The Chemistry Of Life
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Four major categories of of organic molecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
broad concept
chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life
6 most common elements
C, H, O, N, P, S
isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons but same protons
ex carbon 12 vs carbon 14
What are the uses of radioactive isotopes?
age of rocks/fossils, treating cancer/killing bacteria, tracers to follow substances
ionic bond
transfer of electrons
covalent bond
shared electrons
single: 2 electrons
double: 4 electrons
triple: six electrons
polarity (polar molecule)
electrons are shared unequally between atoms in a molecule causing regions of positive and negative charge
ex: oxygen has a stronger attraction to electrons making it slightly negative
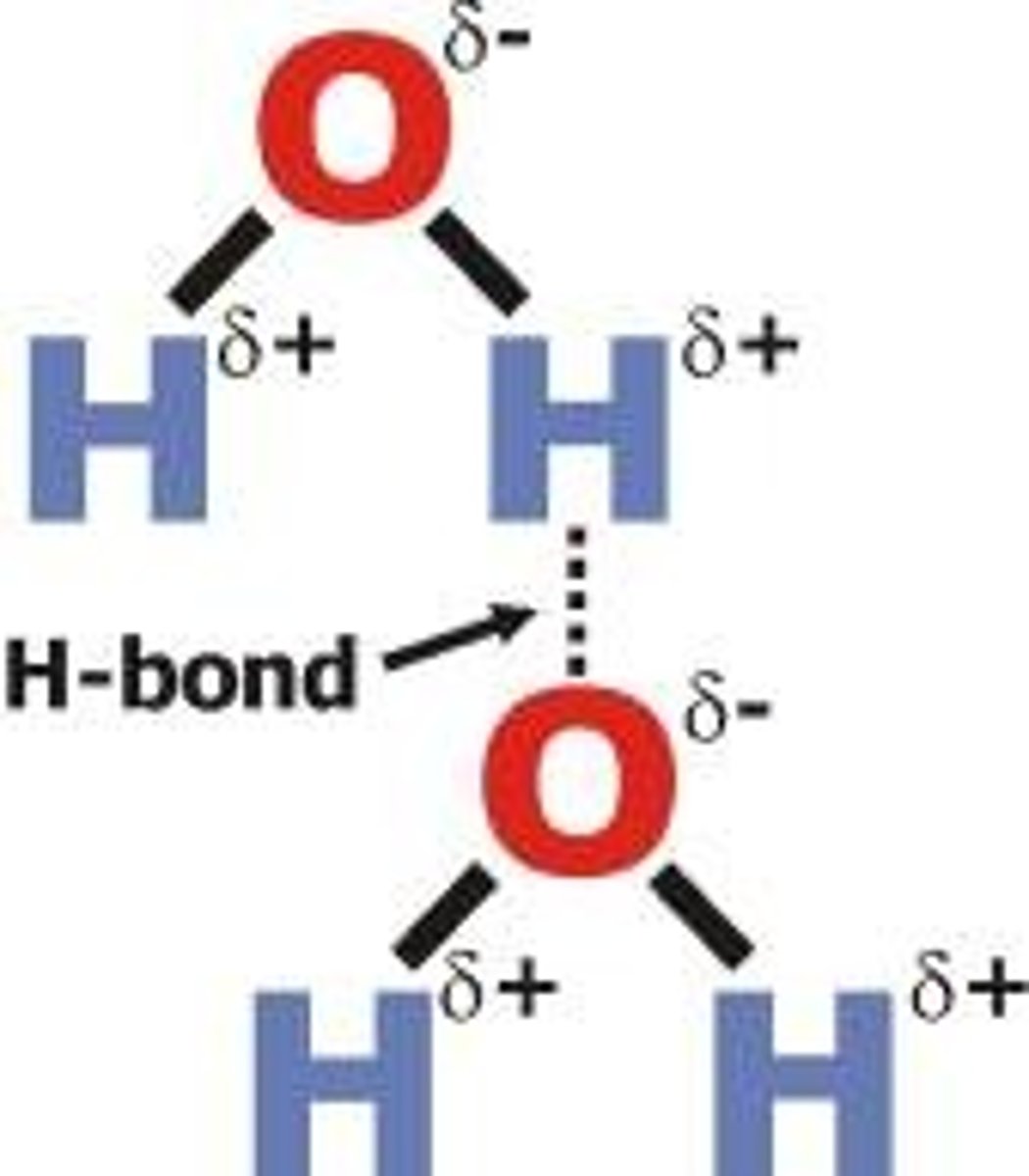
hydrogen bond
attraction between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen of another water molecule
cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance which causes molecules of water on the surface to be drawn inward
adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
meniscus forms in a graduated cylinder because adhesion > cohesion
capillary action
adhesion between water and glass causes water to rise in a small tube
one of the forces that helps water rise in trees
solute
substance that is dissolved
solvent
substance that does the dissolving
hydrophobic
water fearing substances that will not dissolve in water
fats and oils
hydrophilic
water loving substances that will dissolve in water
acid
a compound that donates H+ ions to a solution
base
a compound that removes H+ ions from a solution
why are carbon atoms so common in living things
bonding ability depends on # electrons in its outermost energy level
carbon has only 4 electrons outer shell so it can form up to 4 bonds
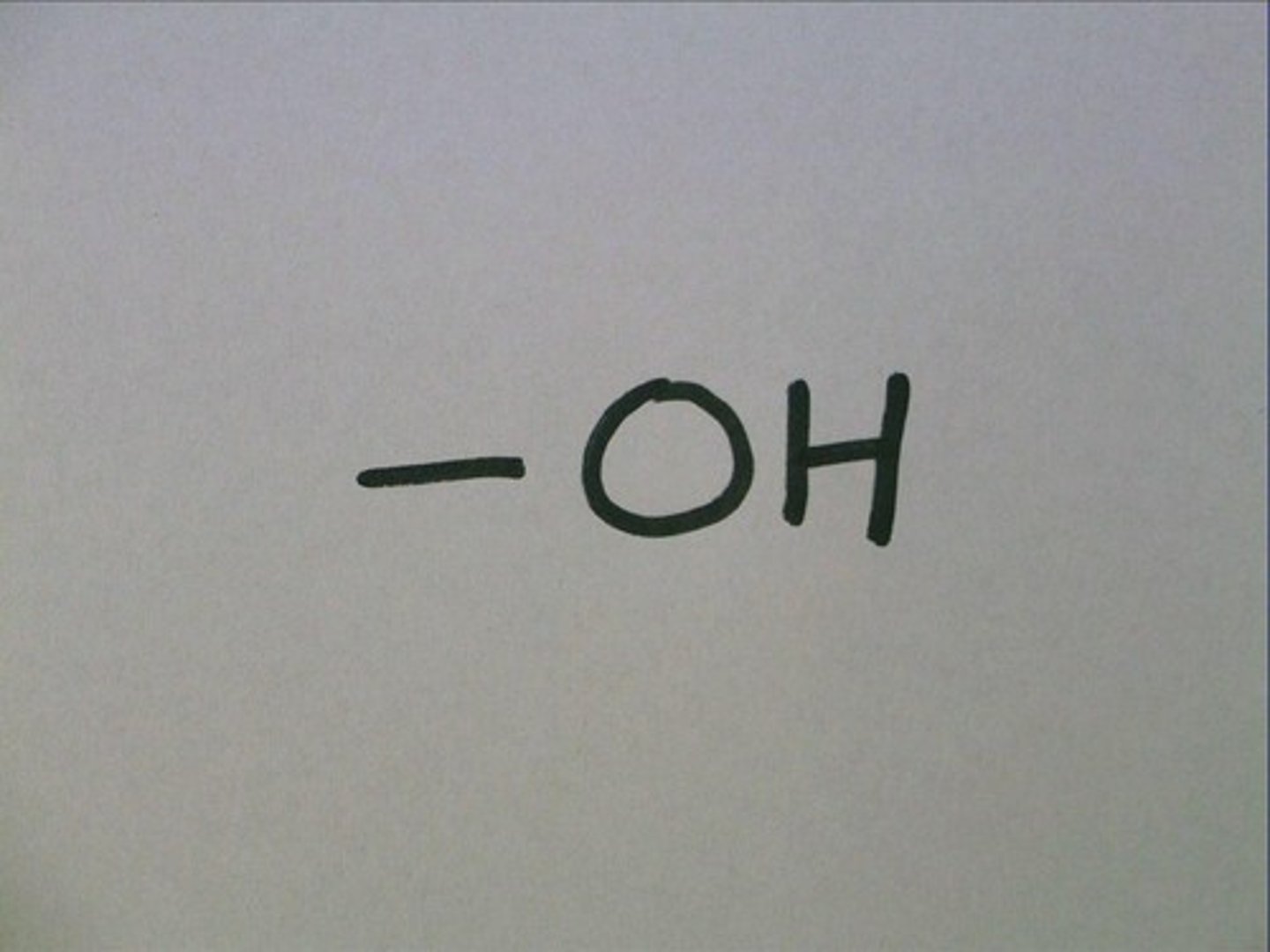
hydroxyl group
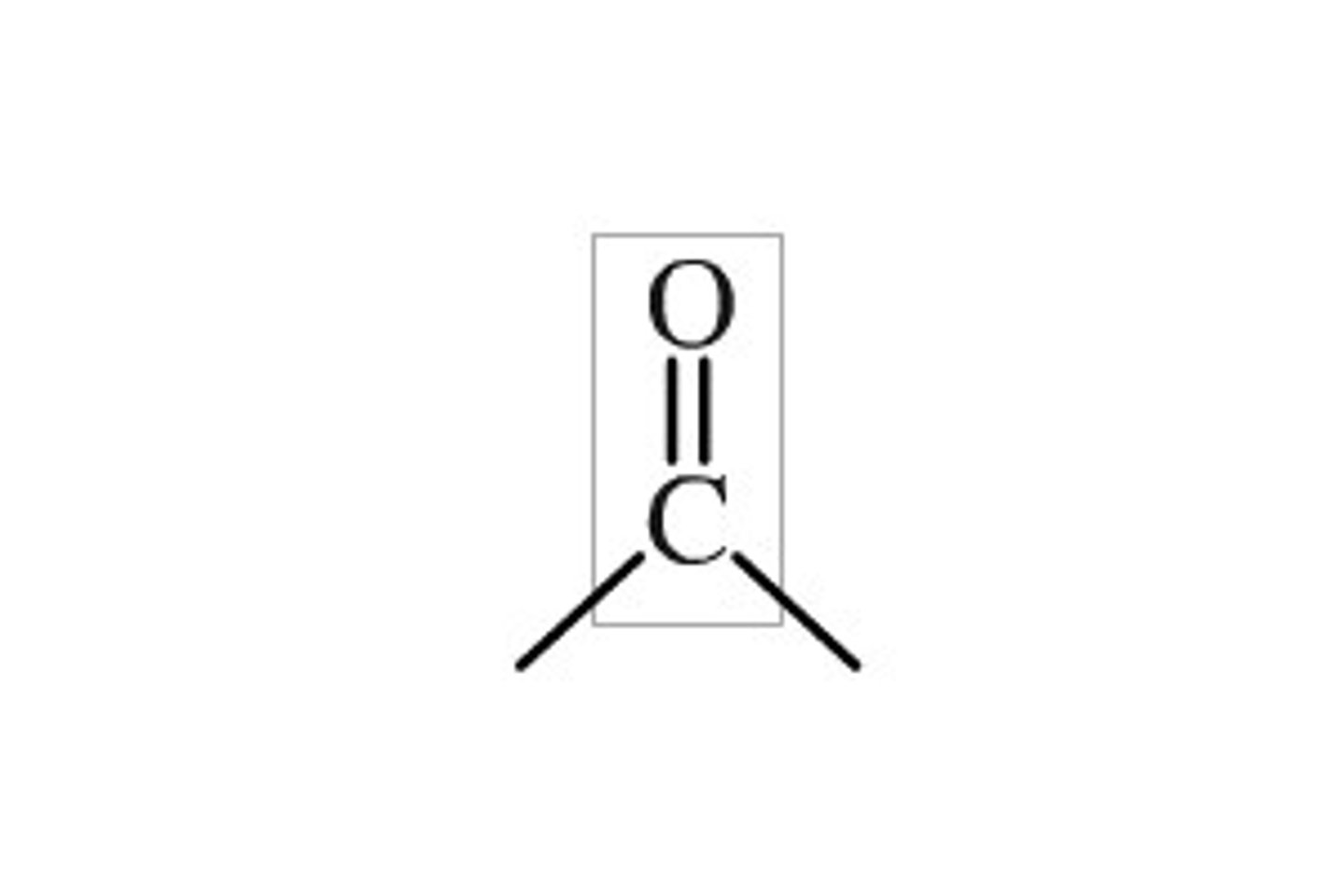
carbonyl group
C=O
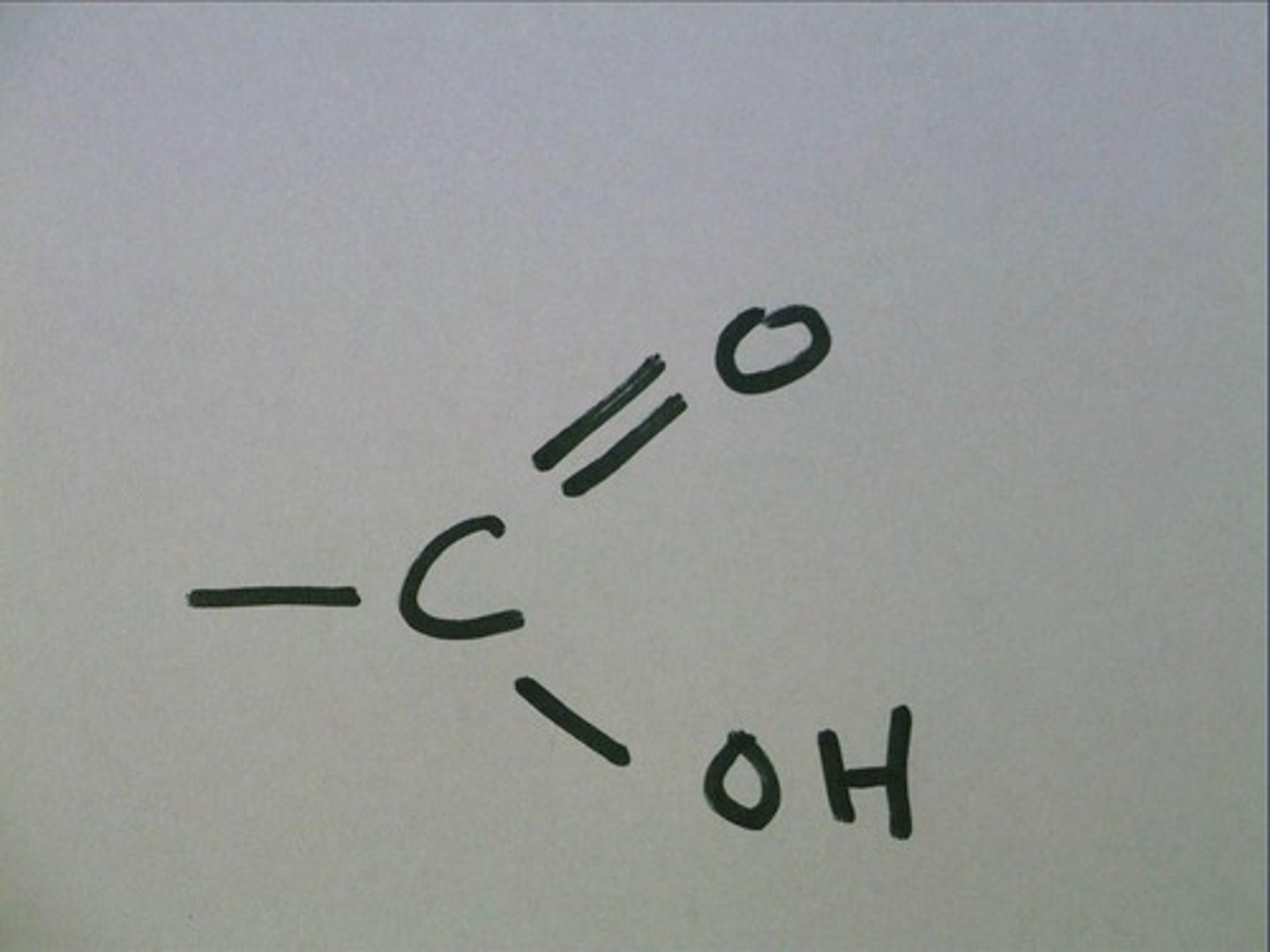
carboxyl group
COOH
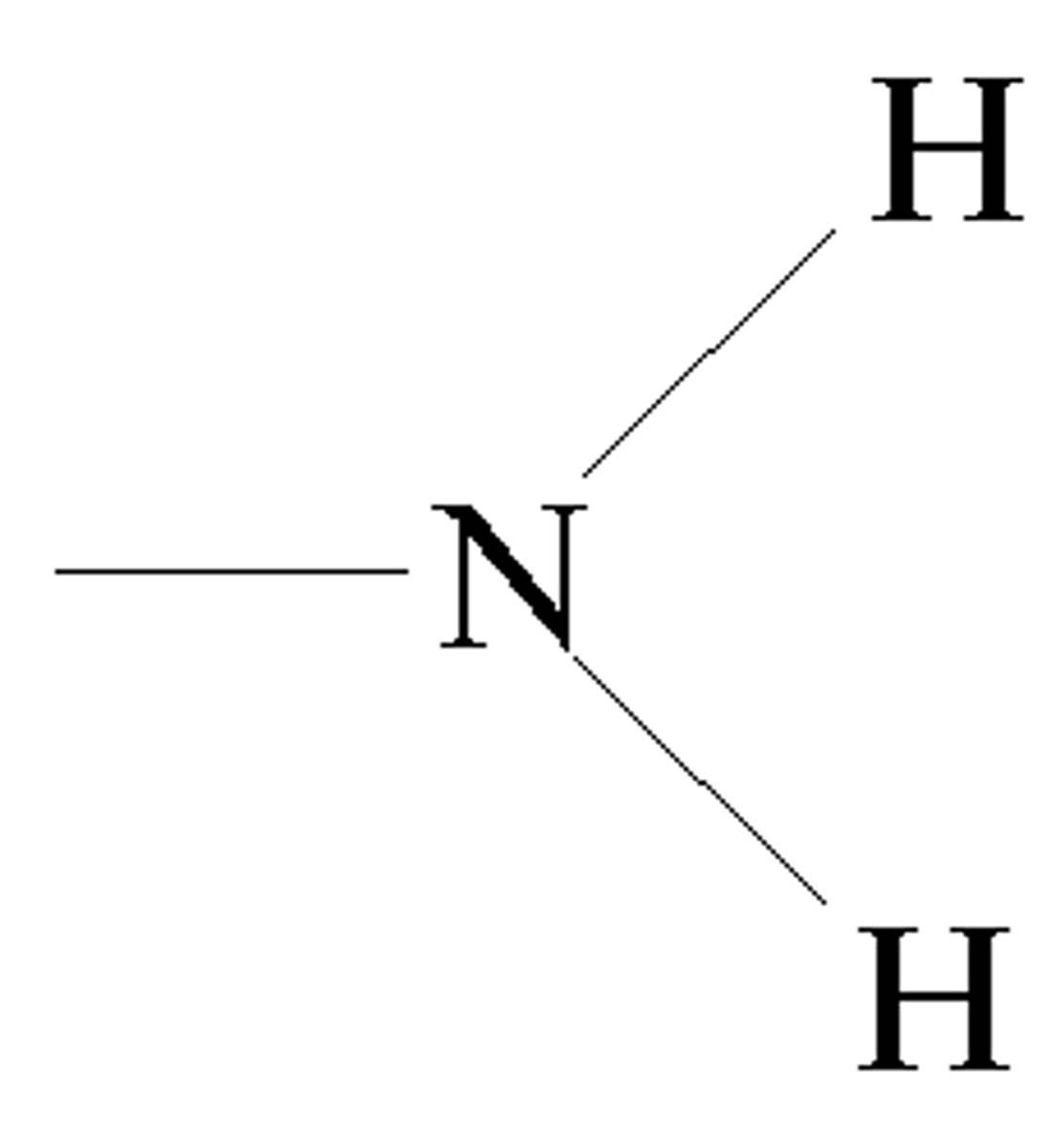
amino group
A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
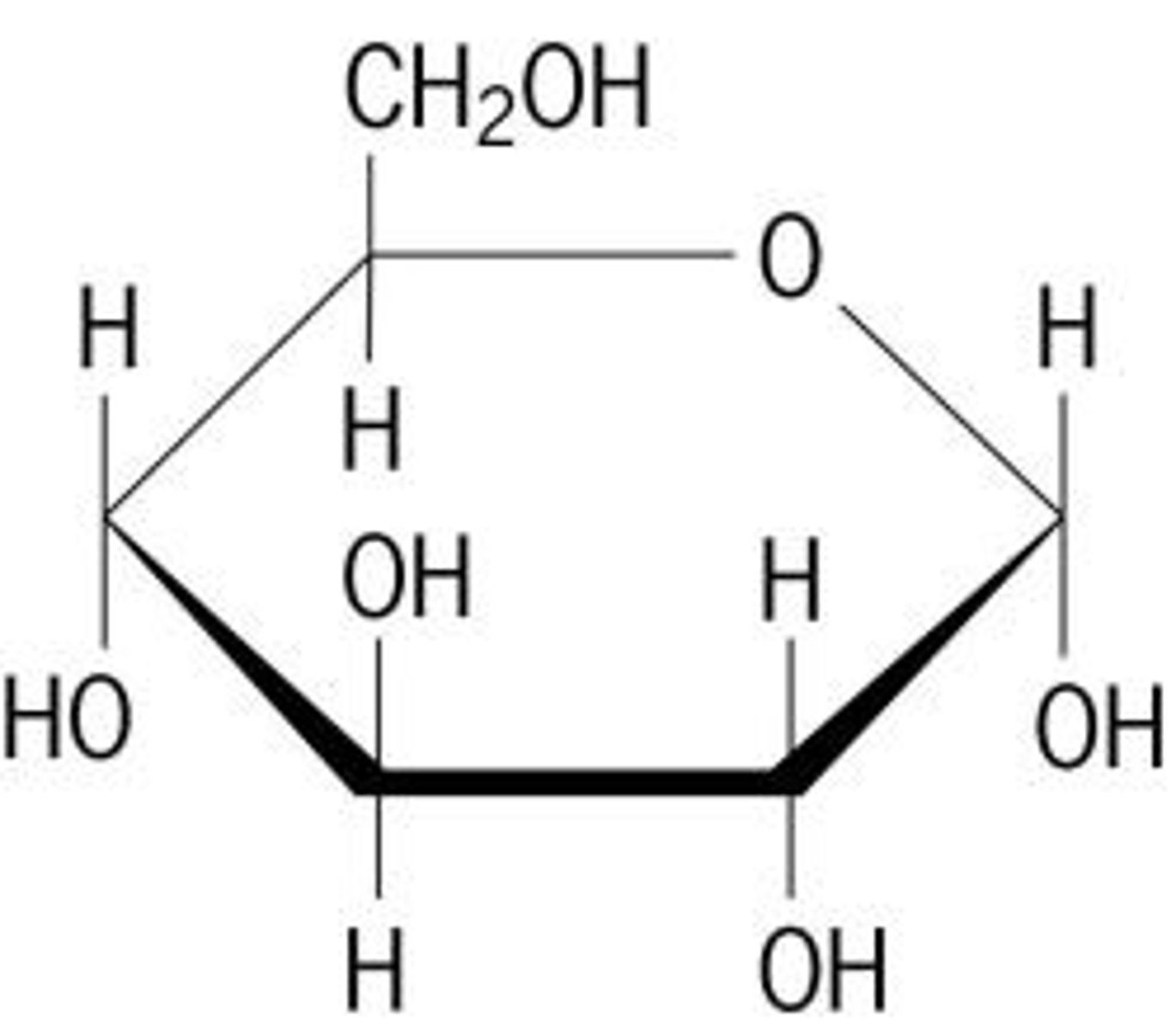
carbohydrates
Elements: C, H, O
Functions: energy quick and stored
monomers: glucose, fructose
polymers: starch, cellulose, glycogen
To test simple sugars use benedicts (red)
for starch use Iodine (black)
Monosaccharides are
glucose
broken down by cells to get energy
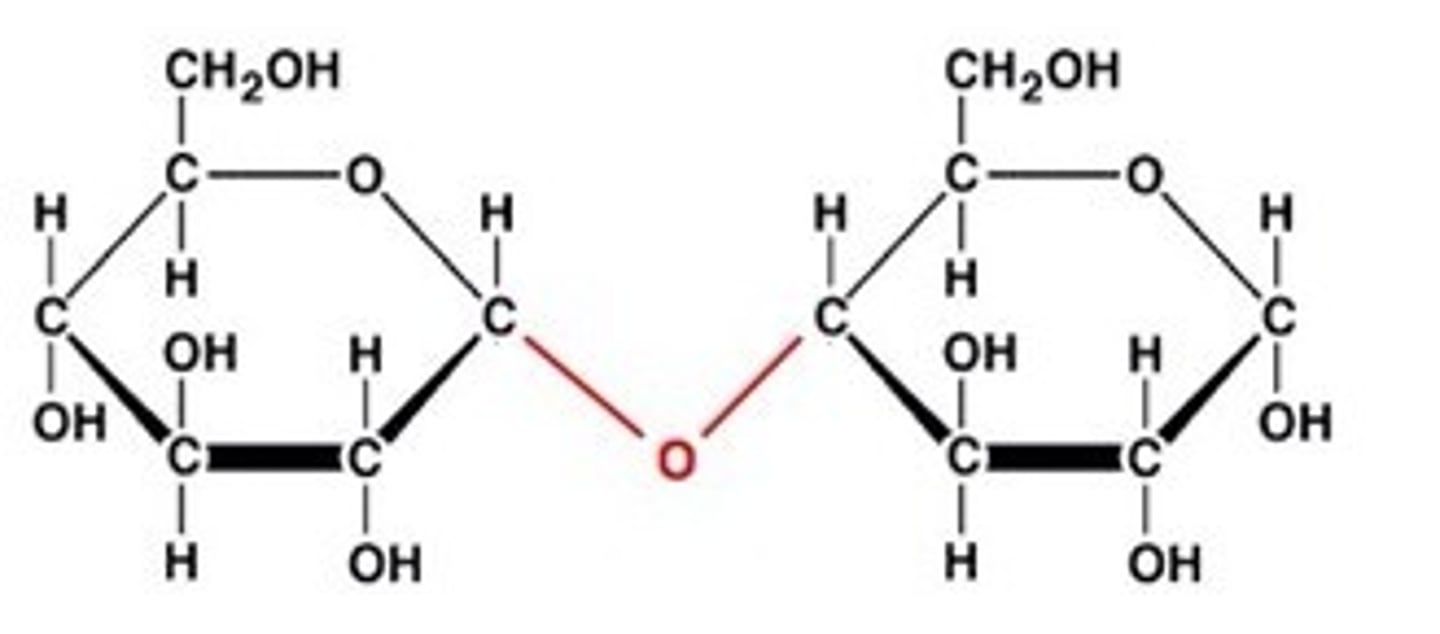
disaccharide
sucrose
main carb in plant sap
table sugar
lipids
Elements: C, H, O
Functions: for long term energy storage
insulation,
makes up cell membrane
monomers: glycerol, fatty acids
polymers: triglyceride, steroids
other: cholesterol
hydrophobic dissolve in oils not water

fat
three carbon backbone called glycerol attached to 3 fatty acids which contain long hydrocarbon chains
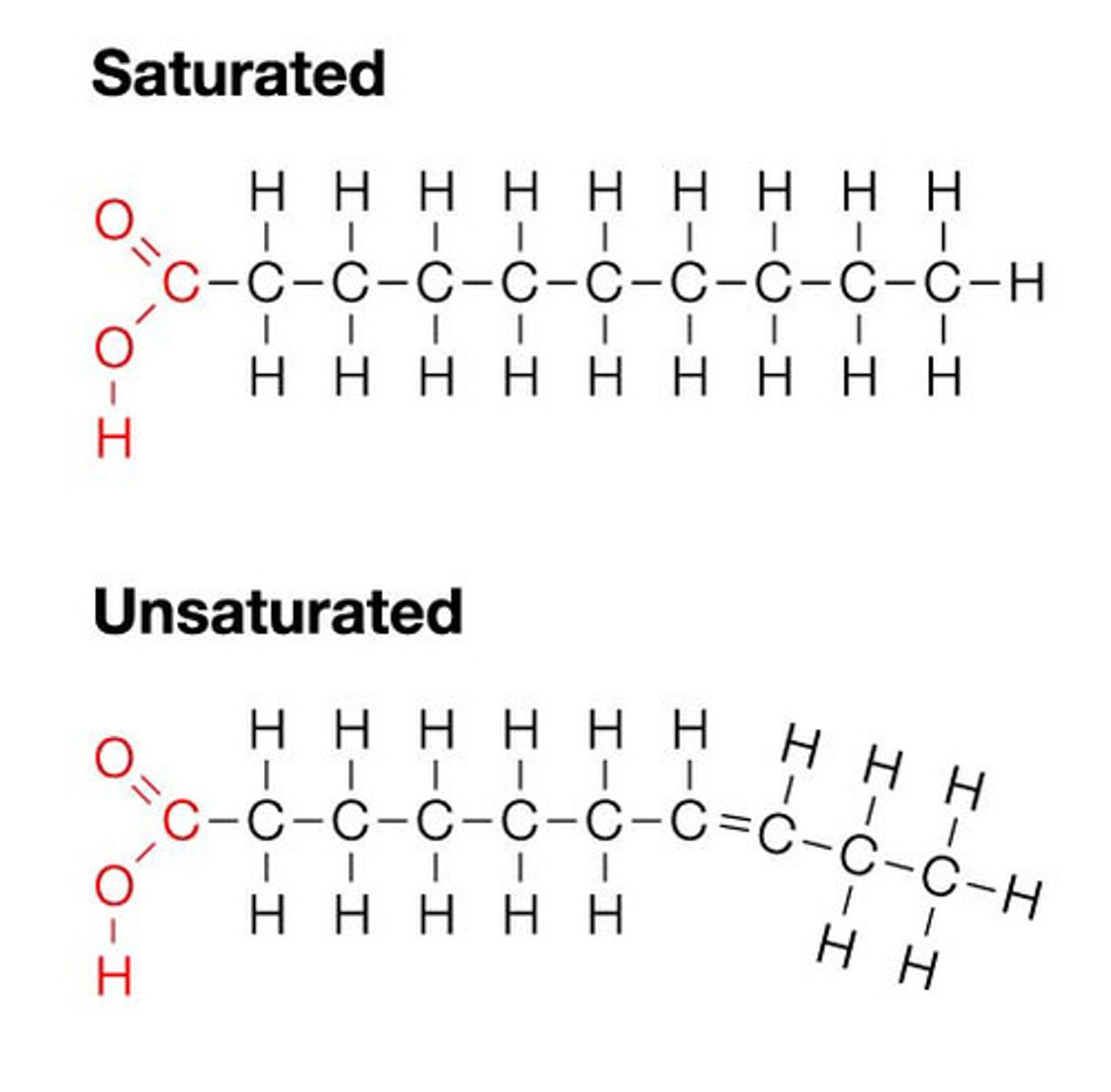
saturated fatty acid vs unsaturated
steroids
lipid molecule in which the carbon skeleton forms four fused rings
hydrophobic
chemical signal
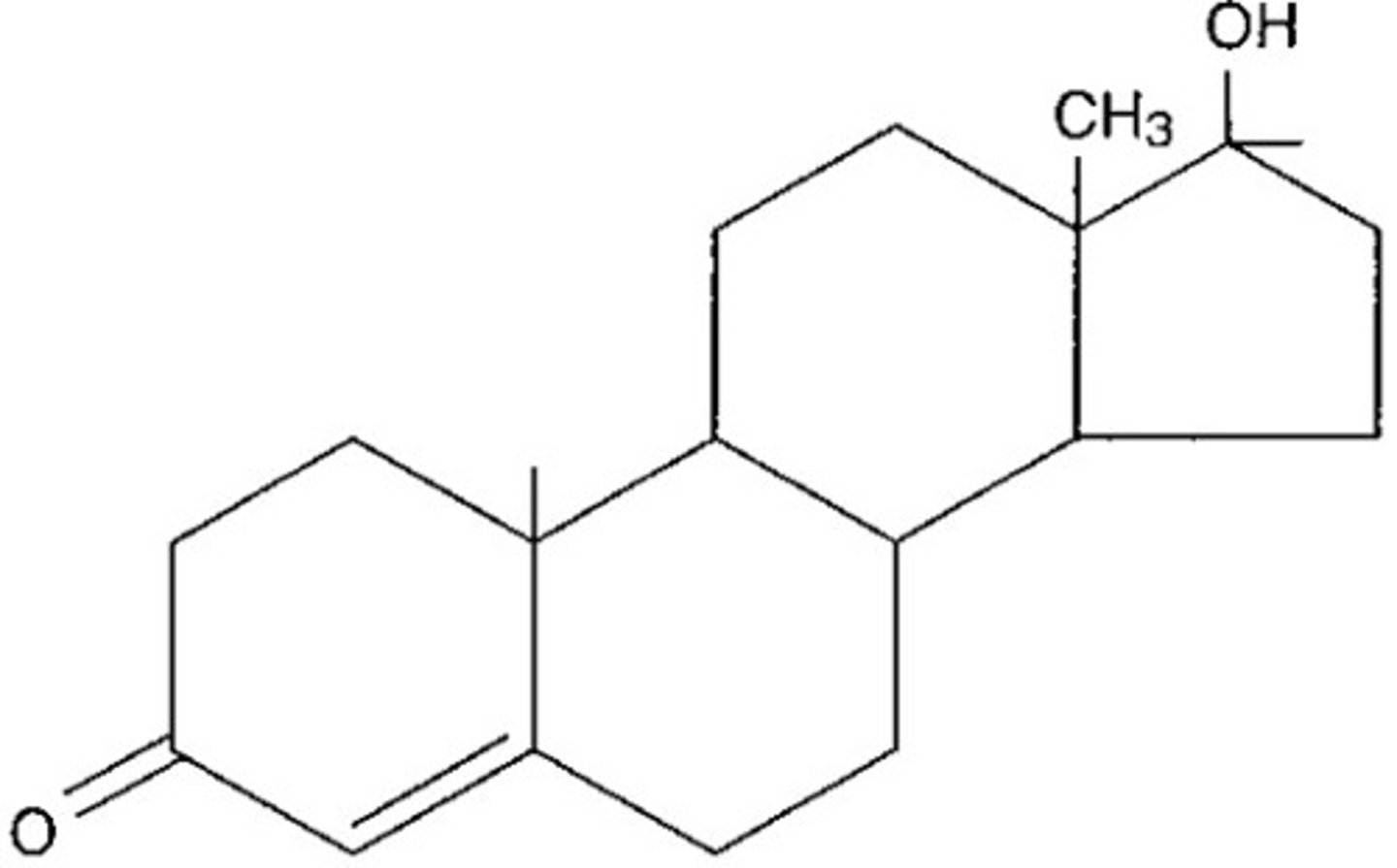
proteins
elements: C,H,O,N
functions: for chemical messengers
repairing cells
building muscle
long lasting energy
helps immune system
movement
hormone signals
helps transport oxygen with hemigloben
chemical receptors
monomers: amino acid
polymers: polypeptide
(amino acids linked by peptide bonds)
USE BIURET (purple)
nucleic acids
elements: C, H, O, N, P
uses: hereditary information,genetic code
monomers: nucleotide
polymers: Dna and rna
what is dna
threalike double-helical macromolecule
deoxyribonucleic acid
subunits called nucelotides
hydrolysis
adding water breaks down the polymer
dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction
hydroxyl group of one monomer reacts with a hydrogen from another monomer to release h20
peptide bond
a molecule of water is removed from two glycine amino acids to form a peptide bond
organic molecules
molecules in a cell including a skeleton of carbon atoms
inorganic molecules
molecules that do not contain carbon skeletons like water
hydrocarbons
organic molecules composed of only carbon and hydrogen
functional groups
different arrangements of atoms bonded to a carbon skeleton which give specific properties to molecules
monomers
small, similar molecular units
polymers
long chains of monomers
monosaccharides
simple sugars that contain just one sugar molecule
Disaccharide
sugars constructed from 2 monosaccharides
fatty acids
long chain hydrocarbons that end in a single carboxyl acid (COOH group)
-poorly soluble
tryglicerides
lipids composed of three fatty acids that are covalently bonded to a 3 carbon glycerol molecule ex: solid fats and liquid oils
phospholipids
main structural component of cell membrane
glycolipids
the outer membrane of most cells and sit in membranes
enyzme
made of protein
speeds up reaction rate but must overcome activation energyf
without reactions are too slow for body needs
active site
part of the enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reactions takes place
denaturation
proteins lose shape as thermal energy breaks down hydrogen bonds holding secondary and tertiary structure together
ph changes/salt concentrations
becomes nonfuctional
pH of blood and bodily fluids
7.4
maintained by bicarbonate buffering system
Steps in an Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction
1. substrate binds to active site of enzyme forming enzyme-substrate complex
2. substrate-products
3. product is released
4. enzyme can be used again