Neuroanatomy chap 6 : blood supply of brain
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Arterial supply of brain/ spinal cord (2 pairs of vessels)
Carotid & Vertebral arteries
Internal carotid artery proceeds superiorly along optic chiasm and forks (bifurcates) into
middle and anterior cerebral arteries
2 smaller branches
Anterior choroidal artery and posterior communicating artery
Anterior choroidal artery (long and thin) -
Frequently involved in cerebrovascular accidents. Supplies the optic tract; chroid plexus of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle ; and some so,e deep brain structures
Posterior communicating artery passes posteriorly, inferiorly-
To the optic tract and towards the cerebral penduncle and joins the posterior cerebral artery.
Anterior cerebral artery-
Runs medially, superiorly to the optic nerve and enters the longitudinal fissure
Carotid arteries
Provide about 80 % of blood supply. most to the telencephalon and much of the deincephalon
Vertebral system
Provides 20% supply to the brain stem and cerebellum, as well as parts of the diencephalon, spinal cord, occipital and temporal lobe.
Ophthalmic artery
First divisions of the internal carotid arteries. Travels along the optic nerve to the orbit, where it supplies the eyes orbital contents.
Conduit
All the ascending and descending pathway fibers have to pass through here to get to the brain
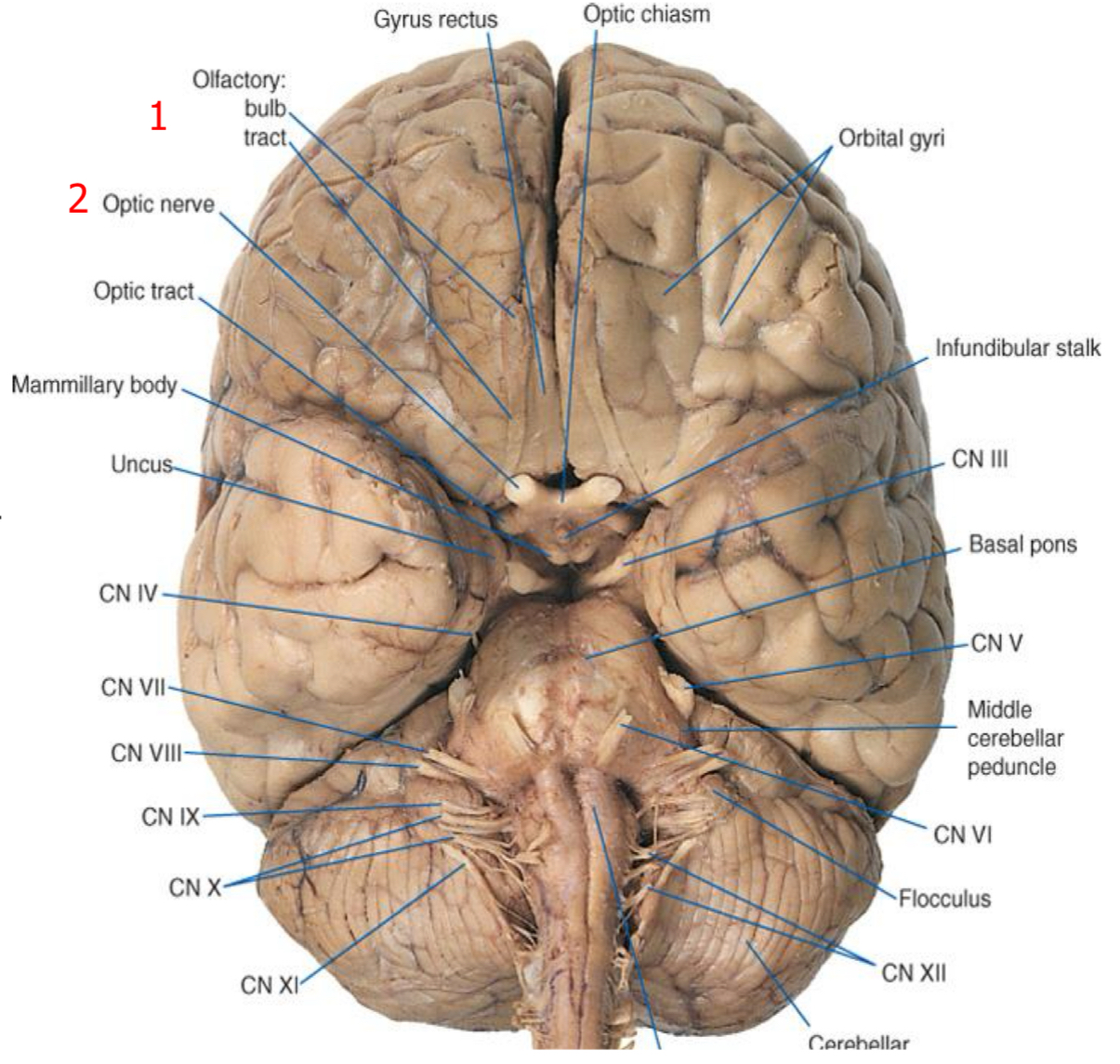
Cranial nerves
10 of the 12 cranial nerves are attached to the brainstem
Integration
Respiration, cardiovascular control, consciousness, sleep
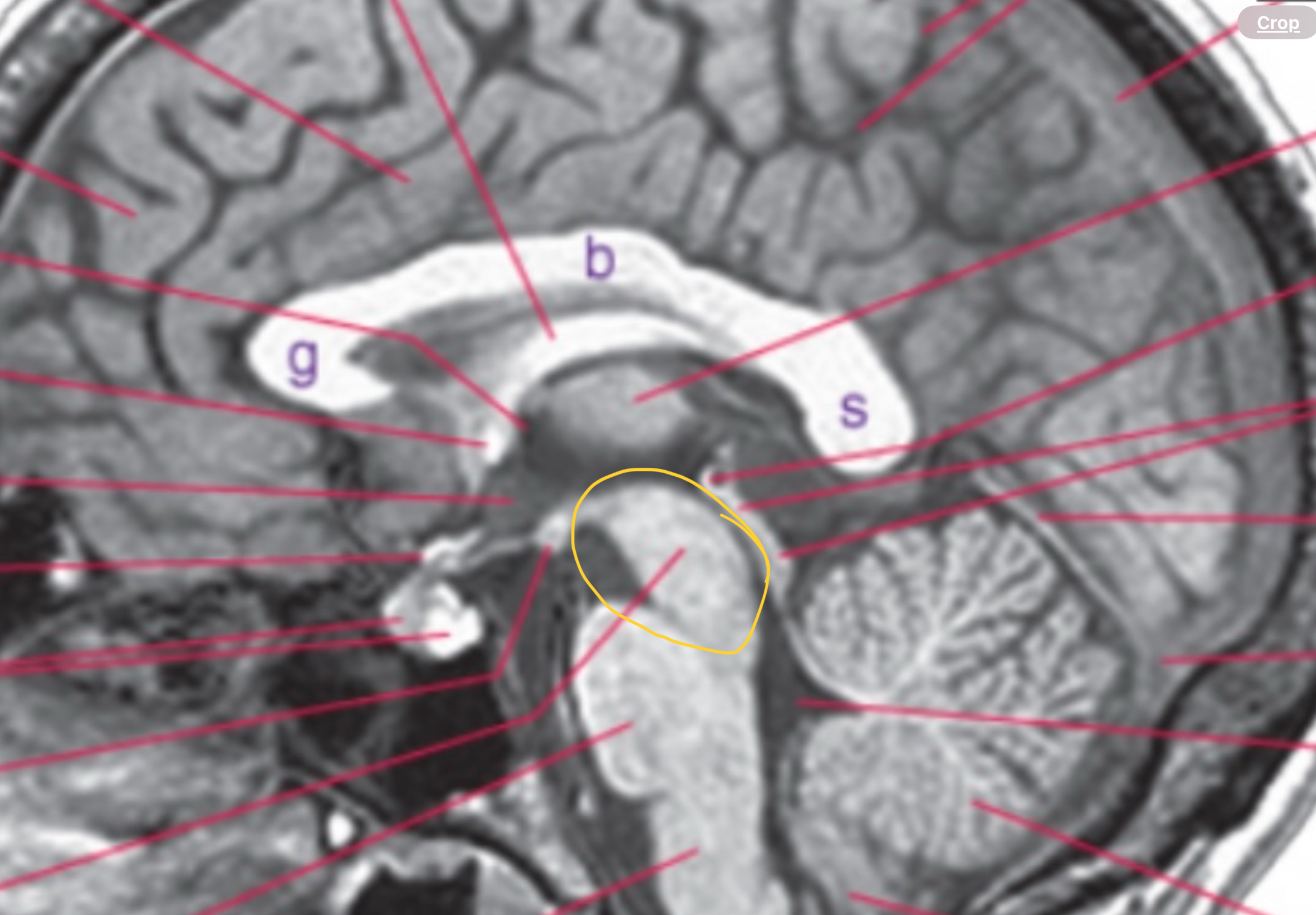
Midbrain
Includes cerebral penduncle, superior and inferior colliculus, and aqueduct
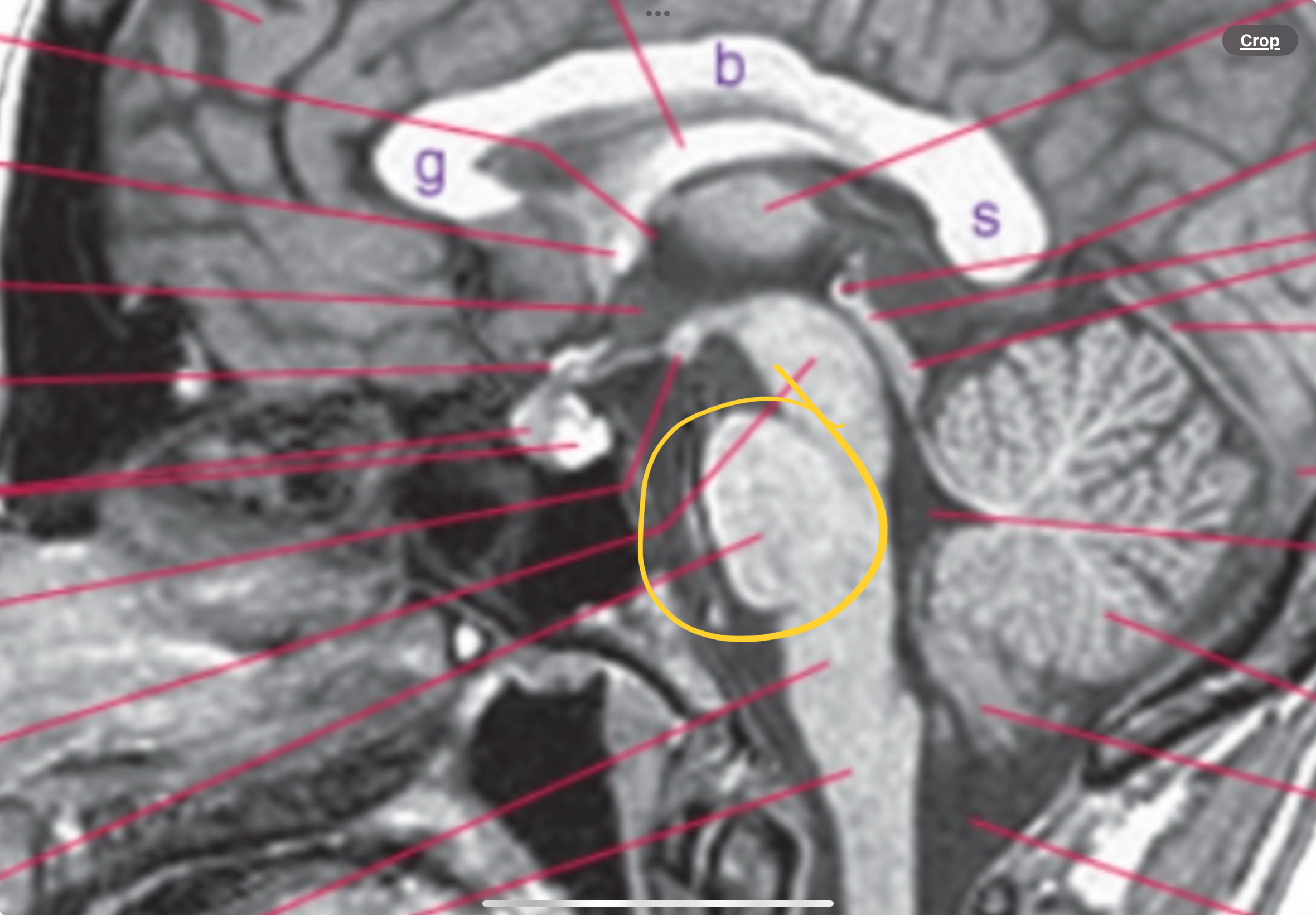
Pons “bridge”
Basal pons and fourth ventricle
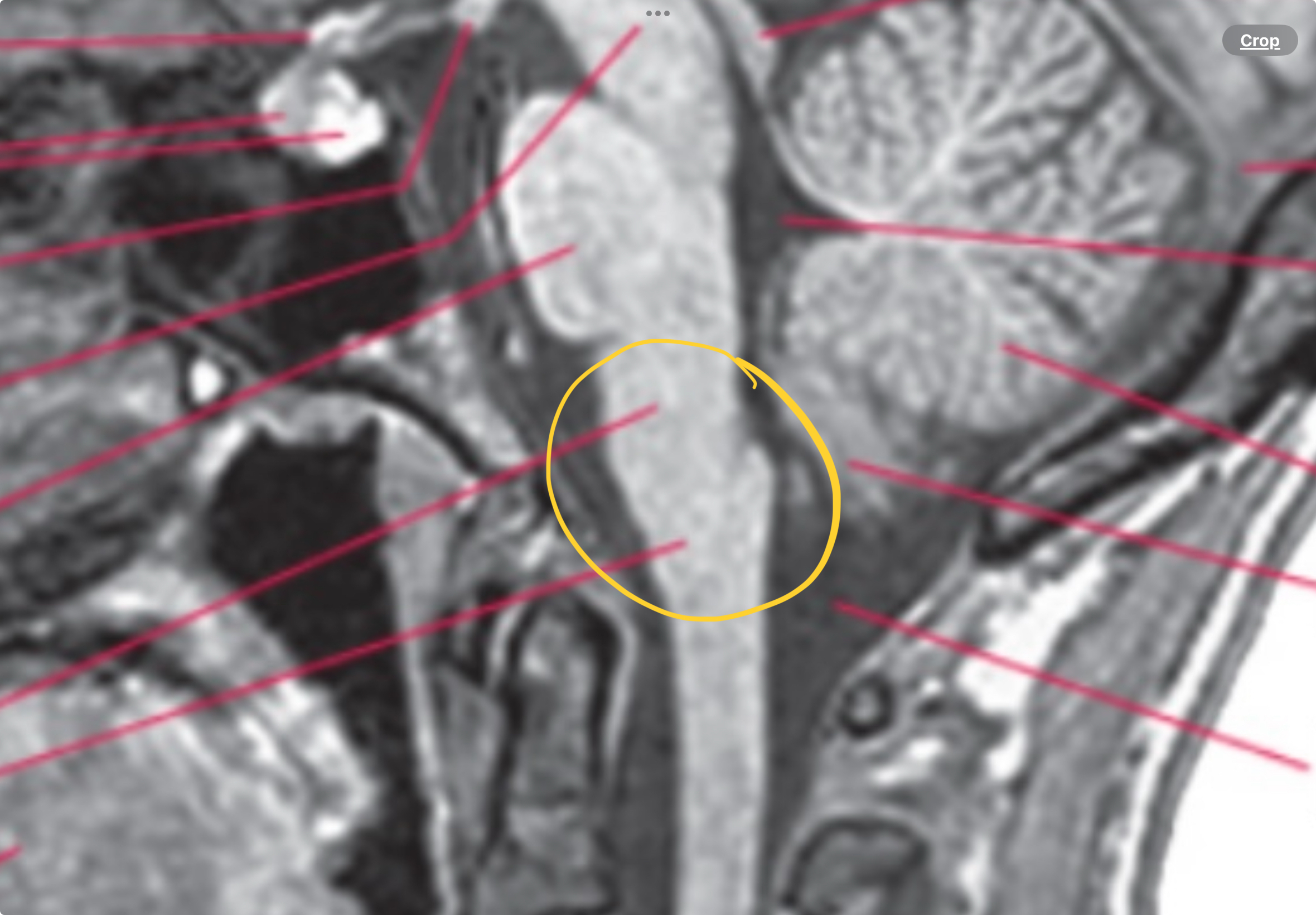
Medulla
Contain pyramids, a part of the fourth ventricle, part of the central canal and flows with the spinal cord
Obex
Where 4th ventricle becomes continuous with central canal
10 seconds without blood/oxygen (ischemia) -
Loss of consciousness
20 seconds without blood/oxygen -
Electrical activity in brain stops
Anterior system
Carotid
Posterior system
Vertebral-basilar
Anterior cerebral=
Medial wall of frontal and parietal
Midbrain
Cerebral penducle, superior/inferior collicus, aqueduct
Pons “bridge”
Basal pons, 4th ventricle
Medulla
Pyramids, part of 4th ventricle, central canal/ spinal cord
The brainstem-
Keeps us alive
Ventral view (pyramids)
Descending/ ascending motor cortocospinal tract fibers
Olives (ventral view)
Contain inferior olivary nuclei (motor coordination)
Pons (ventral view)
Dominated by transverse fibers —> contralateral cerebral hemispheres
Posterior view
Floor of 4th ventricle
Obex
“V” where the vent becomes central canal
Corticospinal tract
Motor cortex 2. Internal capsule 3. Cerebral penducles 4. Basal pons 5. Medullary pyramids 6. Crosses at pyramidal decussation (medulla) 7. Lateral corticospinal tract = voluntary movement