L9 QMOT: Molecular Orbitals and Geometry
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
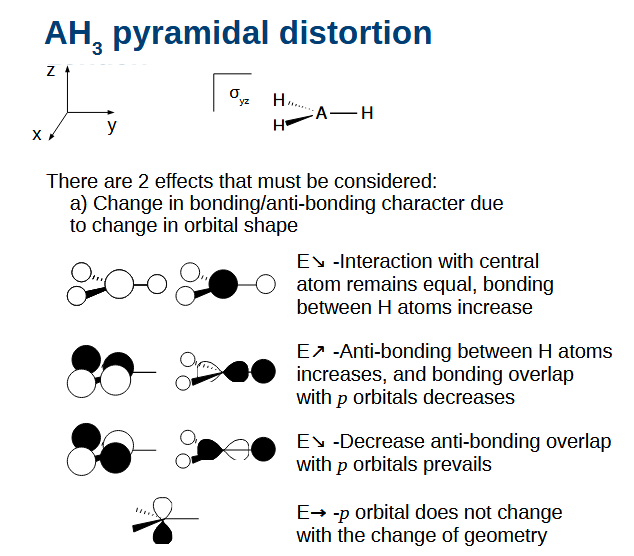
AH3 pyramidal distortion effect 1
The yz plane of symmetry remains, while the xy plane of symmetry disappears.
H atoms bonding increases.
H atom anti-bonding increases and bonding overlap with p orbitals drop due to directionality of the p orbital.
Anti-bonding decreases between p orbitals which prevails over increased anti-bonding of H
Non-bonding p orbital does not change as no contribution from H.
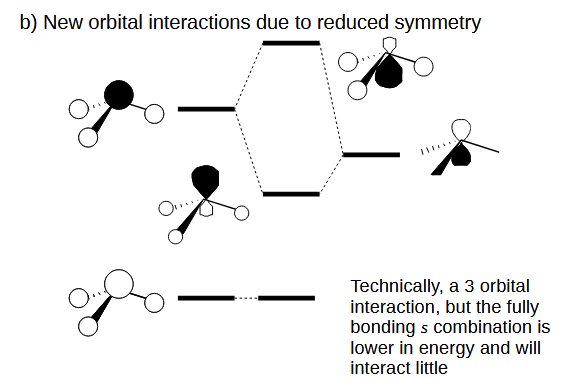
AH3 pyramidal distortion effect 2
The loss of asymmetry plane permits an additional interaction.
One of the orbitals is too low in energy to interact in any real capacity.
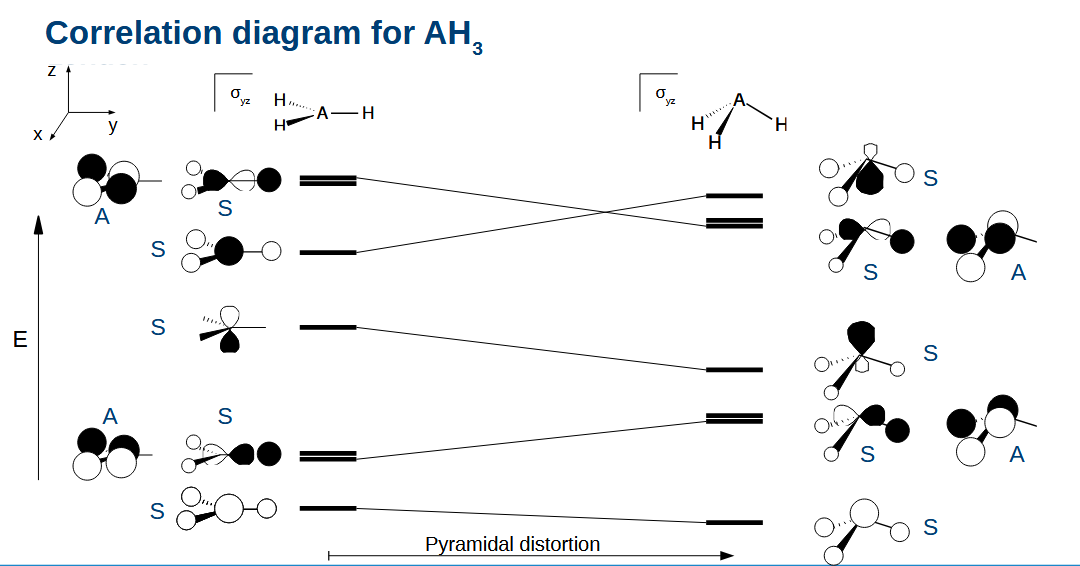
Correlation diagram for AH3
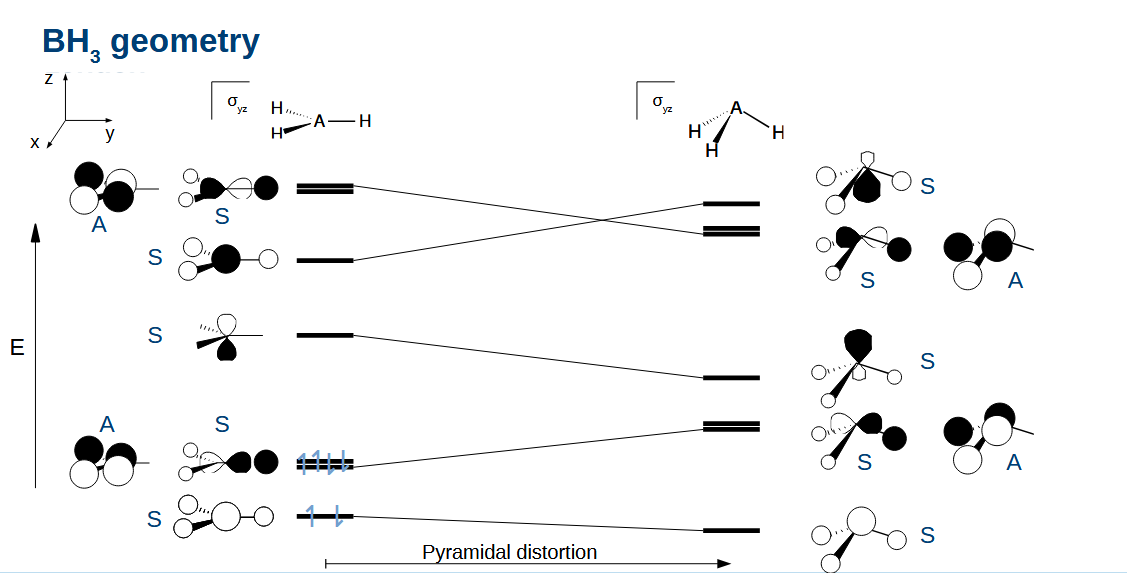
Explaining the geometry for BH3
Planar is better as this has the lowest HOMO. Note how this leaves an empty p orbital - important in boron chemistry
Explaining the geometry for NH3
Now we have added 2 electrons so the HOMO is lowest now if we switch to a pyramidal geometry
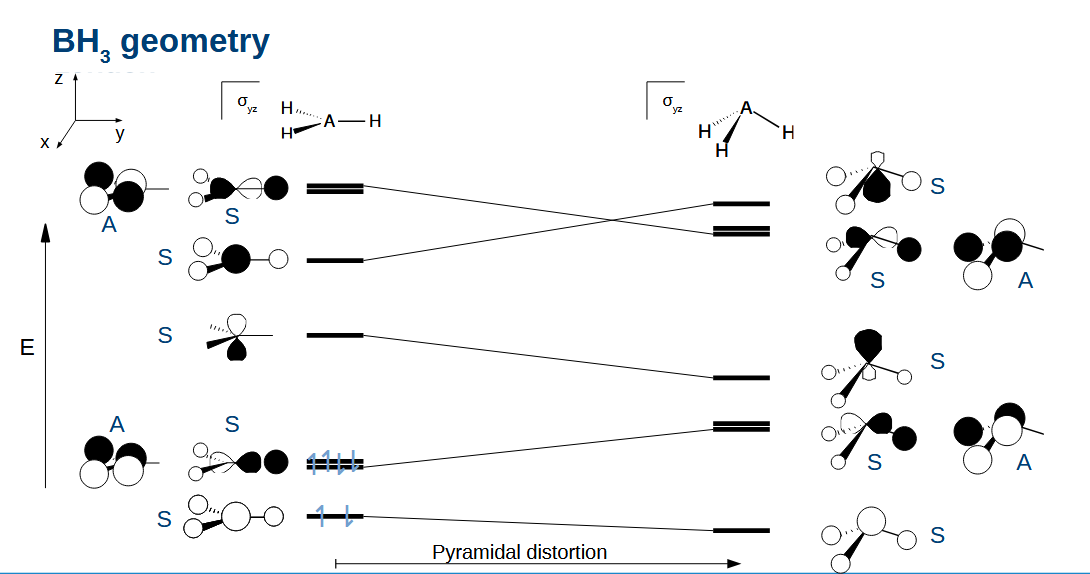
Does the rule for stability of the HOMO apply to SOMOs
Yes, but in a reduced capacity as there is only 1 electron now.
Combining CH3 fragments into ethane approximations/simplifying factors.
Only fragments with the same number of nodal planes and same symmetry can combine (same colour circle).
Only orbitals with the same energy are considered to interact as an approximation.
We also can ignore the highest energy orbitals as they aren’t going to be filled with electrons.
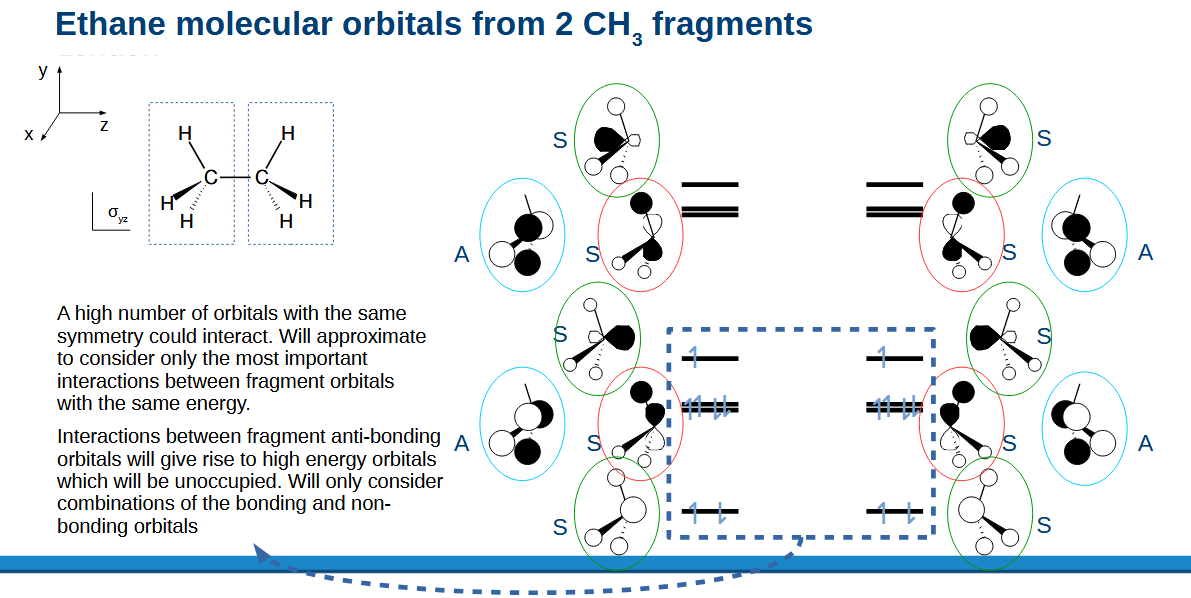
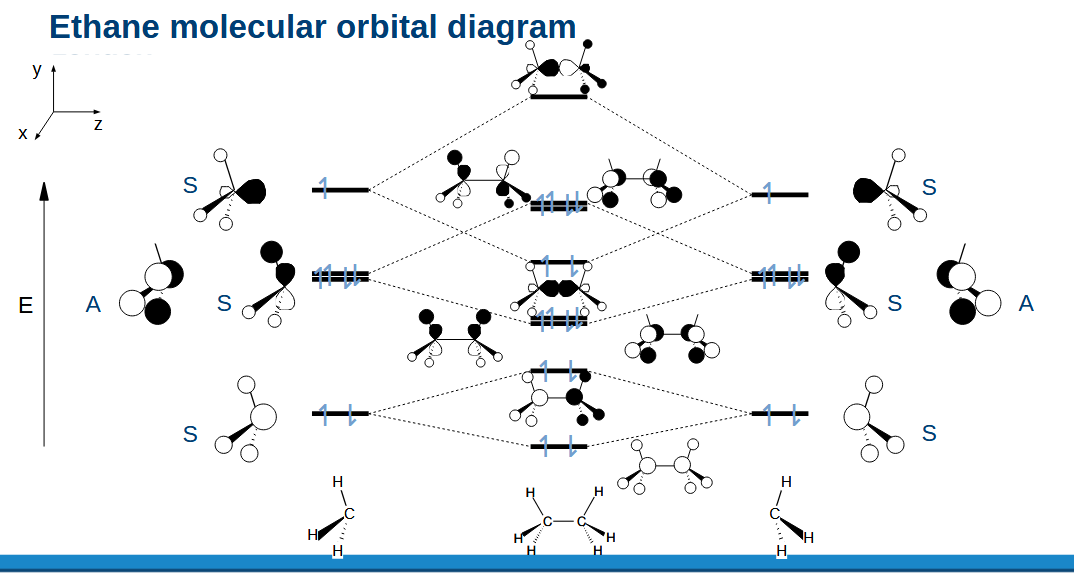
Ethane MO diagram
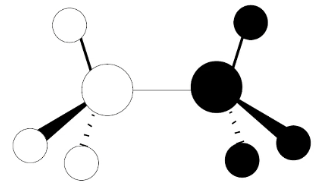
Is this bonding or anti-bonding
Both/Neither
It is anti-bonding with repsect to the C-C
And bonding with respect to the C-H
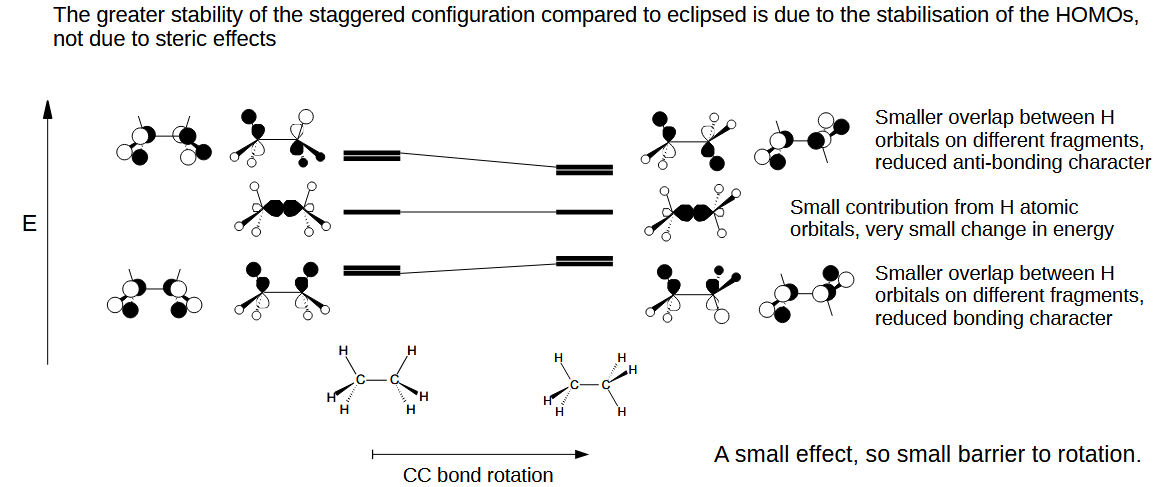
How do MOs explain the preference for the staggered conformation
The staggered conformation reduces the antibonding character between the H orbitals compared to eclipsed as the HOMOs are stabilised.
Therefore staggered geometry is favoured due to electronic effects and not steric ones.
Look at ethene MO diagram construction at the end of lecture 9 (27/10) if you want