2. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
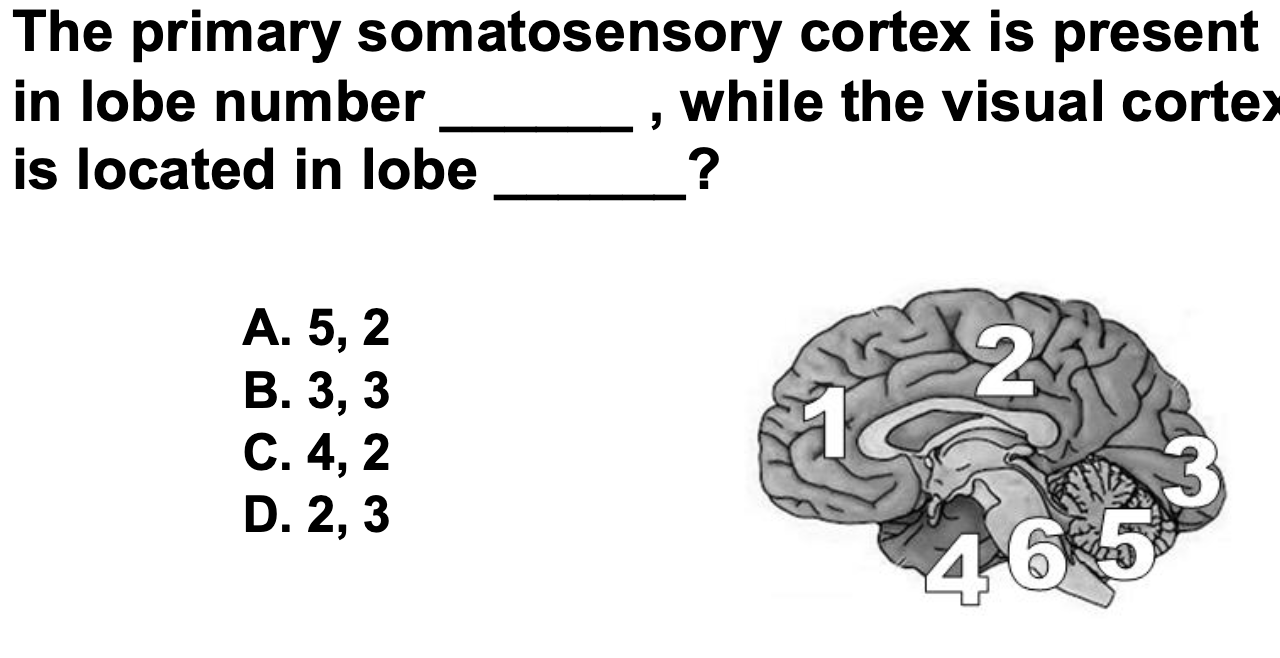
The primary somatosensory cortex is present in lobe number ___, while the visual cortex is located in lobe ___?
D
____ ___ _____ is crucial for generating cellular diversity and maintaining cell-specific functions
Differential gene expression
How to study gene expression via mRNA
ISH (in-situ hybridization)
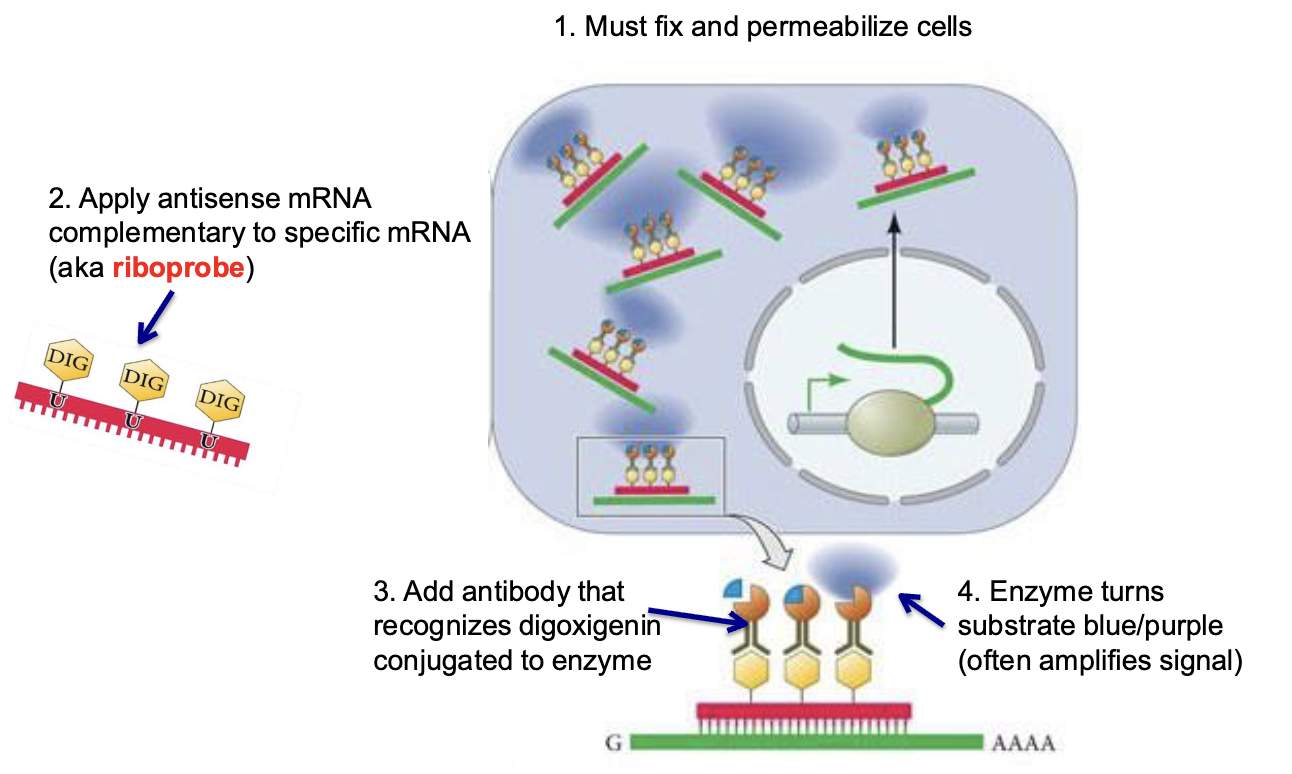
Steps of ISH
fix and permeablize cells
apply antisense mRNA complementary to specific codons
add antibody that recognizes conjugated enzyme
enzyme turns substrate blue/purple
3 examples of transcirptomics
microarrays
next-generation sequencing (NGS)
single cell RNA sequencing
2 techniqes to studt proteins
western blotting
Immunohistochemistry
Western blotting (qualitative or quantitative)? Function?
Qualitative
Analyze protein levels (from homogenized tissue samples)
Immunohistochemistry (qualitative or quantitative)? Function?
Qualtitative
Detects protein of interest for labeling
Definition of “cell”
Fundamental unit of structure, function, and organization in all living organisms
3 conserved functions of neurons
highly polarized and compartmentalized
transmit electrical signals
post-mitotic
3 components of the neurons
cell body
axon
dendrite
Aproximately how many neurons are in the human nervous system
~100 billion neurons
Reticular vs neuron theory
Reticular theory (Golgi): nervous system is continuous
Neuron theor (Cajal): each neuron is individual
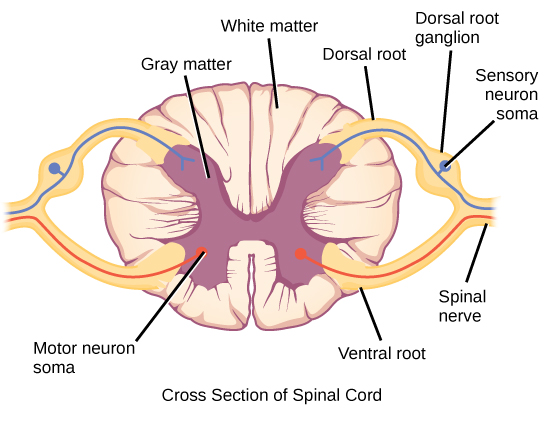
Neuron type: spinal motor neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: ventral horn of spinal cord
primary neurotransmitter: ACh
target: peripheral skeletal muscles
Neuron type: cortical inhibitory neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: cerebral cortex
primary neurotransmitter: GABA
target: pyramidal cells (regulate excitation)
Neuron type: interneuron Purkinje neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: cerebral cortex
primary neurotransmitter: GABA
target: deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN), output of cerebral cortex
Neuron type: retinal ganglion cell
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: retina
primary neurotransmitter: glutamate
target: brain
Neuron type: DRG sensory neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: dorsal root of sensory spinal nerve
primary neurotransmitter: glutamate
target: peripheral tissues
Neuron type: medium spiny neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: basal ganglia of brain
primary neurotransmitter: GABA
target: basal ganglia nuclei
Neuron type: pre-ganglionic sympathetic neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: lateral horns of spinal cord
primary neurotransmitter: ACh
target: paravertebral ganglia
Neuron type: layer 5 projection neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: cerebral cortex
primary neurotransmitter: glutamate
target: thalamus
Neuron type: mitral cell
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: olfactory bulb
primary neurotransmitter: glutamate
target: olfactory cortex
Neuron type: CA3 pyramidal neuron
location:
primary neurotransmitter:
target:
location: hippocampus
primary neurotransmitter: glutamate
target: inhibitory interneurons
Glia cells
Vital supportive functions (support, protect, insulate)
(T or F) glial cells are iactive connective tissue
false
7 functions of glial cells
structural support
insulation
myelination
modulate neurotransmitter levels
immune functions (clear debris from scars)
regulate metabolic components
act as stem cells