2.2 - Wireless Technologies
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
802.11 Committee
Sets the standards for Wireless technologies.
Everyone followed these standards.
Wireless Generations
802.11ac is WiFi 5
802.11ax is WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E (extended)
802.11be is WiFi 7
Future versions will increment accordingly.
802.11 Frequencies
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz - Sometimes a combination.
802.11 Channels
Groups of frequencies, numbered by the IEEE.
Frequencies are managed by governing entities.
Using non-overlapping channels would be optimal.
802.11 Bandwidth
Refers to the amount of frequency in use.
20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz, etc.
Bluetooth
For PAN wireless devices.
Uses the 2.4 GHz range
Unlicensed ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band.
Same as 802.11
Short-range
Most consumer devices operate to about 10 meters.
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
It’s everywhere.
Access badges.
Inventory/assembly line tracking.
Pet/Animal identification.
Anything that needs to be tracked.
Radar technology
Radio energy transmitted to the tag.
RF powers the tag, ID is transmitted back.
Bidirectional communication.
Some tag formats can be active/powered.
NFC (Near Field Communication)
Two-way wireless communication
Builds on RFID, which is mostly one-way.
Payment systems - Major credit cards, online wallets.
Bootstrap for other wireless.
NFC helps with Bluetooth pairing.
Access token, identity “card”.
Short range with encryption.
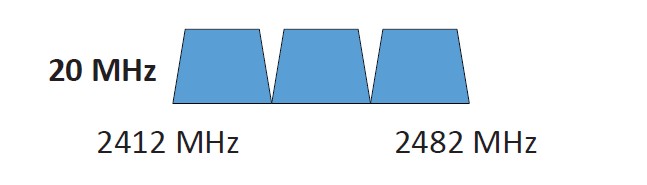
2.4 GHz Spectrum for 802.11 - North America
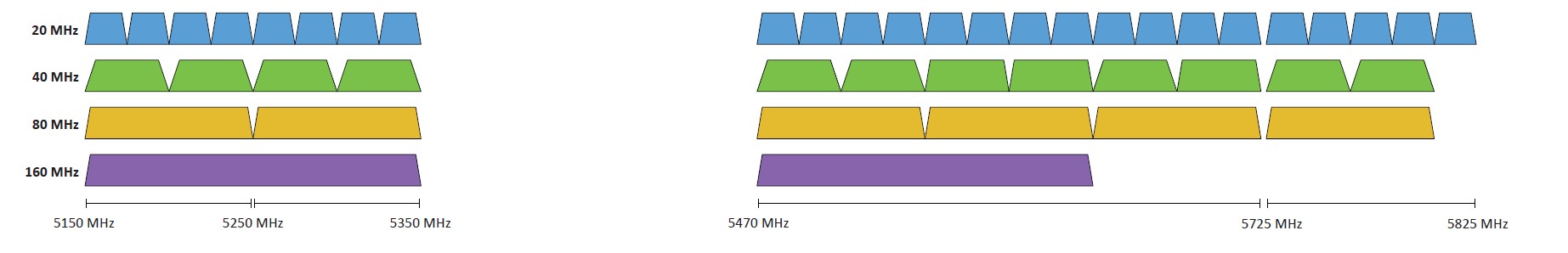
5 GHz Spectrum for 802.11 - North America
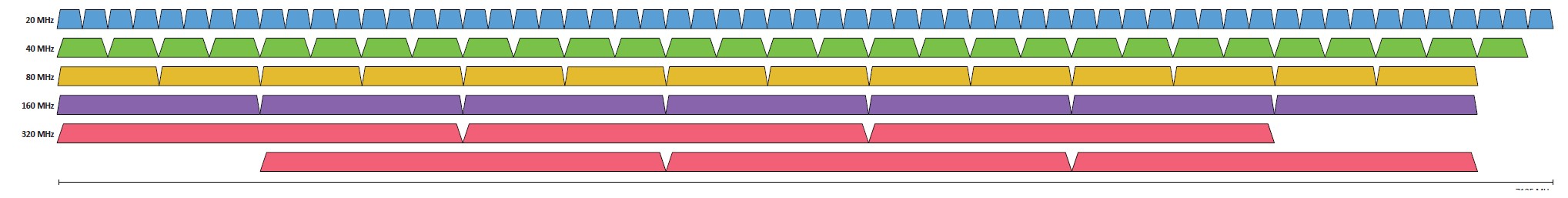
6 GHz Spectrum for 802.11 - North America