Biology CSUCI Norris Exam 3/4 2024
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Virus
Extremely Small
Not living
Non-cellular
No metabolism
Cannot reproduce independently
Obligate intercellular parasites
100nm
Basic Parts of a virus
Coat (box) → genetic material (DNA + RNA)
Lythic Cycle
1) Breaks open the cell
2) Infects the cell
3) The cell creates more
Lysogenic Cycle
1) breaks open the cell
2) Infects the cell
3) Splices the infection
4) Permanently in the body
How to stop viruses from spreading?
Vaccines, implants a small amount of the virus so your immune system can build a resistance
What doesn’t work again viruses?
Anti-biotics
Domain Eukyra
Protists, Kingdom Animalia, Kingdom Plantae, Kingdom Fungi
Domain Bacteria and Archeae
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic Cell
A single-celled organism without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, typically smaller than eukaryotic cells.
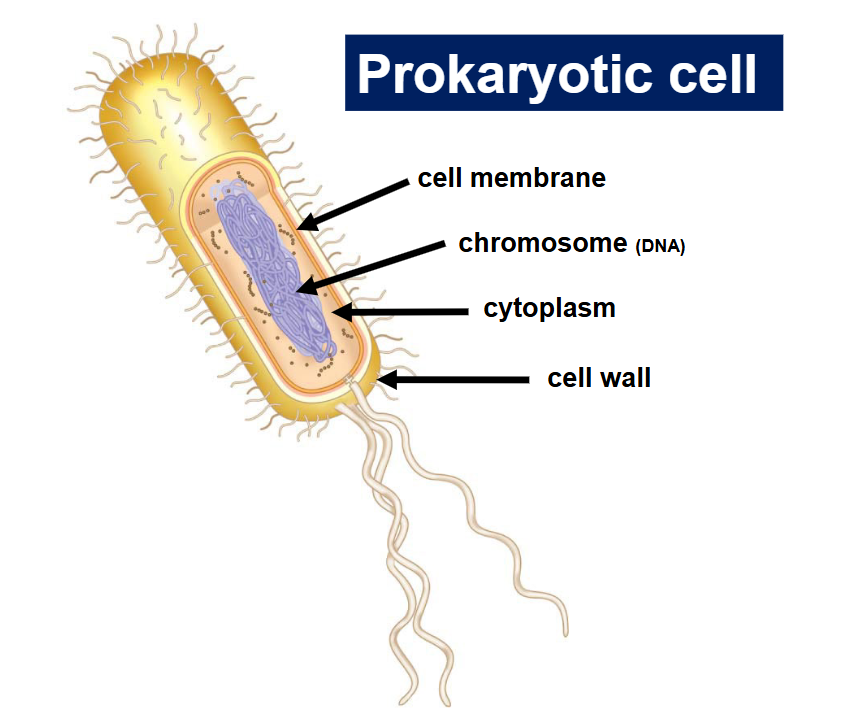
Prokaryotic Cell Shapes
-Coccus
-Spirillum
-Bascillus
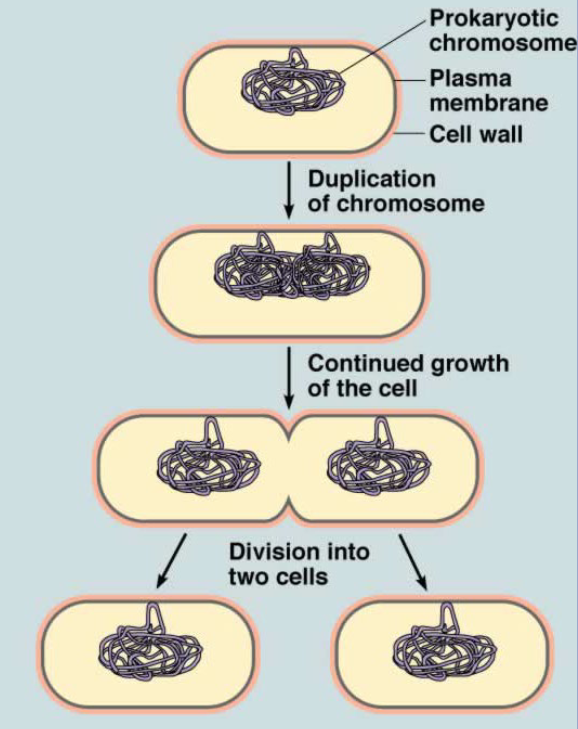
Binary Fission
Process of duplicating a cell
Endosymbiotic Origin
eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship where one prokaryotic cell engulfed another, leading to the development of organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts within the host cell, essentially creating a more complex eukaryotic cell structure
Protist
Mostly Microscopic
Many unicellular
Much diveristy
Habitats
Mainly damp soil, dormant in dry areas
Eukaryotic Reproduction
Sexual reproduction, gamate=zygote
Asexual reproduction, offspring is a clone
Protist Reproduction
Binary fission-asexual- 1 into 2
sexual- conjugation
Animal Like protists
Heterotrophic, most have locomotion
Plant-like protists
Autotrophic that can photosynthesize
Fungi-like protists
heterotrophs, and they have cells with cell walls and reproduce by forming spores
Origin of land plants
evolved from green algae and evolved to have vascular tissue that transfers water to all of the plant
Alternation of generations
Gametophyte- Haploid
Sporophyte- Diploid
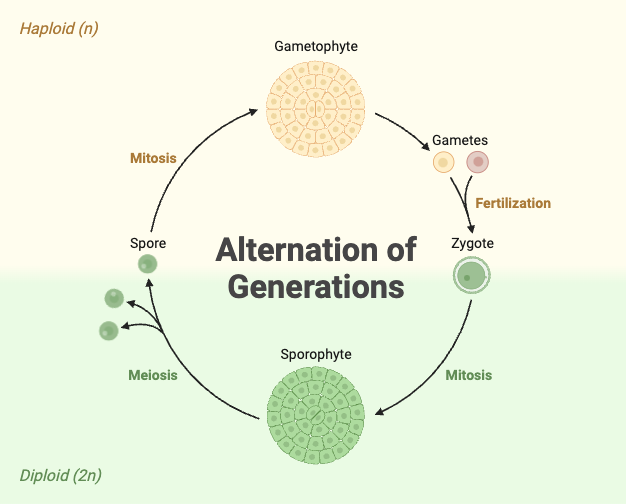
Diploid
Two sets of chromosomes
Haploid
One set of chromosomes
Groups of Plants
Non-Vascular Plants
Seedless Vascular Plants
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Non-Vascular Plants
Plants that lack the vascular tissues that transfers water and oxygen to the plant
Seedless Vascular Plants
Plants that have the vascular tissue but do not reproduce through seeds.
Vascular tissue
specialized tissue within plants responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and other substances throughout the plant body
Gymnosperms
Seeds develop in things like cones.
Angiosperms
Seeds develop in fruits and flowers
Flower
reproduction by releasing sporangiums into the air which are carried by the animals in the environment
Fruit
Fruits is whatever the flower ovary becomes (seed pod)
Seed vectors move the seeds
Stoma and Guard cells
A "stoma" (plural: stomata) is a tiny pore on a plant leaf, while "guard cells" are specialized cells that surround each stoma and control its opening and closing
Double fertilization
process where two male gametes (sperm cells) from a pollen grain fuse with two different female cells within the ovule, resulting in the formation of both an embryo and endosperm within one seed.
Fungal Biology
Phyllomate filled organism
Cell walls (chitin)
Absorptive feeders
Agents of decomp
Can be parasitic
Phyllomates
Called hyphae, a collection is called mycellium
Reproduction and Dispersal
Spores, most reproduce asexually (some sexually)
Fungal Symbiosis
Lichens, two part symbiosis protects algae cells and is fed
Mycorrhizae
Animals use fungi for digestive aid
5 types (phyla)
Chrytrids- primitave aquatic fungi
Zygomycota- bread mold
Mycorrhizae- fungus that lives on roots (mutualism)
Ascomycota- sac fungi, yeast, mold
Basidiomycota- mushrooms
Kingdom Animalia
All animals have one common anscestor
Main traits
Multicellular, Blastula, cell to cell signaling, different cell types
Characteristics
All heterotrophic
All multicellular
Generally sexually reproduce
Unique developmental patterns (embryos)
Do not have cell walls
Active movement
Diverse in form
Unique cell types
Diverse in habitat and niche
Animal origins
Choanoflagellate, protist, closest animal ancestor
Animal Body Plans
Tissue, symmetry, germ layers, body cavities
Protostome
Spiral cleavage, determinate
Mouth before anus
Deuterostome
Radial cleavage, indeterminate
Anus before mouth
Veterbrates
Chordata
Invertebrates
Porifera to Anthropoda
Parazoa
Basic creatures, Phyla Porifera
Phyla Porifera
Irregular symmetry, sponges, no germ layers, no organs or tissues, made up of fibers
Eumetazoa
Radial symmetry, tissues and diploblastic (two germ layers)
Phyla Ctenophora, Cnidaria
Phyla Ctenophora
Comb jellies, marine carnivore, extremely fragile
Phyla Cnidaria
Mostly marine, jellyfish, stinging cells, tentacles for food
Bilateria
Bilateral Symmetry, 3 germ layers, two divisions
Deuterostomia and Protostomia
Lophotrochozoan
Animals that don’t shed their cuticle
Phyla Platyhelminthes
Phyla Rotifer
Phyla Mollusca
Phyla Annelida
Phyla Platyhelminthes
Flatworms, most are marine + parasitic, simple construction, no body cavity, monoecious
Phyla Rotifer
Marine and freshwater, rotifer, eat small organisms
Phyla Mollusca
A foot and mantle for movement, radula with scraping, complex, diecious. squid
3 classes of Mollusca
Gastropoda, Cephalopoda, Bivalivia
Phyla Annelida
Segmented organisms, extensive body, all 3 types, detritus
Ectozoans
Animals that shed their cuticles
Phyla Nematoda
Phyla Arthropoda
Phyla Nematoda
Round worms, monecious, marine freshwater and parasitic
Phyla Arthropoda
Ancient group, exoskeleton, segmented, 4 major types
Chelicerates
Myriapod
Cretacean
Insect
Chelicerates
Spiders, stinging parts
Myriapod
Many feet, centipede
Cretacean
mostly marine aquatic, start as larvae, some have become terrestrial (rollypolly), lobster
Insect
mostly terrestrial, have air pipes, butterfly
Deuterostomes (phyla)
Phyla Echindermdata
Phyla Hemichordata
Phyla Chordata
Phyla Echindermdata
Marine, endoskeleton, water vascular system, starfish
Phyla Hemichordata
marine, filter feeders perforated pharynx, earthworm
Phyla Chordata
Mostly vertebrates, 4 main parts
Notochord, Dorsal nerve cord, Gill slits, Post anal tails
Urochordata
exclusively marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata, sea squirts
Cephalochordata
Have all Chordata features, lancelets, does not have a skull
Vertebrata
Animals that posses a vertebrate and a caninum or skull
Fish evolution
Jawless fishes (vertebrate)→ Cartilage fishes(Jaws)→ Bony fishes pt 1(ray-finned fishes)(Lungs or lung derivatives)→ Bony fishes pt 2(lobe-finned)
Jawless Fish
Hagfish + Lampreys
Bony skeleton
Cartilage Fish
Sharks
Cartilage instead of boney skeletons
Rayfinned Fishes
Rayfinned fish
fins supported by the spine
Lobefinned Fishes
Coelacanths and lung fishes
Small lobes at the end of the fin
Tetrapods
4 limbs/limbs with digits(Amphabia) → Amniotic egg (Reptiles) → Milk (Mammalia)
Amphabia
Terrestial + Freshwater
4 limbs with digits
Frogs
Reptiles(Non avaian)
Diopsid skull
Turtles - armoured reptiles
Lizards - eyelids + eardrums
Crocs- Archosaur
Aves
Avian reptile
Type of dino
all have feathers (keratin)
bones are hallow
warm blooded
no boney tails
two parent care