Microbes-L15- Adaptive Immunity 3:antiviral immunity (especially flu)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
how do vaccines work?
vaccines introduce an antigen- non infectious
PC- antigen presenting cells like dendritic cells and macrophages in the innate immune system aka cup the antigen
to make CD4 helper cells by presenting via MHC II cells to activate B cells and CD8 cells cytotoxic cells
gives long term immunity
difference between being infected and vaccination?
with a vaccination you don’t need to get ill to be immunised
influenza virus structure
has neuraminidase- which is a target for anti viral drugs like Tamiflu
haemagglutin which triggers and immune response either by infection of vaccines
nucleoprotein
matrix protein
how does immunity to influenza virus work?
control of the infection: mediated by NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes
cytotoxic T lymphocytes target the nucleoprotein on the virus- as it doesn’t change across subtypes
-CTL can recognise nucleoproteins across subtypes giving cross reactive immunity
prevention of re-infection by antibodies- HA is the target point of neutralisation - also targeted by CD4
HA is highly variable
difference between nucleoprotein and hemagglutin on influenza?
nucleoprotein is quite conserved across subtypes and so doesn’t vary much and recognised by the immune system
HA/hemagglutin- varies a lot through subtypes
innate and adaptive production in influenza
innate: production of interferon alpha, beta and TNF alpha and IL-12, NK cells killing of infected cells
adaptive: T cell mediated killing of infected cells
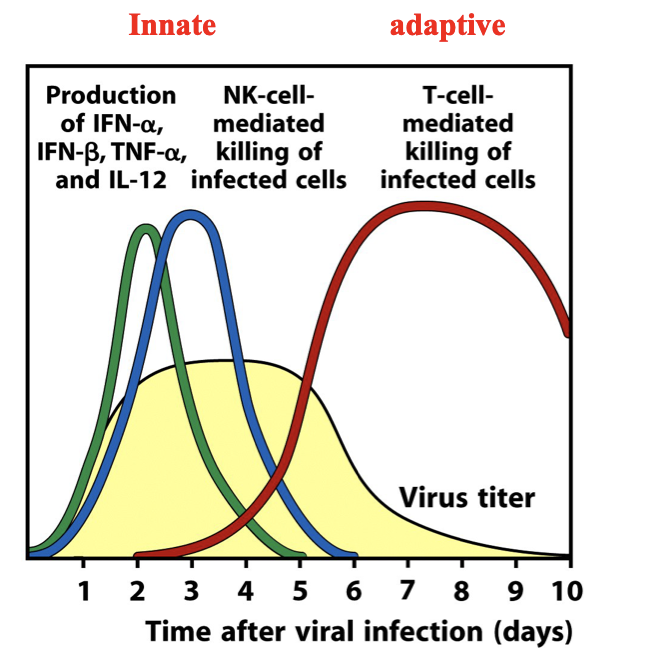
steps of immunity to the influenza virus:
virus enters the body and produces viral proteins- warning signals
macrophages- detect and phagocytose
NK cells kill infected cell
Th1 releases-interferon gamma
adaptive:
Th1/2 release IL-4 and IFN gamma which release B cells IgA/IgG antibodies
NK cells kill infected cells
along with macrophages
how do neutralising antibodies work in immunity?
virus binds to the receptors on cell surface
receptor mediated endocytosis
acidification of endosome- triggers fusion of virus with cell - entry of viral DNA
antibody blocks binding to the virus receptor and block fusion event
how does influenza virus evade immune response?
by antigenic variation- RNA segments are exchanged between viral strains in a secondary host
as influenza have segmented genomes
second host- is infected with 2 strains- RNA from both viruses mix- host no longer recognises HA
or- mutations in the epitopes- no longer recognised HA
adaptive immunity to bacteria: humoral and cell mediated- explain cells involved and what they do
humoral immunity:
B cells and antibodies- presentation of infection and reinfection
usually EXTRACELLULAR bacteria
cell mediated immunity
T cells- help in making antibody production
control of infection
INTRACELLULAR bacteria
how does bacteria trigger inflammation?
bacteria triggers macrophages to release chemokines and cytokines
vasodilation and increased vascular permeability- heat, redness, swelling
inflammatory cells migrate to tissues- and cause pain
cell mediated immunity to bacteria- examples of those that are resistant
many intracellular bacteria- resistance to antibodies and compliment-TB and mycobacterium leprae
CD4 Th1- produce IFN gamma and activates macrophages, MHC expression, killing mechanisms
CD8+ T play a role in salmonella
NK cells- early IFN-gamme production
discuss mycobacterium tuberculosis
2b people have latent- 10% will develop active
Latent- immune responses control the infection
active infection- weakened immune response- HIV,, older people
antibiotics used to treat- but drug resistant have emerged
vaccines against Mycobacterium tuberculosis- and what are new vaccines based on?
BCG- bacille calmette guerin
prevents TB meningitis
poor efficacy against pulmonary TB
new generation vaccines based on purified antigens- in development
AIM: to induce cell mediated immunity
what does an infected viral macrophage trigger?
Th1- to produce IFN gamma
what does a granuloma consist of?
outside: Th1 cells releasing IFN - keeps the virus inside
inside- epitheloid macrophages cells, multi nucleated giant cell
what can TB also result in? and what is the response?
mycobacterium leprae
tuberculoid- trigger Th1 cell mediated immunity- IFN - gamma, IL-2, TNF-beta
lepromatous- trigger Th2 cytokines- IL4, IL-5, IL-10