Science Chapter 11 - The Production and Reflection of Light
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Where do organisms in the Earth recieve light from?
The sun
One form of energy the sun releases as a result of nuclear reactions is “light“
What are the properties of light?
Travels at VERY high speed
Travels in straight lines
Doesn’t require a medium (object that acts as a carrier for the transmission of energy)
Transferred through radiation
Electromagnetic wave
What is electromagnetic wave?
A wave that…
doesn’t require a medium
has electric and magnetic parts
travels at the speed of light
What is visible light?
Any electromagnetic wave that human eye can detect
Can we see all forms of light?
No, we can only see visible light
Other forms of light must reflect off a surface and then enter our eyes to see it
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
Classification of electromagnetic waves based on their energy
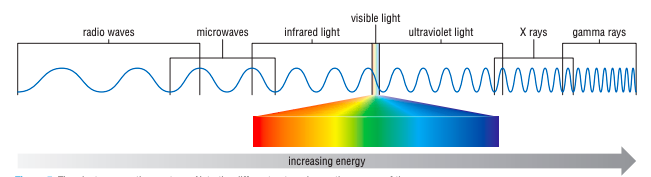
What are some examples of electromagnetic waves?
(Increasing ENERGY as the list goes down)
Radio waves (TV signals)
Microwaves
Infrared light (Lasers)
Visible light (Rainbows)
Ultraviolet (UV) light (Causes tan/sunburn)
X-rays
Gamma rays (cancer treatment & nuclear decay)
What are the colors associated with visible light? This color sequence is called the visible spectrum.
Colors of the rainbow
White light is composed of continuous spectrum of colors (as shown in the light & prism experiment)

The sun is luminous. What does luminous mean?
It produces its own light
Other ex of luminous: light bulb, lit match, flashlight
Non-luminous means that it doesn’t produce its own light
How is light produced? (5 ways)
Incandescence - heated at high temperature (candle)
Electric discharge - electric current passing through gas (neon signs -red)
Phosphorescence - absorbing UV light (emitted over long time)
Fluorescence - absorbing UV light (emitted immediately - laundry)
Chemiluminescence - chemical reaction without increase in temperature (glow sticks - bending causes 2 chemicals to mix & cause light)
Bioluminescence - chemiluminescence in organisms like fish
Triboluminescence - scratching/crushing crystals
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) - device produces light by allowing electric current to flow in one direction; uses semiconductors (light bulbs at home)
What is a laser?
Consists of electromagnetic waves of exactly the same energy level, travelling in unison in exactly the same direction.
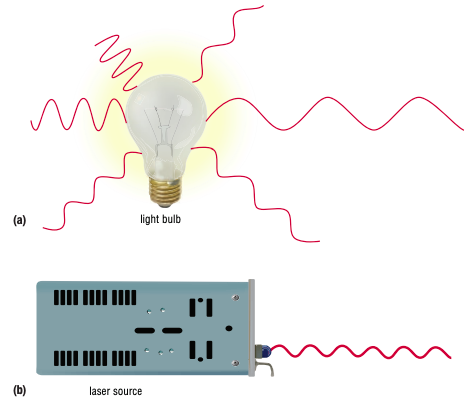
What are the special properties of lasers?
pure in color
intense and concentrated in one narrow beam
can travel great distances without spreading out
What are some uses of laser?
measuring long distances (earth to moon)
burning a hole
Candles radiate lights in all direction. Show this by drawing light rays
Red lines = light rays
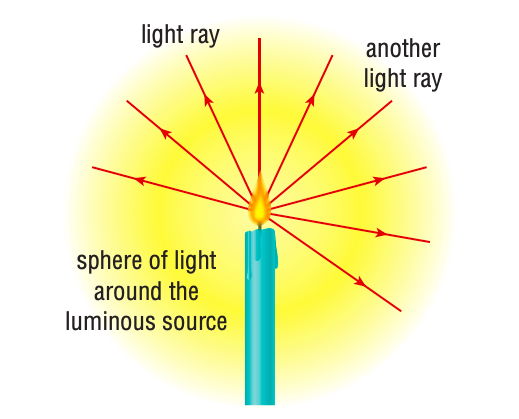
What is geometric optics?
using light rays to determine the path of light when it strikes an object
What is incident light?
When light emitted from a source (sun) strikes an object (Earth)
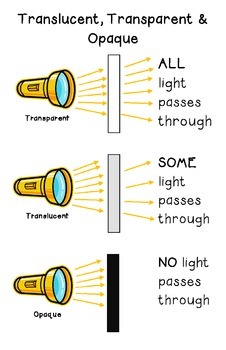
3 categories of matter based on how it behaves when light strikes it":
Transparent (clear glass)
Translucent (frosted/불투명한 glass)
Opaque (Cardboard - all light is absorbed or reflected)
What is an image?
Reproduction of an original object that is produced through the use of light
Eg. When you look at a mirror, you see a image of yourself
What is the definition of a mirror?
Any polished surface that displays reflection
What is a reflection?
Bouncing back of light from any surface (mirror, ground, ball, etc)
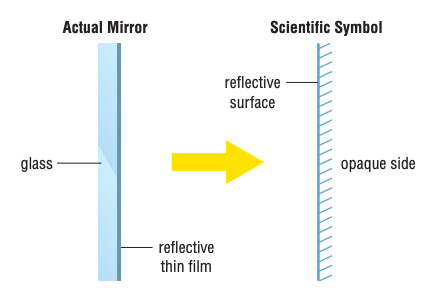
Mirrors consist of two parts: sheet of glass (front) and thin layer of reflective silver/aluminum (back). Which part actually performs the function of a mirror?
Back - the reflective part
*Glass is for
How do we represent a diagram of a mirror in physics?
Define these terms of reflection:
Plane mirror
Incident ray
Reflected ray
Normal
Perpendicular
Angle of incidence
Angle of reflection
Flat mirror
3. 4. 5. 6. 7
* Normal = perpendicular that is drawn to the reflecting surface
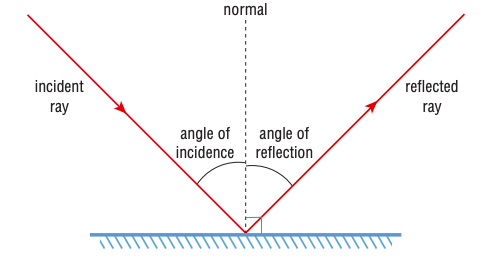
What happens when you shine a light ray at a plane mirror?
Light is reflected off the mirror and forms a reflected ray.
It follows the law of reflection.
This is true (for all light) even when there is more than on light reflecting off the plane mirror
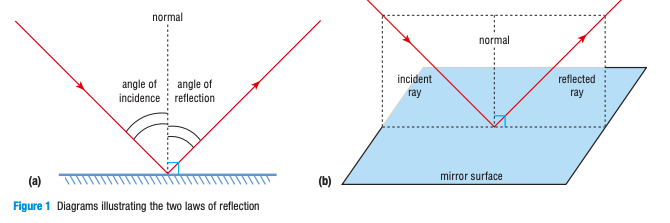
What is the law of reflection? (2 parts)
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane
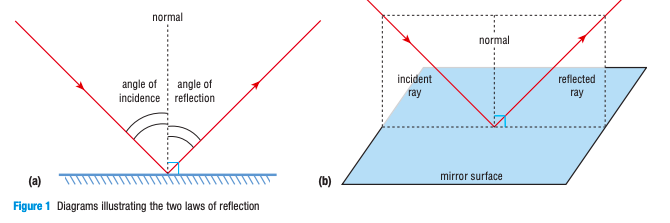
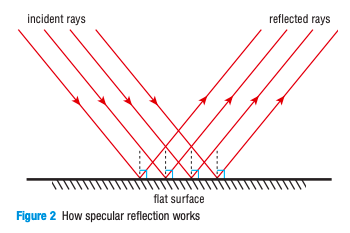
What is specular reflection?
Reflection of light off a smooth, shiny surface (e.g. plane mirror, flat aluminum foil, water without waves, or disco mirror ball)

What would happen if the parallel incident rays were directed at an irregular surface?
Incident rays would hit the surface at different angles and have different angles of reflection
Reflectedrays would be scatter or in many different
What is the term for when incident rays are reflected off a irregular/dull surface?
Diffuse Reflection
When does diffuse reflection occur?
When light is reflected
on a carpet
lake with many ripples (waves)

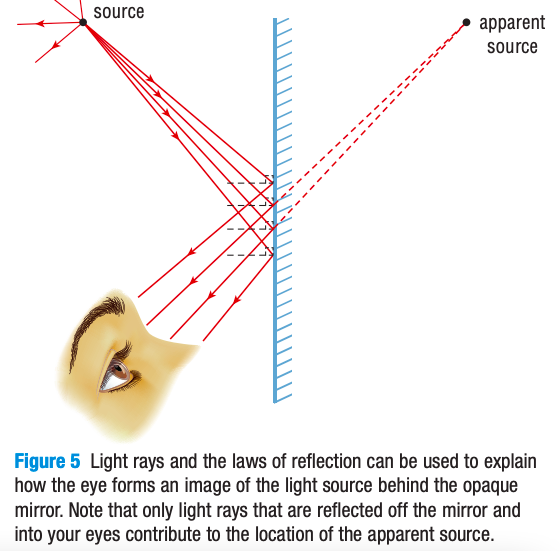
How do our eyes use light rays to locate an lmage?
When our eyes detect reflected light from a plane mirror → our brain project these light rays backwards in a straight line → our brain IMAGINES that the object is behind the mirror → we see a virtual (not real) image
This is because we believe that light rays ALWAYS travels in a straight line,
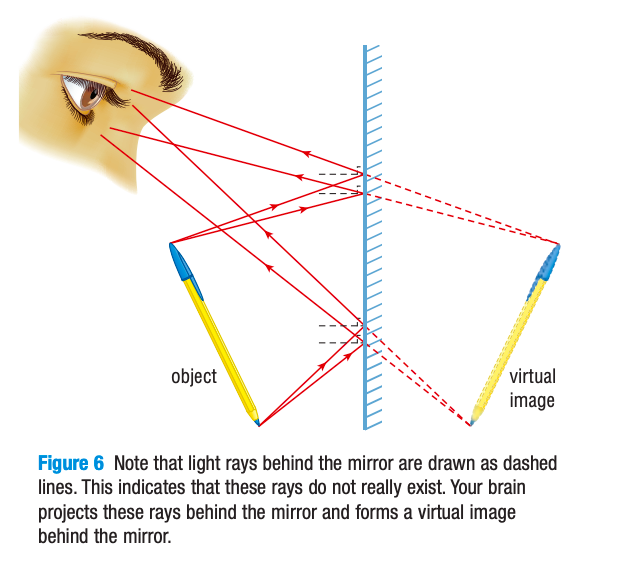
1. The distance from the object to the mirror is ___ ______ as the distance from the (virtual) image to the mirror.
2. The object−image line is ________ to the mirror surface
the same
perpendicular
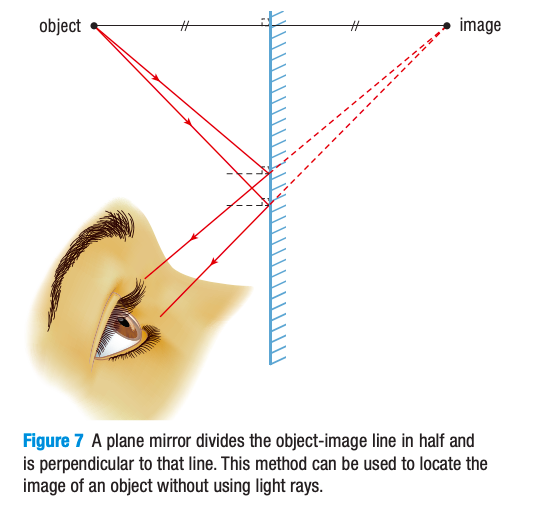
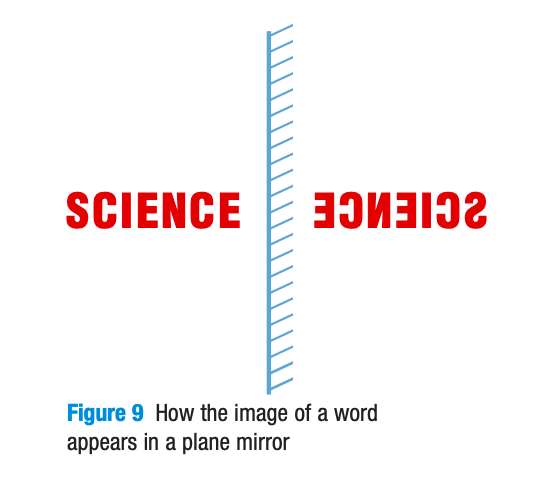
What are the characteristics of an image in a plane mirror?
The image in the plane mirror is always… (SALT)
the same size as the object (S: size)
Upright but LATERALLY INVERTED (reverse order) (A: attitude)
Object to mirror & image to mirror is same distance (L: location)
Virtual (not real; just our brain’s imagination) (T: type)
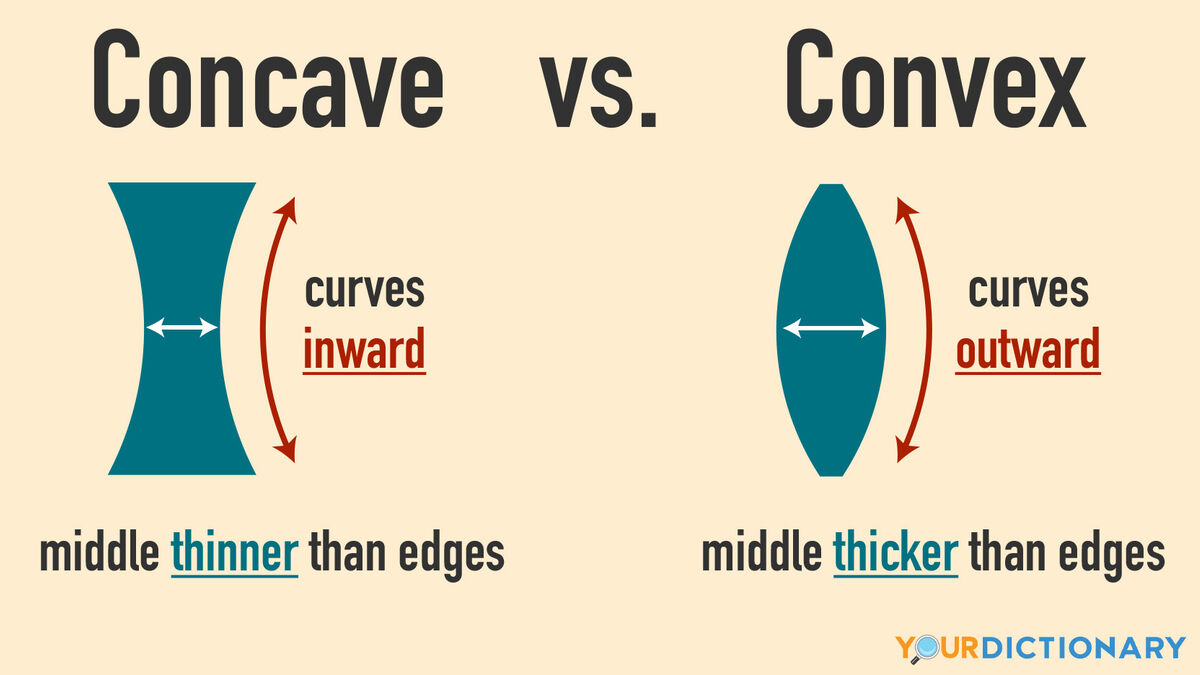
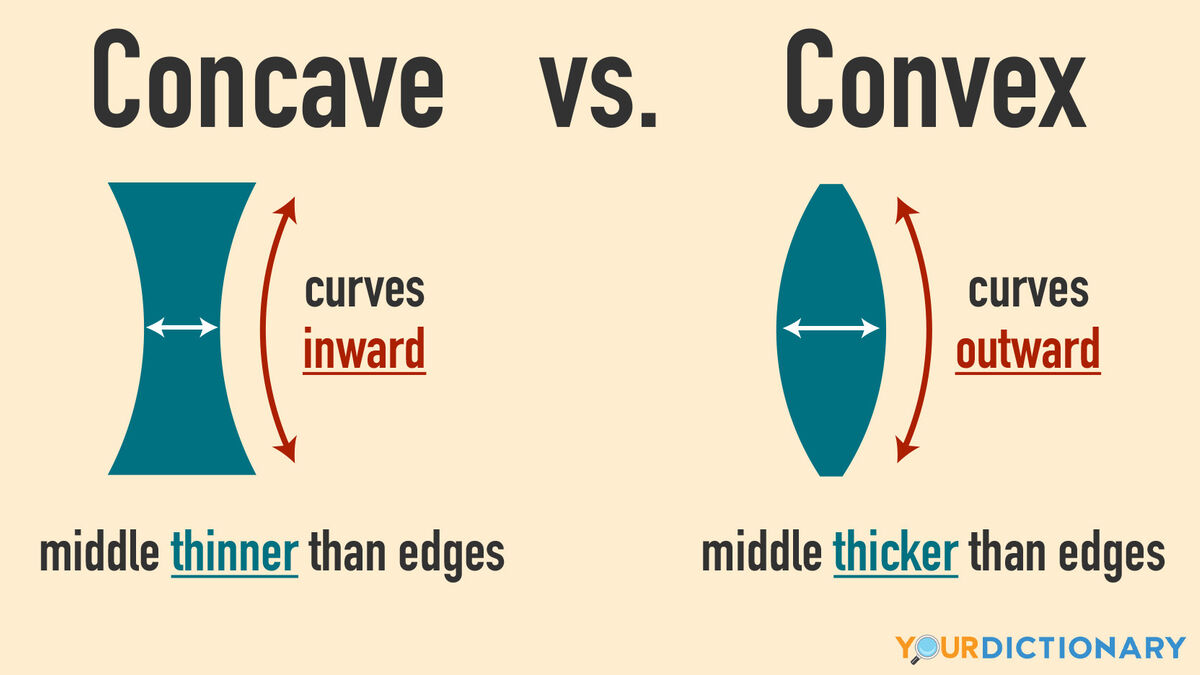
Security mirror at stores is a type of curved mirror. The two types of curved mirror are concave and convex. What are other names of these mirrors? How do they look like?
Concave = converging
Convex = diverging
Define these terms related to concave mirrors
Center of curvature (C)
Principal axis
Vertex (V)
Focus (F)
Converge
the center of the sphere that forms the curved mirror
the line going through the center of curvature and the center of the mirror
the point where principal axis intersects the mirror
the point where light rays parallel to the principal axis come together when they are reflected off a concave mirror
to meet at a common point
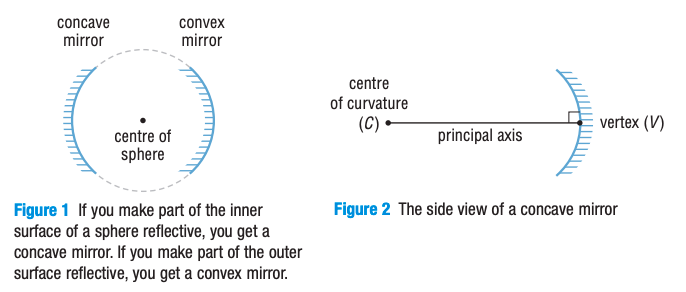
Draw a concave mirror and label center of curvature, vertex, and focus on a concave mirror
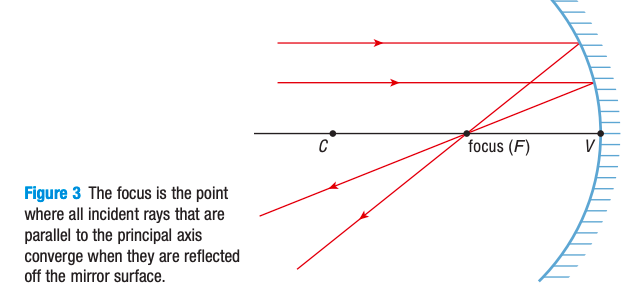
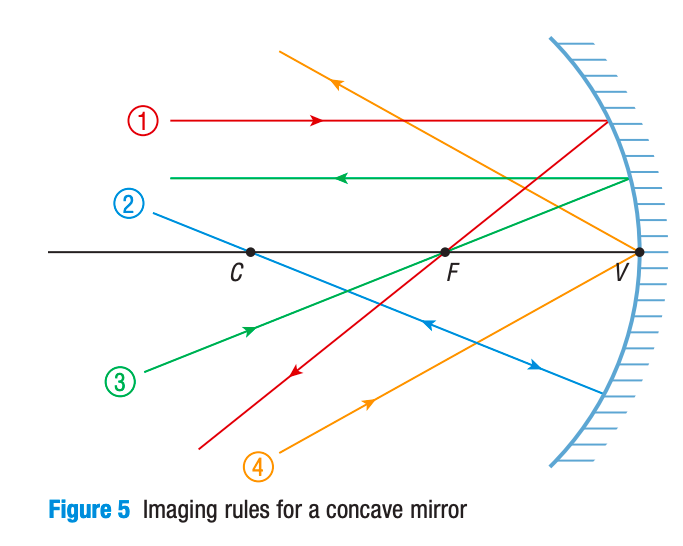
What are some rules that you can use to draw the incident and reflected rays on a converging/concave mirror?
A light ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the focus.
A light ray through the center of curvature will always hit the mirror surface perpendicularly and reflect back onto itself. (Angle of incidence & reflection = 0)
A light ray through F will reflect parallel to the principal axis (Angle of incidence = reflection; only direction changes)
A light ray aimed at the vertex will follow the law of reflection (Angle of incidence = reflection)
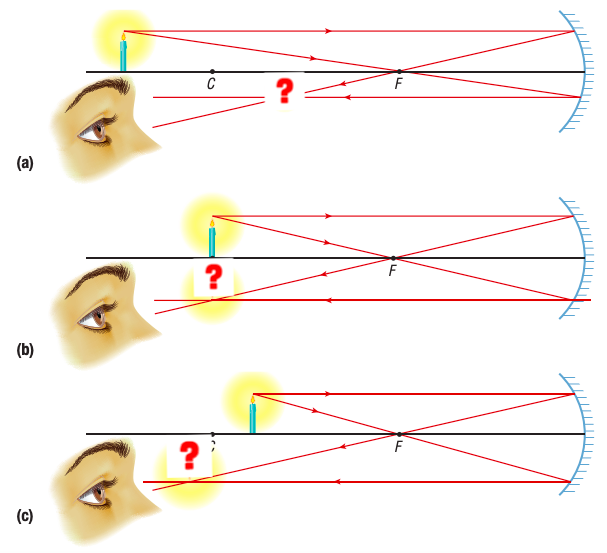
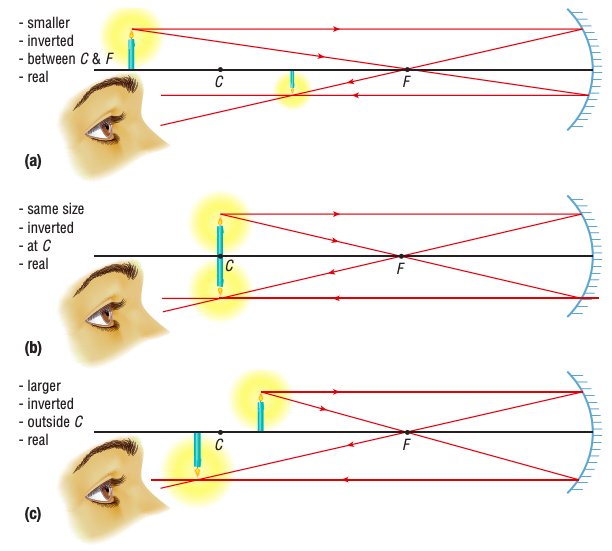
What kind of image do you see when the object is located
beyond C
at C
somewhere between C & F
in a converging (concave) mirror?
real, smaller, inverted, located somewhere between C & F
real, same size, inverrest, at C
real, larger, inverted, beyond C (outside C & F)
What kind of image do you see when the object is located
at F (focus)
in front of F (between F and concave mirror)
in a converging (concave) mirror?
No image (reflected rays are parallel and don’t intersect to form an image)
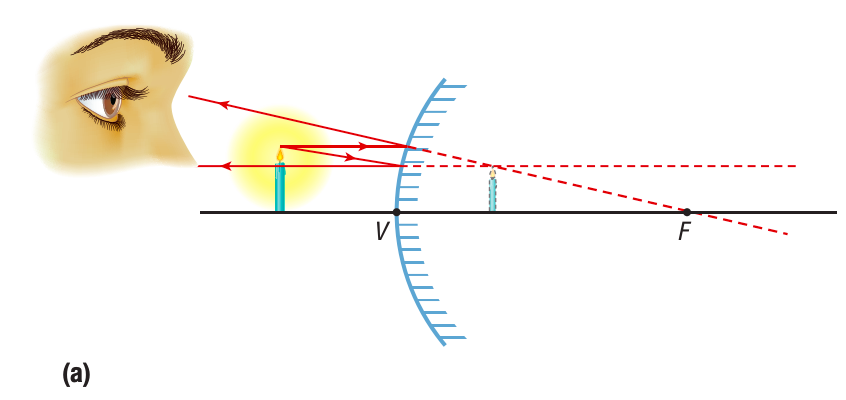
virtual image behind the mirror, larger, upright
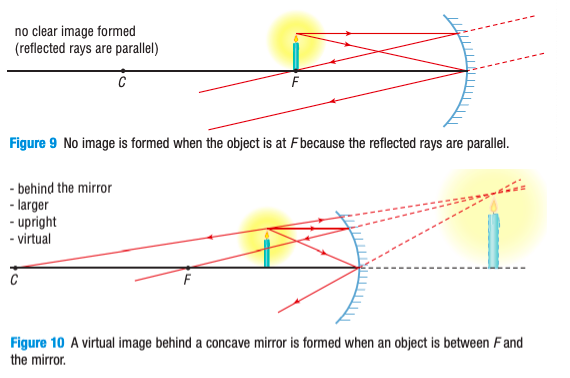
How do searchlights of cars work?
Light gets radiated from the Focus (F) so that the reflected rays are always parallel

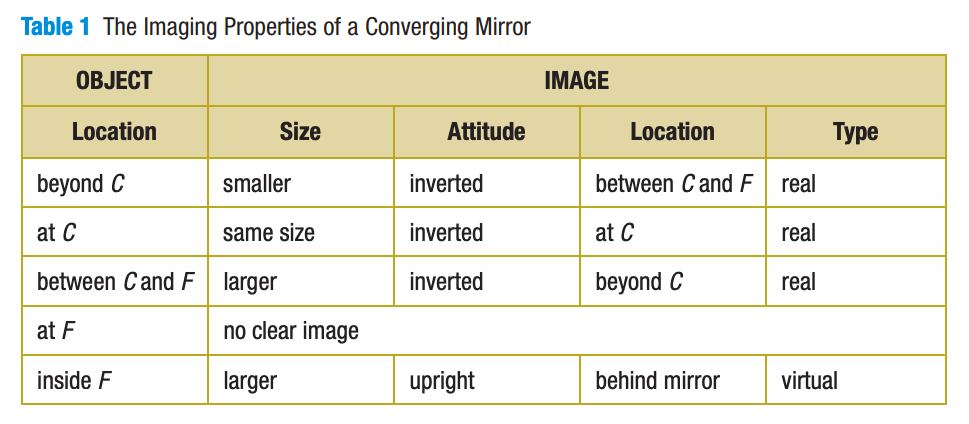
A reflecting telescope is the reverse of the searchlight application. How does a reflecting telescope work?
Parallel rays (electromagnetic waves; not visible light) from the sun coverage (get together) at the focus (F), where there is a detector that absorb energy
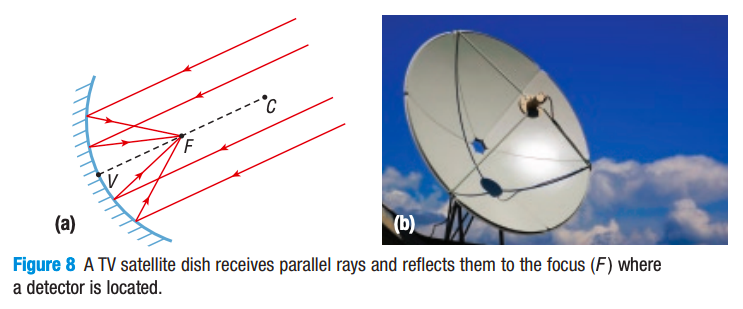
Summary of the characteristics in converging (concave) mirror
A converging (concave) mirror produces an inverted, real image if the object is beyond F; if the object is at F, no image is formed; and if the object is between F and the mirror, a larger, upright, virtual image is formed.
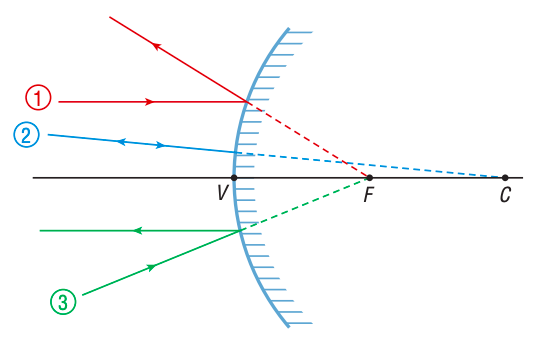
What are 3 rules that you can use to draw the incident and reflected rays on a converging/concave mirror?
A ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected as if it had come through the focus (F).
A ray aimed at the centre of curvature (C) is reflected back upon itself.
A ray aimed at the focus (F) is reflected parallel to the principal axis.
What does diverge mean?
separate from another route and go in a different direction
How does images in a diverging/convex mirror look like?
Rays reflected off a diverging/convex always diverge
That’s why ALL images produced by diverging/convex mirror is smaller,
upright, virtual image
What are some differences between concave VS convex mirror?
In terms of their:
Focus
Direction of the light ray that is parallel to the principal axis
Concave = F on the same side as the obj; convex = F behind the mirror
Concave = reflected through the focus; reflected as if it had come through the focus
At least __ incident rays are drawn to determine whether or not an image is formed and, if so, its characteristics. These rays usually originate from the top of the object.
2