Ancient China Vocabulary
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Genghis Khan
Mongol leader Genghis Khan (1162-1227) rose from humble beginnings to establish the largest land empire in history. After uniting the nomadic tribes of the Mongolian plateau, he conquered huge chunks of central Asia and China.
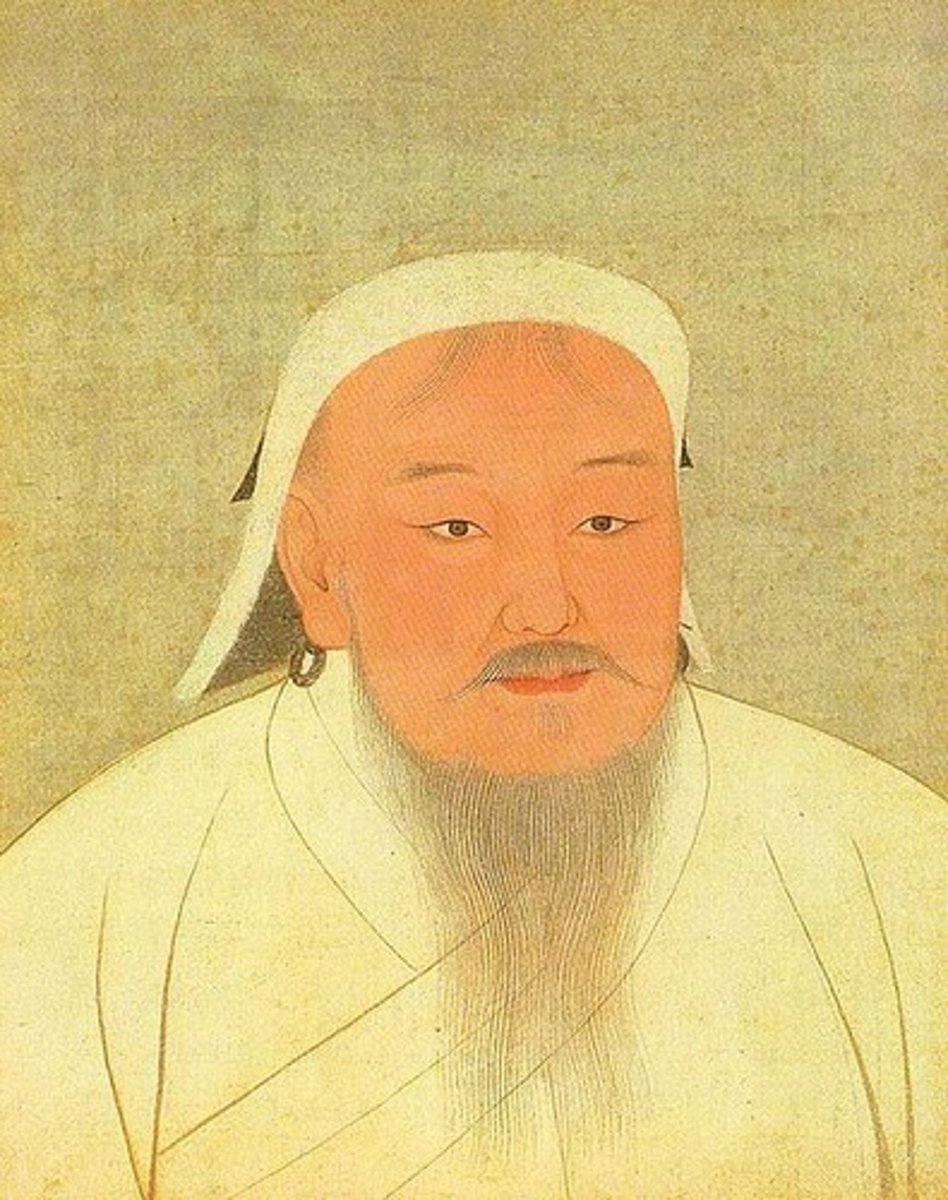

Kublai Khan
Mongol ruler and grandson of Genghis Khan, he completed the conquest of China and founded the Yuan Dynasty.

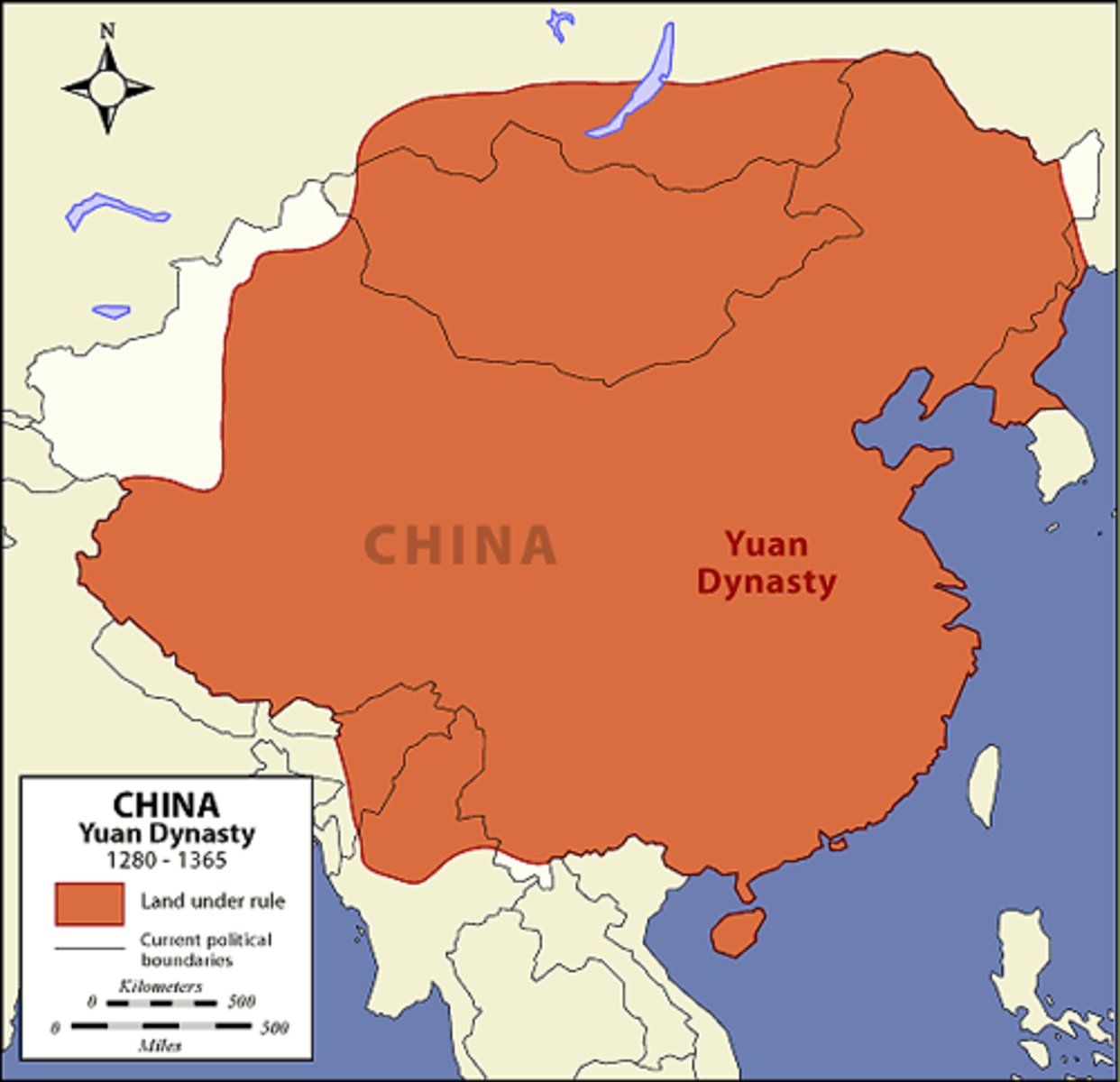
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan Dynasty was a period of time when China was under the rule of the Mongol Empire. The Yuan ruled China from 1279 to 1368. It was followed by the Ming Dynasty.
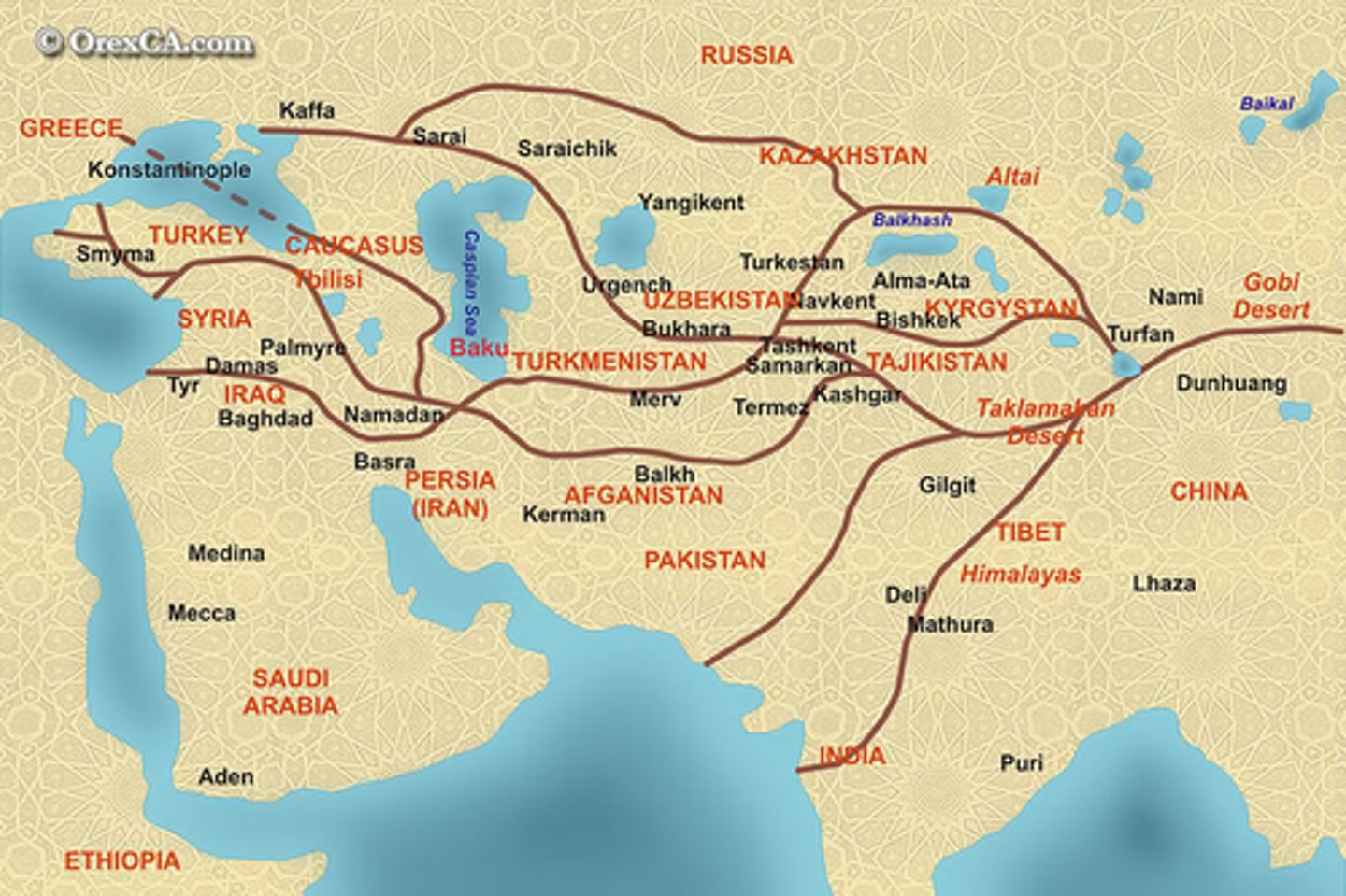
Silk Road
A network of trade routes that stretched across Asia from China to the Mediterranean Sea.
Marco Polo
Italian trader, he traveled the Silk Road to China and later wrote about his trip. During his time in China, he served as a government official in Kublai Khan's Court.

Daoism
A Philosophy that developed in China and stressed the belief that one should live in harmony with the Dao, the guiding force of reality. Daoism emphasizes nature in its teachings.

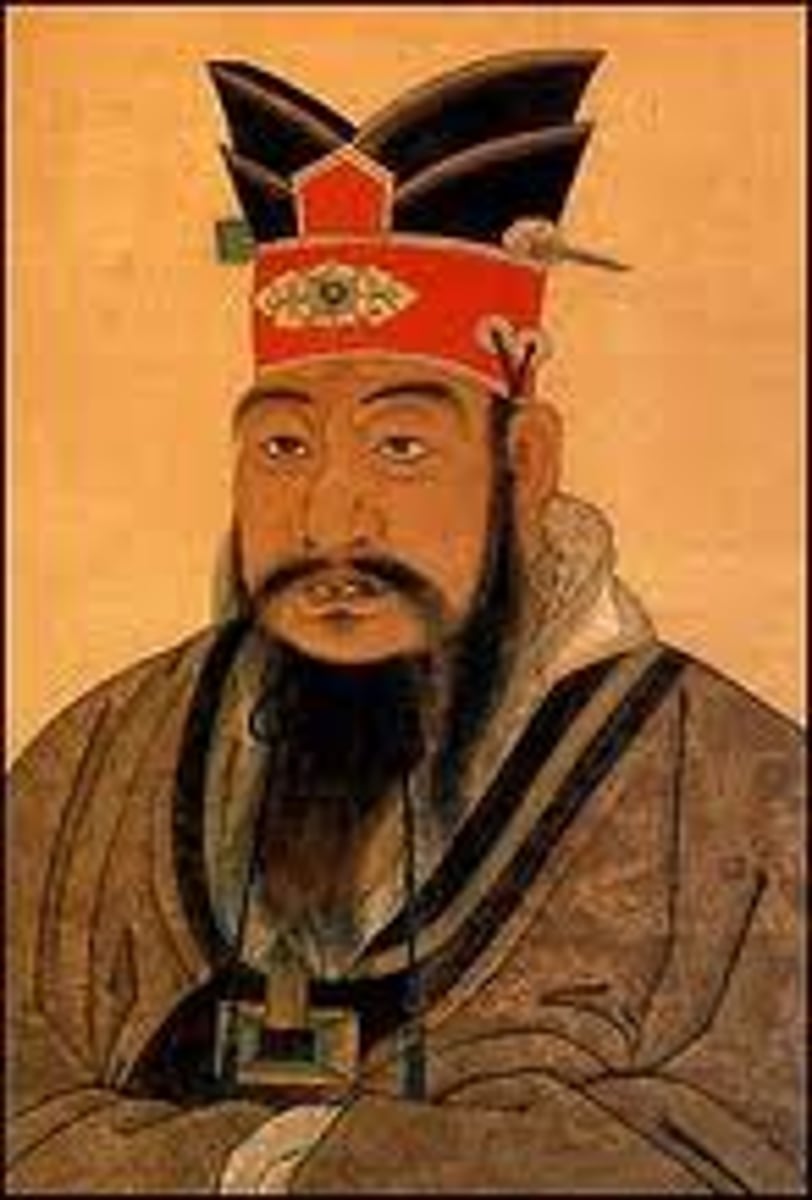
Confucianism
A philosophy based on the ideas of Confucious that focuses on morality, family order, social harmony, and government.The worldly concern of this philosophy rests upon the belief that human beings are fundamentally good, and teachable

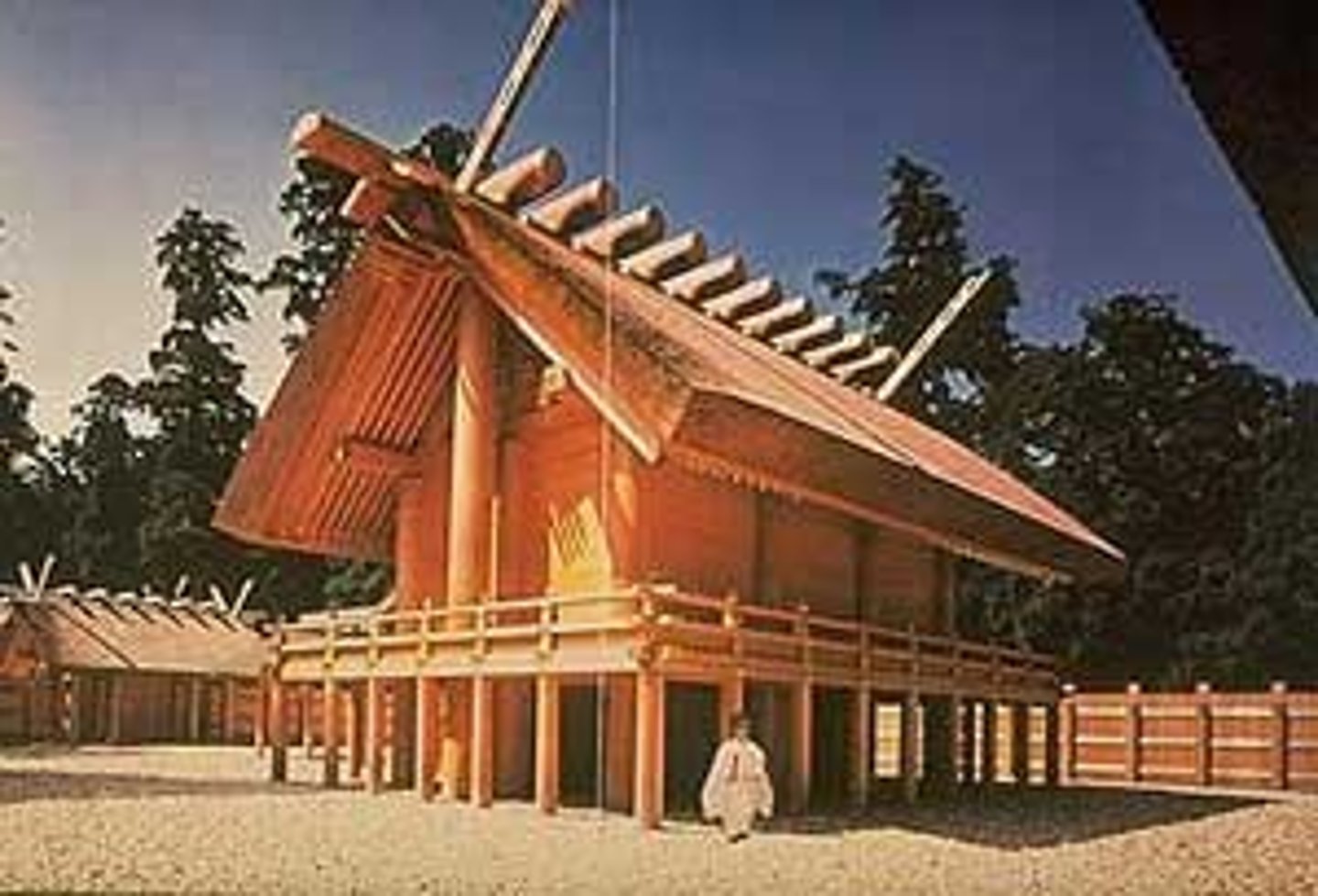
Shinto (Japan)
The traditional religion of Japan; teachings enforce that everything in nature-the Sun, Moon, trees, waterfalls, and animals- has kami, or nature spirits. Shintoists believe that some kami help people live and keep them from harm.

Legalism
The Chinese belief that people are bad by nature and need to be controlled. Widely implemented during the Qin Dynasty.

Buddhism
A religion founded by Siddhartha Gautama. It teaches people how to end their suffering by cutting out greed, hatred and ignorance. When people do bad things, they will get bad consequences. When people do good things, they will get good consequences. Good and bad things do not cancel out.

Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven is what the Chinese people believed gave their rulers the right to be king or emperor. It meant that the gods had blessed that person with the right to rule.

Isolationism
A policy of avoiding contact with other countries.

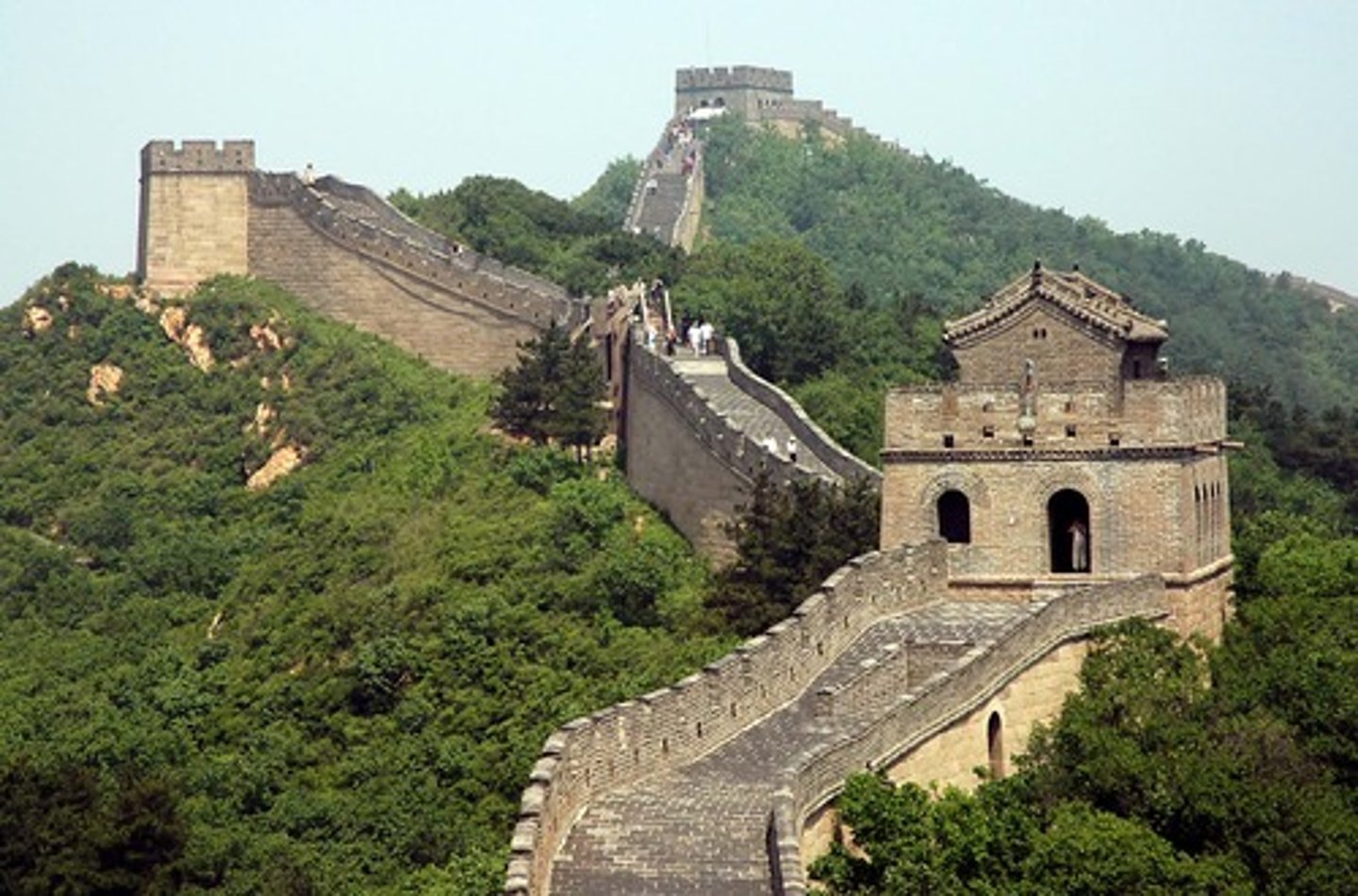
Great Wall
A barrier of walls across China's northern wall. The first section of the wall had been built in the 600s BC to keep invading groups out of China.

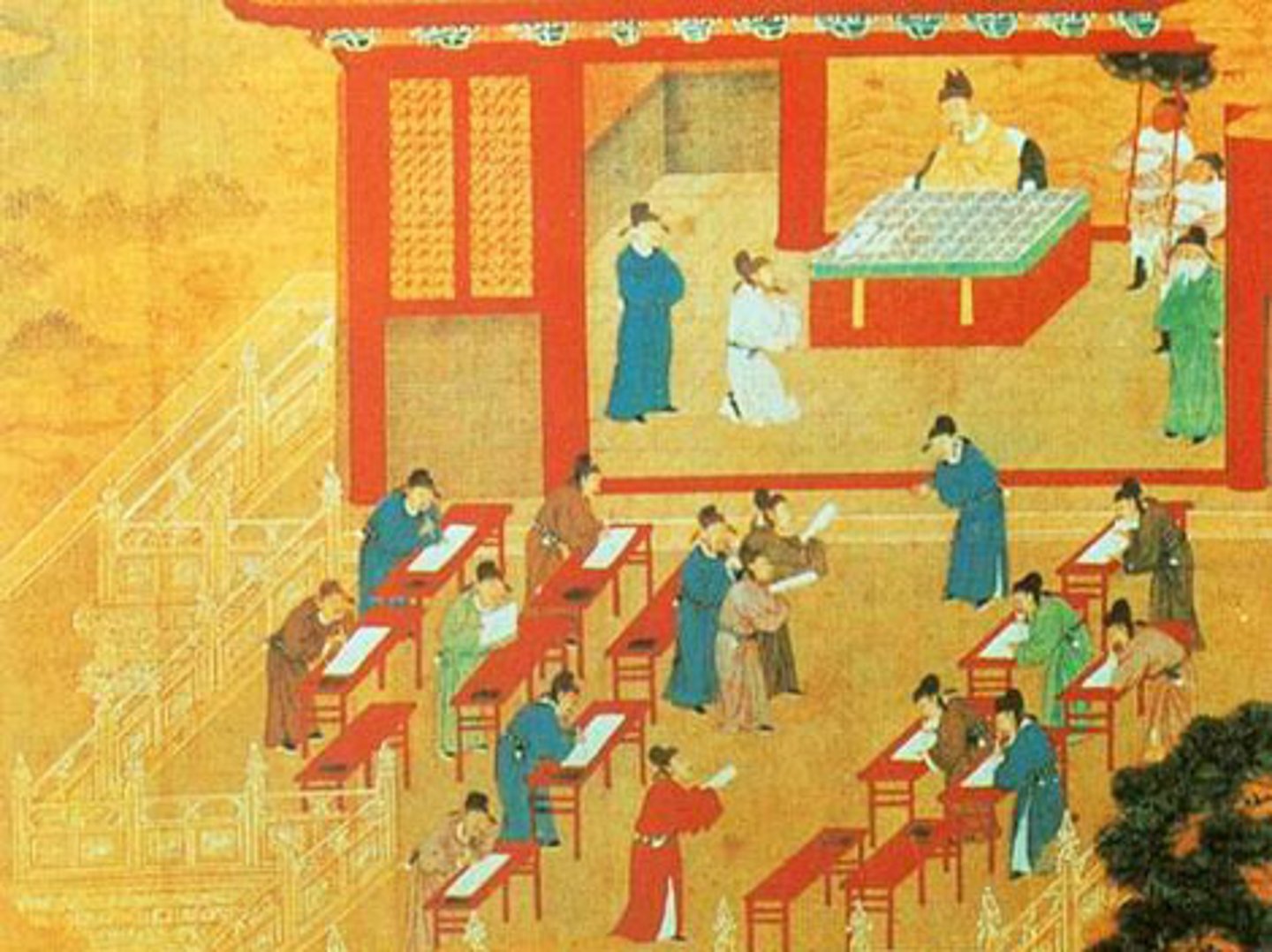
Civil Service
Service as a government official. However, people were chosen for these positions based on they did on "Civil Service Exams". Those who scored the highest typically came from wealthy and powerful families.

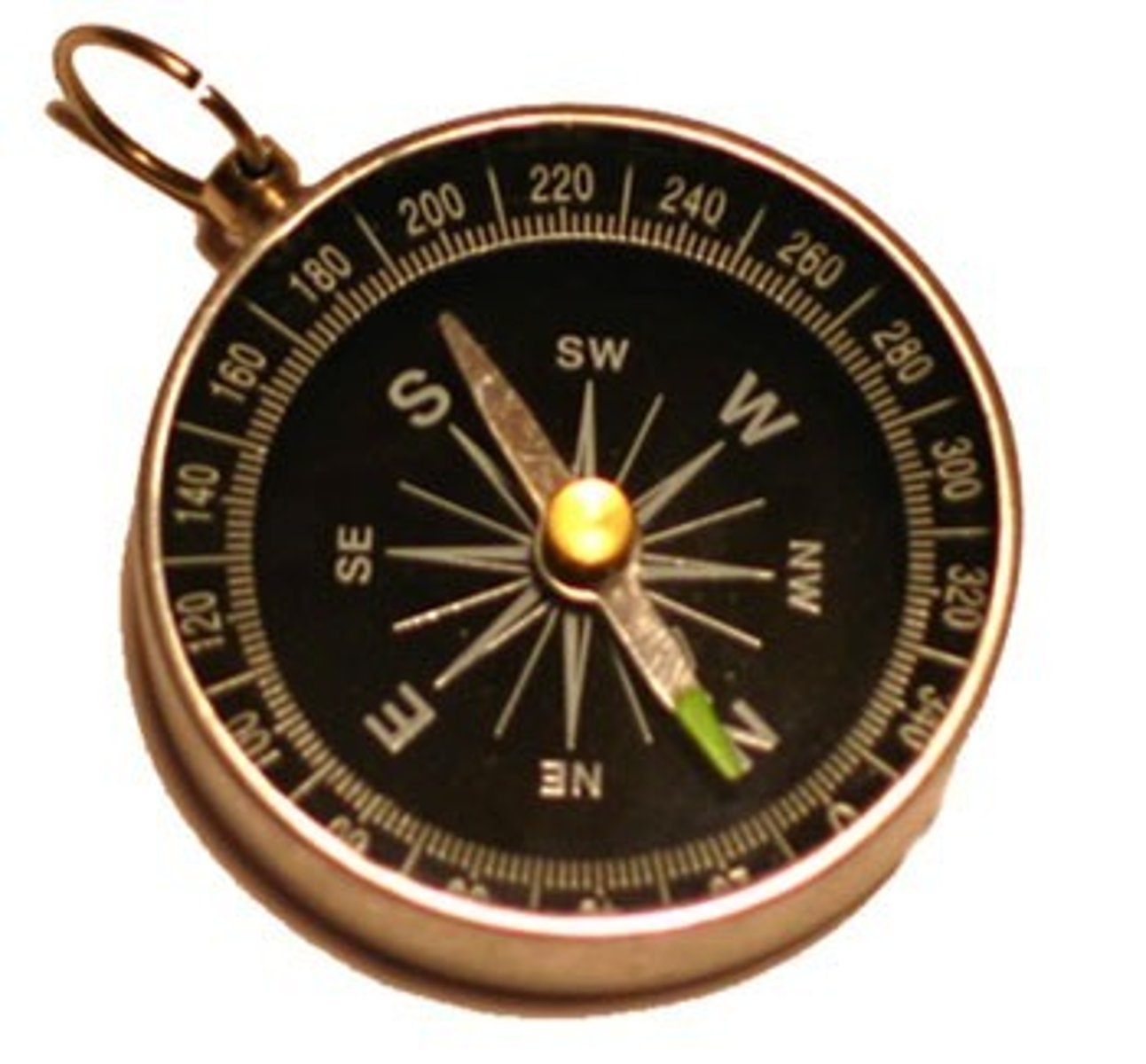
Compass
An instrument containing a magnetized pointer which shows the direction of magnetic north and bearings from it. Fun Fact: It was invented during the Han Dynasty and first used for geometry and fortune telling!

Movable Type
Printing type made up of individual pieces each carrying usually a single letter or other character so that the pieces can be freely assembled or reassembled for printing any desired combination or line. This helps in the mass production of items such as books. This was invented during the Song Dynasty.
Silk
A soft, light, and highly valued fabric developed in China. The Chinese kept the process of how to produce silk a secret for many centuries.
Paper
This item was invented around 100 CE, during the Han dynasty, when the national civil service was set up. It was was made from rags, but later plant materials were used, such as bark, hemp, and bamboo.
Porcelain
A thin, beautiful pottery invented in China. It was invented during the Han Dynasty.

Gunpowder
A mixture of powders used in guns and explosives. It was discovered by a scientist in China during the late Tang Dynasty.

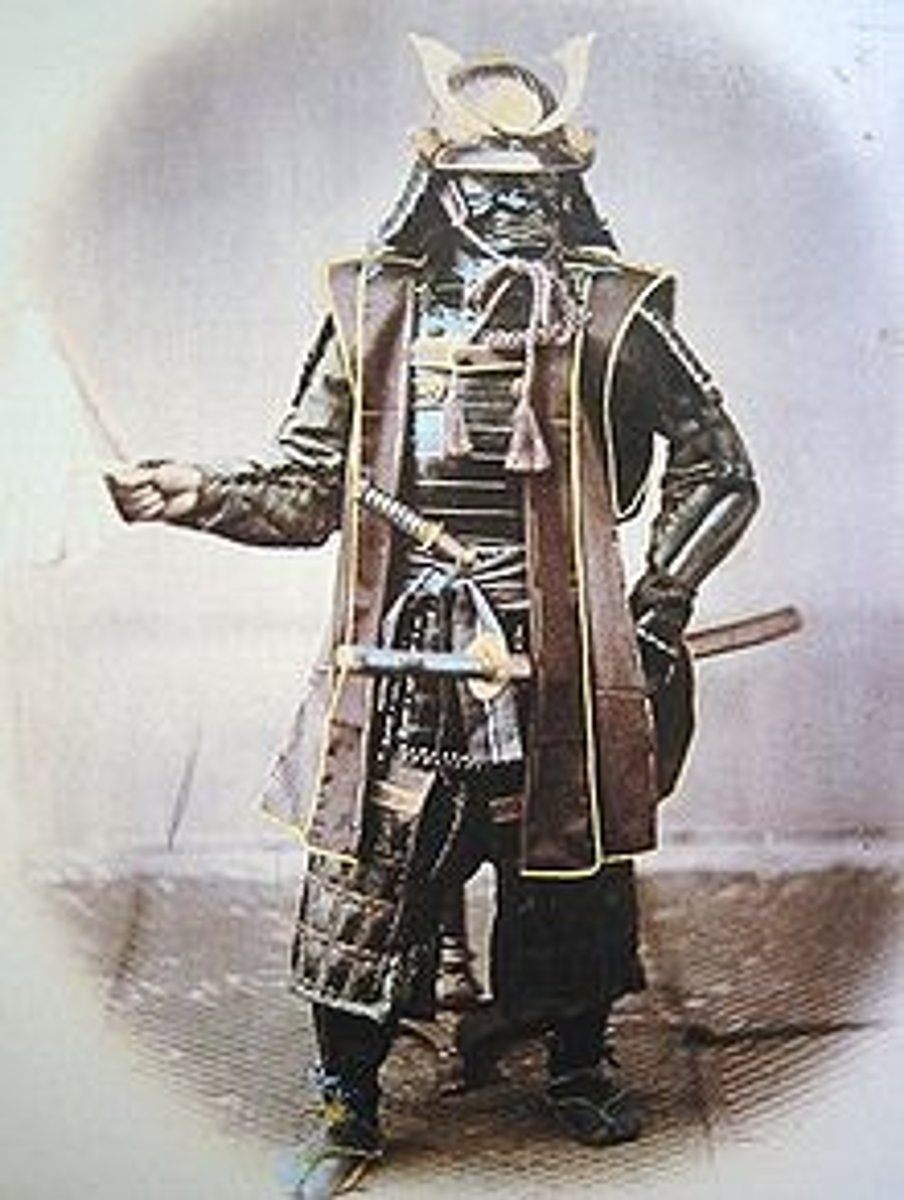
Samurai (Japan)
A trained professional warrior in feudal Japan. The word samurai comes from the Japanese verb saburai, which means to serve someone

Shogun (Japan)
A general who ruled Japan in the emperor's name.The word "shogun" comes from the Japanese words "sho," meaning "commander," and "gun," meaning "troops."

Feudalism (Japan)
a type of government where a weak monarchy (emperor) tries to control an area of land through agreements with wealthy landholders. Typically, land is exchanged for loyalty/power.
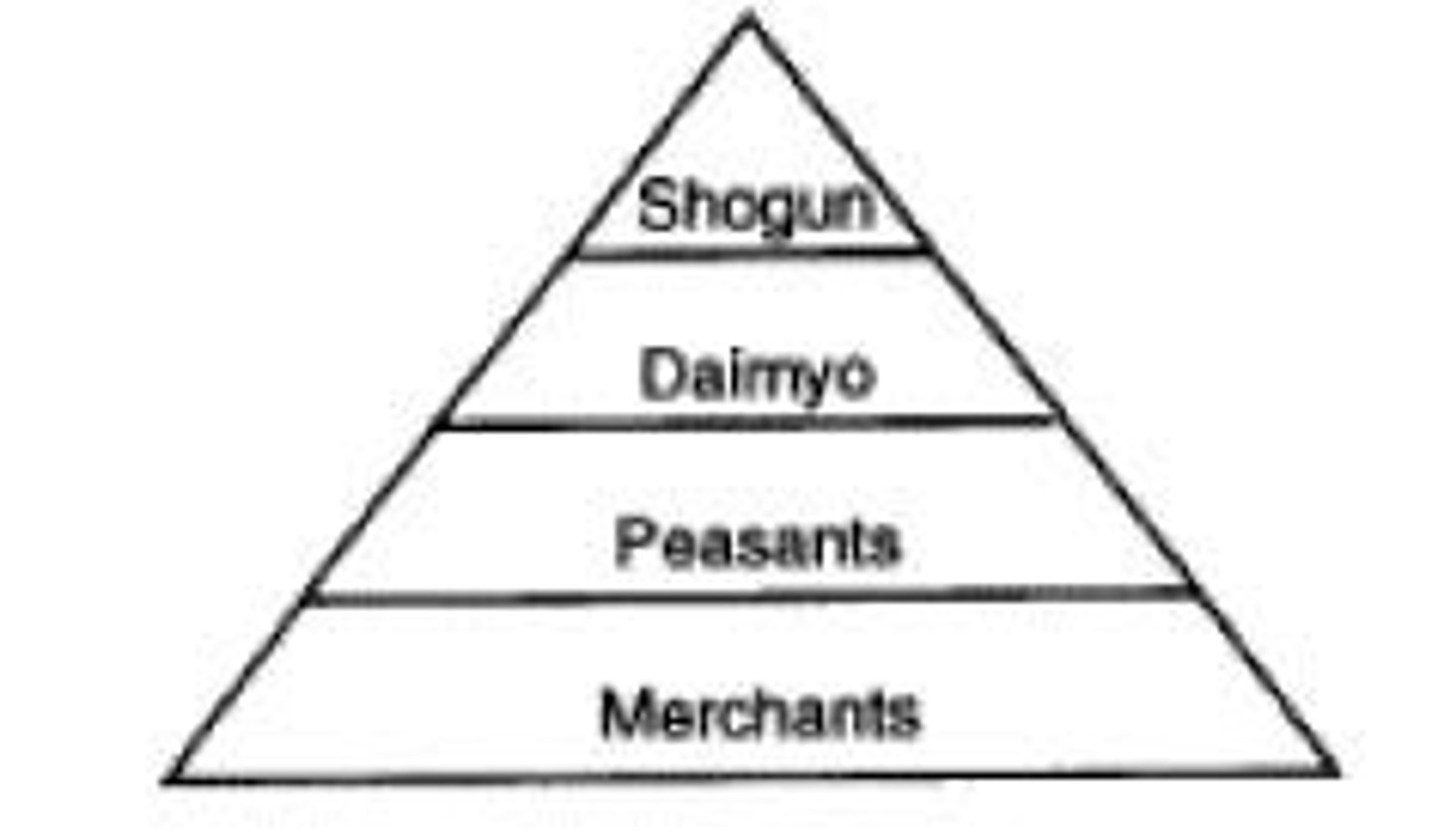
Hierarchy
a system of organizing people into ranks-- those with higher rank have more power and privileges
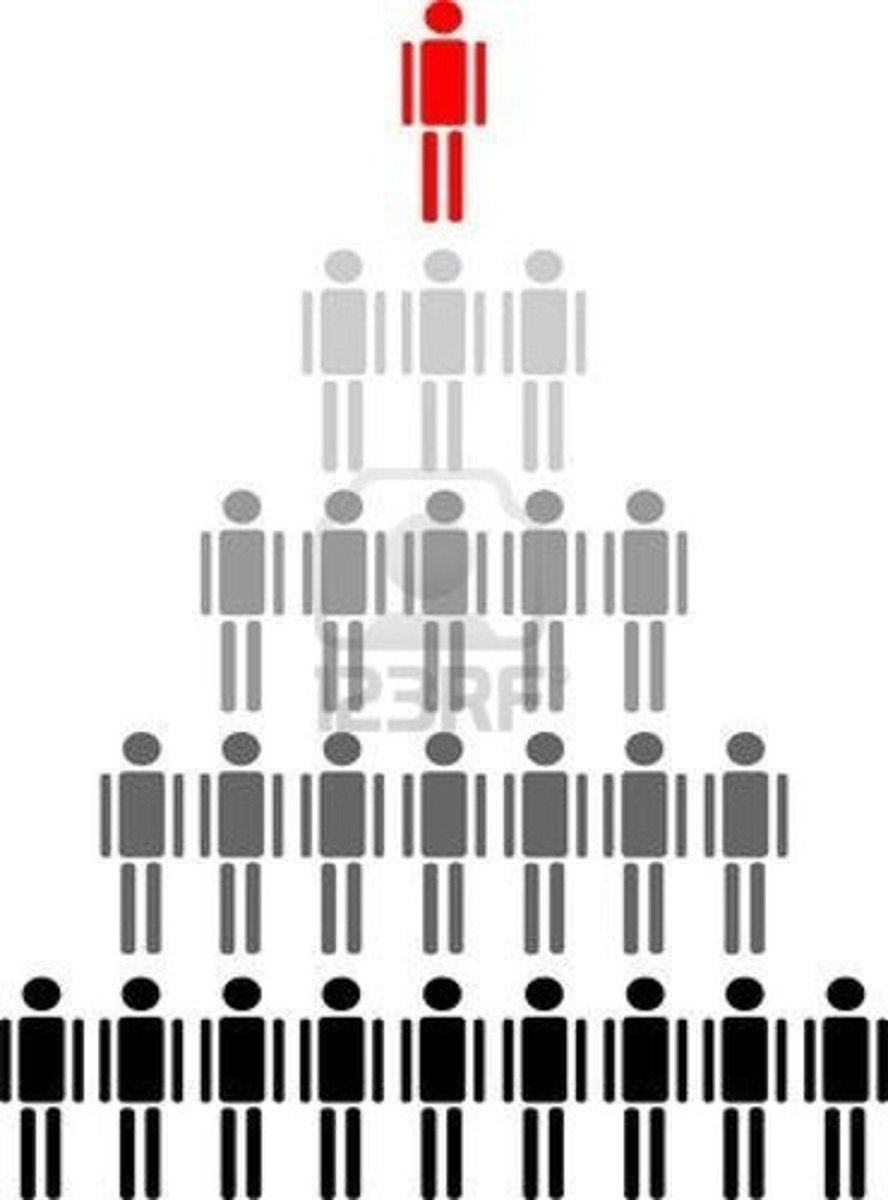
Social Class
a division of a society based on social and economic status.