cardiovascular system 🫀
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the cardiovascular system?
A closed system of the heart and blood vessels
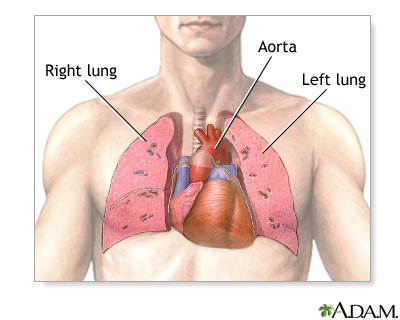
Where is the heart located?
thorax between the lungs
How much does the heart weigh?
less than 1lb
What membrane is the heart covered by?
pericardium
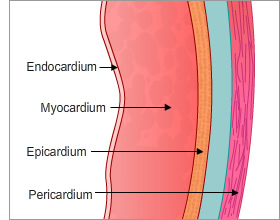
List the three layers of the heart wall:
epicardium (outer), myocardium (middle cardiac muscle), endocardium (inner endothelium)
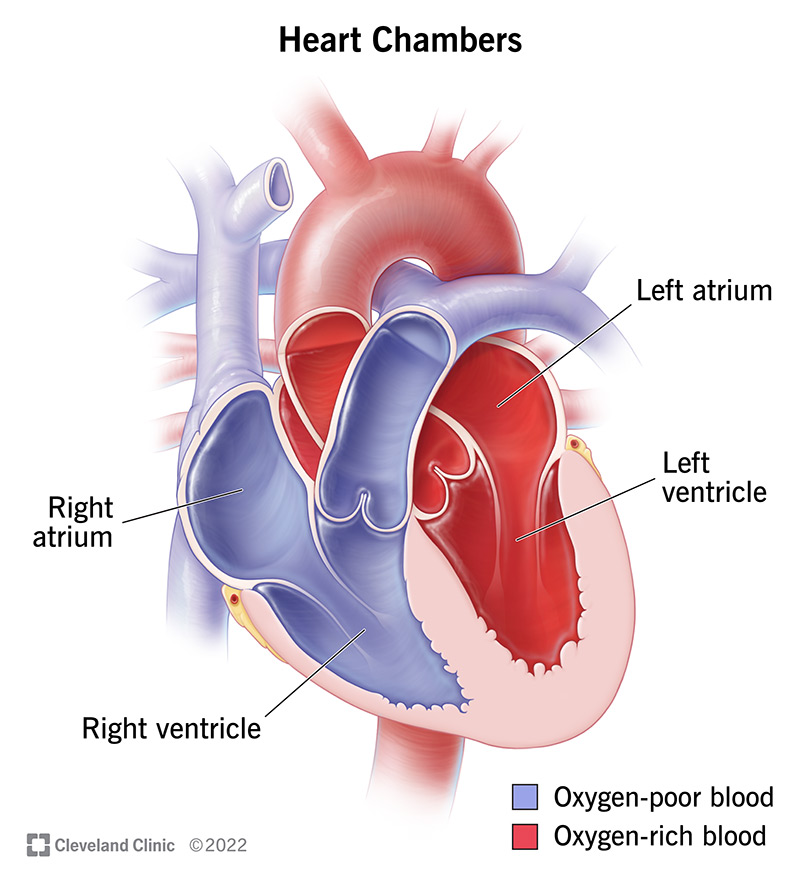
List the four heart chambers:
right atrium & left atrium (receiving chambers), right ventricle & left ventricle (discharging chambers)
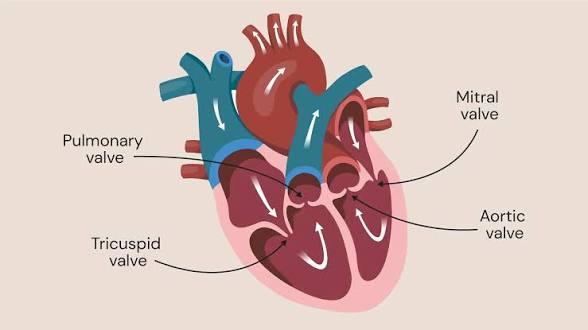
what are the four valves that ensure unidirectional blood flow?
atrioventricular (biscupid & tricuspid) and semilunar valves (pulmonary & aortic)
heart valves _____
prevent back flow of blood
What vessels are associated with the heart?
aorta, arteries, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and pulmonary veins
what circulation nourishes the heart muscle?
Coronary arteries & veins
Heart pathologies include ______
filtration, tachycardia, and bradycardia
What does the cardiac cycle consist of?
the contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the heart
Cardiac Output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped by heart per minute
What is considered normal blood pressure?
120/80 mm Hg
What are blood vessels classified into?
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, & veins
name the three tunics:
tunica intima (endothelium), tunica media (smooth muscle), tunica externa (connective tissue)
How is blood pressure measured?
systolic/diastolic
What is blood pressure influenced by?
neural, renal, temperature, chemical, and dietary factors
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
Myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
endocardium
inner lining of the heart
atria
Upper chambers that receive blood
Ventricles
Lower heart chambers that pump blood out
valves
prevent back flow of blood
chordae tendineae
tendinous cords anchoring valves
Coronary circulation
flow of blood to and from the tissues of the heart
sinoatrial node (SA node)
Heart natural pacemaker
atrioventricular node (AV node)
relay station between atria & ventricles
electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG)
A test that records the electrical heart activity
systole
Contraction phase of the heart
diastole
Relaxation phase of the heart
cardiac output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute
stroke volume (SV)
Volume of blood pumped per heartbeat
Sympathetic nervous system
increase heart rate
parasympathetic nervous system
decreases heart rate
congestive heart failure (CHF)
heart is too weak/unable to pump its required amount of blood
tunics
layers of blood vessel walls
Capillaries
Microscopic vessels for exchange between blood and tissue
pulse
Pressure waves in arteries from heartbeat
blood pressure
Force of blood on artery walls
Hypertension
high blood pressure
hypostension
low blood pressure
hypotension is systolic below _____
110 mm Hg
hypertension is systolic above ____
140 mm Hg
heat causes what in the blood vessels?
vasodilation (widening vessels)
cold causes what in blood vessels?
vasoconstriction (narrowing vessels)
_______ and ______ affect blood pressure
neutral factors (sympathetic nervous system) & renal factors (blood volume regulation)
what valve conditions increase the heart workload?
incompetence and stenosis
blood pressure decreases with _______
distance from the heart
Pulse points are locations where _____
arterial pulses can be easily felt