Econ 26 - Chapters 1 - 4
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Trade
Basis is diversity in resources and wants
Gains from trade
Specialization, efficiency, mutual benefit.
Forms of trade
Goods/services, lending, insurance, forward transactions
Life-cycle saving
Borrow when young, save in middle age, dissave in retirement
Precautionary reserves
Assets held against income/spending fluctuations
Investment types
Working capital: Funds for day-to-day operations.
Fixed capital: Long-term investments in equipment/facilities.
Gains from lending
Borrowers fund investments; lenders earn interest
Insurance
Reciprocal insurance: Mutual aid within a community.
External insurance: Third-party assumes risk for a premium.
Forward transactions: Agreement to buy/sell at a future date at a preset price.
Price risk: Uncertainty in future prices.
Speculators: Trade to profit from price changes.
Reliance on promises
Default risk
Incentive problems
Moral hazard: Insured takes more risks.
Adverse selection: High-risk individuals more likely to buy insurance.
Liquidity
Ease of converting assets to cash
Transactions costs
Costs of information, contracting, monitoring
Warehouse bank
Stores cash, facilitates payments via checks
Fractional reserve bank
Holds only a fraction of deposits as reserves; creates money through lending.
Clearinghouse
Nets checks between banks to reduce cash transfers.
Direct lending: Through financial markets (stocks, bonds).
Primary market: New securities.
Secondary market: Existing securities.
Dealers vs. brokers: Dealers buy/sell; brokers arrange trades.
Indirect lending: Through financial intermediaries (banks, insurance companies).
Advantages: Lower risk, better liquidity, diversification, expertise.
Insurance companies risk
Pool risks, charge premiums.
Futures markets
Standardized forward contracts; exchange guarantees performance
Forward intermediaries (e.g., banks)
Offer forward contracts in currencies, commodities.
Four Basic Techniques of Financial Systems
Delegation: Assign tasks to specialists.
Credit substitution: Replace borrower’s credit with intermediary’s credit.
Pooling: Combine assets/liabilities to reduce risk or improve liquidity.
Netting: Offset transactions to reduce settlement volume.
Gains from lending
Net benefit after transactions costs
Conditions for efficiency
Competitive pricing: Price = cost.
Minimum transactions costs.
Integration: Similar loans available on similar terms everywhere.
Market failure
Inefficiency due to lack of competition, economies of scale, or natural monopoly.
Types of instability
Banking panics: Runs on many banks simultaneously.
Securities market crashes: Sharp fall in asset prices.
Price-level instability: Inflation/deflation.
Causes of instability
Composition problems, externalities, excessive risk-taking.
To promote competition
Antitrust laws, regulate monopolies
To promote stability
Regulation (e.g., deposit insurance, lender of last resort).
Consumer protection
Truth-in-Lending Act, disclosure laws
Social policy
Equal credit access, community reinvestment
Government failure
Intervention can be costly, ineffective, or serve special interests.
Present Value (PV)
Value today of a future sum
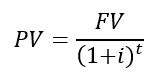
Future Value (FV)
Value in the future of a sum invested today
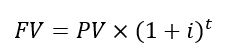
Compounding
Earning interest on interest
Market yield
Interest rate that equates PV of future payments to market price
Zero-coupon bond (Zero)
Single payment at maturity
Yield to maturity (YTM)
Single discount rate that equates PV of all bond payments to its price.
Coupon bond price:
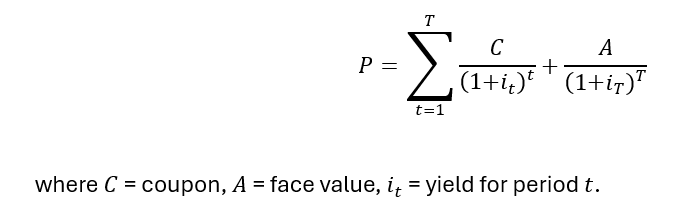
Selling at discount, premium, or par
Based on coupon vs. market yield
Price sensitivity
for a zero-coupon bond
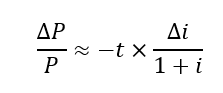
Duration
Weighted average maturity of a bond’s cash flows; measures sensitivity to interest rate changes
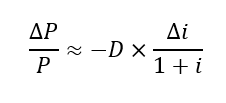
Holding period yield in dollars
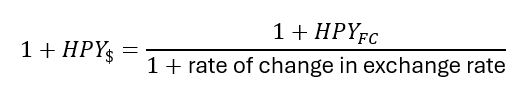
Approximation (Holding period yield)

Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Measures price changes
Real interest rate
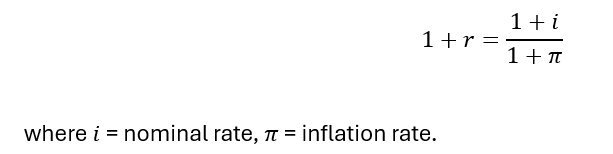
Approximation (real interest rate)
