Nikhil's FULL YEAR BIO STUDY FLASCARDS
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bro im cooked for this test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Hydroxyl
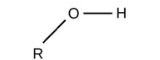
Esters
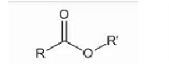
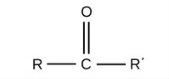
Carbonyl
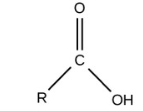
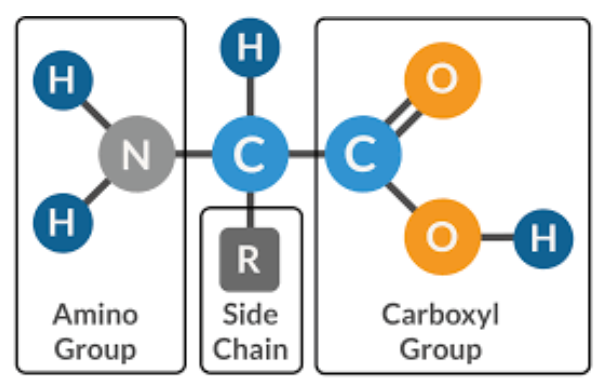
Carboyxl
Amino
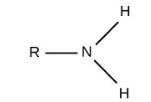
Phosphate
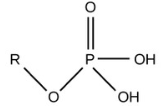
Sulfhydryl
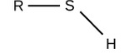
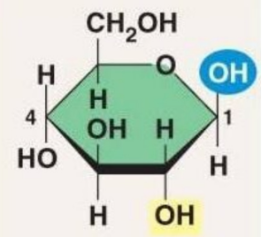
Alpha Glucose
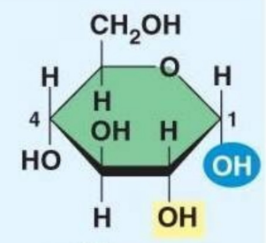
Beta Glucose
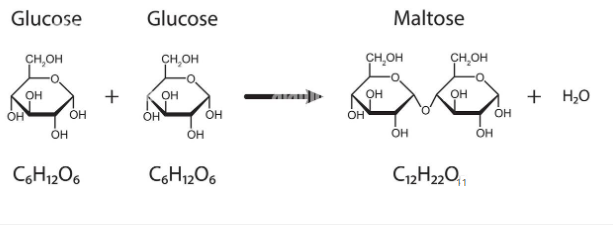
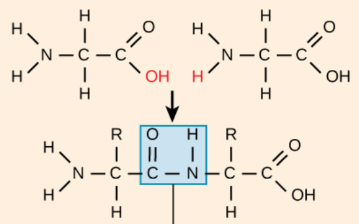
Dehydration Synthesis
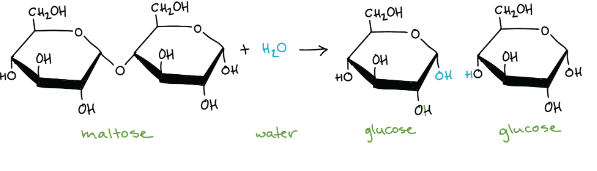
Hydrolysis
Starch
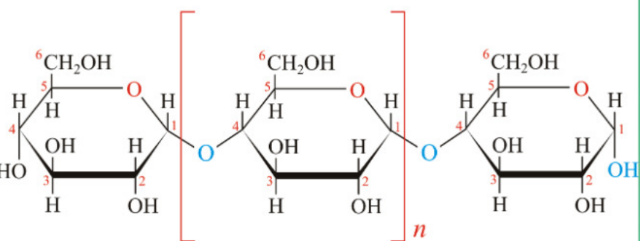
Cellulose
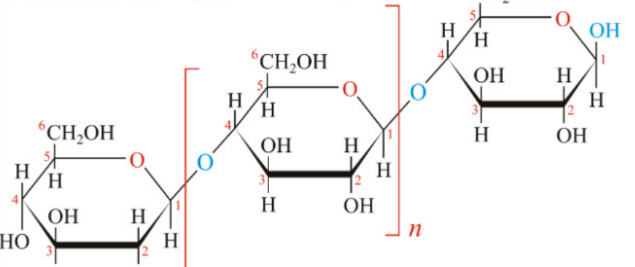
Amylase
breaks down starch into maltose
Maltase
breaks maltose into glucose
Monomer of protein
Peptide Bond
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur in our body
Catabolism
Breaking down of complex molecules to form simpler ones
Anabolism
Building of complex molecules from smaller subunits, requires energy
Trans fatty acids
have double bonds/ no bonds and behave like unsaturated fats, clogging arteries and our bodies cant break it down
Cis fattty acids
have double bonds with bends, and have H on the same one side, it causes a bend
Unsaturated fats
can be liquid at room temperature because they are less packed, they have less hydrogens and double bonds
Saturated fats
solid at room temperature, no double bonds
Triglycerides
Unused calories are converted into these. They are stored in fat cells until used, between meals and during exercise. Glycerol + three fatty acids through dehydration synthesis.
Phospholipids
Similar to triglycerides
They have hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
Heads are polar, tails are nonpolar
Cholesterol
Maintains cell membrane structure
SYsntehsis basis for some structures
LDL is bad, HDL is good
Hormones are a type of steroids
Variants include cortisone, deoxycholic acid, albumin, etc
nucleotide
Made of:
Phosphate group
Pentose Sugar
Nitrogenous base
Pyramidines
Cytosine
Uracil
Thymine
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
Nucleotide Monomers
A,C,T,G,U
Adenine
Cytosine
Thymine
Guanine
Uracil
Phosphodiester bonds:
Basically duplicate ester but replace c with o. Forms through dehydration synthesis. Bonds for nucleic acics.
Cohesion
H-bonding between like molecules
Surface Tension
measure of how difficult it is to break or stretch surface of liquid
Adhesion
bonding between unlike molecules
Adhesion of H2O to vessel walls counters ↓ pull of gravity
Transpiration
how water moves up plants
H2o clings to each term by cohesion and clings to the xylem tubes by adhesion
Solution
liquid, homogeneous mixture of 2+ substances
Solvent
dissolving agent (liquid
Solute
dissolved substance
Water
versatile solvent
Covalent Bonds
Share electrons
Polar covalent bonds are between differing electronegativity atoms like H2O
Nonpolar are between equal electron sharing like O2 or H2
Ionic bonds
Two ions (+/-) bond
Na+ Cl - forms NaCl
Affected by environment
Hydrogen bonds
Weak
Hydrogen of a polar covalent molecule bonds to electronegative atom of other polar covalent molecules
Bond between two water molecules is hydrogen
H atom on a water molecule bonds to the N on a ammonia molecule (NH3)
Main elements of life
CHNOPS/SPONCH
DNA
Double stranded
Deoxyribose sugar
Bases:
Thymine
Cytosine
Adenine
Guanine
RNA
Single stranded
Ribose sugar
Bases:
Uracil
Cytosine
Adenine
Guanine
Protien Folding
4 levels of peptide chains
Primary:
Chain of amino acids: polypeptide chain
Secondary:
The same chain forms alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
Tertiary:
Same original chain
Folds in half on its self
Makes a blob
Disulfide bonds do this, sulfhydryl is important
Cysteine has sulfur and methionine
Quaternary:
Multiple tertiaries come together to form this
GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein)
a protien that is stuck to other proteins in order to track their movement.
Never back down never WAHT?
NEVER GIVE UP