Meiosis Quiz
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:19 AM on 1/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Genetics
the study of heredity
2
New cards
Heredity
transfer of traits from one generation to the next
* Parents pass genes to offspring consisting of a specific sequence of DNA in a specific locus
* Passed genes provide code for enzymes or proteins whose cumulative action produces a trait
* DNA passed via gametes
* Parents pass genes to offspring consisting of a specific sequence of DNA in a specific locus
* Passed genes provide code for enzymes or proteins whose cumulative action produces a trait
* DNA passed via gametes
3
New cards
Meiosis (definition)
type of cell division that results in cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell
4
New cards
Asexual Reproduction
1. A single parent passes on its genes; Daughter cells have identical genes as parent cells called clones
1. Only exception is when mutations occur
1. Examples: Hydra (budding); Bacteria (binary fission)
2. **Advantages**
1. Faster; doesn’t require wasting energy on seeking out to find a sexual partner
2. Reproduce when conditions are favorable
3. **Disadvantages**
1. No genetic diversity; if it’s an environment that has changed, it does not have the diversity needed to survive
5
New cards
Genome
all the genes necessary to make an organism
6
New cards
somatic cells
all body cells except sex cells; contain 46 chromosomes in humans
7
New cards
gametes
sex cells which contain 23 chromosomes in humans
8
New cards
homologous chromosomes
pair of chromosomes that contain the same genes in the same loci; pairs of those same genes which code for same trait are called alleles
* exception are the sex chromosomes in males (XY)
* exception are the sex chromosomes in males (XY)
9
New cards
autosomes
all chromosomes other than sex chromosomes
10
New cards
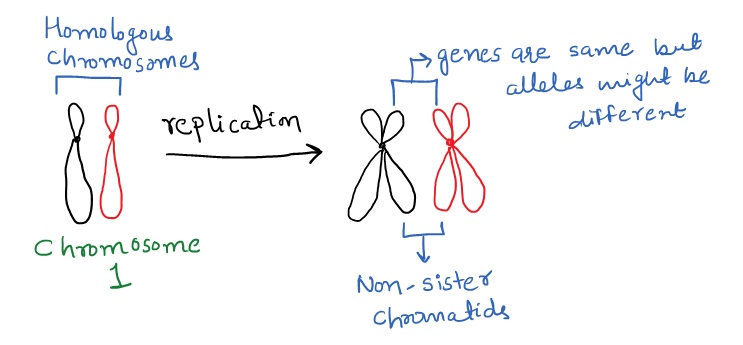
sister chromatids
two identical copies formed by the DNA replication (S phase) of a chromosome
11
New cards
nonsister chromatids
chromosome couples having the same length, patterns and position of the centromere
12
New cards
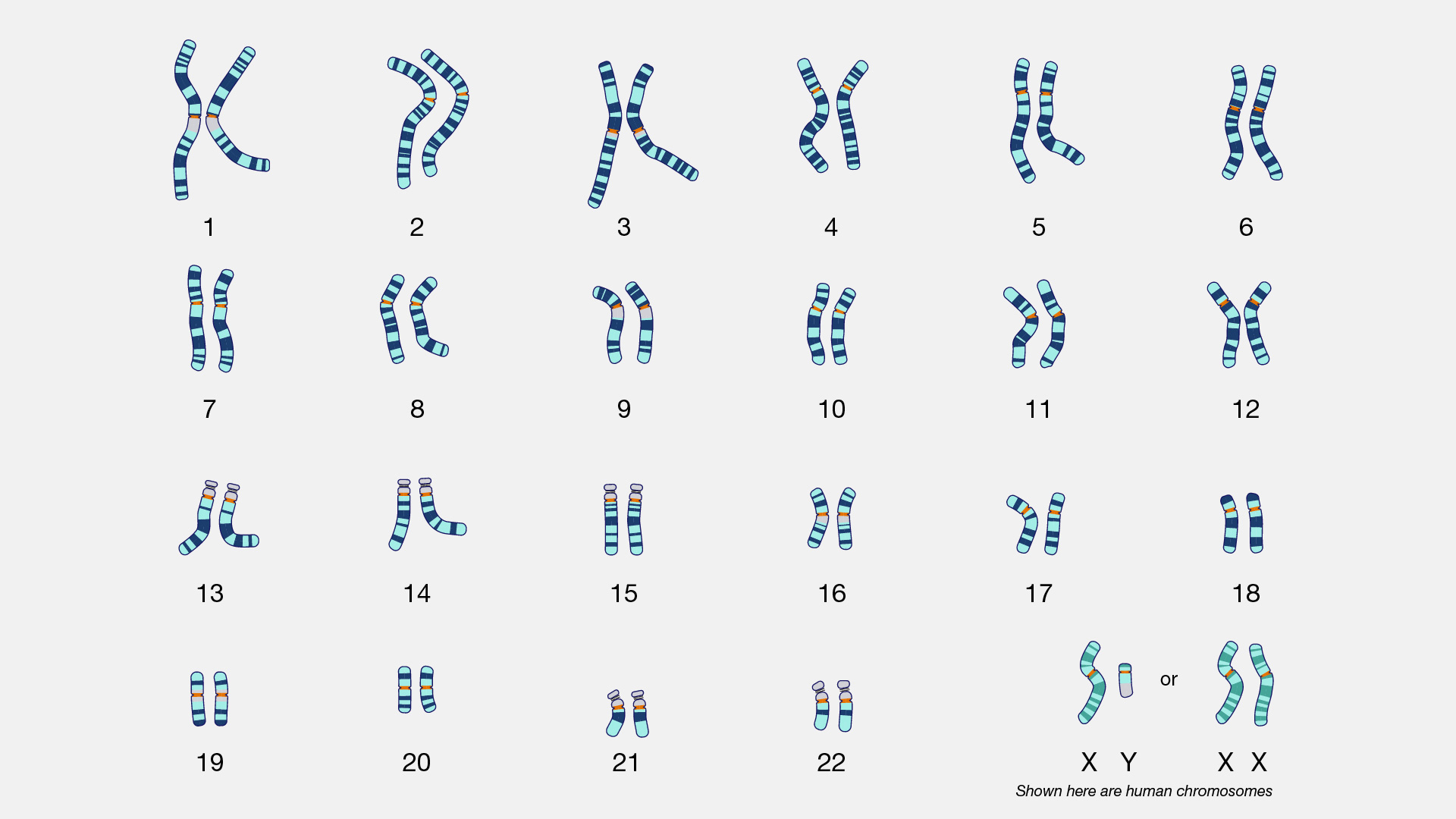
karyotype
an individual's complete set of chromosomes; usually refers to the image
13
New cards
diploid
2n; has two sets of chromosomes
14
New cards
haploid
n; has one set of chromosomes
15
New cards
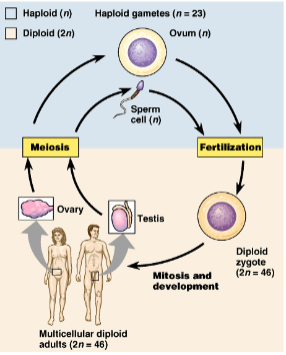
Sexual Reproduction
When 2 individuals contribute genetic material
* Male contributes sperm made in the testis; female with egg made in ovaries
* Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of a somatic cell (**haploid; n**)
* When the 2 gametes unite, fertilization occurs; sperm dumps its nucleus into the egg (**diploid; 2n**)
* Zygote now contains 2 sets of chromosomes
* Zygote grows into multicellular organism through mitosis
* Advantages
* More genetic variation, chose their mate
* the species can adapt to new environments due to variation, which gives them a survival advantage
* Disadvantages
* has to be under specific conditions
* takes longer
* Male contributes sperm made in the testis; female with egg made in ovaries
* Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of a somatic cell (**haploid; n**)
* When the 2 gametes unite, fertilization occurs; sperm dumps its nucleus into the egg (**diploid; 2n**)
* Zygote now contains 2 sets of chromosomes
* Zygote grows into multicellular organism through mitosis
* Advantages
* More genetic variation, chose their mate
* the species can adapt to new environments due to variation, which gives them a survival advantage
* Disadvantages
* has to be under specific conditions
* takes longer
16
New cards
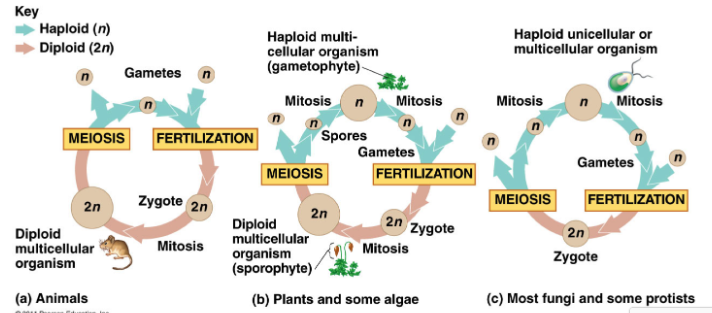
Variation in Sexual Lifecycles
1. **Animals**
1. Two gametes fertilize each other forming a zygote (n + n = 2n)
2. The zygote does mitosis becoming a larger organism
3. The zygote then does meiosis forming gametes
4. Cycle continues
2. **Plants and Some Algae**
1. Two gametes fertilize each other forming a zygote (n + n = 2n)
2. The zygote does mitosis, grows into a multicellular organism (diploid organism called sporophyte)
3. The sporophyte does meiosis and produces spores
4. Spores grow into gametophytes and do mitosis to produce gametes
5. Cycle continues
3. **Most Fungi and some protist**
1. Two gametes fertilize each other forming a zygote (n + n = 2n)
2. Zygote does meiosis immediately (no mitosis)
3. Produces spores that do mitosis and become haploid organism
4. Gametes produced from mitosis
5. Cycle continues
17
New cards
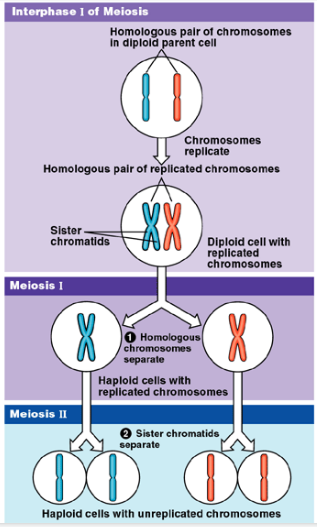
Meiosis (basic overview)
1. Cells start off with two sets of chromosomes
1. Diploid: cells that have two sets of chromosomes
2. DNA replicated; creates two sister chromatids
3. Meiosis I: Homologous chromosomes separated and each goes into daughter
4. Each cell has 1 set of chromosomes
1. Haploid
5. Meiosis II: sister chromatids are pulled apart and each goes into daughter
1. Cells are STILL haploid!!
18
New cards
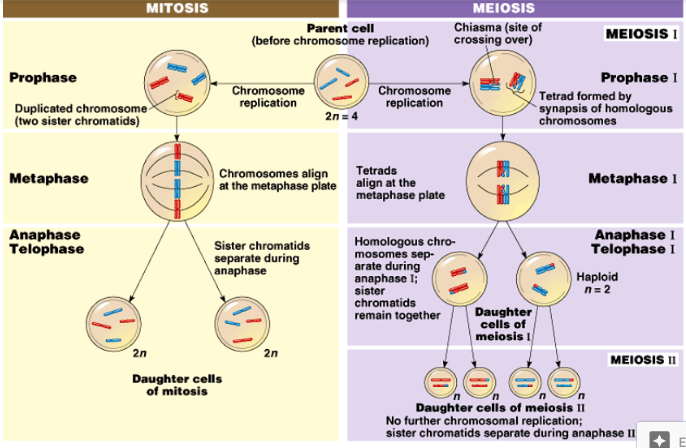
Mitosis
1. S & G2 of Interphase
1. DNA replication (S)
2. Centrosome replication (G2)
2. Prophase
1. Nuclear envelope breaks
2. Centrosomes start to move apart
3. Mitotic spindle starts to form
4. Nucleoli disappear
3. Prometaphase
1. Nuclear envelope disappears
2. microtubules attach to chromosomes and each other
4. Metaphase
1. Chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate
2. Centrosomes are at opposite ends
5. Anaphase
1. Chromosomes are pulled apart
2. cohesion bonds break
3. kinetochore microtubules shorten and pull them apart
4. Cell elongates as nonkinetochore microtubules elongate
6. Telophase
1. 2 nuclear envelopes form creating 2 nuclei
2. nucleolus reappears
3. Remaining spindle is depolymerized
4. chromosomes begin to uncoil
5. contractile ring (actin+myosin) shrinks and pulls membrane inward
6. Cells separate
19
New cards
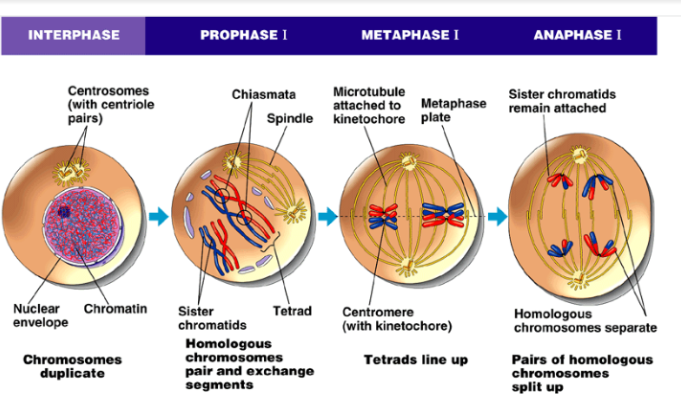
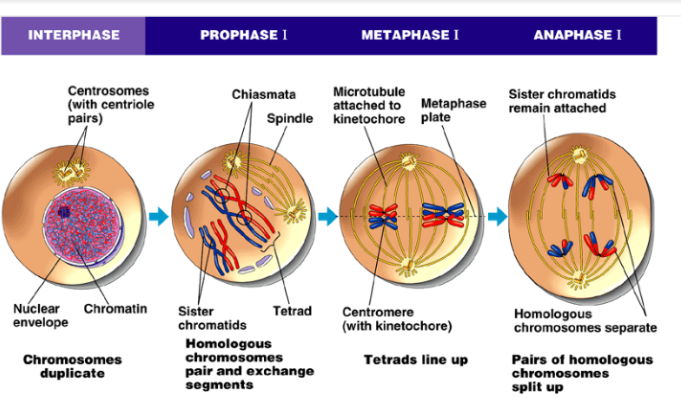
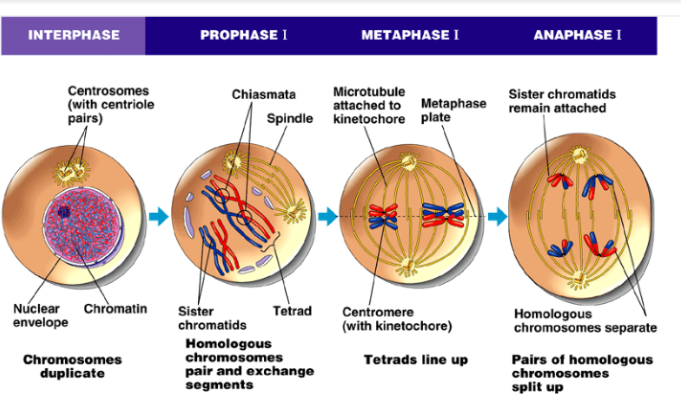
Prophase I
1. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
2. Homologous chromosomes some into contact and match up
1. Synaptomeal complex holds them together
2. **Synaptonemal complex** is protein structure that pairs chromosomes up alone their entire length
3. Crossing over
1. **Synaptonemal complex** is broken down, but homologous chromosomes still attached because of cohesions with sister chromatids
2. Chiasmata: location where crossing over occurs
4. Other Events
1. Spindle starts to form
2. Centrosomes move apart
3. Nuclear envelope breaks down
4. Spindle attaches to chromosomes
20
New cards
Metaphase I
1. Homologous chromosomes (tetrads) line up on plate, one pair one each side
1. Tetrads: 4 chromatids
21
New cards
Anaphase I
1. Cell elongates from spindle
2. Homologous Pairs are pulled apart
22
New cards
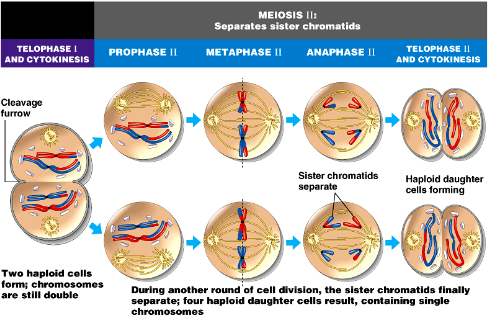
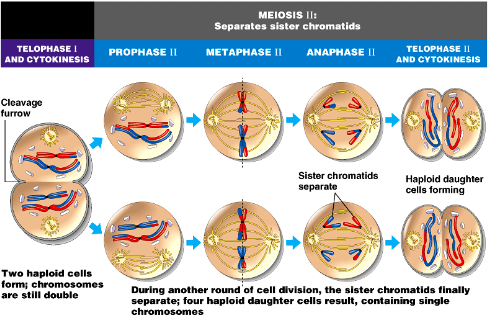
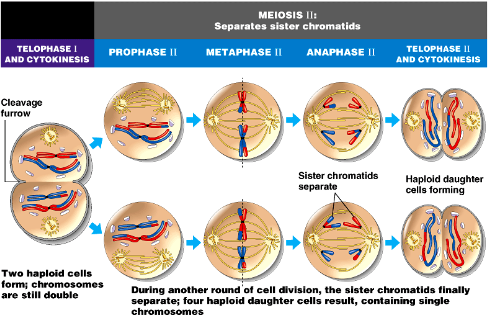
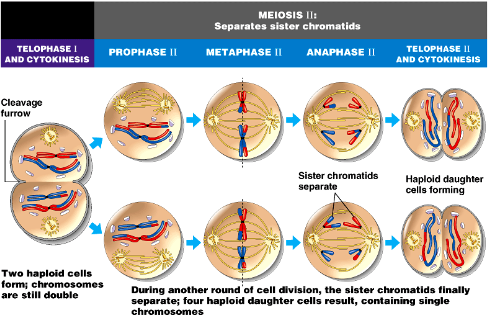
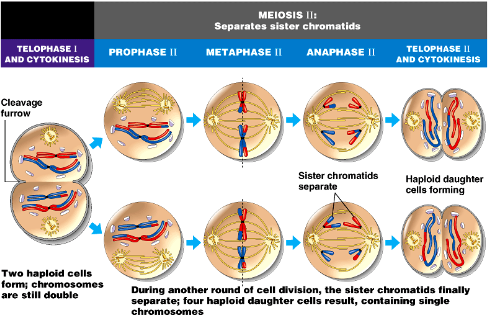
Telophase I
1. Cytokinesis occurs
1. Cleavage furrow
2. 2 haploid cells are formed; chromosomes are still composed of two sister chromatids
3. Centrosomes need to double
23
New cards
Prophase II
1. Centrosomes duplicated and pulled apart
2. Spindle starts to form
24
New cards
Metaphase II
1. Chromosomes line up on metaphase plate
2. Microtubules attach
3. Mitotic spindle formed
25
New cards
Anaphase II
1. Sister chromatids are pulled apart
26
New cards
Telophase II
1. Two cells formed by cytokinesis
2. Chromosomes consist of 1 sister chromatid
27
New cards
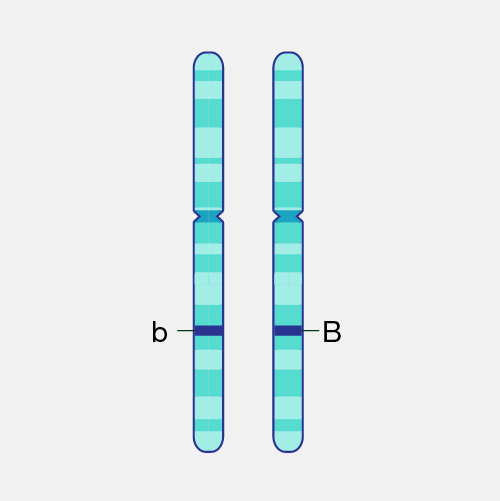
alleles
Different versions of the same gene
28
New cards
Genetic Variation
In species that reproduce sexually, meiosis and fertilization are responsible for most of the variation
1. In Meiosis…
1. Random/Independent Assortment
2. Crossing over
2. In Sexual Reproduction…
1. Random Fertilization
1. In Meiosis…
1. Random/Independent Assortment
2. Crossing over
2. In Sexual Reproduction…
1. Random Fertilization
29
New cards
Independent Assortment
1. During Metaphases I and II
2. The position of each chromosome pair is by chance and independent of any pair
3. 2^n = number of possible combinations of maternal and paternal combinations in an individuals gametes
4. In a human cell, there are 2^23 (8.4 million) possible combinations
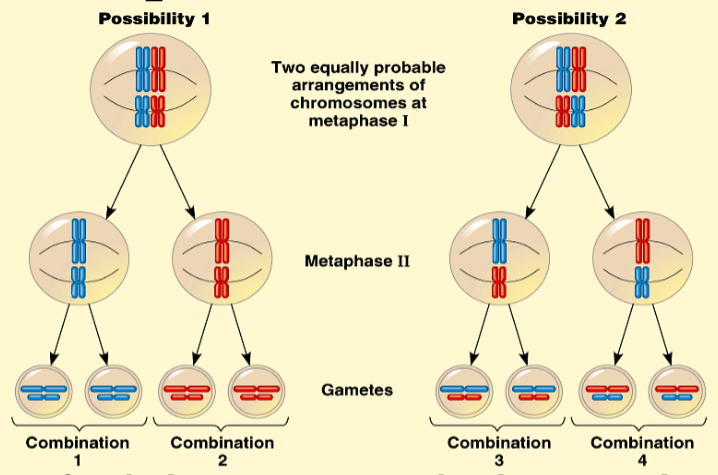
30
New cards
Crossing Over
1. Occurs during Prophase I between homolgous chromosome pairs
2. Corresponding regions of sister chromatids are exchanged
3. Results in **recombinant chromosomes**
4. Increases genetic variation by making “new” chromosomes that are different combinations of maternal and paternal genes.
5. Each gene on one homologous chromosome is aligned with a corresponding gene on another homologous chromosome
6. DNA of 2 nonsister chromatids are broken by specific proteins at points and the 2 segments beyond the crossover point are each joined to the other chromatid
7. In detail
1. During early prophase I the homologous pairs held together along length by protein structure.
1. Protein is synaptonemal complex
2. Process is synapsis
2. During late prophase synaptonemal complex broken down so homologs pull apart slightly but are connect at the chiasmata.
3. Chiasmata are the result of cohesins btw the segments of sister chromatids that have been separated by crossing over.
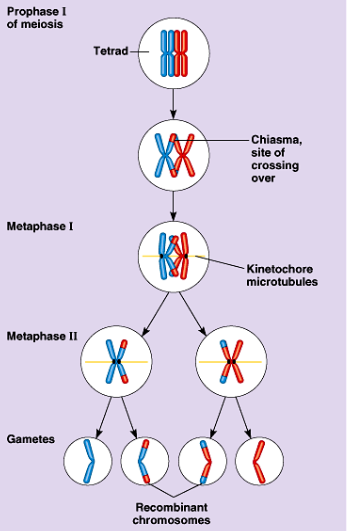
31
New cards
Random Fertilization
1. The fact that a given sperm will randomly fertilize a given egg
2. 2^23 x 2^23 = 70 trillion possible chromosomal combinations in the zygote.
32
New cards
Oogenesis
* female gamete mitosis
* Meiosis produces 1 ovum and 3 small polar bodies
* Polar bodies are normally discarded
* Meiosis produces 1 ovum and 3 small polar bodies
* Polar bodies are normally discarded
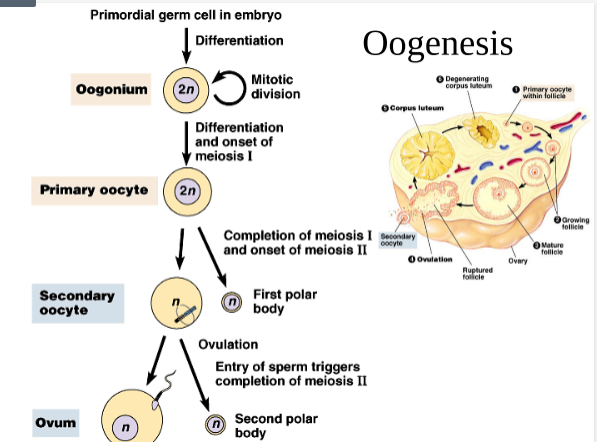
33
New cards
Spermogenesis
* Produces 4 haploid cells of similar size
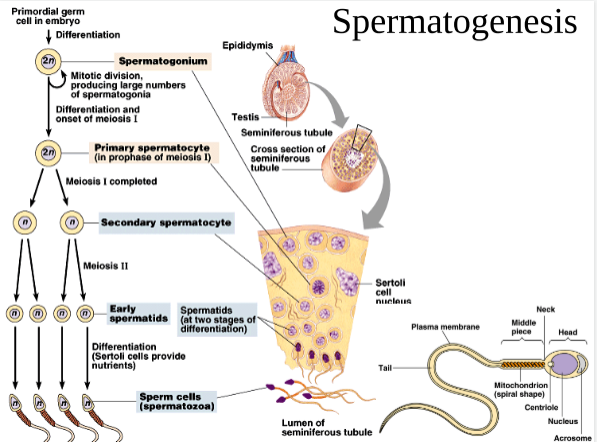
34
New cards
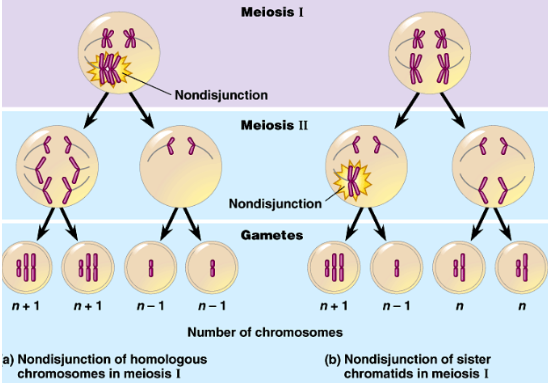
Non-disjunction
* Occurs during meiosis I or meiosis II when sister chromatids/homologous chromosomes do not separate properly during anaphase
* Chromosomes not properly aligned or pulsed apart resulting in extra chromosomes in one cell
* Examples: Down Syndrome and Klinefelter Syndrome
* Chromosomes not properly aligned or pulsed apart resulting in extra chromosomes in one cell
* Examples: Down Syndrome and Klinefelter Syndrome
35
New cards
Down Syndrome
* Chromosome pair 21 has 3 chromosomes
* Results in characteristic facial features, short stature, intellectual challenges, and increased risk of heart problems
* Results in characteristic facial features, short stature, intellectual challenges, and increased risk of heart problems
36
New cards
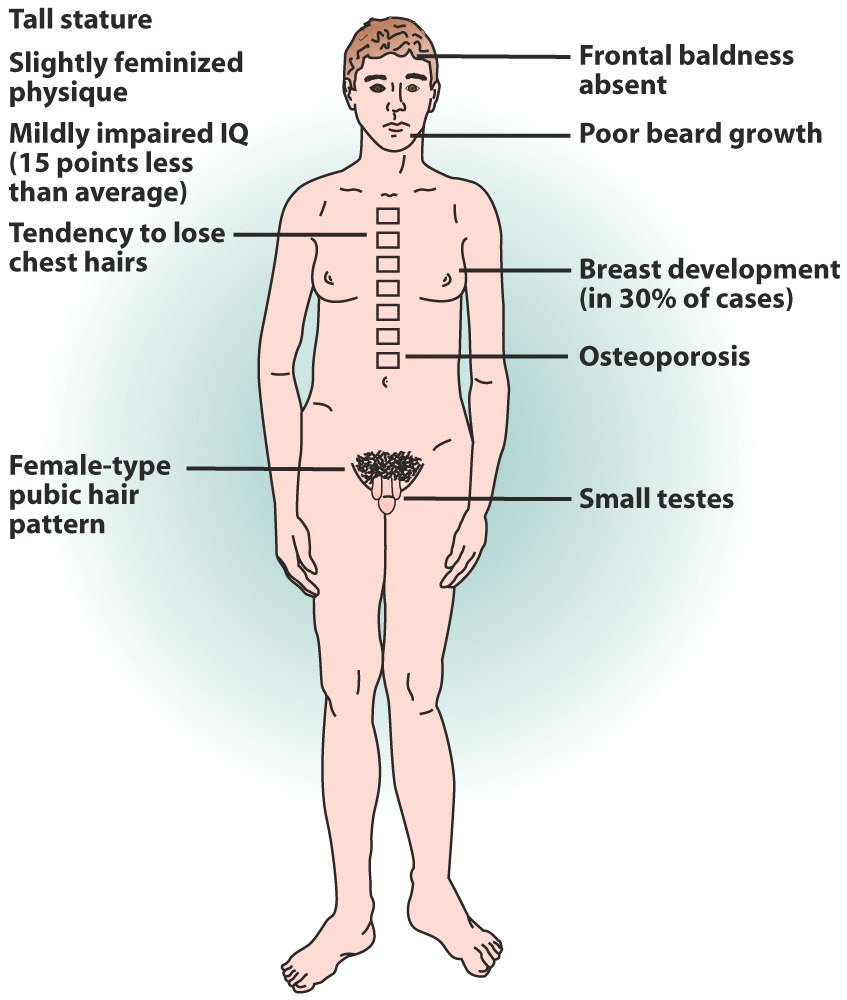
Klinefelter Syndrome
* In male, Sex chromosomes have additional chromosome (XXY)
* Secondary sexual characteristics from more estrogen
* Characterized with long arms and legs, wider hips, narrower shoulders, breast tissue growth
* Secondary sexual characteristics from more estrogen
* Characterized with long arms and legs, wider hips, narrower shoulders, breast tissue growth