Perfect Competition (Chapter 13)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
competitive market
a market in which fully informed, price-taking buyers and sellers easily trade a standardized good or service
Standardized goods and services
are interchangeable.
Transaction costs are the
costs a buyer or seller incurs to make an exchange take place.
For firms that sell one product in a perfectly competitive market, the market price
is equal to a firm's average revenue.
For firms that sell one product in a perfectly competitive market, marginal revenue is always
equal to the market price.
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market is producing at a level of output where marginal costs exceed marginal revenue, then the firm's profits:
A. must be negative.
B. are maximized.
C. will increase if production decreases. Correct
D. The answer to this question cannot be determined without more information.
will increase if production decreases.
In the short run, when a firm stops producing, it:
A. avoids paying fixed costs.
B. avoids paying variable costs. Correct
C. can avoid earning profits that are less than zero.
D. must have an average total cost that is lower than the market price.
avoids paying variable costs.
Formula for Revenue
Price x Quantity
Formula for Average Revenue
revenue/quantity
Marginal Revenue
by how much the revenue increased when selling the last unit.
In a competitive market, what is the relationship between the price, average revenue, and marginal revenue?
Price = average revenue = marginal revenue
What is a firm's objective?
To maximize profts
Take a firm that produces nothing. What if it increases its production (of bananas)? What variable would be the marginal cost and what variable would be the marginal revenue?
- Marginal Cost: The cost increases by a certain amount
- Marginal Revenue: The price of bananas
When does profit maximisation occur?
when MC=MR
Suppose a firm's total cost and marginal cost of producing Q units are:
TC (Q) = 5Q^2 ,and MC = 10Q .
If the firm operates in a perfectly competitive industry and the price of the good is $200, what is its short-run profit?
(A) $500
(B) $1,000
(C) $2,000
(D) $4,000
(C) $2,000
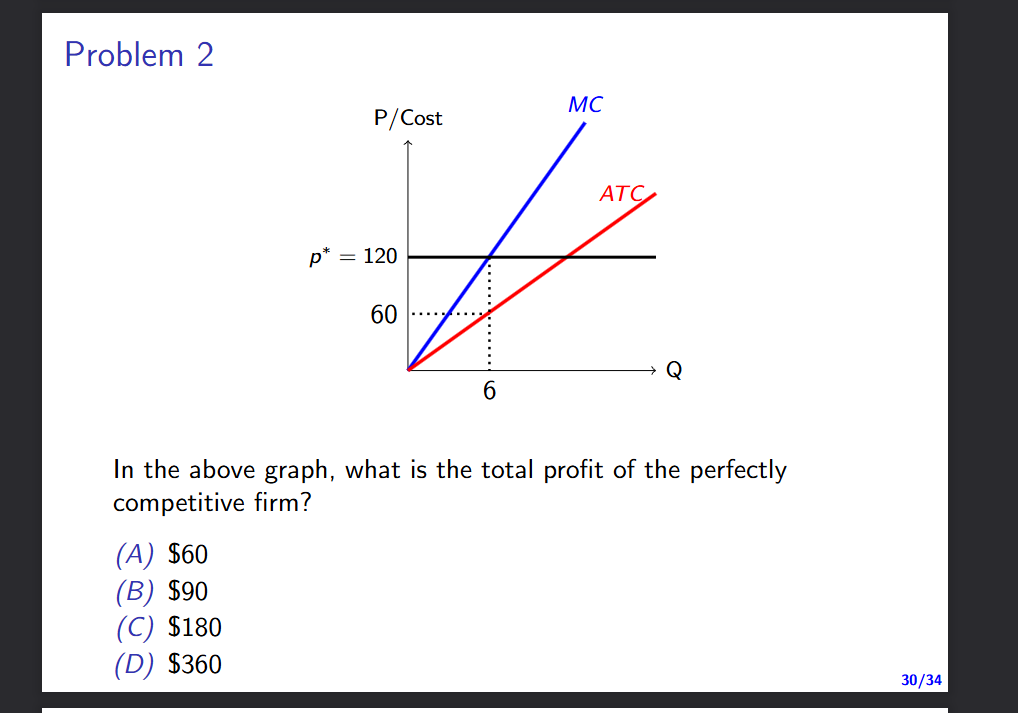
In the above graph, what is the total profit of the perfectly
competitive firm?
(A) $60
(B) $90
(C) $180
(D) $360
(D) $360
When this potato chips company increases production from 1000
to 1200 bags, it exhibits
(A) diseconomies of scale because the total cost rises as output
rises.
(B) diseconomies of scale because the average total cost rises as
output rises.
(C) economies of scale because the total cost rises as output rises.
(D) economies of scale because the average total cost rises as
output rises.
(B) diseconomies of scale because the average total cost rises as
output rises.
