum
Cannon, splint, P1, P2, radius tibia
Cs: Draining tract
Tx: removal & curettage
Septic - open fracture
Cs: may lead to failure
Hematogenous- FPT / sepsis foals
Cs: Osteomyelitis, physitis, septic arthritis
Tx: curettage, limb perfusion, lavage
Px: Guarded
Tendons & Ligaments Anatomy
Both attached to periosteum of bone, near joint capsule
painful injury!!→ digital flexor and navicular bursae
Tendons: connect muscle to bone
Type I collagen bundles → high tensile strength
Longitudinal orientation
ECM of proteoglycans → tenocytes
Allow stretch during flexion and extension
Ligaments: connect bone to bone
Dense bands of collagen
Collateral, interosseous, intra-articular types
Suspensory apparatus: supports distal limb
Tendon Injuries
Et: Overstretching or Infection
Attached closely to periosteum near joints
Heal slowly! prone to reinjury
Cs: Acute lameness, heat, swelling, pain on palpation
Dt: US
Tx: Cold therapy, NSAIDs, support wraps, rest and gradual exercise/return, PRP, stem cells
Contaminated tendon sheaths + navicular bursa = medical emergency
Traumatic Arthritis
Path: Final common pathway of articular injury → Progressive cartilage loss, irreversible
Et:
Type 1: chronic strain, “Wear and tear”
chronic low grade synovitis
Type 2: acute injury
acute synovitis
Cs: Pain, lameness, synovial effusion
Dt: lameness exam, nerve block localization, Imaging, fluid analysis 10-30,000 WBC/μl
Type 1: mild effusion, no bony lesions
Type 2: fragments, fracture lines, marked effusion
Tx: Rest, NSAIDs, cold therapy (acute), intra-articular steroids + HA, casts, Arthroscopy, Arthrodesis
avoid steroids with fractures
Px: Irreversible
collateral ligament injury = guarded
Septic Arthritis
Et:
Hematogenous infection → FPT foals
Penetrating or Iatrogenic wounds
Cs: Pain, non weight baring lameness, marked synovial effusion
Dt: lameness exam, nerve block localization, Imaging, fluid analysis 30-50,000 WBC/μl
Severe joint distention and destruction
Tx: Irrigation, curettage, antibiotics
Joint contamination = emergency
avoid steroids with sepsis
Px:
Poor: multiple septic joints or physes
Ok: <2 appendicular joints
Developmental Arthritis
Et: Osteochondrosis and angular limb deformities
Articular and physeal cartilage defects
Cs: Pain, lameness, ↓ ROM
Progressive
Dt: lameness exam, nerve block localization, Imaging, fluid analysis
Sclerosis, lysis, narrow joints spaces, minimal effusion changes
Tx: Rest, NSAIDs, intra-articular steroids + HA, Arthroscopy, Arthrodesis
Irreversible
Specific Arthritis Medications
NSAIDS
Use: Mainstay treatment
Types:
Phenolbutazone → Firocoxib
Topicals → Diclofenac + DMSO
Intra-articular steroids
Use: suppress inflam
NOT fractures or sepsis
Types: Triamcinalone + HA (unsulfated GAG)
Congenital flexure deformity
“Contracted tendons”
Genetic, rapid growth leads to crowding/malposition in utero
Distal interphalangeal joint (DDF)
forelimbs and bilateral
CS: Clinically obvious
TX:
Mild: spontaneous
Mod: splints 7-10d
Severe: sx
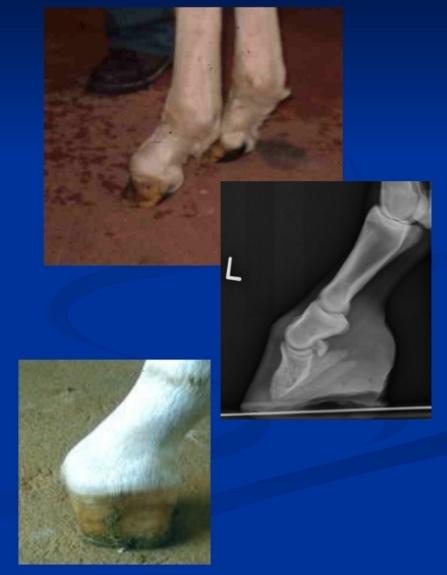
Club foot
Et: Deformities in coffin joint (DDF) and fetlock(SDF)
tendons don’t stretch
Acquired flexural limb deformities (DDF contracture) 6w-6m
Rapid growth of MC3 + radius → steep dorsal hoof wall → Heal grows boxy
Cs: ↓ weight bearing, boxy foot, Steep hoof wall, high heel, worn toe
Tx: early intervention, ↓ feed, correct Ca:P ratio, sx check lig desmotomy
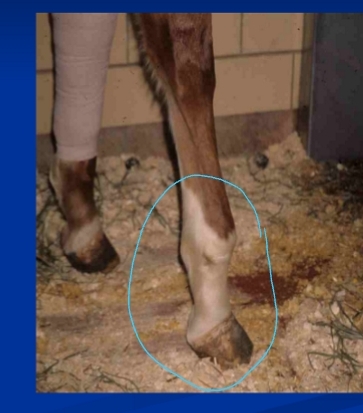
Fetlock Contracture
SDF contracture
Et: Acquired flexural limb deformities → rapid growth, pain, inactivity
Continued growth of radius
Sig: Yearlings
Cs: Upright pastern, ↓ weight bearing, Physeal Dysplasia, Osteocondrosis
Tx: early intervention, ↓ feed, corrective trimming, sx superior check lig desmotomy
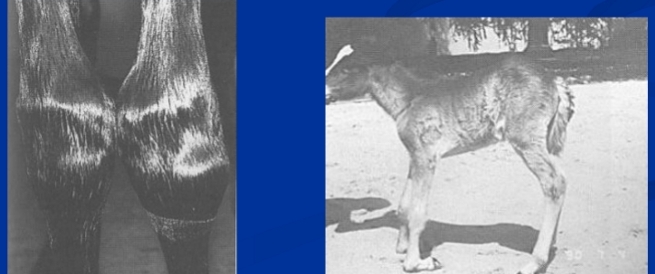
Common Digital Extensor and Extensor Carpi Radialis Rupture
Et: Congenital flexural deformity
Extensor tension
Common Digital Extensor = bilateral
Cs: Knuckling
Tx: splint 2-4 wks
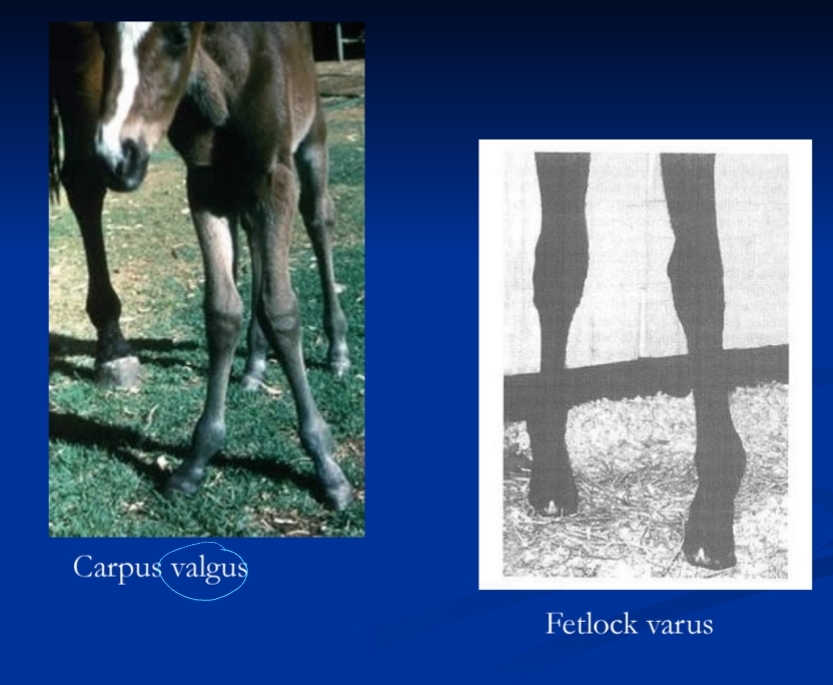
Angular Limb Deformities
Et:
Congenital: lig laxity, overfeeding late preg, malposition, incomplete ossification
Acquired: physeal dysplasia, trauma, overfeeding, contralateral lameness
Cs: deviation, joint laxity
Lateral (valgus) or medial (varus)
Tx: Correct before physeal closure
Mild: Self limiting, rest, ↓ feed, trimming, splints
Severe: physis changes, >15o deviation → surgical correction
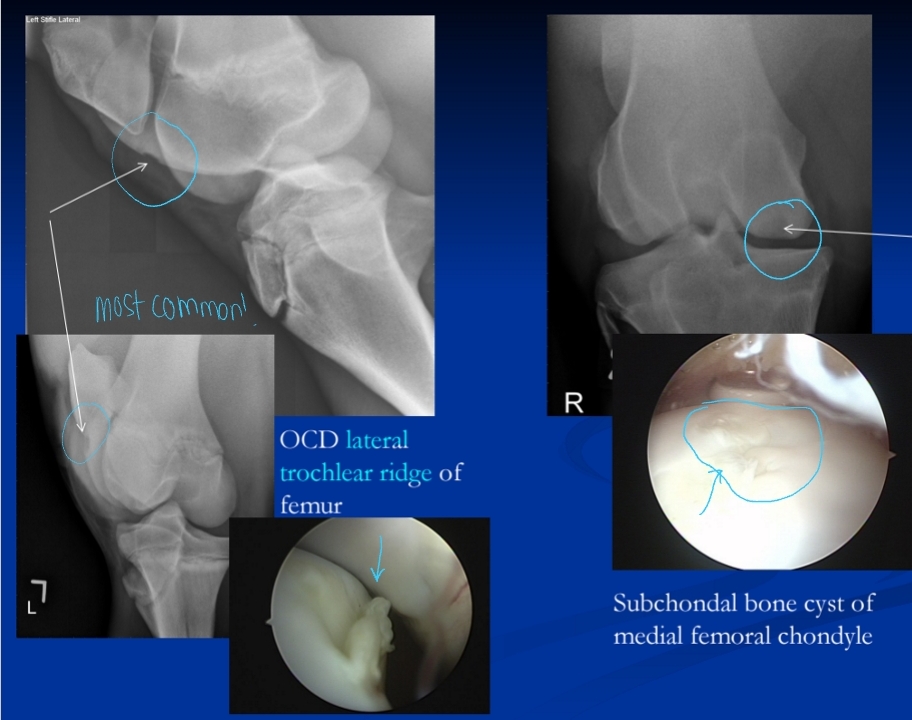
Osteochondrosis
Et: Defect in articular cartilage and subchondral bone
genetics, rapid growth, Ca:P imbalances
Thick cartilage + delayed ossification → soft cartilage, focal necrosis
Cs: Effusion, lameness, arthritis, physeal dysplasia, OCD, subchondral cysts, angular limb deformities, cervical stenotic myelopathy
Stifle > hock > fetlock > shoulder
Dt: Rads
Tx: Rest, ↓ feed, 2:1 Ca:P ratio, NSAIDs, arthroscopic debridement
Subchondral Cystic Lesions and Osteochondrosis Dissecans (OCD)
Et: Osteochondrosis lesion
genetics, rapid growth, Ca:P imbalances
Sig: Young, TB, QH, male
Common
Cs: Effusion, lameness
Stifle > hock > fetlock > shoulder
Dt: Rads
Tx: Arthroscopic debridement, ↓ feed, 2:1 Ca:P ratio
Physeal Dysplasia (Physitis)
Et: Enlarged growth plate of long bones
Osteochondrosis lesion
genetics, rapid growth, Ca:P imbalances
Sig: Foals 2-18m
Cs: Physeal swelling, pain, mild lameness, metaphyseal flaring, angular limb deformities, fetlock contracture
Distal metacarpal, metatarsal 3, proximal pharynx 1, distal radius, distal tibia, vertebral bodies
Dt: rads
Often bilateral, check both limbs
Tx: Time, Correct diet, rest, manage pain
Transient in mild cases
General lameness
forelimb lameness (75%)
below the carpus in 95%
Hindlimb lameness
hock and below
Foot is most common
Lameness Signalment
Neonatal foals: hematogenous septic arthritis, dev orthopedic disease
Weanlings, yearlings: dev orthopedic disease, osteochondrosis
2-yr-olds in training: bucked shins, splints, bowed tendons, suspensory problems
“too much too soon”
Adults: navicular, laminitis, arthritis
TB racehorses: arthritis, fractures, suspensory lig & sesamoid injuries, carpal chips, hyperextension injuries
STB: rear limb fractures, bowed tendons, suspensory/sesamoids, myositis, sore backs
Western: ringbone, bone spavin, navicular, phalangeal fractures
Hunter-jumpers: ringbone, suspensory injuries, back & SI problems
Lameness Exam
Observe at rest
Weight shifting in front is abnormal
Palpate limbs for swelling, heat, or pain → start at foot and work proximal
Foot most common site
Observe at walk and trot → straight line and circles
Turning accentuates lameness on the inside limb
Forelimb lameness: #1
Head bob → down on sound
Choppy gait → bilateral lameness
Hindlimb lameness: hip hike
Perform flexion tests, hoof testers, and limb manipulation
Apply even pressure across hoof wall, sole, frog, heels → observe reaction
Flex joint 60sec → trot horse off → increase in lameness = positive
Intrasynovial or Perineural blocks
Block nerves from distal to proximal to isolate pain source → evaluate gait 10min pre + post-block
Normal horse Posture and Gait
Standing: stand square, only hind end shifting
Front end shifting is abnormal
Stride: breaks over toe, smooth, heel before toe, foot lands square
Grading Lameness
0 = Not lame
1 = Not lame on straightaway, inconsistent on turn
2 = Inconsistent on straightaway, consistent on turn
3 = Lameness consistent on straightaway & turn
4 = Obvious lameness at walk
Sole bruise, abscess, sepsis, laminitis, acute trama
5 = Non-weight baring
Sole bruise, abscess, sepsis, laminitis, acute trama
Limb Blocks
Start distally then move up the leg
Palmar Digital Block: Desensitize heel region, navicular area, frog, digital cushion (foot)
Inject lateral and medial palmar digital nerves at collateral cartilage level
Abaxial Sesamoid Block: Desensitize foot + pastern
Inject at base of sesamoid bones, medial and lateral
Low Palmar (Low 4-Point) Block: Desensitize fetlock and distal limb
Inject lateral/medial palmar nerves and palmar metacarpal nerves distal to buttons of splint bones
Intrasynovial: desensitize joint
intra-articular, tendon sheath, navicular bursa
Risk of infection
Specialized Orthopedic Imaging
Radiographs: Primary means of imaging bones & joints
MRI: Soft tissue imaging
Scintigraphy: Identify lesions not visible on x-rays → stress fractures
Nuclear medicine → technetium-99, gamma camera
US: Soft tissue → tenons + lig
Thermography: Detect abnormal surface temp
Hotspots → inflam
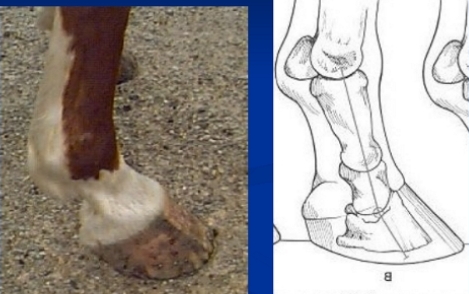
Heel Abnormality's
Under-Run Heels
Et: Long Toe–Low Heel → improper trimming, inactivity
Cs: “Broken back” hoof < pastern axis, white line separation, heel bruising, arthritis, suspensory + coffin joint strain
Tx: corrective trimming
Short Toe-High Heel
Cs: hoof > pastern axis, chronic sole bruising, arthritis, suspensory + coffin joint strain
Tx: corrective trimming
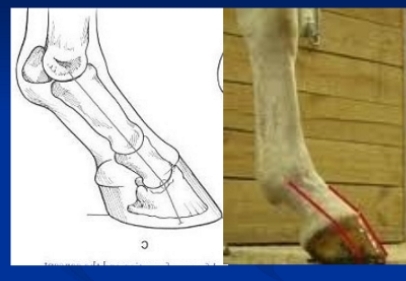
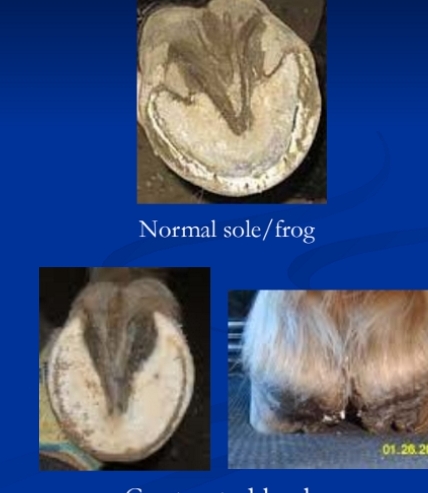
Heel issues
Contracted Heels
Et: Immobility → pain, no exercise
Cs: Narrow heels, recessed frog, concave sole, ↓ weight baring
Tx: Exercise, corrective shoeing
Sheared Heels - uneven heels
Et: 1 longer heel bulb displaced upward → improper trimming,
Cs: pain, bruising, cracks
Tx: Balance trim, full bar shoe

Underdeveloped hooves
Flat Feet
Et: Lack of concavity
Sig: Draft breeds
Cs: Bruising
Thin Sole and Wall
Et: Inactivity and genetic
Cs: Bruising, pedal osteitis
Dt: Hoof tester
Tx: Protective shoes/pads, diet
Hoof Wall Incongruity
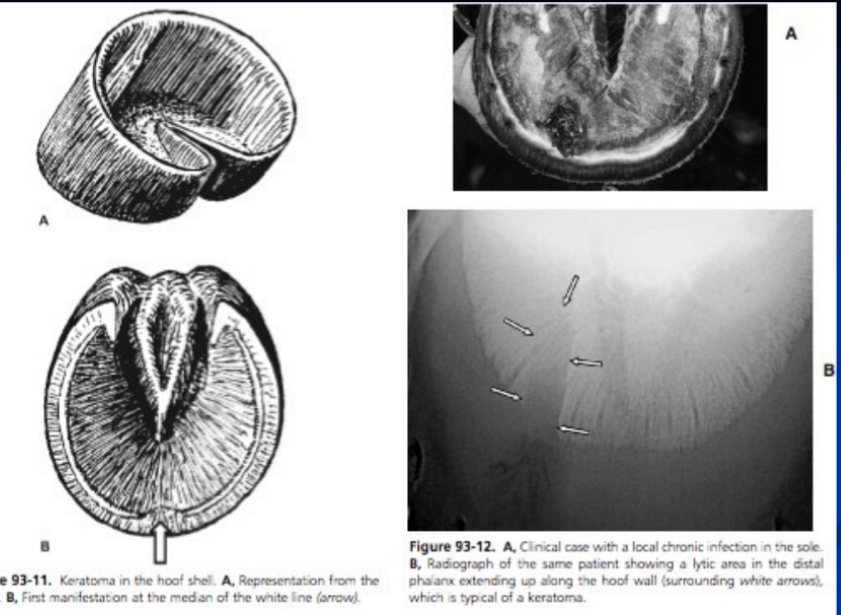
Keratoma
Et: Hyperplastic keratin mass in hoof wall
Grows down inner hoof wall
Cs: Hoof deformity, white line distortion
Dt: Rads
Tx: Sx removal
Hoof Cracks
Et: Dry hooves, poor trimming

Hoof Wall Trauma
Avulsion
Et: disrupts germinal epithelium
Tx: remove separated segment, bandage, protective boot
Coronary Band Laceration
Cs: hoof defects
Dt: evaluate DIP
Tx: Must suture, slipper cast
Heel Laceration
Tx: suture, bandage, slipper cast
Puncture
Et: Sharp metal object → nails
Cs: Lameness, pain, inflammation, infection, digital pulse
Dt: Hoof testers, rads
Tx: Poultice, tetanus toxoid, clean, Sx lavage + antibiotics
frog puncture = emergency = Surgical, check for synovial involvement!! to avoid (septic DIP)!!!!!
Px:
Good: Subsolar
Poor: Frog, DIP, navicular bursa, flexor sheath, sepsis
Inflammation of the external hoof structures
Coronitis
Et: Inflam of coronary band
pemphigus, idiopathic, systemic dz, laminitis
Cs: Wall separation + sloughing
Sole Bruising
Et: Hard ground, thin soles, stones, over-trimming
Cs: Hematoma, sole abscess, pedal osteitis, ↑digital pulse
Dt: Hoof testers
Tx: Pare out sole, remove shoes, cold therapy, NSAIDS, rest, pads
Infection of the Hoof
Thrush
Et: Horn + sulci infection → Wet ground, recessed frog
Cs: Black, foul-smelling exudate
Tx: Debride, dry enviro, clean
Canker
Et: Chronic hypertrophic infection of Frog’s germinal epithelium
Sig: Draft horses, humid enviro
Cs: Odorous, caseous discharge, of the hind feet
Tx: Sx debridement, antibiotics, bandage, dry enviro
Quittor
Et: Infection/necrosis of collateral cartilage
heel laceration, overreaching, abscess extension
Tx: Surgical debridement
Hoof abscesses
Subsolar Abscess
Et: Sole bruise, FB, misplaced nail, laminitis
Cs: grade 4-5 lameness, digital pulse
Dt: Hoof testers, rads
Tx: Debride, ventral drainage, soaks, antiseptic, tetanus toxoid, NSAIDs
Subdural Abscess “gravel”
Et: Infection ascending through white line to coronet
Puncture, chronic lamanitis
Dt: rads
Tx: Ventral drainage, antibiotics

Laminitis
Et: Inflam of laminae → P3 rotation
Systemic illness → Endotoxemia, colitis, endometritis, shock, EMS, PPID, trauma, toxins, grain overload
Acute CS: pain in all four feet, shifting weight, bounding pulses, laminitis stance, heel-loading choppy gait, bulging of sole
Chronic CS: Abnormal hoof growth, bilateral forelimb lameness
Dt: toe sensitive to hoof testers, rads with P3 rotation
Tx: Cold therapy (dev phase), NSAIDs, sedation, Corrective trimming (lower heel + shorten toe + pads), dietary management
Acute = medical emergency
Px: potentially life + career ending
Mild → no chronic changes
Severe → chronic bilateral forelimb lameness


Pedal Osteitis - traumatic + septic
Et: Repeated bruising, thin-soled, laminitic horses
Cs: Chronic bilateral forefoot lameness, choppy gait, digital pulse, soreness, heat
Dt: Rads with demineralized P3 solar margin
Septic: extension of sole abscess or direct injury
Tx: Rest, Bute, pads, curettage + antibiotics + sx debridement (septic)
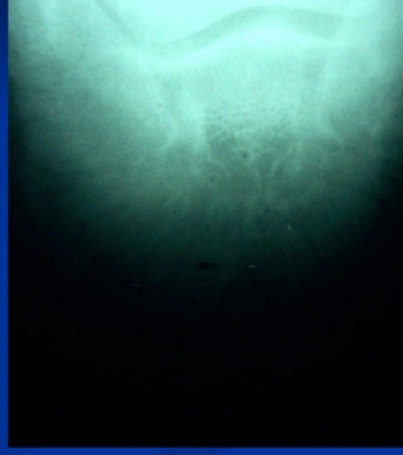
Navicular Syndrome (Podotrochleosis)
Chronic bilateral forelimb lameness “athletes dz”
Et: navicular bone and soft-tissue degeneration, erosion, and lysis
Chronic concussion, poor conformation, unbalanced trimming, repetitive strain
Sig: Middle-aged QH, TB, athletes
Cs: contracted heels, shifting Bilateral forelimb lameness, choppy gait, shortened stride
Dt: Hoof tester pain over ⅓ frog, improvement with heel block, MRI
Tx: Corrective shoeing, trimming (shorten toe, raise heel)
Permanent → no cure
Distal phalanx fracture
uncommon
Most articular
CS: acute bilateral lameness, severe/non-weight bearing lameness, bounding pulse
Dx: radiographs, re-x-ray if negative on the 1st one.
No periosteum, heals w/ fibrous union!
Conservative tx: non-articular
Tx: lag screws, sx removal
OA common sequela from fractures
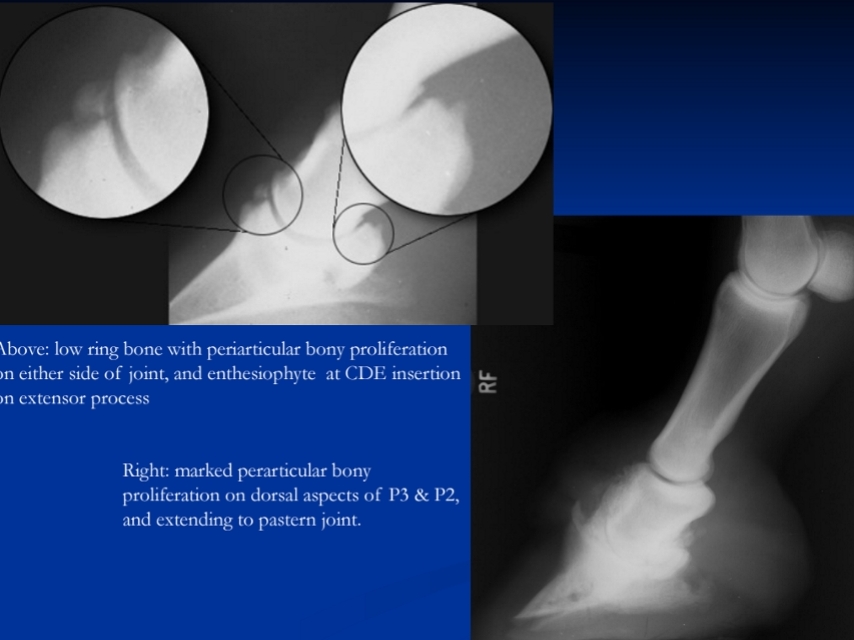
Low Ringbone
Et: Periarticular bony proliferation of DIP joint
Type 1: Chronic synovitis (bilateral)
Type 2: trauma (unilateral)
collateral ligament tear
Cs: Short, choppy bilateral gait, pain on flexion, weight shifting, bone proliferation, joint narrowing
Dt: Rads, perineural + intraarticular anesthesia response
Tx: Rest, NSAIDs, steroids + HA, arthrodesis, neurectomy
Standard arthritis treatments
Synovitis + Capsulitis of the Pastern Joint (PIP)
Type 1: often bilateral
Et: Chronic repetitive impact + lig strain
Sig: QH, polo → quick turns + starts + slides
Cs: Low-grade synovitis, bilateral, Pain on flexion
Dt: Rads to assess OA, improvement with local anesthetic
Tx: rest, cold therapy, NSAIDs
Px: good w/ early tx
Type 2: collateral lig tear
Et: Acute tear of collateral lig, P2 fractures
Sig: QH, polo → quick turns + starts + slides
Cs: synovitis, sprain, joint instability
Tx: rest, cold therapy, NSAIDs, wraps
Px: guarded
Middle phalanx fractures
P2 fractures
Rear limbs of western horses
catastrophic articular fractures
comminuted/caudal, uniaxial, biaxial
CS: hear “pop”, intermediate lameness, crepitus
AVOID nerve blocks
biarticular/comminuted: poor prognosis
High Ringbone
High ringbone OA= distal P1 & proximal P2 bony proliferation
Et: Pastern arthritis
Chronic synovitis or lig injury
bony proliferation, joint space narrowing, sclerosis/lysis, osteophytes
Cs: Chronic bilateral lameness w/ choppy gait, pain on flexion
Dt: rads
Tx: Correct foot balance, rest, IA steroids + HA, Arthrodesis (restore fxn)
Standard arthritis tx
Px: Guarded for performance
Synovitis of the Fetlock
Idiopathic
Cs: Not painful, “windpuffs”
Tx: none
Traumatic
Type 1: “occult osselets” Common Hyperextension, Twisting motions
Type 2: Acute bone + cartilage + lig damage
Cs: Lameness, Effusion, All get arthritis
Tx: early intervention(key), rest, cold therapy, NSAIDs, IA steroids + HA
Px: ok if early, guarded if arthritic
Chronic Proliferative Synovitis (Villonodular Synovitis)
Et: Synovial pinching of synovium → chronic hypertrophy
Cs: Low-grade bilateral lameness, dorsal fetlock enlargement, effusion
Dt: US
Tx: Sx resection of synovium
Suspensory Branch Desmitis *
Et: Injury to the branch
Medial > lateral
Cs: Swelling, lameness, pain
Dt: US of lig, sesamoid rads
Tx: Ice, wrap, NSAIDs, 1y rest
Px: guarded, ↑ recurrence
Osteochondrosis of fetlock (OCD)
Unilateral or bilateral
Medial condyle cannon bone
beneath proximal joint of P1
Tx: removal and debridement till bleeding bone
low 4-point block (improves): IA block specific
P1 dorsal chip and comminuted fractures
Chip:
proximodorsal (OCD) chip fracture
synovitis/effusion
arthroscopic removal
Comminuted: life threatening
Emergency splint or immobilization
Internal fixation required
Distal Sesamoidean Ligament Desmitis
Et: Hyperextension → tearing
Near sesamoid origin
Cs: Pain, Swelling, lameness
Dt: US
Tx: Ice, support wrap, NSAIDs, 1y rest
Px: Guarded, ↑ re-injury risk
desmitis suspensory lig injury: Medial branch
Sesamoiditis
Et: Excessive suspensory pull on immature bone
“Too much too soon” → tear suspensory ligament
Sig: Young athletic horses
Cs: lameness, swelling, enthesiopathy, osteitis
Dt: Rads → periosteal new bone + osteolytic lesions
Tx: Prolonged rest
Px: Guarded
Suspensory Apparatus Failure
Et: Failure of suspensory branches, sesamoids, or DSLs
concurrent phalangeal &/or MC/MT fractures
Sig: racehorses
Cs: Acute non-weight-bearing
Tx: humane euth race horses, arthrodesis (salvage)
Emergency stabilization
Sesamoid fractures
excessive tensile force
Pulls bone apart
CS: acute painful lameness
most are articular
Apical(88%) > basilar > midbody
Sx removal
good: apical/abaxial
Digital Flexor Sheath Tenosynovitis
Idiopathic
Cs: Painless, windpuffs, no lameness
Tx: None required
Traumatic: tears DDF or manica florexia
Et: fetlock + pastern injuries
Dt + Tx: Arthroscopy
Px:
Good = manica flexoria tears
Poor = DDF
Septic
Et: Contamination of tendon sheath
Cs: Marked lameness, Suppurative effusion
Tx: debridement & lavage, antibiotics, regional limb perfusion, annular lig desmotomy
Prompt surgical tx required
Px: Guarded
Deep Digital Flexor Tendonitis (Low Bow)
Et: Traumatic strain/tearing
Crimp of type 1 collagen → scar w/ type 3 collagen
Cs: Acute pain, swelling, hemorrhage, edema
Often concurrent tenosynovitis or PAL constriction
Dt: US
Tx: Aggressive cold therapy 72h, wraps, heel elevation, NSAIDs, annular lig desmotomy, rest for months
Px: Guarded, ↑ recurrence
Palmar/Plantar Annular Ligament Syndrome
Et: Constriction of flexor tendons + digital sheath
Complication of acute DDF tendinosis, tendosynovitis
Tx: relief w/ Annular lig desmotomy
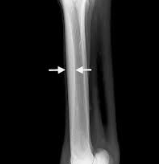
Bucked Shins
Shin splits
Et: Dorsal metacarpal thickening and soreness
Sig: Young, TB (2y)
Cs: Bilateral lameness, Visible dorsal MC enlargement, Heat
Tx: Rest, anti-inflammatories
Px: Good
Cortical fissure fracture: saucer shaped fracture dorsal lateral MC, does NOT enter medullary cavity
CS: lameness, firm swelling, fracture line(xray)
Tx: stall rest 6m, sx if needed(lag screw)
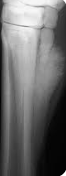
Splints
Et: Exostosis of MC/MT II & IV
Tearing of IO lig → periosteal reaction → new bone formation
Cs:
Acute: variable lameness
Chronic: painless bony enlargement
suspensory desmitis = blind splint
Tx:
Acute: cold therapy, topicals, steroid injection, bandaging, rest
Blind splint: surgical removal of periosteal/bony growth
Cannon Bone Sequestrum + Osteomyelitis
Et: Focal impact injury → cortical fragment death → sequestrum formation
Cs: Draining non-healing wound
Dt: Rads
Tx: surgical debridement and drainage
Suspensory Desmitis
Tramatic
Et: Acute tear at branches or body
Body: secondary to blind splints
Proximal: tear at origin
Cs: Lameness, pain on palpation
Dt: US
Degenerative
Et: Systemic CT disease
Cs: Bilateral, dropped fetlocks, progressive pain
Tx: euth
Inferior Check Ligament Desmitis
Et: Athletic strain
Cs: Palpable painful swelling between DDF and suspensory lig
Dt: Perineural anesthesia, US
Tx: Rest, NSAIDs, controlled exercise
Px: Guarded