Eggs
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what are the four types of egg production systems?
barn
free range
organic
enriched colony cages
what are features of barn production systems?
hens housed in buildings with one or more levels
free to move around
litter for dust-bathing and scratching
nest boxes and perches - 15cm of perch per hen
EU Welfare of Laying Hens Directive - max stocking density of 9 hens per square metre of usable area
electrical lighting to mimic optimal day length
British Lion Barn Eggs - 16.5 birds per metre square of usable floor area (more space per bird than EU welfare laying hens directive)
what are features of free range systems?
hens have continuous daytime access to runs which are mainly covered with vegetation
EU - max stocking density of 2,500 birds per hectare (2,000 birds per hectare in UK)
hen house conditions must comply to regulations for birds kept in barns
outdoor shading in absence of a veranda
One pop-hole per 600 birds open for 8 hours daily to allow access to the outside
what are features of organic systems?
Hens producing organic eggs are always free range
hens must be fed an organically produced diet and range on organic land
maximum stocking density of 6 hens per square metre of useable area and a maximum flock size of 3,000 birds
must have nest boxes, adequate perches - 18cm of perch per hen
litter provided
what are features of enriched colony cage systems?
battery cages banned - replaced by enriched colony cages
contain between 40-80 birds, enabling better use of the space and giving them more room to move around the colony
750cm² per bird
nest box for the birds to lay their eggs in, perching space for the birds to sleep on and a scratching area to perform natural behaviours
what do stamps on eggs show?
method of production:
0 = organic
1 = free-range
2 = barn
3 = caged
country of origin
farm ID
additional marking for Lion Quality eggs
what sizes of eggs do we see?
<53g = small
53-63g = medium
63-73g = large
>73g = very large
what are the egg quality grades?
grade A - naturally clean, fresh eggs, internally perfect with shells intact and the air sac not exceeding 6mm in depth, yolk doesn’t move away from the centre of the egg on rotation
grade B - eggs are broken out and pasteurised
eggs worse than grade B are for non-food use only and are used in products such as shampoo and soap —> industrial eggs
what eggs would fall under grade A in terms of appearance?
pink shell
brown shell
brown speckled shell

what are the 3 main parts of the anatomy of an egg?
the shell or cuticle
the white or albumen
the yolk
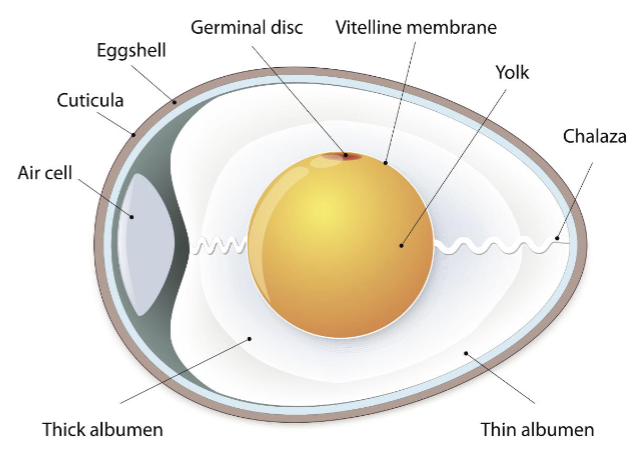
what does the yolk contain?
fats, vitamins and minerals, and about half of the egg’s total protein
what affects the colour of the yolk?
the hen’s diet - no connection with food value
what does the albumen (white) contain?
rich in protein and vitamins
what are common eggshell faults?
rough shelled eggs - due to two eggs in the shell gland at the same time
pale shelled eggs - cosmetic change
soft and weak shelled eggs - commonly from older birds, especially if nearing the end of laying period
cracked eggs
dirty and glazed shells - contaminants e.g. faecal material, dust, mud and litter, blood
what are common internal faults?
double yolked eggs - young, highly productive laying hens
blood spots in eggs - tiny blood vessel in ovary breaking when yolk is released, more likely at ovulation
meat spots in eggs (brown in colour) - consist of small pieces of body tissue e.g. internal wall of oviduct
watery whites - more in older birds, can be due to viral disease e.g. infectious bronchitis
abnormal yolk colour - e.g. green yolk due to birds consuming green herbage in excess
mobile and bubbly airspaces - usually due to ruptured inner membrane within albumen
bacterial and fungal contamination - produce black, red or green dots
misshaped eggs - when albumen quality if very poor
what types of cracks do we see in eggs?
hairline cracks - difficult to identify
star cracks - visible under normal light, more easily sen during candling
pinhole and toehole cracks - caused by hen or any sharp protrusion coming into contact with egg
how did the Lion Quality Mark Scheme 1998 change number of eggs with salmonella?
requires hens to be vaccinated against salmonella
how did the National Control Programme 2009 change the number of eggs with salmonella?
farms with more than 350 laying hens have to test their flocks for salmonella