Biology Midterm Exam
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
Independent Variable
The variable in an experiment that is manipulated or changed to test its effects on the dependent variable.
Dependent variable
The variable that is measured or observed in an experiment to assess the effect of the independent variable.
List and describe each step of the scientific method
make observation: research →
form hypothesis: a problem you want to solve →
conduct experiment: to experiment the hypothesis →
analyze data →
draw conclusions
What are the 8 characteristics of all living things must have?
organization - made of one or more cells
metabolism - obtain and use energy
reproduce
DNA - instructions
respond to environment (stimuli)
homeostasis
growth and development
evolve - as a group, changes over time
What is growth?
An increase in the size and mass over time
What is development?
An organism becomes more complex (gains cells, tissues, and organs) over time.
Are viruses considered living things?
No → only have 3 of the 8 characteristics of life: DNA, reproduction, and evolution
The 7 levels of classification developed by Linnaeus (biggest to smallest)
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species
What are the 6 kingdoms?
Animal, plant, protist, fungi, eubacteria, and archaebacteria
What are the similarities of Animalia and Plantae?
Both are eukaryotes, multicellular, and have sexual reproduction
What are differences of Animalia and Plantae?
Animalia are heterotrophs, have no cell walls and only have sexual reproduction while Plantae are autotrophs, have cell wall of cellouse, and can be both asexual and sexual
Prokaryote
a cell without a nucleus
Eukaryote
a cell with a nucleus
Unicellular
organisms made of only 1 cell
multicellular
organisms made of many cells
Heterotroph
gets energy by consuming other living things —> food
Autotroph
gets energy by sunlight/chemicals → food
Which elements are found in all organic compounds?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
Carbohydrate’s function?
main source of energy
Carbohydrate’s primary elements?
CHO (1:2:1)
Carbohydrate’s monomer?
glucose/fructose
Carbohydrate’s polymer
polysaccharide
Lipid’s function
to store long term energy, and is the main component of the cell membrane.
Lipid’s primary elements
CHO
Lipid’s monomer
fatty acid tail
Protein’s function
structural movement, transport, catalyze
Protein’s primary elements
CHON (sulfur)
Protein’s monomer
amino acid
Nucleic acid’s function
store and transmit genetic information
Nucleic Acid’s primary elements
CHONP
Nucleic Acid’s monomer?
nucleotides
monomer
a single compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
polymer
a long molecule consisting of many similar/identical monomer linked together
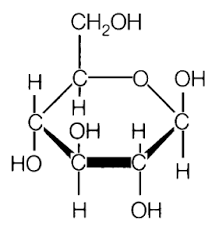
Carbohydrate
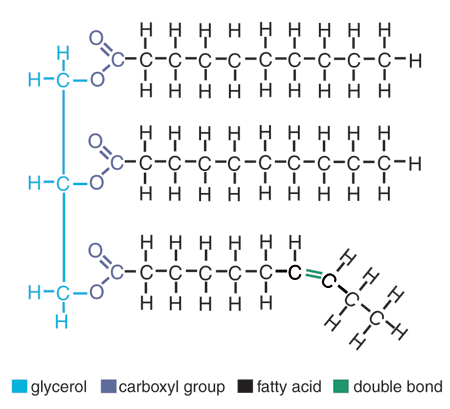
Lipid

Protein
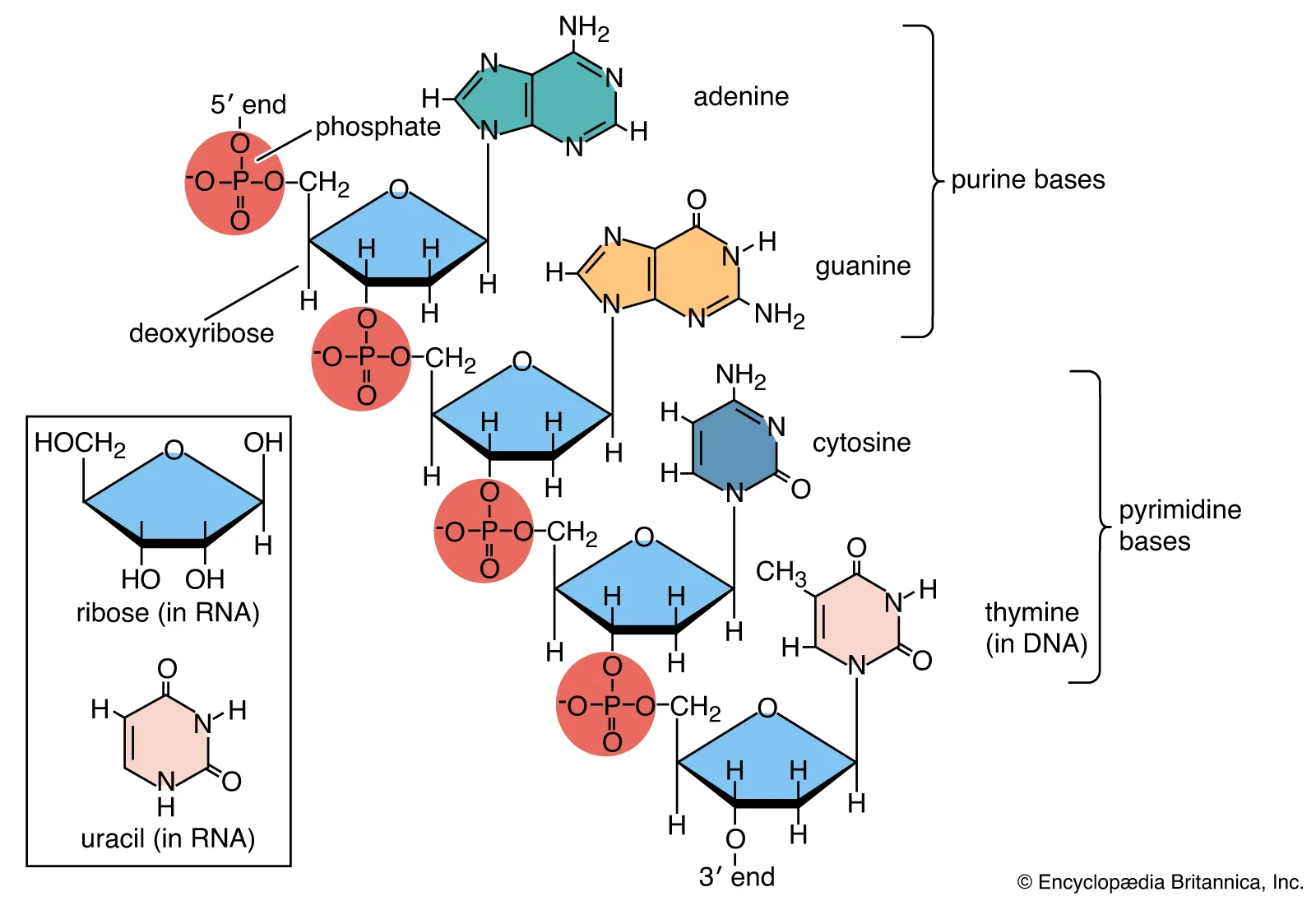
Nucleic Acid
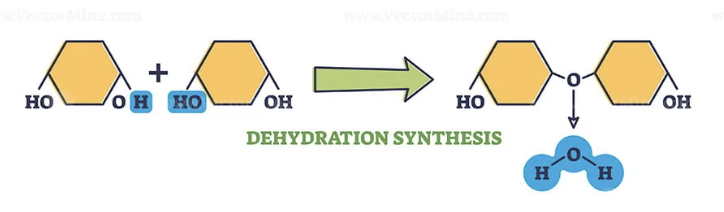
Dehydration synthesis
A process that combines monomers by removing water
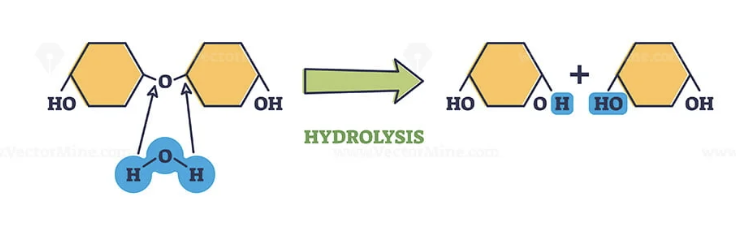
Hydrolysis
A process that separates monomers by adding water
Enzyme
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
Substrate
the specific item an enzyme can only catalyze once
Active Site
the place where the enzyme and substrate meet and the substrate may be broken apart or joined together.
Activation energy
energy required to start a chemical reaction
With an enzyme, activation energy…
decreases
Without an enzyme, activation energy…
increases
Denaturing
when a enzyme goes beyond its optimum temperature and pH, and loses its shape. The enzyme can no longer function at all
What are the 3 parts of the cell theory?
all organisms are made of one of more cells
the cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms
all cells come from pre-existing cells
Which organelles are present in only eukaryotes?
Nucleus, mitochondria, vacuoles, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus
Which organelles are present only in plants?
Chloroplasts, and cell wall
Primary Function: Cell membrane
regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell
Primary Function: Cytoplasm
holds the internal components of cells in place and protects them from damage
Primary Function: Ribosomes
translates genetic code from RNA into amino acid sequences, builds protein
Primary Function: Nucleus
the control center, regulates the cell’s activity
Primary Function: Centriole
organizes microtubules that serve as the cell’s skeletal system
Primary Function: Mitochondria
generates energy/powerhouse
Primary Function: Endoplasmic reticulum
produces proteins for the rest of the cell
Primary Function: Golgi Apparatus
transports, sorts, modifies proteins and lipids
Primary Function: Chloroplast
produces energy through photosynthesis/plants
Primary Function: Nuclear Membrane
Barrier around the nucleus, protects DNA from cytoplasm
Primary Function: Vacuole
Helps waste management
Primary Function: Cell wall
provides strength and protection, controls and regulates the direction of cell growth
Primary Function: Vesicle
transports materials to the cell
Primary Function: Lysosome
breaks down waste materials into the cell
Primary Function: Nucleolus
Synthesizes and assembles ribosomes
Why do we have different organelles in each cell?
Each organelle has a unique job to do → more efficient
Homeostasis
The body regulating/keeping balance throughout.
What are the key parts of the cell membrane?
Protein channel, hydrophilic head, phospholipid bilayer, molecule and cholesterol
Protein channels/pumps
Help transport or channel a way for items to pass through the membrane.
Active Transport
A way to get through the cell membrane: requires energy, does both high to low and low to high, and uses a pump.
Passive Transport
A way to get through the cell membrane: doesn’t require energy, does only high to low, and uses a channel
Simple Diffusion
gases and hydrophobic/nonpolar molecules move directly through the membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
hydrophilic/polar molecules pass through with the help of a protein channel
Osmosis
Water diffuses through the membrane (goes where there is more solute)
Isotonic
Solution with equal concentration of solute to another
Hypotonic
Solution has a lower concentration of solute to another
Hypertonic
Solution has a higher concentration of solute to another
How will water move if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution?
Out of the cell
How will water move if a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution?
In the cell
How will water move if a cell is placed in a isotonic solution?
in and out of the cell
endocytosis
When proteins are too large to pass through diffusion, uses this to go into the cell
exocytosis
When proteins are too large to pass through diffusion, uses this to go out of the cell
What kind of things are moved across a cell membrane by endocytosis and exocytosis?
large proteins
The original source of energy in foods used by living things comes from?
the sun
How do heterotrophs get energy?
Their environment → other living things
How do autotrophs get energy?
Their own cells → photosynthesis
chemosynthesis
the process by which food is made by bacteria or other living things using chemicals as the energy source, typically in the absence of sunlight.
Where would chemosynthesis take place?
Deep sea
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate, it’s the main source of energy that cells use for most of their work
What is ADP?
Adenosine Diphosphate, when a phosphate group is removed from ATP it releases energy.
Why do most plants appear green?
All the other wavelengths get absorbed while green is reflected
How can changes in temperature or pH affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis depends on enzymes in order to function.
Anaerobic respiration
enzymes in the cytoplasm split glucose to gain a small amount of ATP energy the process occurs without oxygen
Alcohol fermentation formula
C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₂H₆O + 2CO₂
Glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
Lactic fermentation formula
C₆H₁₂O₆ → C₃H₆O
Which fermentations are anaerobic?
lactic, alcohol (both require ATP)
Reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide and water
Reactants of cellular respiration
oxygen and glucose
Product of photosynthesis
oxygen and glucose
Product of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, and water
What type of organism is photosynthesis?
autotroph