Perception
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Gilchrist and Nesberg aim
Gilchrist and Nesberg aimed to find out if food deprivation affects the perception of pictures of food. |
Gilchrist and Nesberg Method
Two groups of students: one group deprived of food for 20 hours and a control group (not hungry). Students were shown four slides, each one showing a meal. The slide was displayed for 15 seconds. The picture was shown again, but dimmer, and participants had to adjust the lighting to make it look the same as it did before. |
Gilchrist and Nesberg Results
Participants perceived the food as brighter the longer they were deprived of food. The control group (who were not deprived of food) didn't perceive the food as brighter. |
Gilchrist and Nesberg Conclusion
Being deprived of food increased perceptual sensitivity. This shows that hunger is a motivating factor that affects the way food-related pictures are perceived. |
Bruner and Minturn study aim
Bruner and Minturn aimed to find out whether an ambiguous figure was seen differently if the context of the figure was changed. |
Bruner and Minturn Method
An independent groups design was used where participants were either presented with a sequence of letters or a sequence of numbers with the same ambiguous figure in the middle. The ambiguous figure could be seen as either the letter B or as the number 13. Participants had to report and also draw what they saw. |
Bruner and Minturn Results
Those who saw a sequence of letters were more likely to report the figure as being the letter B and tended to draw a 'B'. If shown numbers they were more likely to say it was the number 13 and drew a '13'. |
Bruner and Minturn Conclusion
This shows that expectation of what the figure represented was affected by the context that the figure was presented in. |
Bruner and Minturn Real world relevance evaluation
Ambiguous figures are used to purposely trick participants, this isn’t a common event in every day life
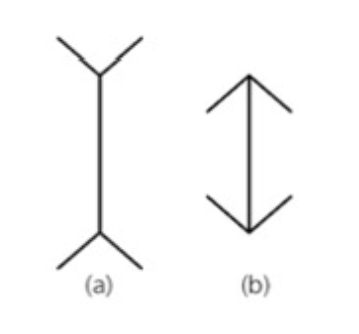
What Illusion is this and what causes it?
Ponzo Illusion - Misinterpreted depth
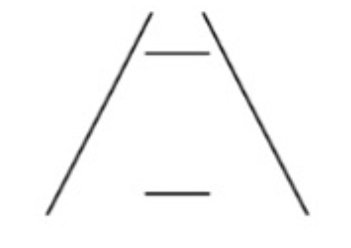
What Illusion is this and what causes it?
Muller Lyer - Misinterpreted depth cue

What Illusion is this and what causes it?
Rubin’s vase - Ambiguous figure
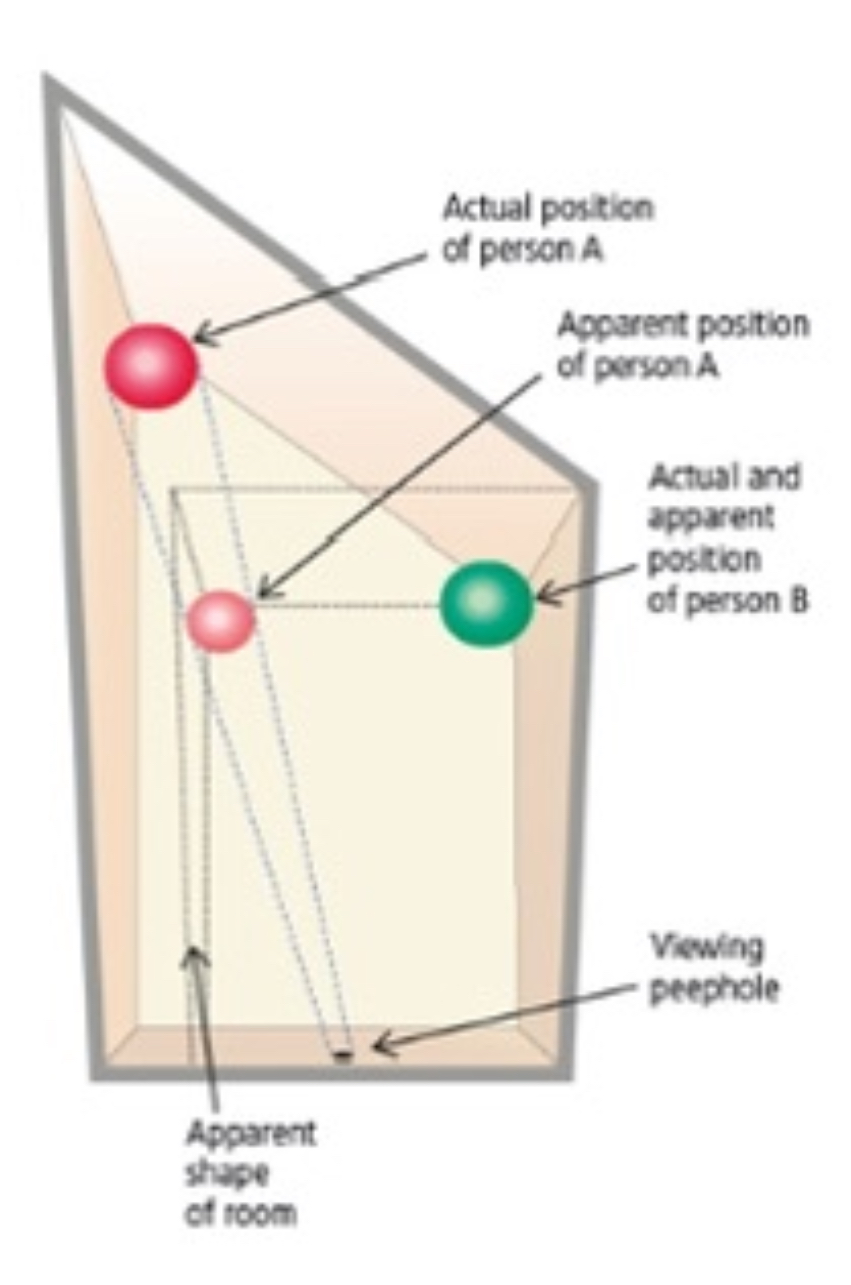
What Illusion is this and what causes it?
Ames Room - Misinterpreted depth cue
Sensation
Physical stimulation of the five senses processed by sense receptors
Perception
Brain interpreting and organising the sensory information
Difference between sensation and perception
Sensation is the detection of stimulus, perception is interpreting what it means
Gibsons Direct theory
Perception doesn’t draw on past experience.
Sensation and perception are the same, eyes detect everything we need without having to make inferences.
Gibsons Theory Real world meanig Evaluation
Research was based on 2nd world war pilots, relevant to every day life
Gibsons Direct theory struggles to explain visual illusions
Perception is seen as accurate but illusions trick the brain so theory is incomplete
Gibsons direct theory supports role of nature
Gibson and walk showed few infants who would crawl off the visual cliff, so they’re born with depth perception
Size constancy
Objects perceived as constant size despite size on retina changing with distance
Visual cues and constancies
Information about movement, distance etc
Retinal disparity (Binocular)
Difference between view of one eye and the other
Gilchrist and Nesberg support from similar studies
Sanfords study found similar results which strengthens the validity of the conclusions
Gilchrist and Nesberg ethical issues
Depriving people of food causes discomfort, a case of physical harm
Gilchrist and Nesberg Not like everyday life
Participants judged pictures rather than real food so it may not apply to the real world
relative size
Smaller objects appear further away
Gregory’s theory of perception
Proposes that sensation and perception are not the same. Brain uses incoming information and information which we already know to form a guess