BFCP1 S18
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
S18: ECM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
3 components of ECM
Fibrous proteins
Carbs
Multi-adhesive proteins
Fibronectin vs fibrilin
Fibronectin: important multiadhesive protein
Fibrilin: works independently to bind GFs like TGFB (microfibril) or binds elastin (elastic fiber)
Collagen, fibrilin, and elastin are examples of ________
fibrous proteins
proteoglycans and GAGS are examples of _______
carbs
fibronectins, integrins, and laminins are examples of _______
multi-adhesive proteins
Difference in function of the ECM in connective tissue vs BM
Connective tissue: 3D mesh, providing toughness and resilience
BM: 2D mesh
Connective tissue consists mostly of ____ with embedded ____ and immune cells.
ECM
embedded fibroblasts
What synthesizes and secretes the ECM molecules of connective tissue?
Fibroblast
What clear out the proteins of the ECM? What about the cells of the ECM?
Proteins: proteases
Cells: immune cells (macrophages, neutrophils, etc)
Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs)
A type of protease that degrades the ECM and releases GFs
Cancer is associated with (increased/decreased) ECM clearance
increased
Lysosomal storage diseases are associated with _______ ECM clearance.
decreased
Colllagen are ______ proteins of the ECM
major fibrous proteins
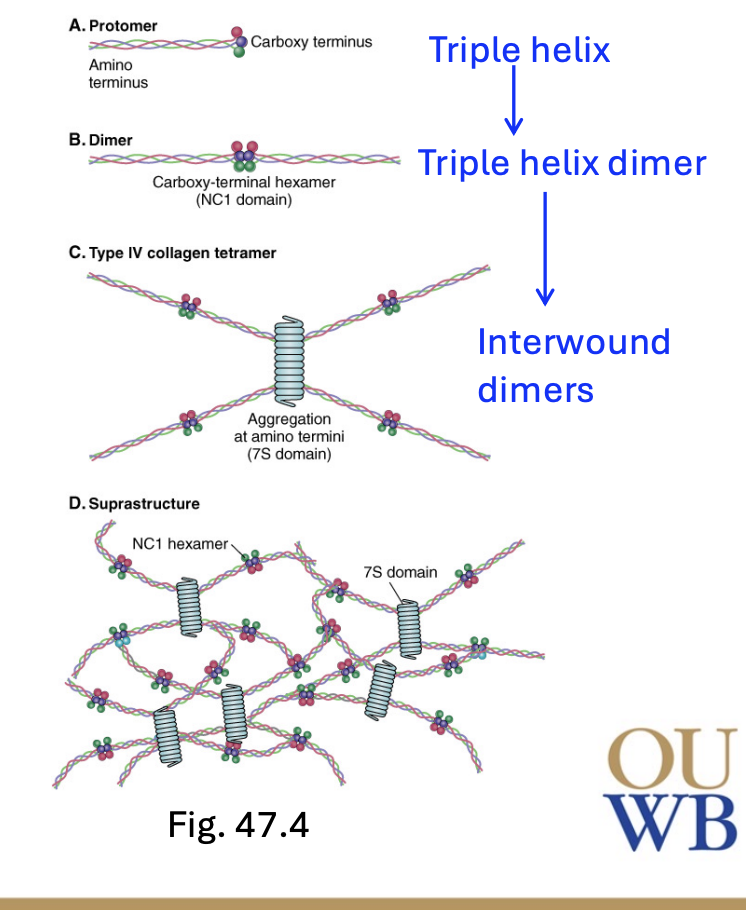
How does collagen bundle?
Triple helix → triple helix dimer → interwound dimers (tetramer)
Collagens contain what AA sequence?
Gly-X-Y-Gly-X-Y etc
Where Y is often hydroxyproline
Which types of collagen are found in bone, skin, and tendon?
Type I and II
Which type of collagen is found in the BM?
Type IV
Fibrous vs mesh collagen - location and function
Fibrous: type I and II, tensile strength
Mesh: type IV, flexibility
Collagen synthesis:
Protein undergoes 2 post-translational modifs: ________ and _______
Protein disulfide isomerases then rearrange ______ bonds to allow for ________ formation.
_______ out of cell
N and C proteases remove ________ to allow for ______ of collagens.
Lysyl oxidase creates lysine ______ for strength.
Collagen synthesis:
Protein undergoes 2 post-translational modifs: hydroxylation and glycosylation
Protein disulfide isomerases then rearrange disulfide bonds to allow for triple helix formation.
Exocytosis out of cell
N and C proteases remove N and C terminal peptides to allow for self-bundling of collagens.
Lysyl oxidase creates lysine crosslinks for strength.
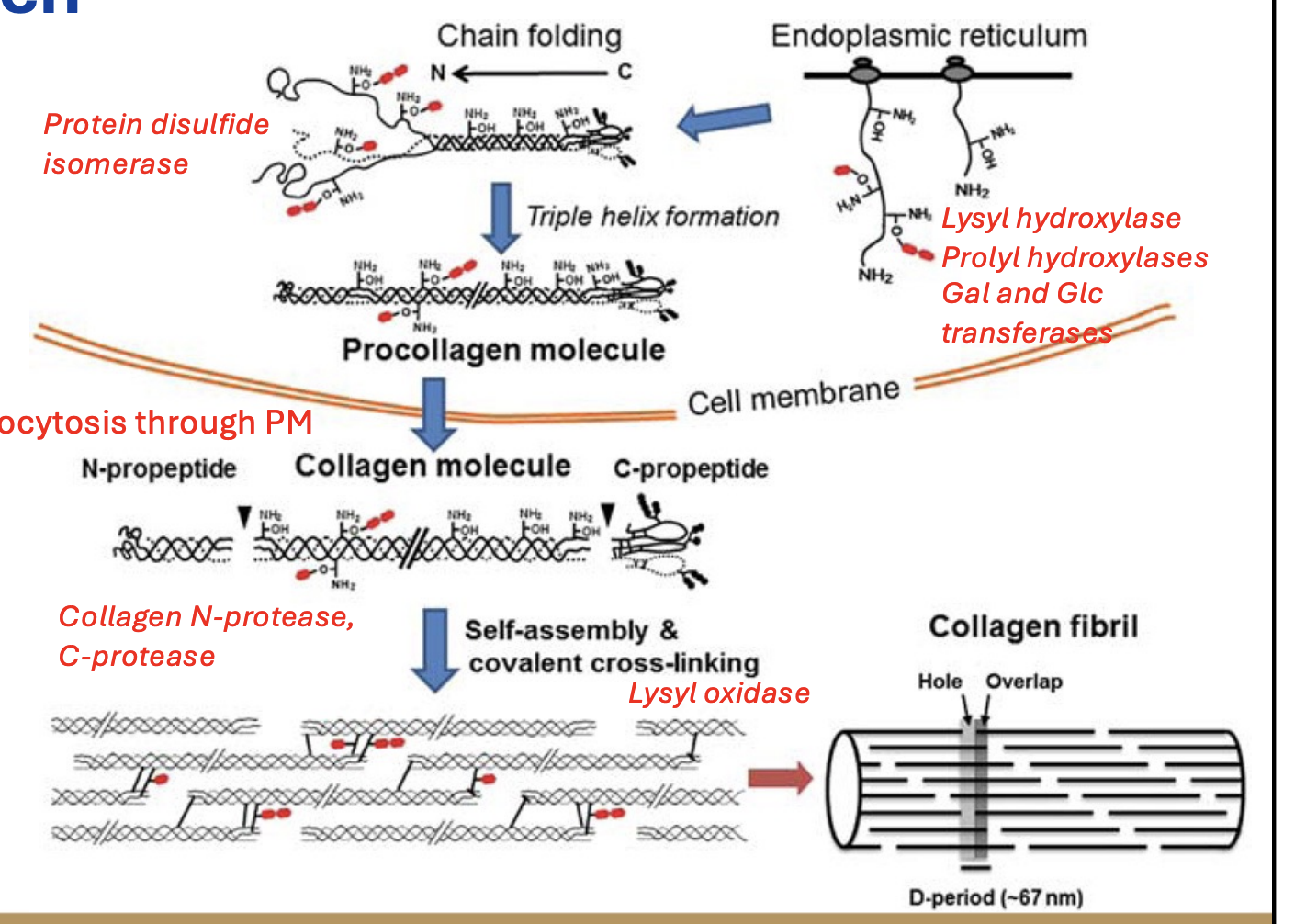
Hydroxylation of collagen occurs at which AAs?
Lysine and proline
Lysyl hydroxylase
What does this allow for?
Hydroxylates lysines on newly formed collagen
Allows for glycosylation
Prolyl hydroxylase
What does this allow for?
Hydroxylates prolines on newly formed collagen
Triple helix formation
Gal and Glc transferases
What does this allow for?
Glycosylate newly formed collagen
Increased tensile strength
Protein disulfide isomerase
Rearranges disulfide bonds for triple helix formation
N and C proteases
What does this allow for?
Cleaves N and C terminal peptides of collagen
Allows them to self-assemble into multimers
Lysyl oxidase
What does this allow for?
Crosslinks collagens
Permanent linkage for strength
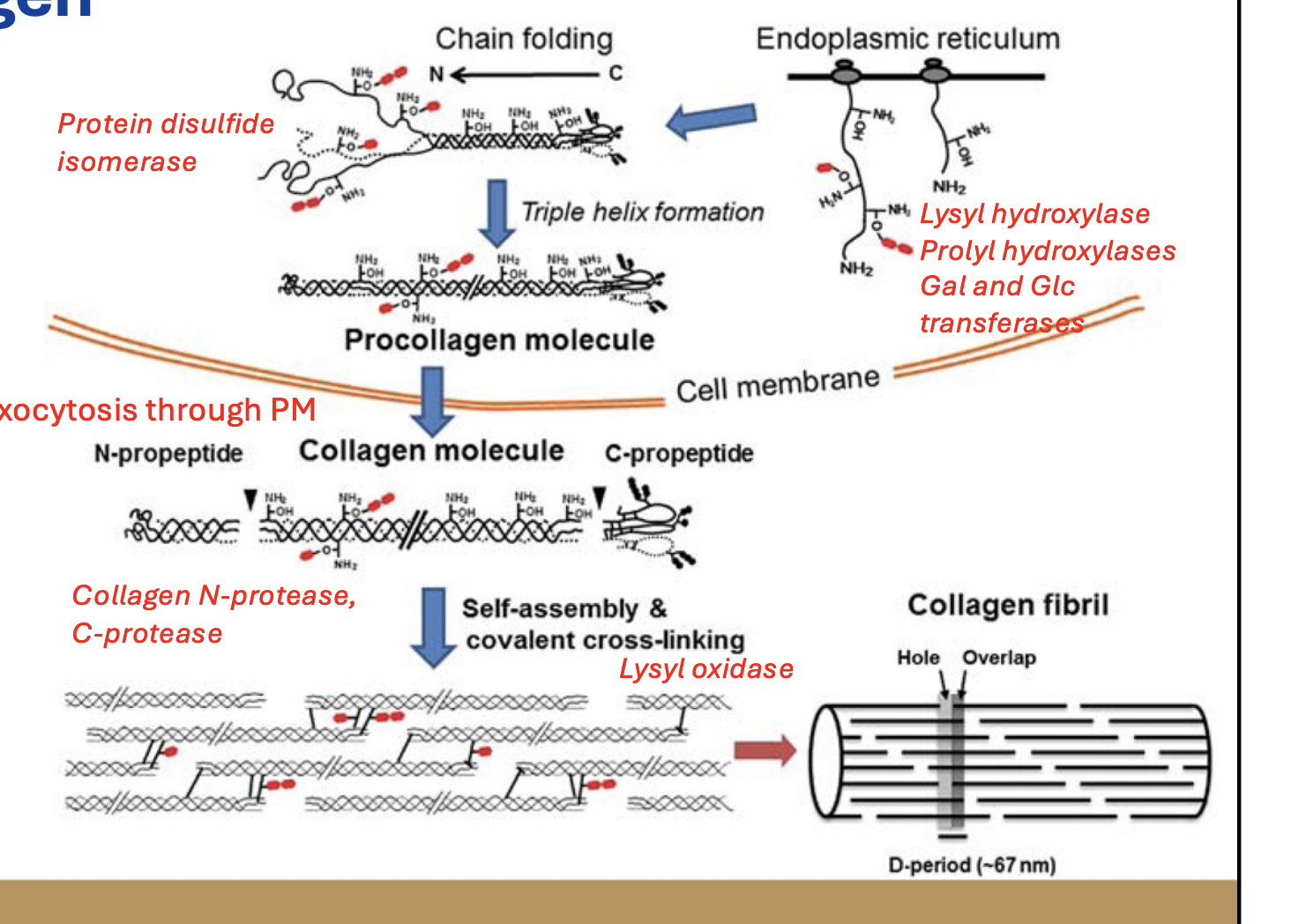
Protoprocollagen → protocollagen → collagen
After post-translational modifs: protoprocollagen
After triple helix formation: procollagen
After exocytosis: collagen
Which cells are collagen made in?
Fibroblasts
Proline and lysine hydroxylation require which 2 molecules?
Vitamin c, iron (Fe2+)
Scurvy is caused by a lack of ______.
vitamin C
A vitamin C deficiency leads to what collagen effects?
Less hydroxylation → inefficient collagen synthesis → weak collagen effects
In the ECM, collagen can be non-enzymatically glycated. Why does this occur? What can it lead to?
If there is exposure to too much glucose
Leads to uncontrolled crosslinking → stiffness in tissues
How does non-enzymatic glycosylation of collagen lead to CVD?
Too much glycosylation → too much crosslinking and hardening in BVs
Which tissues would elastin be found abundantly in?
Those that have to repeatedly stretch and change shape
Smooth muscle, vasculature, lungs, ligaments
Elastase
Degrades elastin in the ECM
What are the 2 forms that fibrilin can take and what are their functions?
Microfibrils (elasin free): binds GFs like TGFB
Elastic fiber (with elasin): mediates elasticity
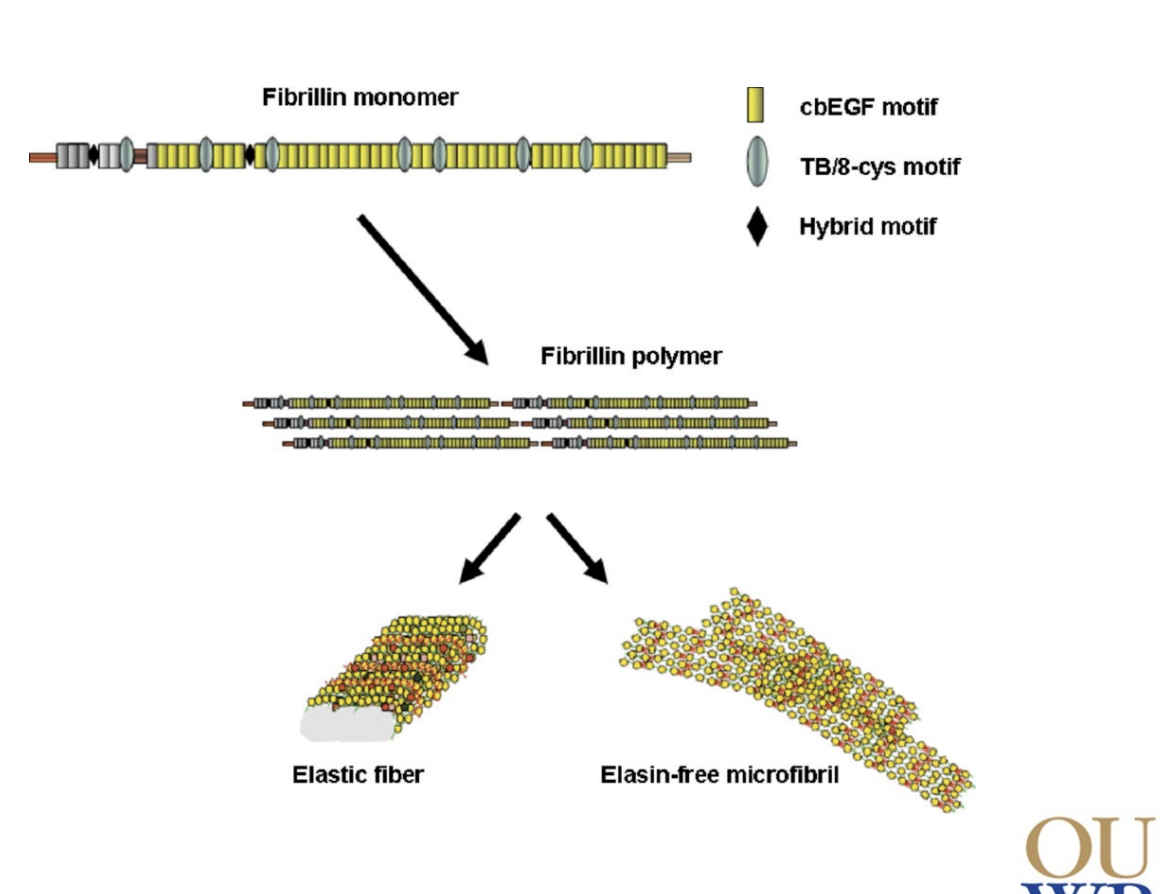
Elastic fiber vs microfibril characteristics
Elastic fiber: stretchy, mechanical elasticity
Microfibril: more tough
TGFB
Growth hormone that binds microfibrils
a1-antitrypsin
Inhibits elastase
Low a1-antitrypsin = (low/high) elastase = (low/high) = (low/high) elastin breakdown = (no/yes) emphysema
Low a1-antitrypsin = high elastase = high elastin breakdown = yes emphysema
Emphysema
Low elastin leading to loss of lung elasticity and decreased surface area
2 main causes of emphysema
Mutation in a1-antitrypsin gene (low levels)
Smoking
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGS) are which type of molecule?
Polysaccharides (carbs)
GAGs have a (+/-) charge and bind large amounts of ____
negative
water
Proteoglycans are which type of molecule? How are they composed
Glycoproteins
A core protein with GAG extensions
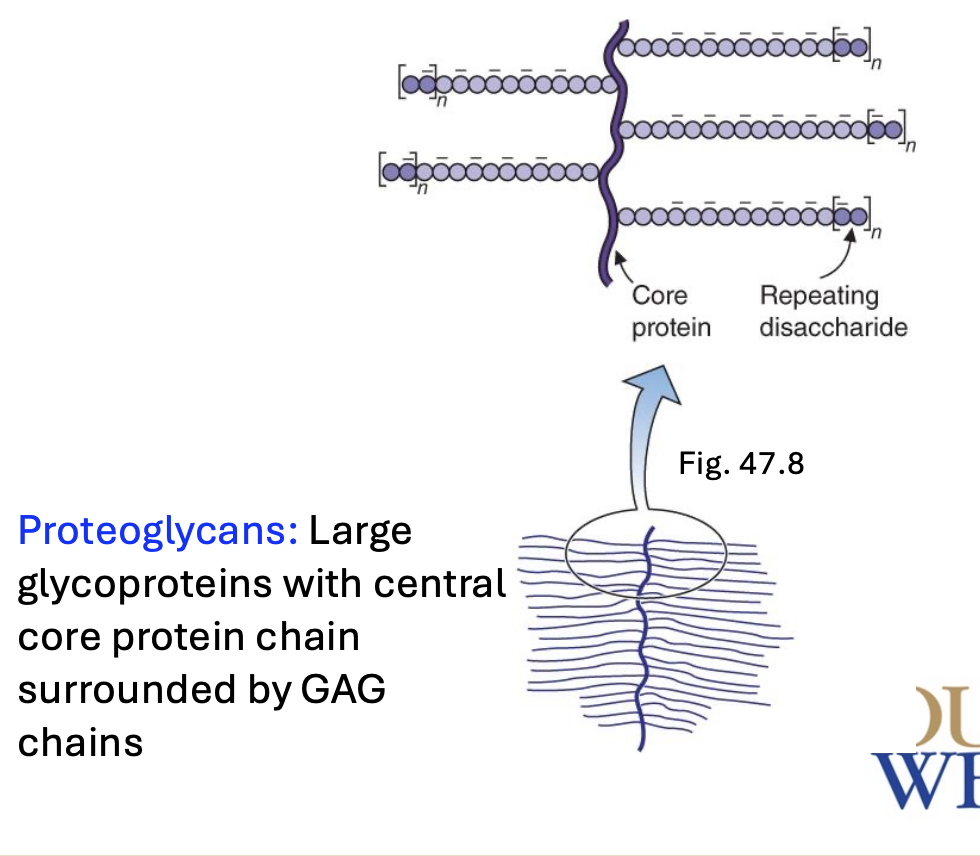
Hyaluronan and aggregan are examples of what?
Proteoglycans
Hyaluronan
Most abundant proteoglycan that is involved in pressure resistance and joint lubrication
Aggregan
Most abundant proteoglycan in cartilage
Binds to hylaronan to form huge aggregates
T/F: proteoglycans can form massive aggregates
T
The 3 important fibrous proteins in the ECM are
Collagen
Elastin
Fibrilin
The 2 important carbs in the ECM are what?
GAGs
Proteoglycans (hyaluronan, aggregan)
The 2 important multi-adhesive proteins in the ECM are what?
Fibronectin
Integrin
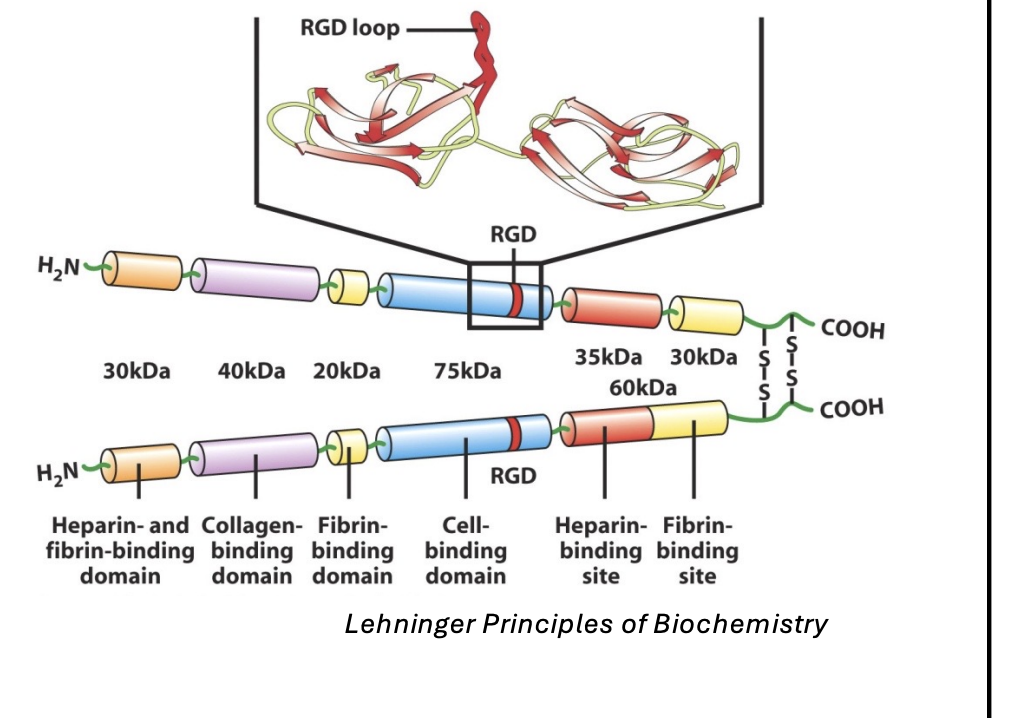
Fibronectin is a ____ protein that functions to ____
multiadhesive protein
bridge molecules together
Fibronectin contains a _____ motif that binds ____
RGD (arginine, glycine, aspartate)
Integrin
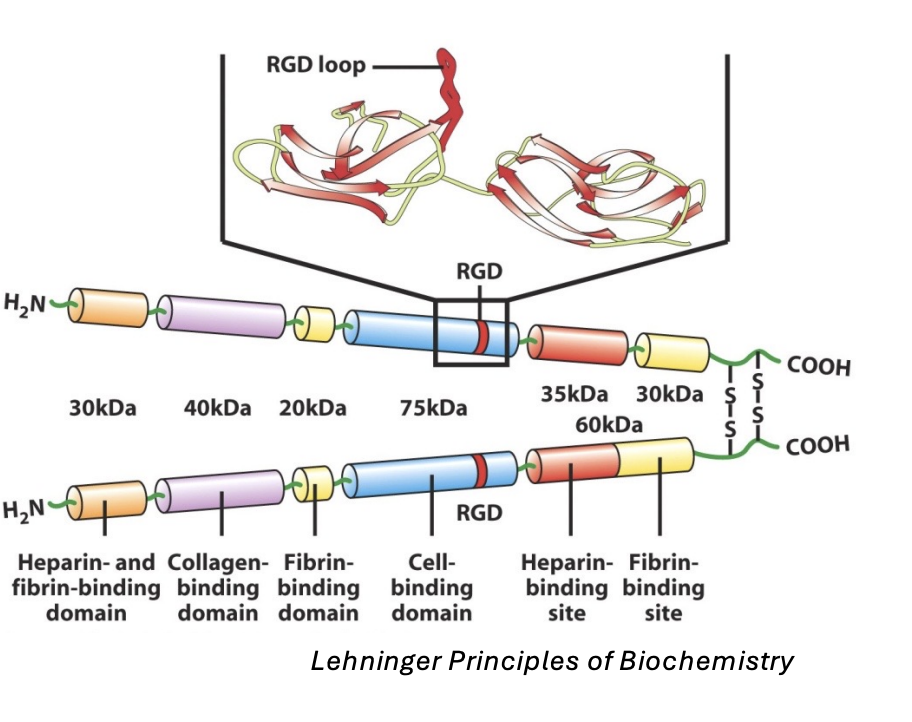
Plasma fibronectin
Involved in blood clotting by trapping platelets
Fibronectin composition
2 polypeptide chains that are disulfide-linked
Integrins are ______ glycoproteins that link the _____ to the _____ of cells
transmembrane
ECM to cytoskeleton
What allows integrins to recognize and bind fibronectin?
The RGD motif on fibronectin
Integrins composition
Heterodimeric - a and b chains
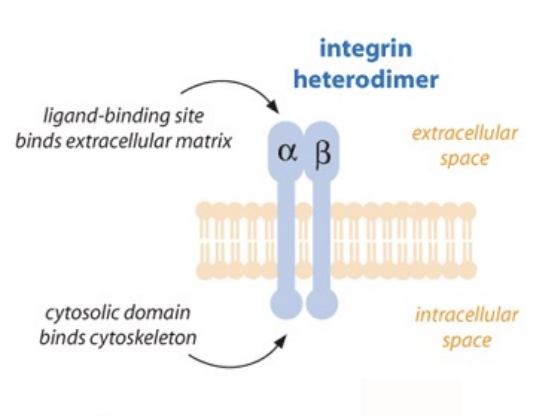
T/F: individual integrins are strong
F - many of them together form a strong bond
Along with clearing the ECM, MMPs are responsible for what?
Releasing growth factors in the ECM to convert ECM molecules to their active form
MMPs are ____-dependent proteases
Zn2+
TIMPs vs a2-macroglobulins
Both inhibit MMPs
TIMP: in solid tissues
a2-macrogolbulin: in blood
Where are lipids and GAG components sent to after they are broken down?
Lysosomes in macrophages
Osteogenesis imperfecta
What inheritance does it have?
Defects in type I collagen
Autosomal dominant
Ehlers-Dahnlos syndrome
Disorders in collagen
Hyperflexible joints, extensible skin, mitral valve prolapse are characteristics of which disease?
Ehlers-Dahnlos
Marfan syndrome cause
Defects in fibrilin-1 that cause it to be cleared too quickly
Causes free floating TGFB → rapid growth
Marfan syndrome characteristics
Tall, thin physique
Long fingers
CV symptoms need to be monitored
Integrin binds to ______ in the connective tissue ECM and ______ in the BM to connect cells to the matrix.
fibronectin in connective tissue
laminin in BM
Laminin in the BM binds _____ to ______
type IV collagen to integrin
Alport syndrome is caused by disorders in ______
Disorder in type IV collagen
Alport syndrome characteristics
Impaired kidney function
Eyes and ears defects
Goodpasture syndrome causes
Autoimmune reaction where pt develops antibodies against their own type IV collagen
Goodpasture syndrome affects what organs?
Kidneys, lungs