Functions of Business
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Last updated 11:23 PM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 4 functions of management and explain them
**Planning**
(Setting Goals) Planning is the process of setting short- and long-term goals and deciding how to achieve them
**Organizing**
(Allocating Resources) Organizing is arranging people and tasks to carry out the business’s plans and objectives
**Leading**
(Motivating and Communicating) Through leadership, managers achieve organizational goals by motivating, communicating, and encouraging participation. Can be **External:** Positive or Negative Methods, **Internal:** Comes from within the person and is usually stronger than external
**Controlling**
(Checking everyone is doing what they’re supposed to) Involves activities, such as employee discipline, performance appraisals, and budgeting. Managers use these methods to increase, maintain, or decrease the resources that are allocated to them to ensure productivity. In production this would be as checking quality and meeting numbers, in marketing and distribution this would be ensuring sales revenue and expenses are in line. Finance would be in conjunction with an accountant keeping company records and financial transaction and ensuring money is spent responsibly. In human resources this wold be ensuring employees receive training, and assessments.
(Setting Goals) Planning is the process of setting short- and long-term goals and deciding how to achieve them
**Organizing**
(Allocating Resources) Organizing is arranging people and tasks to carry out the business’s plans and objectives
**Leading**
(Motivating and Communicating) Through leadership, managers achieve organizational goals by motivating, communicating, and encouraging participation. Can be **External:** Positive or Negative Methods, **Internal:** Comes from within the person and is usually stronger than external
**Controlling**
(Checking everyone is doing what they’re supposed to) Involves activities, such as employee discipline, performance appraisals, and budgeting. Managers use these methods to increase, maintain, or decrease the resources that are allocated to them to ensure productivity. In production this would be as checking quality and meeting numbers, in marketing and distribution this would be ensuring sales revenue and expenses are in line. Finance would be in conjunction with an accountant keeping company records and financial transaction and ensuring money is spent responsibly. In human resources this wold be ensuring employees receive training, and assessments.
2
New cards
How would controlling look in all the sectors
Production: This would be as checking quality and meeting numbers
Marketing and Distribution: This would be ensuring sales revenue and expenses are in line
Finance: Would be in conjunction with an accountant keeping company records and financial transaction and ensuring money is spent responsibly
Human Resources: This wold be ensuring employees receive training, and assessments
Marketing and Distribution: This would be ensuring sales revenue and expenses are in line
Finance: Would be in conjunction with an accountant keeping company records and financial transaction and ensuring money is spent responsibly
Human Resources: This wold be ensuring employees receive training, and assessments
3
New cards
Autocratic Leadership, Advantages and Disadvantages
The leader(s) make all decisions and employee participation is not allowed
Advantages
* Works great where quick decisions are necessary
* Works great when employees are entry level
Disadvantages
* Used all the time, it causes too much discontentment among staff
* Few people like being told what to do constantly
Advantages
* Works great where quick decisions are necessary
* Works great when employees are entry level
Disadvantages
* Used all the time, it causes too much discontentment among staff
* Few people like being told what to do constantly
4
New cards
Laissez-Faire Leadership, Advantages and Disadvantages
Leaves employees alone to do their work
Advantages
* Beneficial to those employees who like independence, are self disciplined and experts
* Management/leaders have to do less actual managing
Disadvantages
* Can be difficult for new workers or those who require more direction
Advantages
* Beneficial to those employees who like independence, are self disciplined and experts
* Management/leaders have to do less actual managing
Disadvantages
* Can be difficult for new workers or those who require more direction
5
New cards
Democratic Leadership, Advantages and Disadvantages
Encourages employees to have a say in the decision-making process
Advantages
* Employees creative ideas and contributions can improve the company
* It increases morale, and team spirt through collaboration, and the recognizing of employee achievements
* Most effective style to keep employees content and increase productivity
Disadvantages
* May not always be practical because of time constraints
Advantages
* Employees creative ideas and contributions can improve the company
* It increases morale, and team spirt through collaboration, and the recognizing of employee achievements
* Most effective style to keep employees content and increase productivity
Disadvantages
* May not always be practical because of time constraints
6
New cards
What is and what kind of situation is best for using Committee Team structures
A committee is made up of people from different areas who do ongoing work on a specific task.
It is best to use committee team structure when personalities are compatible and those involved have specific expertise in the topic or issue.
It is best to use committee team structure when personalities are compatible and those involved have specific expertise in the topic or issue.
7
New cards
What is and what kind of situation is best for using Cross Functional Team structures
Team has members from different functional areas.
This allows for a diversity of input and quick decision making
Best used when you need a variety of perspectives and skills for example a car development team
This allows for a diversity of input and quick decision making
Best used when you need a variety of perspectives and skills for example a car development team
8
New cards
What is and what kind of situation is best for using Virtual Team structures
A virtual team works together across long distances through computer communication instead of face-to-face meetings
Best used when you want to keep expenses low, need to save time and don’t need face to face communication
Best used when you want to keep expenses low, need to save time and don’t need face to face communication
9
New cards
What is and what kind of situation is best for using Task Force structures
A task to accomplish a specific task, after which it is disbanded
Best used when the task or problem is short term.
Best used when the task or problem is short term.
10
New cards
What is and what kind of situation is best for using Self Managed structures
A self-managed team has no official leader
Best for when the higher ups don’t necessarily need/want to be involved and when the team is self motivated to complete all their work
Best for when the higher ups don’t necessarily need/want to be involved and when the team is self motivated to complete all their work
11
New cards
What is and what kind of situation is best for using Informal Team Structures
An informal team is not put together by management but forms naturally
12
New cards
What are the 6 different team structures
Committee
Task Force
Virtual
Self-Managed
Cross-Functional
Informal
Task Force
Virtual
Self-Managed
Cross-Functional
Informal
13
New cards
What is Production
The functional area responsible for turning inputs into finished outputs through a series of production processes
The inputs are the factors or production, and the outputs are goods and services that we sell
The inputs are the factors or production, and the outputs are goods and services that we sell
14
New cards
What is management
To achieve organizational goals, management decides how to utilize human, financial, and material resources.
15
New cards
6 Factors of Production
Natural Resources: 6 Primary industries
Raw Materials: Any goods used in the manufacturing of other goods. Divided into ingredients (in the final product) and supplies (used up while making the product)
Labour: All the physical and mental (cognitive) work needed to produced goods and services. Physical is like moving dough, and capital is logistics and scheduling
Capital/Monetary Capital: Resources invested into to produce product, rarely needs to be replaced (ex. Machinery). Liquid Capital is capital that can be easily turned into cash, items that are non liquid, like buildings these are called capital goods. Intellectual Property are things like patents and copyrights as they have value as well
Information: Businesses require information to reduce risk, enhance it’s probability, and produce goods and services Competition/Consumer Preferences/Suppliers/Newest Technology/Sources of Supply
Management: Management consists of the people who run the business and control or direct the factors of production. Allocating resources, decides on scheduling
Raw Materials: Any goods used in the manufacturing of other goods. Divided into ingredients (in the final product) and supplies (used up while making the product)
Labour: All the physical and mental (cognitive) work needed to produced goods and services. Physical is like moving dough, and capital is logistics and scheduling
Capital/Monetary Capital: Resources invested into to produce product, rarely needs to be replaced (ex. Machinery). Liquid Capital is capital that can be easily turned into cash, items that are non liquid, like buildings these are called capital goods. Intellectual Property are things like patents and copyrights as they have value as well
Information: Businesses require information to reduce risk, enhance it’s probability, and produce goods and services Competition/Consumer Preferences/Suppliers/Newest Technology/Sources of Supply
Management: Management consists of the people who run the business and control or direct the factors of production. Allocating resources, decides on scheduling
16
New cards
6 Natural Resources
1. **Fuel and Energy**
2. **Logging and Forestry**
3. **Water**
4. **Agriculture**
5. **Mining**
6. **Fishing and Trapping**
17
New cards
4 Stages of Production
1. Purchasing: Raw Materials/Capital Resources Considering Quality and Value (price)
* Chocolate Chips
2. Processing: Converting raw materials/inputs into finished or semi finished products
* Mixing and baking ingredients, decorating
3. Quality Control: Make sure product meets quality standards
* Fully baked? Size? Smell? Taste
4. Grading: Offering consumer different level products, could be based on size, quality
* Beef, Gas, Eggs
18
New cards
3 Ways to Increase Productivity
* Increase Speed: Use technology, employee training
* Increase Quality: Train Employees
* Increase Both: Both
* Increase Quality: Train Employees
* Increase Both: Both
19
New cards
What things are apart of branding
* Slogan
* Loga/Trademark
* Brand Name
* Loga/Trademark
* Brand Name
20
New cards
6 Functions of HR
Recruitment: Looking for the right employee. Internal hiring from within the company. External hiring from outside. It involves analyzing job requirements, advertising job vacancy, and shortlisting candidates
\
Selection: Placing the right candidate in a particular positing. Involves interviewing and checking fro qualification, verifying references, advertising skill/experience tests
\
Training: Developing a skill, competency or knowledge that is required by the job. Involves job specific training, company procedures, and WHMIS
\
Development: A long process of upgrading an employee’s performance overtime can be expanding employee responsibilities
\
Compensation and Benefits: Compensation is the money and other benefits received by employees in exchange for their work, eg health insurance, paid vacation, employee allowance.
\
Assessment (Performance Appraisal): Employees are assessed to see if they need to make improvements in their job or see if they qualify for job promotion, annual pay raises, special rewards and bonuses, incentives
\
Selection: Placing the right candidate in a particular positing. Involves interviewing and checking fro qualification, verifying references, advertising skill/experience tests
\
Training: Developing a skill, competency or knowledge that is required by the job. Involves job specific training, company procedures, and WHMIS
\
Development: A long process of upgrading an employee’s performance overtime can be expanding employee responsibilities
\
Compensation and Benefits: Compensation is the money and other benefits received by employees in exchange for their work, eg health insurance, paid vacation, employee allowance.
\
Assessment (Performance Appraisal): Employees are assessed to see if they need to make improvements in their job or see if they qualify for job promotion, annual pay raises, special rewards and bonuses, incentives
21
New cards
What is the human resources department responsible for
The human resources department is responsible for coordinating all activities involving the company’s employees eg. conflict resolution, departures, dismissals, retirement
22
New cards
4 Different Types of Assessment
Top Down: Evaluation by the employee’s direct supervisor
360 Degree Evaluation: The employee is evaluated by four parties, not only by his direct supervisor. These are: the direct supervisor, subordinates, co-workers and customers
Matrix Evaluation: This type of evaluation, the employee is evaluated by different managers
Self Assessment: Employee rates himself/herself on the same criteria used by the direct supervisor to evaluate him/her and then the two evaluations are compared.
360 Degree Evaluation: The employee is evaluated by four parties, not only by his direct supervisor. These are: the direct supervisor, subordinates, co-workers and customers
Matrix Evaluation: This type of evaluation, the employee is evaluated by different managers
Self Assessment: Employee rates himself/herself on the same criteria used by the direct supervisor to evaluate him/her and then the two evaluations are compared.
23
New cards
4 P's of Marketing
Product: Uniqueness, Quality, Features, Benefit, Design
Price: Competitor price, Cost to produce, Target Market what they can
Place: Distribution channels, selling directly, selling indirectly, speciality vending machines
Promotion: Advertising, makes people aware of your brand, Sales Promotion, coupons, samples
Price: Competitor price, Cost to produce, Target Market what they can
Place: Distribution channels, selling directly, selling indirectly, speciality vending machines
Promotion: Advertising, makes people aware of your brand, Sales Promotion, coupons, samples
24
New cards
What is a channel of distribution
Channels of distribution are the paths of ownership that goods follow as they pass from the producer or manufacturer to the consumer
Direct: The business that makes the product sells directly to the consumer
Indirect: The business sells to an intermediary (typically a retailer) who then sells the product to another business or consumer
Speciality: The consumer buys from a place other than a retail store eg. vending machines and catalogue.
Direct: The business that makes the product sells directly to the consumer
Indirect: The business sells to an intermediary (typically a retailer) who then sells the product to another business or consumer
Speciality: The consumer buys from a place other than a retail store eg. vending machines and catalogue.
25
New cards
Slogan
A short identifiable catchy phrase that is usually attached to the company’s name and logo
26
New cards
Logo or Trademark
A logo/trademark is a word, symbol, design and or a combination that a business uses to distinguish its goods or services from others.
27
New cards
2 C’s of Marketing Mix
Consumer, Competition
28
New cards
Explain the 1st C of Two
Consumer: The more marketers know about their potential customers the better they can anticipate or influence there customers buying decisions
***Geographic***
* **Location**
* **Climate**
* **Urban/Suburban**
***Demographics***
* **Age**
* **Gender**
* **Ethnicity**
* **Family lifestyle**
* **Income level**
* **Generation**
***Psychographic***
* **Values**
* **Likes/dislikes**
* **Health**
* **Lifestyle**
* **Hobbies**
***Behaviour***
* **Brand loyalty**
* **Usage rate**
* **Desired features**
***Geographic***
* **Location**
* **Climate**
* **Urban/Suburban**
***Demographics***
* **Age**
* **Gender**
* **Ethnicity**
* **Family lifestyle**
* **Income level**
* **Generation**
***Psychographic***
* **Values**
* **Likes/dislikes**
* **Health**
* **Lifestyle**
* **Hobbies**
***Behaviour***
* **Brand loyalty**
* **Usage rate**
* **Desired features**
29
New cards
Explain the 2nd C of two
Competition: The competitive market refers to the sellers of a specific product, and is often expressed in terms of the total dollars spent annually on the product. The percentage of the market that a company or brand has is called its **market share**
**Indirect competition means products or services are not directly related to each other targeting the same Target Market.**
**Direct competition means products that are similar to one another targeting the same Target Market.**
**Indirect competition means products or services are not directly related to each other targeting the same Target Market.**
**Direct competition means products that are similar to one another targeting the same Target Market.**
30
New cards
5 Stages of the Product Life Cycle
Launch/Introduction: This is a brand new product on the market, at this point the Consumer is unaware of the product and needs to be to be informed…so that would be the focus at this stage. Marketers will focus on advertising through trend setter
\
Growth: As sales increase competition does as well. They often try to add features and quality at this stage. Advertising is focusing on visibility like promoted commercials, billboards, print ads etc.
\
Maturity: Growth is flat; it does not increase or decrease, and brand equity is at its highest. Businesses keep advertising the product to keep it in the consumers’ eye. High income can be used to develop and fund new products.
\
Decline: When sales decrease because customers leave to buy other brands, and they are not replaced, a product can enter the decline stage this is when the product is vulnerable to becoming obsolete. Advertising or change in price can slow down or stop decline
\
The Decision Point: The business may make an effort to regain original sales figures and brand equity or they may discontinue the product altogether. If they try to save the product a variety of options are available: repricing, repositioning, new promotion.
\
Growth: As sales increase competition does as well. They often try to add features and quality at this stage. Advertising is focusing on visibility like promoted commercials, billboards, print ads etc.
\
Maturity: Growth is flat; it does not increase or decrease, and brand equity is at its highest. Businesses keep advertising the product to keep it in the consumers’ eye. High income can be used to develop and fund new products.
\
Decline: When sales decrease because customers leave to buy other brands, and they are not replaced, a product can enter the decline stage this is when the product is vulnerable to becoming obsolete. Advertising or change in price can slow down or stop decline
\
The Decision Point: The business may make an effort to regain original sales figures and brand equity or they may discontinue the product altogether. If they try to save the product a variety of options are available: repricing, repositioning, new promotion.
31
New cards
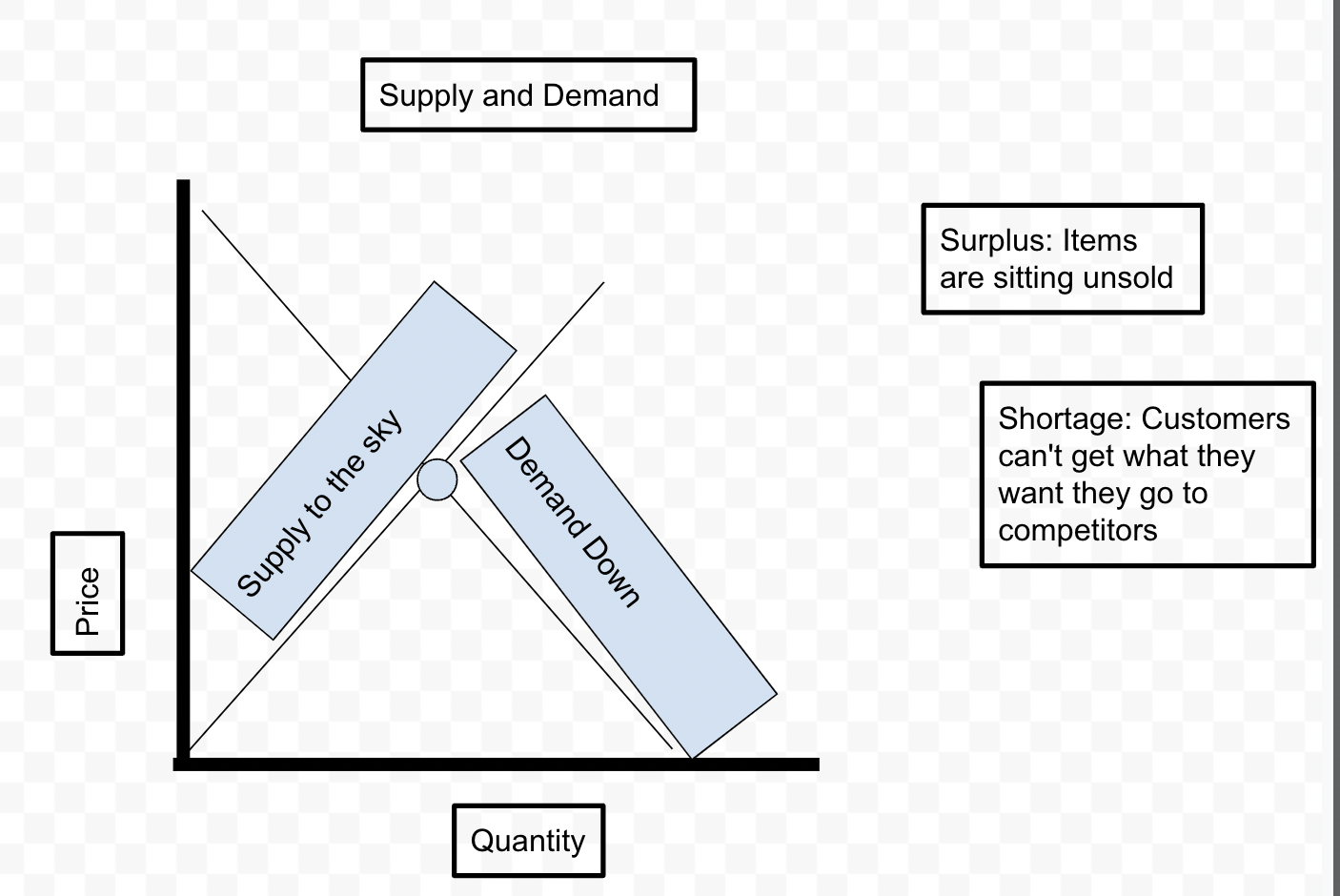
Supply and Demand Graph
32
New cards
Maslows Hierarchy

33
New cards
Assets
Things of value owned by the company
34
New cards
Liabilities
Debts owed by the company
35
New cards
Owner’s equity
Net worth of the company on that day
36
New cards
Balance Sheet Formula
Assets - Liabilities = Owner’s Equity
37
New cards
What is the purpose of the Balance Sheet? What are 3 pieces of information you can find on the balance sheet?
The purpose of a balance sheet is to figure out the net worth of the business at a particular time. You can find out total assets, total liabilities, and owners equity/net worth
38
New cards
Income/Revenue
Money that comes into the company ie. Sales, Investment Interest etc
39
New cards
Expenses
Costs associated with generating revenue for the company ie. rent, phone bills etc
40
New cards
Profit or Loss
The amount of money the company makes in a fiscal period
41
New cards
Income Statement Formula
Revenue – Expenses = Net Profit or Loss (if it’s positive it’s a profit, if it’s negative its a loss)
42
New cards
What is the purpose of the Income Statement? What are 3 pieces of information you find on the Income Statement
The purpose of an income statement is to see if your business is making money (profitable) or is not. You can find out total revenue, total expenses and wether the business is profitable or not