Exam 2 Content
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Measuring voltage
Across two points. Red lead is the positive lead and black is for negative. So if red is on a more negative side than black, will read out a negative voltage.
Voltage
Potential energy or potential difference. Amount of work required to move a charged particle from one place to another.
DC
Direct current. Reasonably constant voltage instead of sinusoidal. What comes out of a battery. The kinds of voltage produced by the body.
AC
Alternating current. Current that comes out of wall outlet. Sinusoidal voltage/current source. Much more efficient for distributing power over a long distance. Can be scaled up or down using a transformer.
Passive sign convention
Place positive sign on side of resistor closest to positive terminal of power source or designate direction of current and from pos o neg.
Ohmic
A circuit element that obeys Ohm’s law, so a linear relationship between current and voltage, related by the slope R.
Diode
Useful non-ohmic element. Current can only flow through the component in one direction. Fluid equivalent is a valve.
KVL
Sum of voltages around any closed loop is zero
KCL
Sum of currents at any node is zero. Based on conservation of mass and volume.
Essential node
A circuit location where 2 or more branches meet.
Branch current method
1) assign a current to each branch without a current source
2) assign a voltage to each element that doesn’t have a specified voltage. Place ± according to passive sign convention
3) Apply KVL to each independent loop, and KCL to each essential node
4) solve the system of equations
Capacitor
Storage of charge
Capacitor capacitance
Defined by surface area of plates, permittivity constant, and distance between plates.
Windkessel Model
Blood vessel model. Vales as diodes, resistance of vessels as resistors, compliance of vessels represented by capacitor (storage of blood volume and potential energy to drive blood flow between heart beats)
Effect of valves
Prevent backflow of blood through body. Close when the pressure on the inside side is lower than on the output side.
Effect of resistive elements
Slow down current/flow rate, allowing for a slow enough flow at capillaries to have exchange of gas and nutrients.
Effect of compliance vessels
Smooth out flow (less pulsatile) and store potential energy to continue moving blood through body between heart beats. Ensures a smoother and more laminal flow is attained in the capillaries to allow for proper gas and nutrient exchange.
Biological membranes
Act as electrical capacitors. Based on selective permeability and charge gradients established by ion pumps, maintain charge difference across membrane.
Membrane resistance and capacitance form the time constant telling you how fast the membrane potential responds to ion channel currents.
Ion flow through membrane
1) passive channels
2) active channels
3) ion pumps
Nernst potential
For each ion in the cellular environment, there is an equilibrium potential where the net flux of the ion across the membrane is zero. Driven by concentration and charge gradients. Also known as equilibrium potential
Dominant ions in cells
Potassium, sodium, and chloride (K+, Na+, Cl-)
Equivalent circuit for the flow of an ion across a membrane
Assembled with a voltage source equivalent to the nernst potential and a resistor representing the resistance the ion faces to move across the cell membrane.

Squid gian axon
Can represent the movement of major ions across the cell membrane as a circuit with an equivalent capacitance. Can use this to solve for the resting membrane potential.
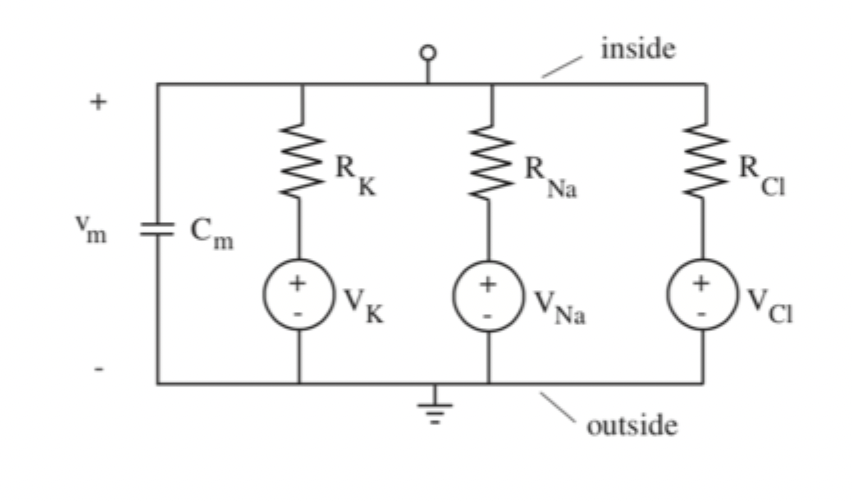
Solving for resting membrane potential
Orient nerns’t potential voltage sources with positive side toward inside of cells. Represent ground as being outside of the cell. Place individual ion circuits in parallel with Cm.
Changes during nerve excitation
Membrane potential increases as resistance for ions decreases. Leads to a smaller time constant and a faster ability for the cell membrane to respond to changes in current.
Action Potential
Upon stimulation, membrane potential rises above a threshold value, leading to full depolarization of the cell driven by increased conductance of Na+. Repolarization driven by increased conductance of K+. Closing of Na+ gates starts the decrease in voltage potential.
-threshold events
-all or none events
-temporarily change the membrane potential from eqm potential